Abstract
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are responsible for the majority of cellular responses to hormones and neurotransmitters as well as the senses of sight, olfaction and taste. The paradigm of GPCR signaling is the activation of a heterotrimeric GTP binding protein (G protein) by an agonist-occupied receptor. The β2 adrenergic receptor (β2AR) activation of Gs, the stimulatory G protein for adenylyl cyclase, has long been a model system for GPCR signaling. Here we present the crystal structure of the active state ternary complex composed of agonist-occupied monomeric β2AR and nucleotide-free Gs heterotrimer. The principal interactions between the β2AR and Gs involve the amino and carboxyl terminal α-helices of Gs, with conformational changes propagating to the nucleotide-binding pocket. The largest conformational changes in the β2AR include a 14 Å outward movement at the cytoplasmic end of transmembrane segment 6 (TM6) and an alpha helical extension of the cytoplasmic end of TM5. The most surprising observation is a major displacement of the alpha helical domain of Gαs relative to the ras-like GTPase domain. This crystal structure represents the first high-resolution view of transmembrane signaling by a GPCR.
Introduction
The β2 adrenergic receptor (β2AR) has been a model system for the large and diverse family of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) for over 40 years. It was one of the first GPCRs to be characterized by radioligand binding, and it was the first neurotransmitter receptor to be cloned1 and structurally determined by crystallography2,3. The β2AR was initially identified based on its physiological and pharmacological properties, but it was not known if receptors and G proteins were separate entities, or parts of the same protein4. Subsequent biochemical studies led to the isolation and purification of functional β2AR and Gs, the stimulatory G protein that activates adenylyl cyclase, and the reconstitution of this signaling complex in phospholipid vesicles5,6. The cooperative interactions of β2AR and Gs observed in ligand binding assays formed the foundation of the ternary complex model of GPCR activation7,8. In the ternary complex consisting of agonist, receptor, and G protein, the affinity of the receptor for agonist is enhanced and the specificity of the G protein for guanine nucleotides changes in favor of GTP over GDP. The GPCR field has evolved dramatically since these initial studies. Isolation of the genes and cDNAs for the β2AR and other GPCRs using protein sequencing and expression cloning led to the expansion of the family by homology cloning. More recently, sequencing of the human genome led to the identification of over 800 GPCR genes9. Experimental tools for identifying protein-protein interactions and for expression and silencing of genes have revealed a complex network of cellular signaling and regulatory pathways including G protein-independent activation of cytosolic kinases10,11. Nevertheless, the β2AR continues to be a relevant model for most aspects of GPCR pharmacology, signaling and regulation.
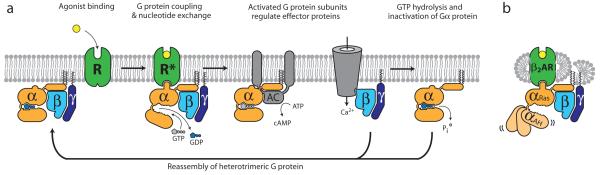
Notwithstanding the remarkable advances in this field, we still know relatively little about the structural basis for transmembrane signaling by GPCRs. Figure 1 shows the G protein cycle for the β2AR-Gs complex. Agonist binding to the β2AR promotes interactions with GDP-bound Gsαβγ heterotrimer leading to the exchange of GDP for GTP, and the functional dissociation of Gs into Gα-GTP and Gβγ subunits. The separate Gα-GTP and Gβγ subunits can modulate the activity of different cellular effectors (channels, kinases or other enzymes). The intrinsic GTPase activity of Gαs leads to hydrolysis of GTP to GDP and the reassociation of Gα-GDP and Gβγ subunits, and the termination of signaling. The active state of a GPCR can be defined as that conformation that couples to and stabilizes a nucleotide-free G protein. In this agonist-β2AR-Gs ternary complex, Gs has a higher affinity for GTP than GDP, and the β2AR has an approximately 100-fold higher affinity for agonists than does β2AR alone. In an effort to understand the structural basis for GPCR signaling, we crystallized the β2AR-Gs complex.
Figure 1. G protein cycle for the β2AR-Gs complex.
a, Extracellular agonist binding to the β2AR leads to conformational rearrangements of the cytoplasmic ends of transmembrane segments that enable the Gs heterotrimer (α, β, and γ) to bind the receptor. GDP is released from the α subunit upon formation of β2AR-Gs complex. The GTP binds to the nucleotide-free α subunit resulting in dissociation of the α and βγ subunits from the receptor. The subunits regulate their respective effector proteins adenylyl cyclase (AC) and Ca2+ channels. The Gs heterotrimer reassembles from α and βγ subunits following hydrolysis of GTP to GDP in the α subunit. b, The purified nucleotide-free β2AR-Gs protein complex maintained in detergent micelles. The Gαs subunit consists of two domains, the Ras domain (αRas) and the α-helical domain (αAH). Both are involved in nucleotide binding. In the nucleotide-free state, the αAH domain has a variable position relative the αRas domain.
Crystallization of the β2AR-Gs complex
The first challenge for crystallogenesis was to prepare a stable β2AR-Gs complex in detergent solution. The β2AR and Gs couple efficiently in lipid bilayers, but not in detergents used to solubilize and purify these proteins. We found that a relatively stable β2AR-Gs complex could be prepared by mixing purified GDP-Gs (approximately 100 μM final concentration) with a molar excess of purified β2AR bound to a high affinity agonist (BI-167107, Boehringer Ingelheim)12 in dodecylmaltoside solution. Apyrase, a non-selective purine pyrophosphatase, was added to hydrolyze GDP released from Gs on forming a complex with the β2AR. Removal of GDP was essential since both GDP and GTP can disrupt the high-affinity interaction between β2AR and Gs (Fig. S1a). The complex was subsequently purified by sequential antibody affinity chromatography and size exclusion chromatography. The stability of the complex was enhanced by exchanging it into a recently developed maltose neopentyl glycol detergent (NG-310, Anatrace)13. The complex could be incubated at room temperature for 24 hrs without any noticeable degradation; however, initial efforts to crystallize the complex using sparse matrix screens in detergent micelles, bicelles and lipidic cubic phase (LCP) failed.
To further assess the quality of the complex, we analyzed the protein by single particle electron microscopy (EM). The results, which are described in detail in a companion manuscript (Westfield et al.), confirmed that the complex was monodisperse, but revealed two potential problems for obtaining diffraction of quality crystals. First, the detergent used to stabilize the complex formed a large micelle, leaving little polar surface on the extracellular side of the β2AR-Gs complex for the formation of crystal lattice contacts. Our initial approach to this problem, which was to generate antibodies to the extracellular surface, was not successful. As an alternative approach, we replaced the unstructured amino terminus of the β2AR with T4 lysozyme (T4L). We previously used T4L to facilitate crystallogenesis of the inactive β2AR by inserting T4L between the cytoplasmic ends of TM5 and TM6 3. Several different amino-terminal fusion proteins were prepared and single particle EM was used to identify a fusion with a relatively fixed orientation of T4L in relation to the β2AR.
The second problem revealed by single particle EM analysis was increased variability in the positioning of the α–helical component of the Gαs subunit. Gαs consists of two domains, the ras-like GTPase domain (GαsRas), which interacts with the β2AR and the Gβ subunit, and the α–helical domain (GαsAH) 14. The interface of the two Gαs subdomains forms the nucleotide-binding pocket (Figure 1), and EM 2D averages and 3D reconstructions show that in the absence of guanine nucleotide, GαsAH has a variable position relative to the complex of T4L-β2AR-GαsRAS-Gβγ (Fig. 1b)(Westfield et al., companion paper).
