Abstract
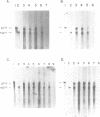
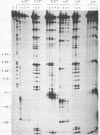
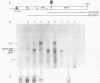
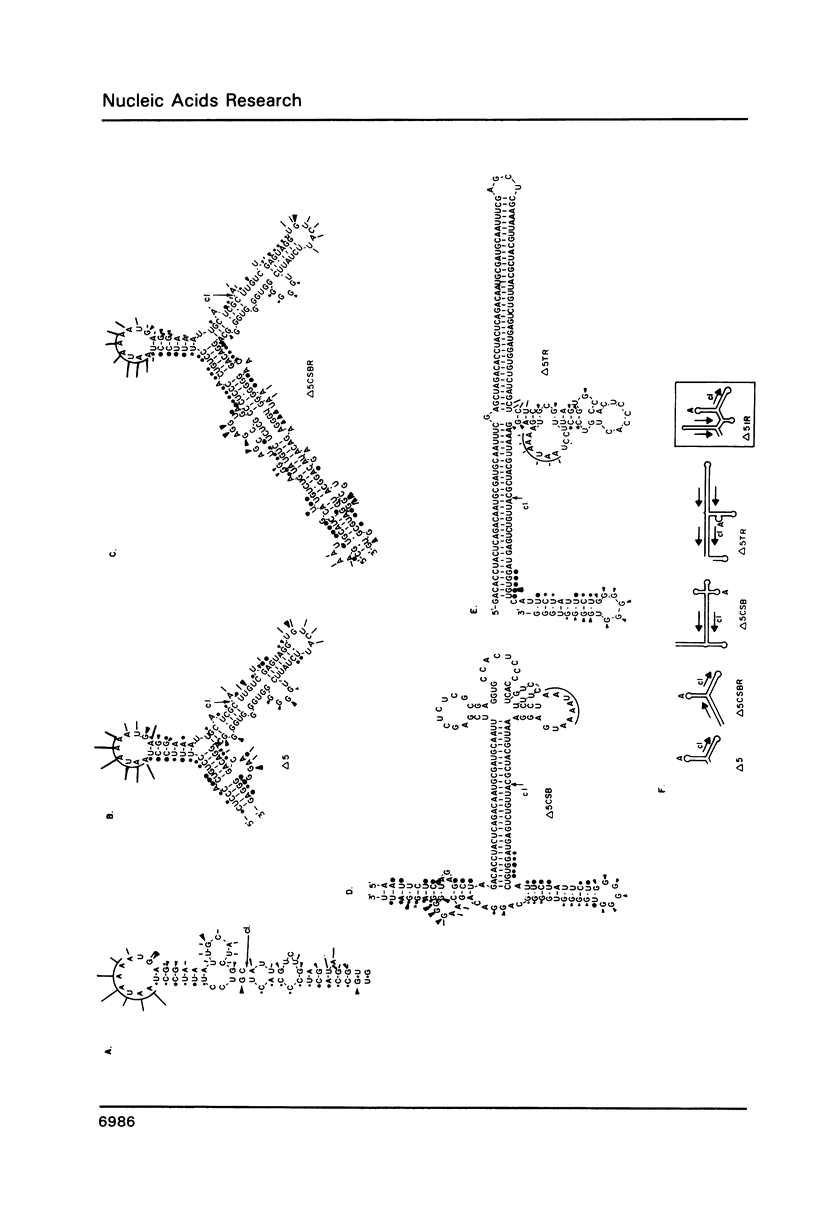
RNase mapping experiments show that the bovine growth hormone (bGH) poly(A) region forms an extensive hairpin loop. Mutants were prepared to change poly(A) region pre-mRNA structure and cleavage site efficiency without altering necessary sequences. An inverted repeat which includes the poly(A) cleavage site was created by insertion of a linker upstream of the poly(A) region to compete with any wild-type secondary structure. RNA mapping analyses show alterations in the nuclease accessibility of this mutant at the natural site of cleavage. This mutant shows a 75% drop in relative reporter gene expression at the steady-state protein and RNA levels. When the linker is inserted as a direct repeat, expression is equivalent to wildtype levels. To show that transcription was not terminated by the inverted repeat, the SV40 late poly(A) region was inserted downstream. These mutants show restored expression and processing at the downstream site. Our experiments reveal that the conformation of the poly(A) site pre-mRNA is important in mediating efficient cleavage-polyadenylation.
