Abstract
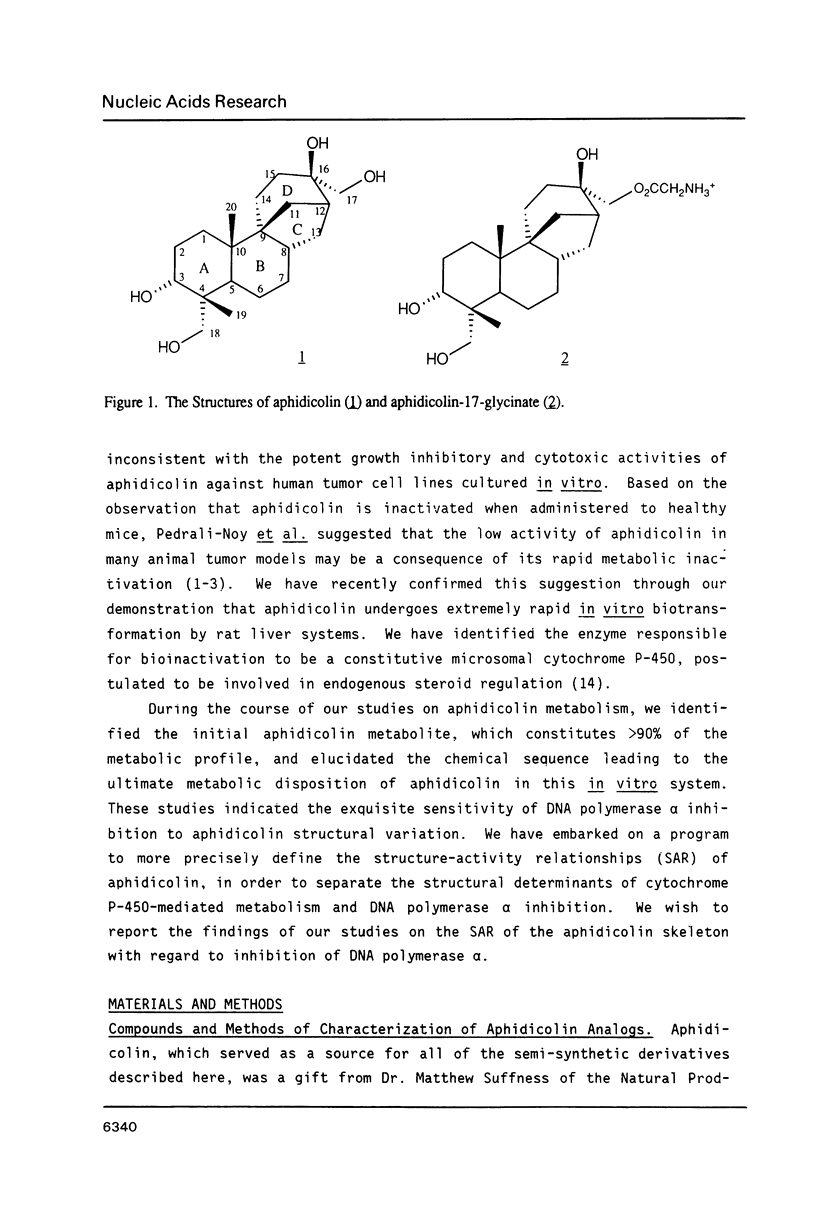
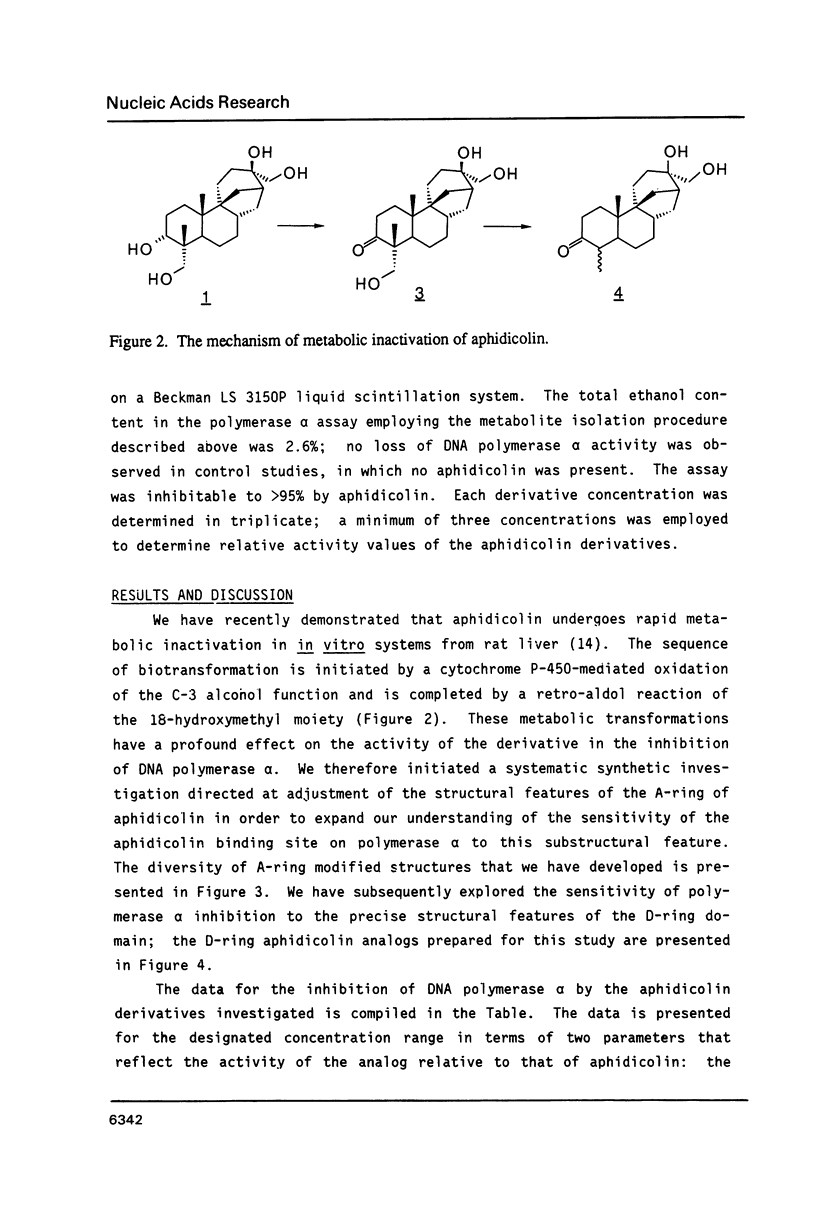
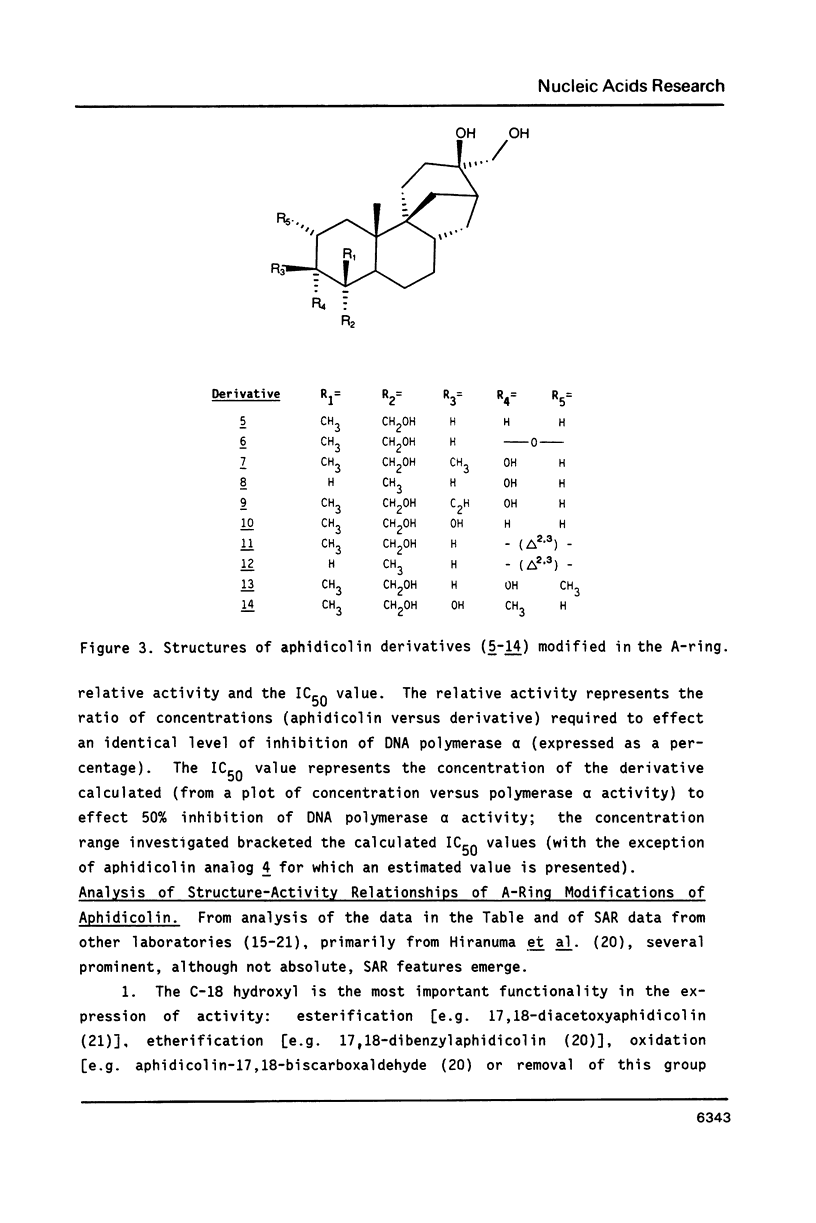
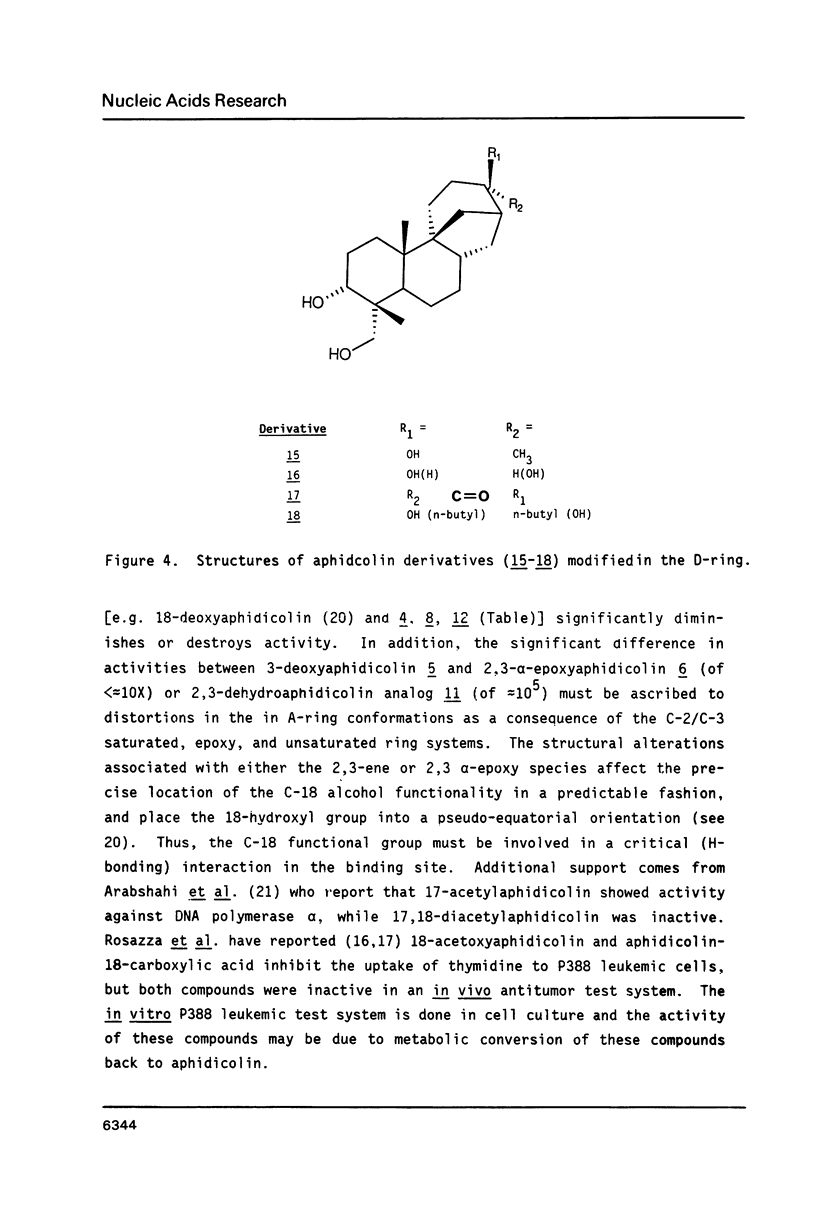
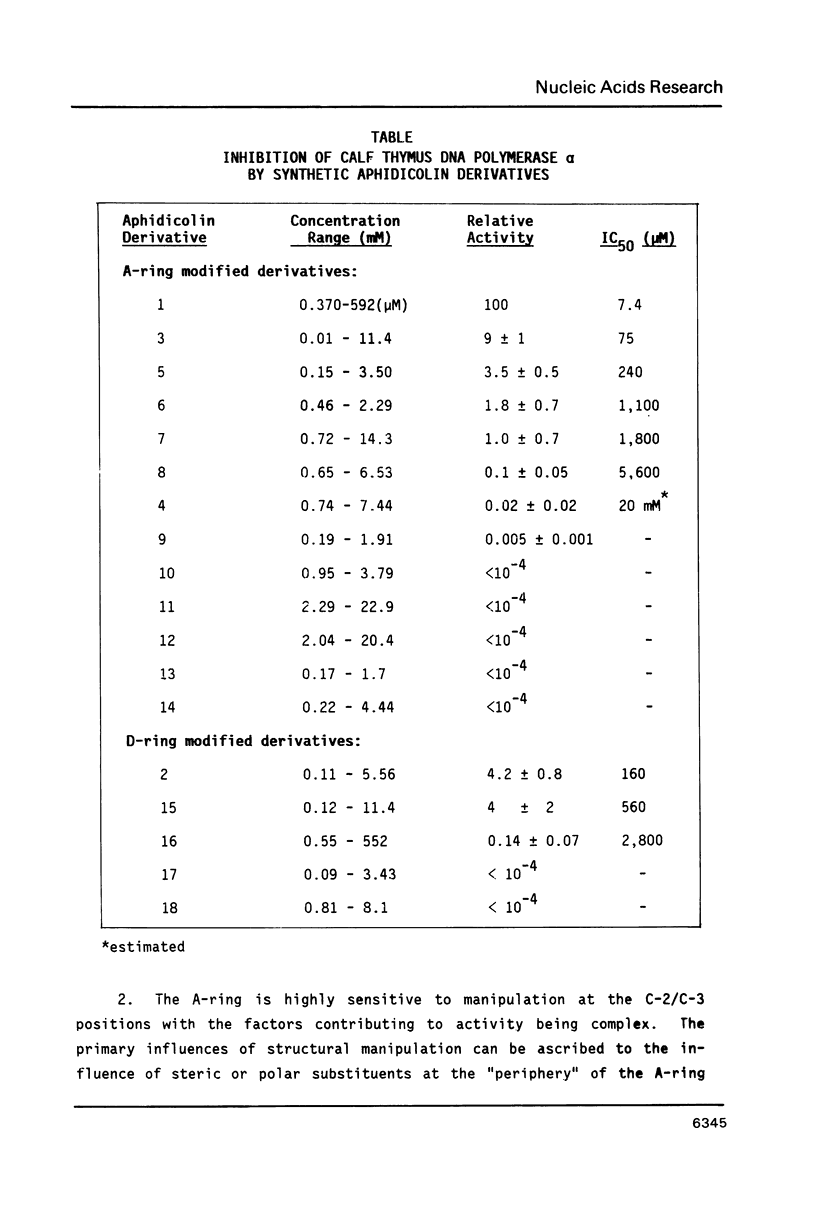
Aphidicolin and 17 derivatives that have been structurally modified in the A- and D-rings were assessed for their ability to inhibit DNA polymerase alpha. No derivative surpassed the activity of aphidicolin; derivatives with structural alterations in the A-ring exhibited significantly greater loss of activity relative to derivatives with structural alterations in the D-ring. The conclusions of these studies indicate a critical role for the C-18 function in the interaction of aphidicolin with polymerase alpha. Molecular modelling studies could not identify structural features of the aphidicolin-dCTP "overlap" that is unique to dCTP, relative to the remaining dNTPs, and that is consistent with the extant structure-activity data.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arabshahi L., Brown N., Khan N., Wright G. Inhibition of DNA polymerase alpha by aphidicolin derivatives. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 10;16(11):5107–5113. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.11.5107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Wassarman P. M. Replication of eukaryotic chromosomes: a close-up of the replication fork. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:627–666. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Focher F., Ferrari E., Spadari S., Hübscher U. Do DNA polymerases delta and alpha act coordinately as leading and lagging strand replicases? FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 29;229(1):6–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond R. A., Byrnes J. J., Miller M. R. Identification of DNA polymerase delta in CV-1 cells: studies implicating both DNA polymerase delta and DNA polymerase alpha in DNA replication. Biochemistry. 1987 Oct 20;26(21):6817–6824. doi: 10.1021/bi00395a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiranuma S., Shimizu T., Yoshioka H., Ono K., Nakane H., Takahashi T. Chemical modification of aphidicolin and the inhibitory effects of its derivatives on DNA polymerase alpha in vitro. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1987 Apr;35(4):1641–1644. doi: 10.1248/cpb.35.1641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A. New views of the biochemistry of eucaryotic DNA replication revealed by aphidicolin, an unusual inhibitor of DNA polymerase alpha. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):647–648. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90426-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ipsen J., Rosazza J. P. Microbial transformations of natural antitumor agents, 25. Conversions of 3-ketoaphidicolin. J Nat Prod. 1984 May-Jun;47(3):497–503. doi: 10.1021/np50033a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb L. A., Liu P. K., Fry M. DNA polymerase-alpha: enzymology, function, fidelity, and mutagenesis. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1986;33:57–110. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60020-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longiaru M., Ikeda J. E., Jarkovsky Z., Horwitz S. B., Horwitz M. S. The effect of aphidicolin on adenovirus DNA synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 25;6(10):3369–3386. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.10.3369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMurry J. E., Webb T. R. Synthesis of a tricyclic aphidicolin analogue that inhibits DNA synthesis in vitro. J Med Chem. 1984 Oct;27(10):1367–1369. doi: 10.1021/jm00376a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oguro M., Nagano H. Reconstitution of endogenous DNA synthesis in isolated nuclei and template activity of chromatin with respect to mode of inhibition by aphidicolin. J Biochem. 1983 Jan;93(1):197–203. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedrali-Noy G., Kuenzle C. C., Focher F., Belvedere M., Spadari S. An enzymatic method for microdetermination of aphidicolin: a promising anticancer drug. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1981 Feb;4(2):113–121. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(81)90024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So A. G., Downey K. M. Mammalian DNA polymerases alpha and delta: current status in DNA replication. Biochemistry. 1988 Jun 28;27(13):4591–4595. doi: 10.1021/bi00413a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spadari S., Focher F., Kuenzle C., Corey E. J., Myers A. G., Hardt N., Rebuzzini A., Ciarrocchi G., Pedrali-Noy G. In vivo distribution and activity of aphidicolin on dividing and quiescent cells. Antiviral Res. 1985 Apr;5(2):93–101. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(85)90035-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spadari S., Focher F., Sala F., Ciarrocchi G., Koch G., Falaschi A., Pedrali-Noy G. Control of cell division by aphidicolin without adverse effects upon resting cells. Arzneimittelforschung. 1985;35(7):1108–1116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spadari S., Sala F., Pedrali-Noy G. Aphidicolin and eukaryotic DNA synthesis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1984;179:169–181. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-8730-5_17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