We attributed the variable position of GαsAH to the empty nucleotide-binding pocket. However, as noted above both GDP and nonhydrolyzable GTP analogs disrupt the β2AR-Gs complex (Fig. S1). The addition of pyrophosphate and its analog phosphonoformate (foscarnet) led to a significant increase in stabilization of GαsAH as determined by EM analysis of the detergent solubilized complex (Westfield et al., companion paper). Crystallization trials were carried out in Lipidic Cubic Phase (LCP) using a modified monolein (7.7, see Online Methods) designed to accommodate the large hydrophilic component of the T4L-β2AR-Gs complex 15. Although we were able to obtain small crystals that diffracted to 7Å, we were unable to improve their quality through the use of additives and other modifications.
In an effort to generate an antibody that would further stabilize the complex and facilitate crystallogenesis, we crosslinked β2AR and the Gs heterotrimer with a small, homobifunctional amine-reactive crosslinker and used this stabilized complex to immunize llamas. Llamas and other camelids produce antibodies devoid of light chains. The single domain antigen binding fragments of these heavy chain only antibodies, known as Nanobodies, are small (15 kDa), rigid and are easily cloned and expressed in E. coli (Online Methods)16. We obtained a nanobody (Nb35) that binds to the complex and prevents dissociation of the complex by GTPγS (Fig. S1). The T4L-β2AR-Gs-Nb35 complex was used to obtain crystals that grew to 250 microns (Fig. S2) in LCP (monoolein 7.7) and diffracted to 2.9 Å. A 3.2 Å data set was obtained from 20 crystals and the structure was determined by molecular replacement (Online Methods).
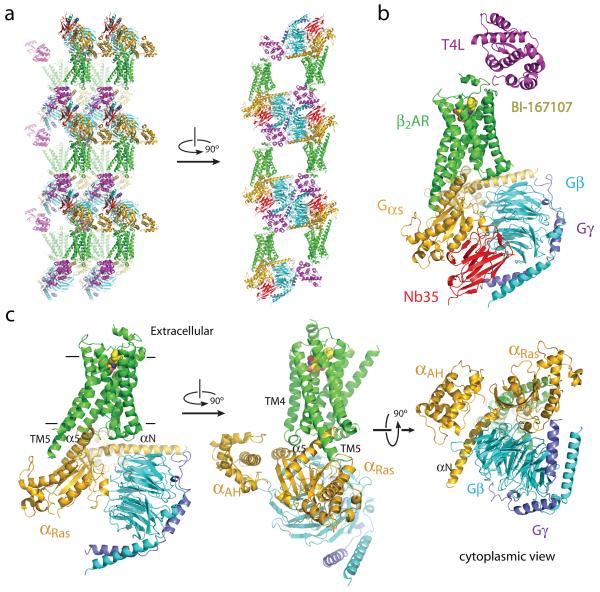
The β2AR-Gs complex crystallized in space group P21, with a single complex in each asymmetric unit. Figure 2a shows the crystallographic packing interactions. Complexes are arrayed in alternating aqueous and lipidic layers with lattice contacts formed almost exclusively between soluble components of the complex, leaving receptor molecules suspended between G protein layers and widely separated from one another in the plane of the membrane. Extensive lattice contacts are formed among all the soluble proteins, likely accounting for the strong overall diffraction and remarkably clear electron density for the G protein. Nb35 and T4L facilitated crystal formation. Nb35 packs at the interface of Gβ and Gα subunits with complementarity determining region (CDR) 1 interacting primarily with Gβ and a long CDR3 loop interacting with both Gβ and Gα subunits. The framework regions of Nb35 from one complex also interact with Gα subunits from two adjacent complexes. T4L is linked to the β2AR only through amino terminal fusion, but packs against the amino terminus of the Gβ subunit of one complex, the carboxyl terminus of the Gγ subunit of another complex, and the Gα subunit of yet another complex. Figure 2b shows the structure of the complete complex including T4L and Nb35, and Figure 2c shows the β2AR-Gs complex alone.
Figure 2. Overall structure of the β2AR Gs complex.
a, Lattice packing of the complex shows alternating layers of receptor and G protein within the crystal. Abundant contacts are formed among proteins within the aqueous layers. b, The overall structure of the asymmetric unit contents shows the β2AR (green) bound to an agonist (yellow spheres) and engaged in extensive interactions with Gαs (orange). Gαs together with Gβ (cyan) and Gγ (purple) constitute the heterotrimeric G protein Gs. A Gs binding nanobody (red) binds the G protein between the α and β subunits. The nanobody (Nb35) facilitates crystallization, as does T4 lysozyme (magenta) fused to the amino terminus of the β2AR. c, The biological complex omitting crystallization aids, showing its location and orientation within a cell membrane.
Structure of the active-state β2AR
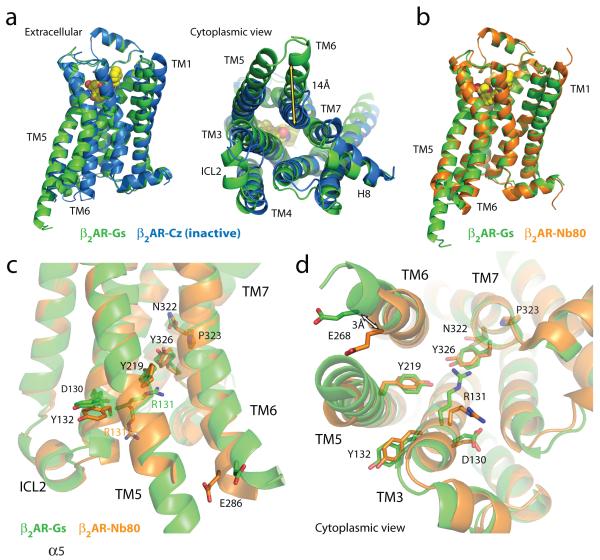
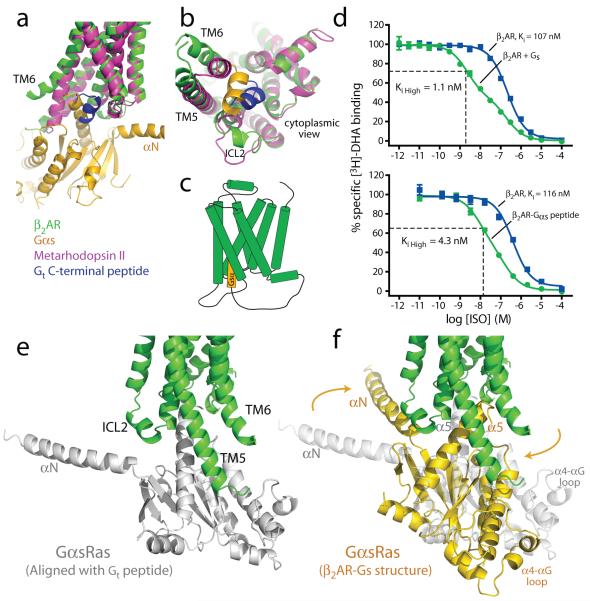
The β2AR-Gs structure provides the first high-resolution insight into the mechanism of signal transduction across the plasma membrane by a GPCR, and the structural basis for the functional properties of the ternary complex. Figure 3a compares the structures of the agonist-bound receptor in the β2AR-Gs complex and the inactive carazolol-bound β2AR. The largest difference between the inactive and active structures is a 14 Å outward movement of TM6 when measured at the Cα carbon of E268. There is a smaller outward movement and extension of the cytoplasmic end of the TM5 helix by 7 residues. A stretch of 26 amino acids in the third intracellular loop (ICL3) is disordered. Another notable difference between inactive and active structures is the second intracellular loop (ICL2), which forms an extended loop in the inactive β2AR structure and an α-helix in the β2AR-Gs complex. This helix is also observed in the β2AR-Nb80 structure (Fig. 3b); however, it may not be a feature that is unique to the active state, since it is also observed in the inactive structure of the highly homologous avian β1AR 17.