Full text
PDF




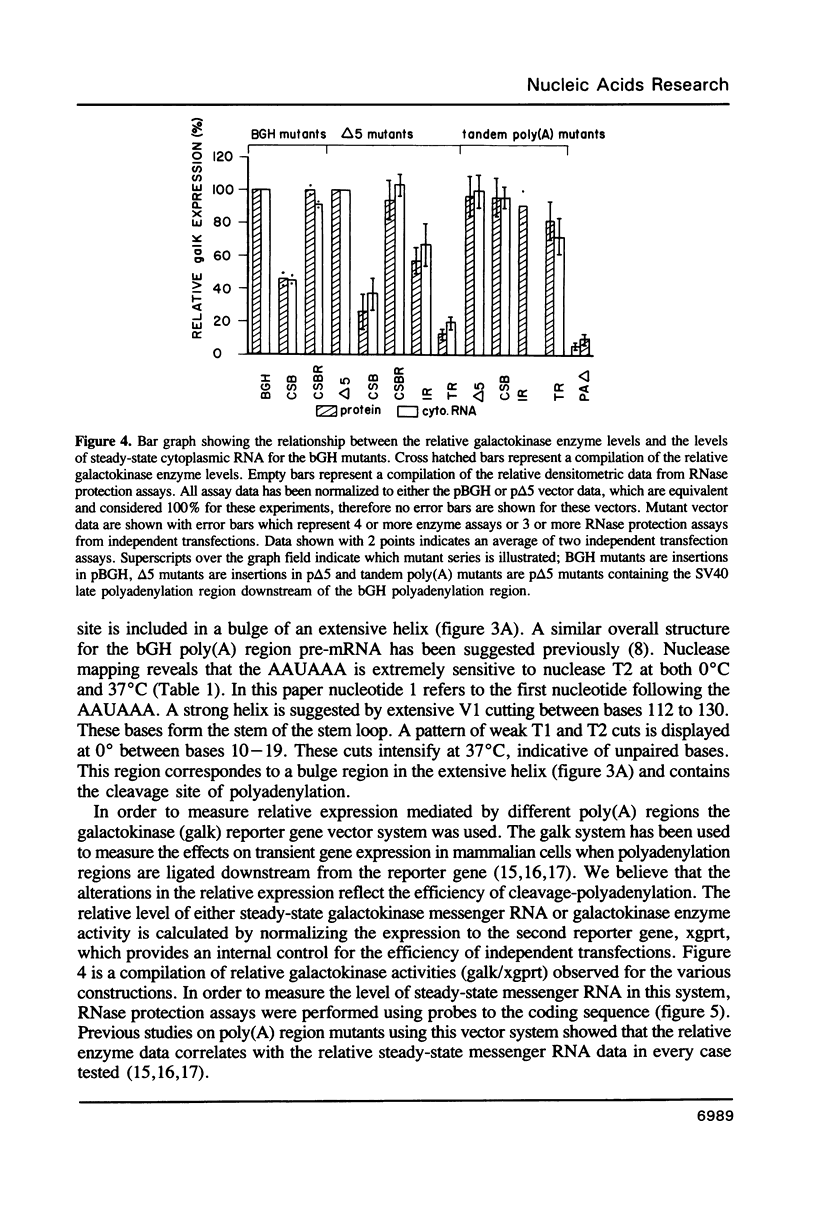

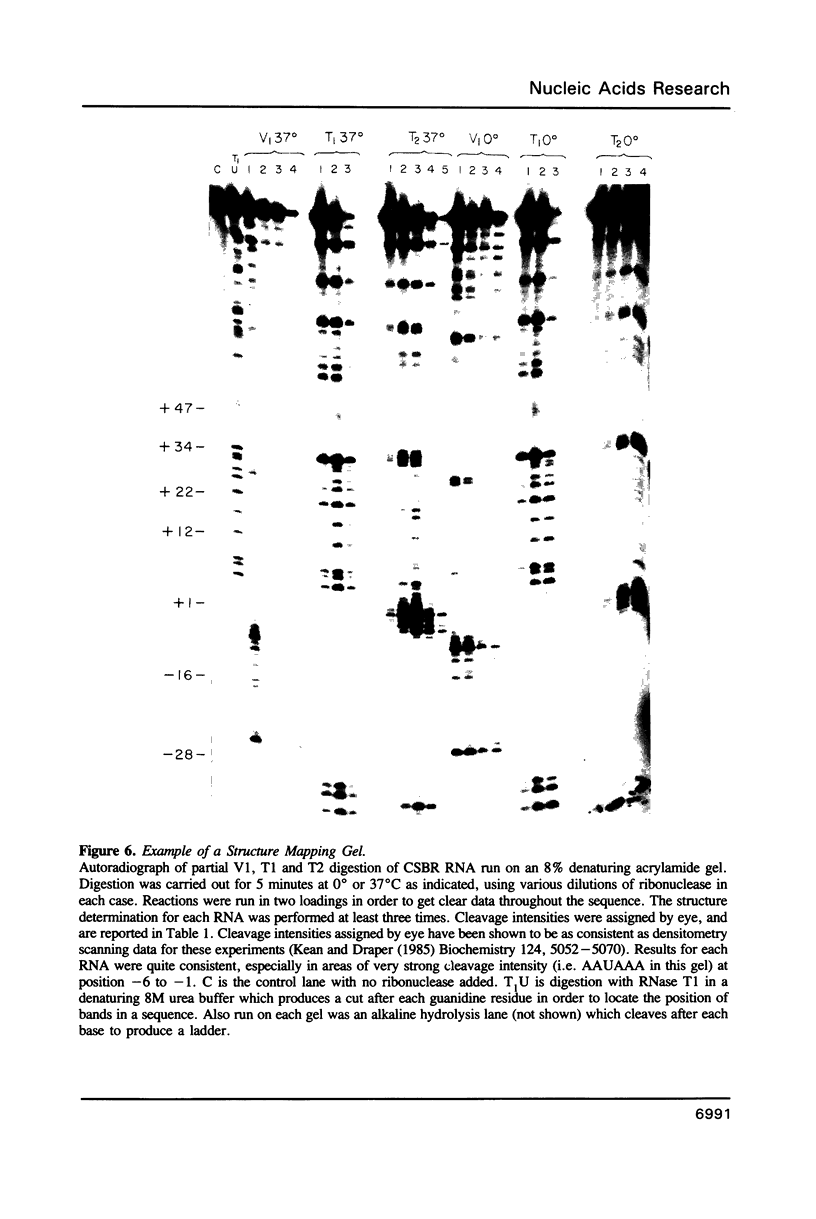







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berget S. M. Are U4 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins involved in polyadenylation? Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):179–182. doi: 10.1038/309179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Stacy T. P. Identification of sequences in the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene required for efficient processing and polyadenylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2104–2113. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deckman I. C., Draper D. E. S4-alpha mRNA translation regulation complex. II. Secondary structures of the RNA regulatory site in the presence and absence of S4. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):323–332. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90693-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denome R. M., Cole C. N. Patterns of polyadenylation site selection in gene constructs containing multiple polyadenylation signals. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4829–4839. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eperon L. P., Graham I. R., Griffiths A. D., Eperon I. C. Effects of RNA secondary structure on alternative splicing of pre-mRNA: is folding limited to a region behind the transcribing RNA polymerase? Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90202-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The sequence 5'-AAUAAA-3'forms parts of the recognition site for polyadenylation of late SV40 mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freier S. M., Kierzek R., Jaeger J. A., Sugimoto N., Caruthers M. H., Neilson T., Turner D. H. Improved free-energy parameters for predictions of RNA duplex stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9373–9377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil A., Proudfoot N. J. A sequence downstream of AAUAAA is required for rabbit beta-globin mRNA 3'-end formation. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):473–474. doi: 10.1038/312473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimmi E. R., Soprano K. J., Rosenberg M., Reff M. E. Deletions in the SV40 late polyadenylation region downstream of the AATAAA mediate similar effects on expression in various mammalian cell lines. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 26;16(18):8977–8997. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.18.8977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goins W. F., Stinski M. F. Expression of a human cytomegalovirus late gene is posttranscriptionally regulated by a 3'-end-processing event occurring exclusively late after infection. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4202–4213. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenh C. H., Deng T. L., Li D. W., DeWille J., Johnson L. F. Mouse thymidylate synthase messenger RNA lacks a 3' untranslated region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8482–8486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kean J. M., White S. A., Draper D. E. Detection of high-affinity intercalator sites in a ribosomal RNA fragment by the affinity cleavage intercalator methidiumpropyl-EDTA-iron(II). Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 10;24(19):5062–5070. doi: 10.1021/bi00340a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowman H. B., Draper D. E. On the recognition of helical RNA by cobra venom V1 nuclease. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5396–5403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marky L. A., Breslauer K. J. Calculating thermodynamic data for transitions of any molecularity from equilibrium melting curves. Biopolymers. 1987 Sep;26(9):1601–1620. doi: 10.1002/bip.360260911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt M. A., Imperiale M. J., Ali H., Nevins J. R. Requirement of a downstream sequence for generation of a poly(A) addition site. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):993–999. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90433-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfarr D. S., Rieser L. A., Woychik R. P., Rottman F. M., Rosenberg M., Reff M. E. Differential effects of polyadenylation regions on gene expression in mammalian cells. DNA. 1986 Apr;5(2):115–122. doi: 10.1089/dna.1986.5.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfarr D. S., Sathe G., Reff M. E. A highly modular cloning vector for the analysis of eukaryotic genes and gene regulatory elements. DNA. 1985 Dec;4(6):461–467. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryner L. C., Manley J. L. Requirements for accurate and efficient mRNA 3' end cleavage and polyadenylation of a simian virus 40 early pre-RNA in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):495–503. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadofsky M., Connelly S., Manley J. L., Alwine J. C. Identification of a sequence element on the 3' side of AAUAAA which is necessary for simian virus 40 late mRNA 3'-end processing. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2713–2719. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiki M., Hattori S., Hirayama Y., Yoshida M. Human adult T-cell leukemia virus: complete nucleotide sequence of the provirus genome integrated in leukemia cell DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3618–3622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solnick D. Alternative splicing caused by RNA secondary structure. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):667–676. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90239-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thirion J. P., Banville D., Noel H. Galactokinase mutants of Chinese hamster somatic cells resistant to 2-deoxygalactose. Genetics. 1976 May;83(1):137–147. doi: 10.1093/genetics/83.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toscani A., Soprano D. R., Cosenza S. C., Owen T. A., Soprano K. J. Normalization of multiple RNA samples using an in vitro-synthesized external standard cRNA. Anal Biochem. 1987 Sep;165(2):309–319. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90274-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tushinski R. J., Sussman P. M., Yu L. Y., Bancroft F. C. Pregrowth hormone messenger RNA: glucocorticoid induction and identification in rat pituitary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2357–2361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M., Stephenson P. Role of the conserved AAUAAA sequence: four AAUAAA point mutants prevent messenger RNA 3' end formation. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1045–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.6208611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilusz J., Shenk T. A 64 kd nuclear protein binds to RNA segments that include the AAUAAA polyadenylation motif. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):221–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90510-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woychik R. P., Lyons R. H., Post L., Rottman F. M. Requirement for the 3' flanking region of the bovine growth hormone gene for accurate polyadenylylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3944–3948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]