Figure 3. Comparison of active and inactive β2AR structures.
a, Side and cytoplasmic views of the β2AR-Gs structure (green) compared to the inactive carazolol-bound β2 AR structure 3 (blue). Significant structural changes are seen for the intracellular domains of TM5 and TM6. TM5 is extended by two helical turns while TM6 is moved outward by 14 Å as measured at the α-carbons of Glu268 (yellow arrow) in the two structures. b, β2AR-Gs compared with the nanobody-stabilized active state β2AR-Nb80 structure 12 (orange). c, The positions of residues in the E/DRY and NPxxY motifs and other key residues of the β2AR-Gs and β2AR-Nb80 structures. All residues occupy very similar positions except Arg131 which in the β2AR-Nb80 structure interacts with the nanobody. d, View from the cytoplasmic side of residues shown in (c).
The quality of the electron density maps for the β2AR is highest at the β2AR-GαsRas interface, and much weaker for the extracellular half. The extracellular half of the receptor is not stabilized by any packing interactions either laterally with adjacent receptors in the membrane or through the extracellular surface. Instead, the extracellular region is indirectly tethered to the well-packed soluble components by the amino terminal fusion to T4 lysozyme (Fig. 2a). Given the flexible and dynamic nature of GPCRs, the absence of stabilizing packing interactions may lead to structural heterogeneity in the extracellular half of the receptor and, consequently, to the limited quality of the electron density maps. However, the overall structure of the β2AR in the T4L-β2AR-Gs complex is very similar to our recent active-state structure of β2AR stabilized by a G protein mimetic nanobody (Nb80)12. In the β2AR-Nb80 crystal, each receptor molecule has extensive packing interactions with adjacent receptors and the quality of the electron density maps for the agonist-bound β2AR in this complex is remarkably good for a 3.5 Å structure. Therefore, the β2AR-Nb80 structure allows us to confidently model BI-167107 here, and provide a more reliable view of the conformational rearrangements of amino acids around the ligand-binding pocket and between the ligand-binding pocket and the Gs-coupling interface12.
The overall root mean square deviation between the β2AR components in the β2AR-Gs and β2AR-Nb80 structures is approximately 0.6 Å, and they differ most at the cytoplasmic ends of transmembrane helices 5 and 6 where they interact with the different proteins (Fig 3b-d). The largest divergence is a 3 Å outward movement at the end of helix 6 in the β2AR-Gs complex. However, the differences between these two structures are very small at the level of the most highly conserved amino acids (E/DRY and NPxxY), which are located at the cytoplasmic ends of the transmembrane segements (Fig 3d). These conserved sequences have been proposed to be important for activation or for maintaining the receptor in the inactive state18. Of these residues, only Arg131 differs significantly between these two structures. In β2AR-Nb80 Arg131 interacts with Nb80, whereas in the β2AR-Gs structure Arg131 packs against Tyr391 of Gαs (Fig. S3). The high structural similarity is in agreement with the functional similarity of these two proteins. The β2AR-Nb80 complex exhibits the same high affinity for the agonist isoproterenol as does the β2AR-Gs complex12, consistent with high structural homology around the ligand binding pocket.
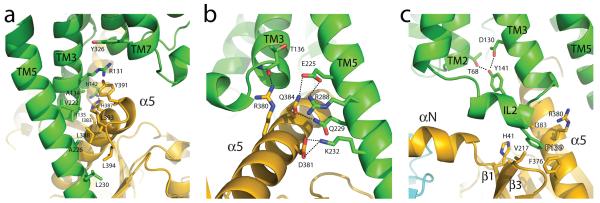
The active state of the β2AR is stabilized by extensive interactions with GαsRas (Fig. 4). There are no direct interactions with Gβ or Gγ subunits. The total buried surface of the β2AR-GαsRas interface is 2576 Å2 (1300 Å2 for GαsRas and 1276 Å2 for the β2AR). This interface is formed by ICL2, TM5 and TM6 of the β2AR, and by α5-helix, the αN-β1 junction, the top of the β3-strand, and the α4-helix of GαsRas (see Table S1 for specific interactions). Some of the β2AR sequences involved in this interaction have been shown to play a role in G protein coupling; however, there is no clear consensus sequence for Gs-coupling specificity when these segments are aligned with other GPCRs. Perhaps this is not surprising considering that the β2AR also couples to Gi and that many GPCRs couple to more than one G protein isoform. Of the 21 amino acids of Gs that are within 4Å of the β2AR, only five are identical between Gs and Gi, and all of these are in the C-terminal alpha helix. The structural basis for G protein coupling specificity must therefore involve more subtle features of the secondary and tertiary structure. Nevertheless, a noteworthy interaction involves Phe139, which is located at the beginning of the ICL2 helix and sits in a hydrophobic pocket formed by Gαs His41 at the beginning of the β1-strand, Val213 at the start of the β3-strand and Phe376, Arg380 and Ile383 in the α5-helix (Fig 4c). The β2AR mutant F139A displays severely impaired coupling to Gs19. The residue corresponding to Phe139 is a Phe or Leu on almost all Gs coupled receptors, but is more variable in GPCRs known to couple to other G proteins. Of interest, the ICL2 helix is stabilized by an interaction between Asp130 of the conserved DRY sequence and Tyr141 in the middle of the ICL2 helix (Fig. 4c). Tyr141 has been shown to be a substrate for the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase 20; however, the functional significance of this phosphorylation is currently unknown.
Figure 4. Receptor-G protein interactions.
a, b The α5-helix of Gαs docks into a cavity formed on the intracellular side of the receptor by the opening of transmembrane helices 5 and 6. a. Within the transmembrane core, the interactions are primarily non-polar. An exception involves packing of Tyr391 of the α5-helix against Arg131 of the conserved DRY sequence in TM3 (see also Figure S3). Arg131 also packs against Tyr of the conserved NPxxY sequence in TM7. b. As α5-helix exits the receptor it forms a network of polar interactions with TM5 and TM3. c, Receptor residues Thr68 and Asp130 interact with the ICL2 helix of the β2AR via Tyr141, positioning the helix so that Phe139 of the receptor docks into a hydrophobic pocket on the G protein surface, thereby structurally linking receptor-G protein interactions with the highly conserved DRY motif of the β2AR.
The lack of direct interactions between the β2AR and Gβγ is somewhat unexpected given that a heterotrimer is required for efficient coupling to a GPCR. While Gβ does not interact directly with the β2AR, it plays an indirect but important role in coupling by stabilizing the N-terminal alpha helix of Gαs (Fig. 2C). Several models involving GPCR dimers propose that one of the protomers interacts predominantly with Gα while the other interacts with Gβγ21,22,23. Consistent with these models, biochemical and biophysical evidence suggests that Gαi2 forms a stable complex with a LTB4 receptor dimer24. While the β2AR efficiently activates Gs as a monomer, extensive biochemical and biophysical evidence supports the existence of β2AR dimers or oligomers in living cells 25. Therefore, we cannot exclude the possibility that in cell membranes one protomer of a β2AR dimer may interact with the Gβγ subunit.
Structure of activated Gs
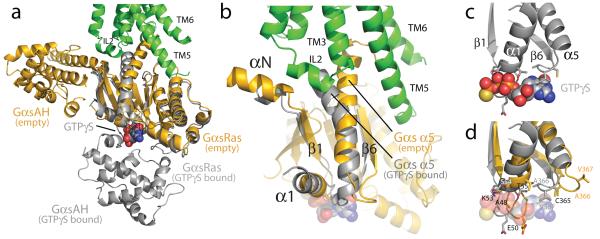
The most surprising observation in the β2AR-Gs complex is the large displacement of the GαsAH relative to GαsRas (an approximately 127° rotation about the junction between the domains) (Fig. 5a). GαsAH moves as a rigid body as shown by the alignment of β2AR-Gs with GαsAH from the crystal structure of Gαs-GTPγS26 (Figure S4). In the structure of Gαs-GTPγS, the nucleotide-binding pocket is formed by the interface between GαsRas and GαsAH. Guanine nucleotide binding stabilizes the interaction between these two domains. The loss of this stabilizing effect of guanine nucleotide binding is consistent with the high flexibility observed for GαsAH in single particle EM analysis of the detergent solubilized complex (Westfield et al., companion manuscript). It is also in agreement with the increase in deuterium exchange at the interface between these two domains upon formation of the complex (Chung et al., companion manuscript). Recently Hamm, Hubbell and colleagues, using double electron-electron resonance (DEER) spectroscopy, documented large (up to 20Å) changes in distance between nitroxide probes positioned on the Ras and α-helical domains of Gi upon formation of a complex with light-activated rhodopsin27. Finally, it has been shown that GαsRas and GαsAH can form a functional GTPase when expressed together as separate proteins28. Therefore, it is perhaps not surprising that GαsAH is displaced relative to GαsRas; however, its location in this crystal structure most likely reflects only one of an ensemble of conformations that it can adopt under physiological conditions, but has been stabilized by crystal packing interactions (Figure S5).
Figure 5. Conformational changes in Gαs.
a, A comparison of Gαs in the β2AR-Gs complex (orange) with the GTPγS-bound Gαs (grey) 26 (PDB ID: 1AZT). GTPγS is shown as spheres. The helical domain of Gαs (GαsAH) exhibits a dramatic displacement relative to its position in the GTPγS-bound state. b, The α5-helix of Gαs is rotated and displaced toward the β2AR, perturbing the β6-α5 loop which otherwise forms part of the GTPγS binding pocket. c, The β1-α1 loop (P-loop) and β6-α5 loop of Gαs interact with the phosphates and purine ring, respectively, of GTPγS in the GTPγS-Gαs structure. d, The β1-α1 and β6-α5 loops are rearranged in the nucleotide-free β2AR-Gs structure.
A potential concern is that Nb35, which was used to facilitate crystallogenesis, may be responsible for the displacement of the GαsAH. However, Nb35, which binds at the interface between Gβ and GαsRas (Fig 2b and Fig. S6), would not be expected to interact with the GαsAH or interfere with its interactions with GαsRas. None of the Nb35 contacts on the Ras domain are involved in interactions with GαsAH based on the crystal structure of Gαs-GTPγS (1AZT). Moreover, if we superimpose the structures of the Ras domains of Gαs-GTPγS (1AZT) and β2AR-Gs, there is no overlap between Nb35 and the alpha helical domain of Gαs-GTPγS (Fig. S6). Similarly, if we align the Gβ subunits of the Gi-GDP heterotrimer (1GP2) with that of β2AR-Gs, there is no overlap between Nb35 and the alpha helical domain of Gi (Fig. S6). This analysis is in agreement with single particle EM studies which provide further evidence that Nb35 does not disrupt interactions between GαsAH and GαsRas (Westfield et al., companion manuscript).
The conformational links between the β2AR and the nucleotide-binding pocket primarily involve the amino and carboxyl terminal helices of Gαs (Fig 4). Figure 5b focuses on the region of GαsRas that undergoes the largest conformational change when comparing the structure of GαsRas from the Gs-β2AR complex with that from the Gαs-GTPγS complex 26. The largest difference is observed for the α5-helix, which is displaced 6Å towards the receptor and rotated as the carboxyl terminal end projects into transmembrane core of the β2AR. Previous studies using a variety of approaches have demonstrated the important role of the α5-helix in GPCR-G protein interactions29,30. Associated with movement of the α5-helix, the β6-α5 loop, which interacts with the guanine ring in the Gαs-GTPγS structure, is displaced outward, away from the nucleotide-binding pocket (Fig. 5b-d). The movement of α5-helix is also associated with changes in interactions between this helix and the β6-strand, the αN-β1 loop, and the α1-helix. The β1-strand forms another link between the β2AR and the nucleotide-binding pocket. The C-terminal end of this strand changes conformation around Gly47, and there are further changes in the β1-α1 loop (P-loop) that coordinates the γ-phosphate in the GTP-bound form (Fig. 5 b-d). The observations in the crystal structure are in agreement with deuterium exchange experiments where there is enhanced deuterium exchange in the β1-strand and the amino terminal end of the α5-helix upon formation of the nucleotide-free β2AR-Gs complex (Chung et al.). The DXMS studies provide additional insights into the dynamic nature of these conformational changes in Gs upon complex formation and are discussed more fully in the companion paper (Chung et al.).
The structure of a GDP-bound Gs heterotrimer has not been determined, so it is not possible to directly compare the Gαs-Gβγ interface before and after formation of the β2AR-Gs complex. Based on the structure of the GDP-bound Gi heterotrimer 31, we do not observe large changes in interactions between GαsRas and Gβγ upon formation of the complex with β2AR. This is also consistent with deuterium exchange studies (Chung et al.). As discussed above, Nb35 binds at the interface between GαsRas and Gβ (Fig. 2b); therefore, we cannot exclude the possibility that Nb35 may influence the relative orientation of the GαsRas-Gβγ interface in the crystal structure.
Assembly of the β2AR-Gs complex
Clues to the initial stages of complex formation may come from the recent active state structures of rhodopsin31,32. Figure 6a,b compares the active-state structure of β2AR in the β2AR-Gs complex with the recent structure of metarhodopsin II bound to a peptide representing the carboxyl terminus of transducin31. The conformational changes in TM5 and TM6 are smaller in metarhodopsin II, and the position of the carboxyl terminal alpha helix of transducin is tilted by approximately 30° relative to the position of the homologous region of Gs. These may represent fundamental differences in the receptor-G protein interactions between these two proteins, but given the conservation of the G-protein binding pocket, the changes more likely reflect the more extensive contacts formed with the intact G protein. The position of the transducin peptide in metarhodopsin II may represent the initial interaction between a GDP-bound G protein and a GPCR. We have attempted to reproduce a similar complex between the β2AR and a synthetic peptide representing the carboxyl terminal 20 amino acids of Gs, but did not observe any effect of this peptide on receptor function, possibly due to the solubility and behavior of the peptide in solution. However, when the carboxyl terminal 20 amino acids of Gs are fused to the carboxyl terminus of the β2AR (Fig. 6c), we observe a 27-fold increase in agonist affinity (Figure 6d). This effect is only 3.5-fold smaller than the effect we observe on agonist binding affinity in the β2AR-Gs complex, and demonstrates that there is a functional interaction between the peptide and receptor that may represent an initial stage in β2AR-Gs complex formation. Figure 6 e and f presents a possible sequence of interactions of β2AR and Gs when forming the nucleotide-free complex. The first interaction of the β2AR with the Gs heterotrimer would require a movement of the carboxyl terminus of the α5-helix away from the β6-strand to permit interactions with the β2AR similar to those observed in metarhodopsin II (Fig 6e). The availability of the carboxyl terminus of the α5-helix for interactions with the β2AR is supported by deuterium exchange studies (Chung et al., companion manuscript) showing that this segment is more dynamic in the Gs-GDP heterotrimer than would be expected from the crystal structure of Gαs26. The subsequent formation of more extensive interactions between the β2AR ICL 2 and the amino terminus of Gαs requires a rotation of GαsRas relative to the receptor and would be associated with further conformational changes in both β2AR and GαsRas (Fig. 6 f). We cannot say when GDP is released during the formation of the complex; however, we speculate that uncoupling of the GαsAH from GαsRas is a consequence of nucleotide release or at least a coincident event. This binding model is in agreement with deuterium exchange experiments (Chung et al., companion manuscript).
Figure 6. Possible sequence of β2AR-Gs complex formation.
a, b, Comparison of the β2AR-Gs structure (green and gold) with metarhodopsin II31 (PDB ID: 3PQR) (purple) bound with the carboxyl-terminal peptide of transducin (blue). TM7 has been omitted in panel a to better visualize the G proteins. c, Cartoon of the β2AR-Gαs peptide fusion construct used in the binding experiments (d). d, Competition binding experiments between [3H]-DHA and full agonist isoproterenol. Top panel shows binding data (reproduced from Rasmussen et al., 201112) on β2AR reconstituted in HDL particles with and without Gs heterotrimer. The fraction of β2AR in the Ki high state for the β2AR with Gs is 0.55. Bottom panel shows binding to β2AR and a β2AR-Gαs peptide fusion expressed in Sf9 cell membranes. The fraction of β2AR in the Ki high state for the β2AR-Gαs peptide fusion is 0.68. e, The initial interaction of agonist bound β2AR and GαsRas may involve an orientation of the carboxyl-terminus of GαsRas similar to that of the carboxyl-terminal peptide of transducin in the structure of metarhodopsin II. f, The final position of GαsRas on the β2AR as observed in the β2AR-Gs complex.
The β2AR-Gs complex crystal structure provides the first high-resolution view of transmembrane signaling for a GPCR. We now have a framework to design experiments to investigate the mechanism of complex formation, GTP binding and complex dissociation. Of particular interest will be studies designed to determine the functional significance of the large movement of GαsAH relative to GαsRas that is observed in the β2AR-Gs complex. A better understanding of the structural basis for G protein activation may provide new approaches for drug discovery. The high degree of structural homology within the ligand-binding pocket has posed challenges for developing highly selective drugs for specific GPCR targets. In contrast, there is relatively low homology at the interface between the β2AR and Gαs, so identifying sequence and structural features that define specificity for particular G proteins may enable the development of selective inhibitors of specific GPCR-G protein interactions.
METHODS SUMMARY
The β2AR-Gs complex was crystallized from β2AR and Gs protein expressed in insect cells. Crystallogenesis was aided by fusing T4 lysozyme to the amino terminus of the β2AR and the addition of a nanobody (Nb35) that binds at the interface between the Gα and Gβ subunits. Crystals were grown in a lipidic cubic phase using MAG7.7, a lipid that accommodates membrane proteins with larger hydrophilic surfaces15. Diffraction data were measured at beamline 23ID-B of the Advanced Photon Source and the structure was solved by molecular replacement. For more experimental details see Online Methods.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge support from National Institutes of Health Grants NS028471(B.K.K.) and GM083118 (B.K.K. and R.K.S.), GM56169 (W.I.W.), P01 GM75913 (S.H.G), and P60DK-20572 (R.K.S.), GM75915, P50GM073210 and U54GM094599 (M.C.), Science Foundation Ireland (07/IN.1/B1836) and FP7 COST Action CM0902 (M.C.),the Mathers Foundation (B.K.K. and W.I.W.), the Lundbeck Foundation (Junior Group Leader Fellowship, S.G.F.R.), the University of Michigan Biomedical Sciences Scholars Program (R.K.S.), the Fund for Scientific Research of Flanders (FWO-Vlaanderen) and the Institute for the encouragement of Scientific Research and Innovation of Brussels (ISRIB) (E.P. and J.S.), The Danish Council for Independent Research, Medical Sciences (J.M.M.). We thank Alan Coughlan for help with lipid synthesis.
ONLINE METHODS
Expression and purification of β2AR, Gs heterotrimer, and nanobody-35
An N-terminally fused T4 lysozyme-β2AR construct with β2AR truncated in position 365 (T4L-β2AR, described in detail below) was expressed in Sf9 insect cell cultures infected with recombinant baculovirus (BestBac, Expression Systems), and solubilized in n-Dodecyl-β-D-maltoside (DDM) according to methods described previously 33 (see figure S4 for purification overview). A β2AR construct truncated after residue 365 (β2AR-365) was used for the majority of the analytical experiments and for deuterium exchange experiments (Chung et al., companion paper). M1 Flag affinity chromatography (Sigma) served as the initial purification step followed by alprenolol-Sepharose chromatography for selection of functional receptor. A subsequent M1 Flag affinity chromatography step was used to exchange receptor-bound alprenolol for high-affinity agonist BI-167107. The agonist-bound receptor was eluted, dialyzed against buffer (20 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl, 0.1% DDM and 10 μM BI-167107), treated with lambda phosphatase (New England Biolabs), and concentrated to approximately 50 mg ml−1 with a 50 kDa molecular weight cut off (MWCO) Millipore concentrator. Prior to spin concentration, the β2AR-365 construct, but not T4L-β2AR, was treated with PNGaseF (New England Biolabs) to remove amino-terminal N-linked glycosylation. The purified receptor was routinely analyzed by SDS-PAGE/Coomassie brilliant blue staining (see figure S8a).
Bovine Gαs short, His6-bovine Gβ1, and bovine Gγ2 were expressed in HighFive insect cells (Invitrogen) grown in Insect Xpress serum-free media (Lonza). Cultures were grown to a density of 1.5 million cells per ml and then infected with three separate Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus each containing the gene for one of the G protein subunits at a 1:1 multiplicity of infection (the viruses were a generous gift from Dr. Alfred Gilman). After 40-48 hours of incubation the infected cells were harvested by centrifugation and resuspended in 75 ml lysis buffer (50 mM HEPES, pH 8.0, 65 mM NaCl, 1.1 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EDTA, 1x PTT (35 μg/ml phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride, 32 μg/ml tosyl phenylalanyl chloromethyl ketone, 32 μg/ml tosyl lysyl chloromethyl ketone), 1x LS (3.2 μg/ml leupeptin and 3.2 μg/ml soybean trypsin inhibitor), 5 mM β-mercaptoethanol (β-ME), and 10 μM GDP) per liter of culture volume. The suspension was pressurized with 600 psi N2 for 40 minutes in a nitrogen cavitation bomb (Parr Instrument Company). After depressurization, the lysate was centrifuged to remove nuclei and unlysed cells, and then ultracentrifuged at 180,000 x g for 40 minutes. The pelleted membranes were resuspended in 30 ml wash buffer (50 mM HEPES, pH 8.0, 50 mM NaCl, 100 μM MgCl2, 1x PTT, 1x LS, 5 mM β-ME, 10 μM GDP) per liter culture volume using a Dounce homogenizer and centrifuged again at 180,000 x g for 40 minutes. The washed pellet was resuspended in a minimal volume of wash buffer and flash frozen with liquid nitrogen.
The frozen membranes were thawed and diluted to a total protein concentration of 5 mg/ml with fresh wash buffer. Sodium cholate detergent was added to the suspension at a final concentration of 1.0%, MgCl2 was added to a final concentration of 5 mM, and 0.05 mg of purified protein phosphatase 5 (prepared in house) was added per liter of culture volume. The sample was stirred on ice for 40 minutes, and then centrifuged at 180,000 x g for 40 minutes to remove insoluble debris. The supernatant was diluted 5-fold with Ni-NTA load buffer (20 mM HEPES, pH 8.0, 363 mM NaCl, 1.25 mM MgCl2, 6.25 mM imidazole, 0.2% Anzergent 3-12, 1x PTT, 1x LS, 5 mM β-ME, 10 μM GDP), taking care to add the buffer slowly to avoid dropping the cholate concentration below its critical micelle concentration too quickly. 3 ml of Ni-NTA resin (Qiagen) pre-equlibrated in Ni-NTA wash buffer 1 (20 mM HEPES, pH 8.0, 300 mM NaCl, 2 mM MgCl2, 5 mM imidazole, 0.2% Cholate, 0.15% Anzergent 3-12, 1x PTT, 1x LS, 5 mM β-ME, 10 μM GDP) per liter culture volume was added and the sample was stirred on ice for 20 minutes. The resin was collected into a gravity column and washed with 4x column volumes of Ni-NTA wash buffer 1, Ni-NTA wash buffer 2 (20 mM HEPES, pH 8.0, 50 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 10 mM imidazole, 0.15% Anzergent 3-12, 0.1% DDM, 1x PTT, 1x LS, 5 mM β-ME, 10 μM GDP), and Ni-NTA wash buffer 3 (20 mM HEPES, pH 8.0, 50 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 5 mM imidazole, 0.1% DDM, 1x PTT, 1x LS, 5 mM β-ME, 10 μM GDP). The protein was eluted with Ni-NTA elution buffer (20 mM HEPES, pH 8.0, 40 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 200 mM imidazole, 0.1% DDM, 1x PTT, 1x LS, 5 mM β-ME, 10 μM GDP). Protein-containing fractions were pooled and MnCl2 was added to a final concentration of 100 μM. Fifty μg of purified lambda protein phosphatase (prepared in house) was added per liter of culture volume and the elute was incubated on ice with stirring for 30 minutes. The eluate was passed through a 0.22 μm filter and loaded directly onto a MonoQ HR 16/10 column (GE Healthcare) equilibrated in MonoQ buffer A (20 mM HEPES, pH 8.0, 50 mM NaCl, 100 μM MgCl2, 0.1% DDM, 5 mM β-ME, 1x PTT). The column was washed with 150 ml buffer A at 5 ml/min and bound proteins were eluted over 350 ml with a linear gradient up to 28% MonoQ buffer B (same as buffer A except with 1 M NaCl). Fractions were collected in tubes spotted with enough GDP to make a final concentration of 10 μM. The Gs containing fractions were concentrated to 2 ml using a stirred ultrafiltration cell (Amicon) with a 10 kDa NMWL regenerated cellulose membrane (Millipore). The concentrated sample was run on a Superdex 200 prep grade XK 16/70 column (GE Healthcare) equilibrated in S200 buffer (20 mM HEPES, pH 8.0, 100 mM NaCl, 1.1 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EDTA, 0.012% DDM, 100 μM TCEP, 2 μM GDP). The fractions containing pure Gs were pooled, glycerol was added to 10% final concentration, and then the protein was concentrated to at least 10 mg/ml using a 30 kDa MWCO centrifugal ultrafiltration device (Millipore). The concentrated sample was then aliquoted, flash frozen, and stored at −80°. A typical yield of final, purified Gs heterotrimer from 8 liters of cell culture volume was 6 mg.
Nanobody-35 (Nb35) was expressed in the periplasm of E. coli strain WK6, extracted, and purified by nickel affinity chromatography according to previously described methods 12 followed by ion-exchange chromatography (figure S9a) using a Mono S 10/100 GL column (GE Healthcare). Selected Nb35 fractions were dialysis against buffer (10 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl) and concentrated to approximately 65 mg ml−1 with a 10 kDa MWCO Millipore concentrator.
Complex formation, stabilization and purification
Formation of a stable complex (see figure S10) was accomplished by mixing Gs heterotrimer at approximately 100 μM concentration with BI-167107 bound T4L-β2AR (or β2AR-365) in molar excess (approximately 130 μM) in 2 ml buffer (10 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl , 0.1 % DDM, 1 mM EDTA, 3 mM MgCl2, 10 μM BI-167107) and incubating for 3 hrs at room temperature. BI-167107, which was identified from screening and characterizing approximately 50 different β2AR agonists (data not shown), has a dissociation half-time of approximately 30 hrs, providing higher degree of stabilization to the active G protein-bound receptor than other full agonists such as isoproterenol 12. To maintain the high-affinity nucleotide-free state of the complex, apyrase (25 mU/ml, NEB) was added after 90 min to hydrolyze residual GDP released from Gαsupon binding to the receptor. GMP resulting from hydrolysis of GDP by apyrase has very poor affinity for the G protein in the complex. Rebinding of GDP can cause dissociation of the β2AR-Gs complex (figure S1a).
The β2AR-Gs complex in DDM shows significant dissociation after 48 hours at 4°C (figure S11a). We screened and characterized over 50 amphiphiles (data not shown) and identified MNG-3 12,13 (NG-310, Affymetrix-Anatrace) and its closely related analogs as detergents that substantially stabilize the complex (figure S11a,b). The complex was exchanged into MNG-3 by adding the β2AR-Gs mixture (2 ml) to 8 ml buffer (20 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl, 10 μM BI-167107) containing 1% MNG-3 for 1 hr at room temperature.
At this stage the mixture contains the β2AR-Gs complex, non-functional Gs, and an excess of β2AR. To separate functional β2AR-Gs complex from non-functional Gs, and to complete the detergent exchange, the β2AR-Gs complex was immobilized on M1 Flag resin and washed in buffer (20 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl, 10 μM BI-167107, and 3 mM CaCl2) containing 0.2% MNG-3. To prevent cysteine bridge-mediated aggregation of β2AR-Gs complexes, 100 μM TCEP was added to the eluted protein prior to concentrating it with a 50 kDa MWCO Millipore concentrator. Of note, it was discovered later that crystal growth improved at even higher TCEP concentrations (above 1 mM) compared to 100 μM TCEP, and that the integrity of the β2AR-Gs complex in MNG-3 was stable to 10 mM TCEP as measured by gel filtration analysis (figure S12c). In contrast, DDM-solubilized β2AR loses its ability to bind the high-affinity antagonist [3H]-dihydroalprenolol ([3H]-DHA) in 10 mM TCEP (data not shown), probably due to disruption of extracellular disulfide bonds. Iodoacetamide could not be used to block reactive cysteines on Gs alpha and beta subunits as it caused dissociation of the β2AR-Gs complex (figure S12b). The final size exclusion chromatography procedure to separate excess free receptor from the β2AR-Gs complex (figure S8b) was performed on a Superdex 200 10/300 GL column (GE Healthcare) equilibrated with buffer containing 0.02 % MNG-3, 10 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl, 10 μM BI-167107, and 100 μM TCEP. Peak fractions were pooled (figure S8b) and concentrated to approximately 90 mg ml−1 with a 100 kDa MWCO Viva-spin concentrator and analyzed by SDS-PAGE/Coomassie brilliant blue staining (figure S8a) and gel filtration (figure S8c). To confirm a pure, homogeneous, and dephosphorylated preparation, the β2AR-Gs complex was routinely analyzed by ion exchange chromatography (figure S8d).
Protein engineering
To increase the probability of obtaining crystals of the β2AR-Gs complex we set out to increase the polar surface area on the extracellular side of the receptor using two strategies. The first approach, to generate extracellular binding antibodies, was not successful. The second approach was to replace the flexible and presumably unstructured N-terminus with the globular protein T4 lysozyme (T4L) used previously to crystallize and solve the carazolol-bound receptor 3 The construct used here (T4L-β2AR) contained the cleavable signal sequence followed by the M1 Flag epitope (DYKDDDDA), the TEV protease recognition sequence (ENLYFQG), bacteriophage T4 lysozyme from N2 through Y161 including C54T and C97A mutations, and a two residue alanine linker fused to the human β2AR sequence D29 through G365. The PNGaseF-inaccessible glycosylation site of the β2AR at N187 was mutated to Glu. M96 and M98 in the first extracellular loop were each replaced by Thr to increase the otherwise low expression level of T4L-β2AR. The threonine mutations did not affect ligand binding affinity for [3H]-DHA, but caused a small, approximately two-fold decrease in affinity for isoproterenol (data not shown).
The β2AR-Gs peptide fusion construct used for [3H]-DHA competition binding with isoproterenol was constructed from the receptor truncated at position 365 and fused to the last 21 amino acids of the Gαs subunit (amino acids 374-394, except for C379A). A Gly-Ser is inserted between the receptor and the peptide. Also an extended TEV protease site (SENLYFQGS) was introduced in the β2AR between G360 and G361.
Stabilization of Gs with nanobodies
From negative stain EM imaging (Westfield et al., companion manuscript), we observed that the alpha helical domain of Gαs was flexible and therefore possibly responsible for poor crystal quality. Targeted stabilization of this domain was addressed by immunizing two llamas (Lama glama) with the bis(sulfosuccinimidyl)glutarate (BS2G, Pierce) cross-linked β2AR-Gs-BI-167107 ternary complex. Peripheral blood lymphocytes were isolated from the immunized animals to extract total RNA, prepare cDNA and construct a Nanobody phage display library according to published methods 16. Nb35 and Nb37 were enriched by two rounds of biopanning on the β2AR-Gs-BI-167107 ternary complex embedded in biotinylated high-density lipoprotein particles 34. Nb35 and Nb37 were selected for further characterization because they bind the β2AR-Gs-BI-167107 ternary complex but not the free receptor in an ELISA assay. Nanobody binding to the β2AR-Gs complex was confirmed by size exclusion chromatography (figure S1d), and it was noted that both nanobodies protected the complex from dissociation by GTPγS, suggestive of a stabilizing Gs-Nb interaction (figure S1d).
Crystallization
BI-167107 bound T4L-β2AR-Gs complex and Nb35 were mixed in 1:1.2 molar ratio. The small molar excess of Nb35 was verified by analytical gel filtration (see fig S9b). The mixture incubated for 1 hr at room temperature prior to mixing with 7.7 MAG (provided by Martin Caffrey) containing 10 % cholesterol (C8667, Sigma) in 1:1 protein solution to lipid ratio (w/w) using the twin-syringe mixing method reported previously 35. The concentration of T4L-β2AR-Gs-Nb35 complex in 7.7 MAG was approximately 25 mg ml−1. We believe the detergent MNG-3 stabilizes the T4L-β2AR-Gs complex during its incorporation into the lipid cubic phase. This may be due to the high affinity of MNG-3 for the receptor. The β2AR in MNG-3 maintains its structural integrity even when diluted below the CMC of the detergent, in contrast to β2AR in DDM, which rapidly loses binding activity (figure S11b). Moreover, MNG-3 improved crystal size and quality, as previously reported 12,13,36. The protein:lipid mixture was delivered through an LCP dispensing robot (Gryphon, Art Robbins Instruments) in 40 nl drops to either 24-well or 96-well glass sandwich plates and overlaid en-bloc with 0.8 μl precipitant solution. Multiple crystallization leads were initially identified using in-house screens partly based on reagents from the StockOptions Salt kit (Hampton Research). Crystals for data collection were grown in 18 to 22% PEG 400, 100 mM MES pH 6.5 (figure S1c), 350 to 450 mM potassium nitrate, 10 mM foscarnet (figure S1b), 1 mM TCEP (figure S12c), and 10 μM BI-167107. Crystals reached full size within 3-4 days at 20°C and were picked from a sponge-like mesophase and flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen without additional cryo-protectant.
Microcrystallography data collection and processing
Diffraction data were measured at the Advanced Photon Source beamline 23 ID-B. Hundreds of crystals were screened, and a final dataset was compiled using diffraction wedges of typically 10 degrees from 20 strongly diffracting crystals. All data reduction was performed using HKL2000 37. Although in many cases diffraction to beyond 3 Å was seen in initial frames, radiation damage and anisotropic diffraction resulted in low completeness in higher resolution shells. Analysis of the final dataset by the UCLA diffraction anisotropy server 38 indicated that diffraction along the a* axis was superior to that in other directions. On the basis of an F/σ(F) cutoff of 3 along each reciprocal space axis, reflections were subjected to an anisotropic truncation with resolution limits of 2.9, 3.2, and 3.2 Angstroms along a*, b*, and c* prior to use in refinement. We report this structure to an overall resolution of 3.2 Å. Despite the low completeness in the highest resolution shells (Supplementary table 3) inclusion of these reflections gave substantial improvements in map quality and lower Rfree during refinement.
Structure solution and refinement
The structure was solved by molecular replacement using Phaser 39,40. The order of the molecular replacement search was found to be critical in solving the structure. In order, the search models used were: the β and γ subunits from a Gi heterotrimer (PDB ID: 1GP2), the Gs alpha ras-like domain (PDB ID: 1AZT), the active-state β2AR (PDB ID: 3P0G), a β2AR binding nanobody (PDB ID: 3P0G), T4 lysozyme (PDB ID: 2RH1), and the Gs alpha helical domain (PDB ID: 1AZT). Following the determination of the initial structure by molecular replacement, rigid body refinement and simulated annealing were performed in Phenix 41 and BUSTER42, followed by restrained refinement and manual rebuilding in Coot 43. After iterative refinement and manual adjustments, the structure was refined in CNS using the DEN method 44. Although the resolution of this structure exceeds that for which DEN is typically most useful, the presence of several poorly resolved regions indicated that the incorporation of additional information to guide refinement could provide better results. The DEN reference models used were those used for molecular replacement, with the exception of NB35, which was well ordered and for which no higher resolution structure is available. Side chains were omitted from 53 residues for which there was no electron density past Cβ below a low contour level of 0.7σ in a 2Fo-Fc map. Figures were prepared using PyMOL (The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 1.3, Schrödinger, LLC.). MolProbity was used to determine Ramachandran statistics 45.
Competition Binding
Membranes expressing the β2AR or the β2AR-Gs peptide fusion were prepared from baculovirus-infected Sf9 cells and [3H]-DHA binding performed as previously described 46. For competition binding, membranes were incubated with [3H]-DHA (1.1 nM final) and increasing concentrations of (−)-isoproterenol (ISO) for 1 hr before harvesting onto GF/B filters. Competition data were fitted to a two-site binding model and ISO high and low Ki’s and fractions calculated using GraphPad prism.
Footnotes
Supplementary Information is linked to the online version of the paper at www.nature.com/nature.
Citations
- 1.Dixon RA, et al. Cloning of the gene and cDNA for mammalian beta-adrenergic receptor and homology with rhodopsin. Nature. 1986;321:75–79. doi: 10.1038/321075a0. doi:10.1038/321075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rasmussen SG, et al. Crystal structure of the human beta2 adrenergic G-protein-coupled receptor. Nature. 2007;450:383–387. doi: 10.1038/nature06325. doi:nature06325 [pii] 10.1038/nature06325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Rosenbaum DM, et al. GPCR engineering yields high-resolution structural insights into beta2-adrenergic receptor function. Science. 2007;318:1266–1273. doi: 10.1126/science.1150609. doi:1150609 [pii] 10.1126/science.1150609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lefkowitz RJ. Seven transmembrane receptors: something old, something new. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2007;190:9–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-201X.2007.01693.x. doi:APS1693 [pii] 10.1111/j.1365-201X.2007.01693.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Brandt DR, Asano T, Pedersen SE, Ross EM. Reconstitution of catecholamine-stimulated guanosinetriphosphatase activity. Biochemistry. 1983;22:4357–4362. doi: 10.1021/bi00288a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cerione RA, et al. The mammalian β2-adrenergic receptor: reconstitution of functional interactions between pure receptor and pure stimulatory nucleotide binding protein of the adenylate cyclase system. Biochemistry. 1984;23:4519–4525. doi: 10.1021/bi00315a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ross EM, Maguire ME, Sturgill TW, Biltonen RL, Gilman AG. Relationship between the β-adrenergic receptor and adenylate cyclase. Studies of ligand binding and enzyme activity in purified membranes of S49 lymphoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1977;252:5761–5775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.De Lean A, Stadel JM, Lefkowitz RJ. A ternary complex model explains the agonist-specific binding properties of the adenylate cyclase-coupled beta-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1980;255:7108–7117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Fredriksson R, Lagerstrom MC, Lundin LG, Schioth HB. The G-protein-coupled receptors in the human genome form five main families. Phylogenetic analysis, paralogon groups, and fingerprints. Mol Pharmacol. 2003;63:1256–1272. doi: 10.1124/mol.63.6.1256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Azzi M, et al. Beta-arrestin-mediated activation of MAPK by inverse agonists reveals distinct active conformations for G protein-coupled receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:11406–11411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1936664100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lefkowitz RJ, Shenoy SK. Transduction of receptor signals by beta-arrestins. Science. 2005;308:512–517. doi: 10.1126/science.1109237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Rasmussen SG, et al. Structure of a nanobody-stabilized active state of the beta(2) adrenoceptor. Nature. 2011;469:175–180. doi: 10.1038/nature09648. doi:nature09648 [pii] 10.1038/nature09648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chae PS, et al. Maltose-neopentyl glycol (MNG) amphiphiles for solubilization, stabilization and crystallization of membrane proteins. Nat Methods. 2010;7:1003–1008. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1526. doi:nmeth.1526 [pii] 10.1038/nmeth.1526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sprang SR. G protein mechanisms: insights from structural analysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1997;66:639–678. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.66.1.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Misquitta LV, et al. Membrane protein crystallization in lipidic mesophases with tailored bilayers. Structure. 2004;12:2113–2124. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2004.09.020. doi:S0969212604003715 [pii] 10.1016/j.str.2004.09.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Domanska K, et al. Atomic structure of a nanobody-trapped domain-swapped dimer of an amyloidogenic beta2-microglobulin variant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:1314–1319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1008560108. doi:1008560108 [pii] 10.1073/pnas.1008560108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Warne T, et al. Structure of a beta1-adrenergic G-protein-coupled receptor. Nature. 2008;454:486–491. doi: 10.1038/nature07101. doi:nature07101 [pii] 10.1038/nature07101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hofmann KP, et al. A G protein-coupled receptor at work: the rhodopsin model. Trends Biochem Sci. 2009;34:540–552. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2009.07.005. doi:S0968-0004(09)00162-5 [pii] 10.1016/j.tibs.2009.07.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Moro O, Lameh J, Hogger P, Sadee W. Hydrophobic amino acid in the i2 loop plays a key role in receptor-G protein coupling. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:22273–22276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Baltensperger K, et al. The beta-adrenergic receptor is a substrate for the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:1061–1064. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.2.1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Jastrzebska B, Tsybovsky Y, Palczewski K. Complexes between photoactivated rhodopsin and transducin: progress and questions. Biochem J. 2010;428:1–10. doi: 10.1042/BJ20100270. doi:BJ20100270 [pii] 10.1042/BJ20100270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Johnston CA, Siderovski DP. Receptor-mediated activation of heterotrimeric G-proteins: current structural insights. Mol Pharmacol. 2007;72:219–230. doi: 10.1124/mol.107.034348. doi:mol.107.034348 [pii] 10.1124/mol.107.034348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Breitwieser GE. G protein-coupled receptor oligomerization: implications for G protein activation and cell signaling. Circ Res. 2004;94:17–27. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000110420.68526.19. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000110420.68526.19 94/1/17 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Baneres JL, Parello J. Structure-based analysis of GPCR function: evidence for a novel pentameric assembly between the dimeric leukotriene B4 receptor BLT1 and the G-protein. J Mol Biol. 2003;329:815–829. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(03)00439-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Angers S, Salahpour A, Bouvier M. Dimerization: an emerging concept for G protein-coupled receptor ontogeny and function. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2002;42:409–435. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.42.091701.082314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sunahara RK, Tesmer JJ, Gilman AG, Sprang SR. Crystal structure of the adenylyl cyclase activator Gsalpha [see comments] Science. 1997;278:1943–1947. doi: 10.1126/science.278.5345.1943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Van Eps N, et al. Interaction of a G protein with an activated receptor opens the interdomain interface in the alpha subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1105810108. doi:1105810108 [pii] 10.1073/pnas.1105810108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Markby DW, Onrust R, Bourne HR. Separate GTP binding and GTPase activating domains of a G alpha subunit. Science. 1993;262:1895–1901. doi: 10.1126/science.8266082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Conklin BR, Bourne HR. Structural elements of Gα subunits that interact with Gβγ, receptors, and effectors. Cell. 1993;73:631–641. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90245-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Oldham WM, Hamm HE. Heterotrimeric G protein activation by G-protein-coupled receptors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:60–71. doi: 10.1038/nrm2299. doi:nrm2299 [pii] 10.1038/nrm2299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Choe HW, et al. Crystal structure of metarhodopsin II. Nature. 2011;471:651–655. doi: 10.1038/nature09789. doi:nature09789 [pii] 10.1038/nature09789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Standfuss J, et al. The structural basis of agonist-induced activation in constitutively active rhodopsin. Nature. 2011;471:656–660. doi: 10.1038/nature09795. doi:nature09795 [pii] 10.1038/nature09795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kobilka BK. Amino and carboxyl terminal modifications to facilitate the production and purification of a G protein-coupled receptor. Anal Biochem. 1995;231:269–271. doi: 10.1006/abio.1995.1533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Whorton MR, et al. A monomeric G protein-coupled receptor isolated in a high-density lipoprotein particle efficiently activates its G protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:7682–7687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0611448104. doi:0611448104 [pii] 10.1073/pnas.0611448104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Caffrey M, Cherezov V. Crystallizing membrane proteins using lipidic mesophases. Nat Protoc. 2009;4:706–731. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2009.31. doi:nprot.2009.31 [pii] 10.1038/nprot.2009.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Rosenbaum DM, et al. Structure and function of an irreversible agonist-beta(2) adrenoceptor complex. Nature. 2011;469:236–240. doi: 10.1038/nature09665. doi:nature09665 [pii] 10.1038/nature09665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Otwinowski Z, Minor W. Processing of x-ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. Methods Enzymol. 1997;276:307–326. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(97)76066-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Strong M, et al. Toward the structural genomics of complexes: crystal structure of a PE/PPE protein complex from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:8060–8065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0602606103. doi:0602606103 [pii] 10.1073/pnas.0602606103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.McCoy AJ. Solving structures of protein complexes by molecular replacement with Phaser. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2007;63:32–41. doi: 10.1107/S0907444906045975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.McCoy AJ, et al. Phaser crystallographic software. J Appl Crystallogr. 2007;40:658–674. doi: 10.1107/S0021889807021206. doi:10.1107/S0021889807021206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Afonine PV, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Adams PD. A robust bulk-solvent correction and anisotropic scaling procedure. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2005;61:850–855. doi: 10.1107/S0907444905007894. doi:S0907444905007894 [pii] 10.1107/S0907444905007894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Blanc E, et al. Refinement of severely incomplete structures with maximum likelihood in BUSTER-TNT. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2004;60:2210–2221. doi: 10.1107/S0907444904016427. doi:S0907444904016427 [pii] 10.1107/S0907444904016427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Emsley P, Cowtan K. Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2004;60:2126–2132. doi: 10.1107/S0907444904019158. doi:S0907444904019158 [pii] 10.1107/S0907444904019158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Schroder GF, Levitt M, Brunger AT. Super-resolution biomolecular crystallography with low-resolution data. Nature. 2010;464:1218–1222. doi: 10.1038/nature08892. doi:nature08892 [pii] 10.1038/nature08892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Chen VB, et al. MolProbity: all-atom structure validation for macromolecular crystallography. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 66:12–21. doi: 10.1107/S0907444909042073. doi:S0907444909042073 [pii] 10.1107/S0907444909042073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Swaminath G, Steenhuis J, Kobilka B, Lee TW. Allosteric modulation of beta2-adrenergic receptor by Zn(2+) Mol Pharmacol. 2002;61:65–72. doi: 10.1124/mol.61.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.