Abstract
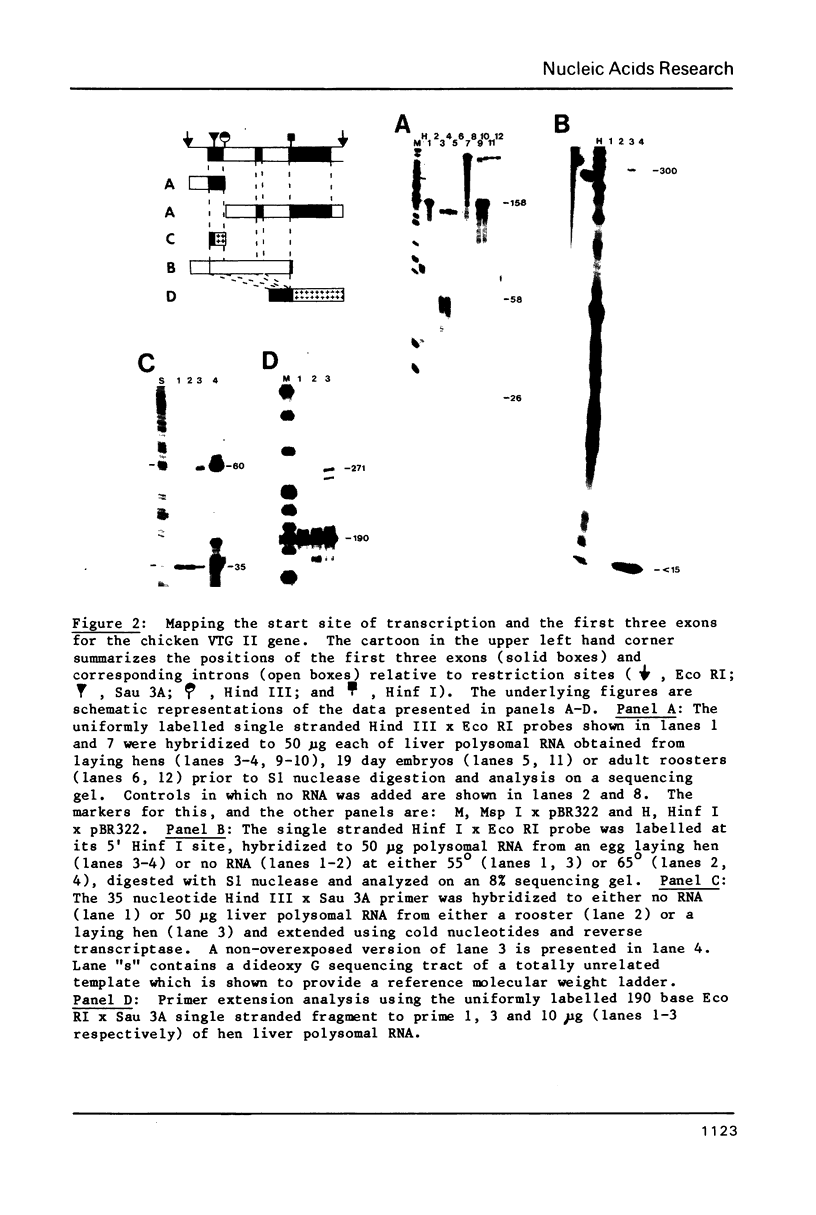
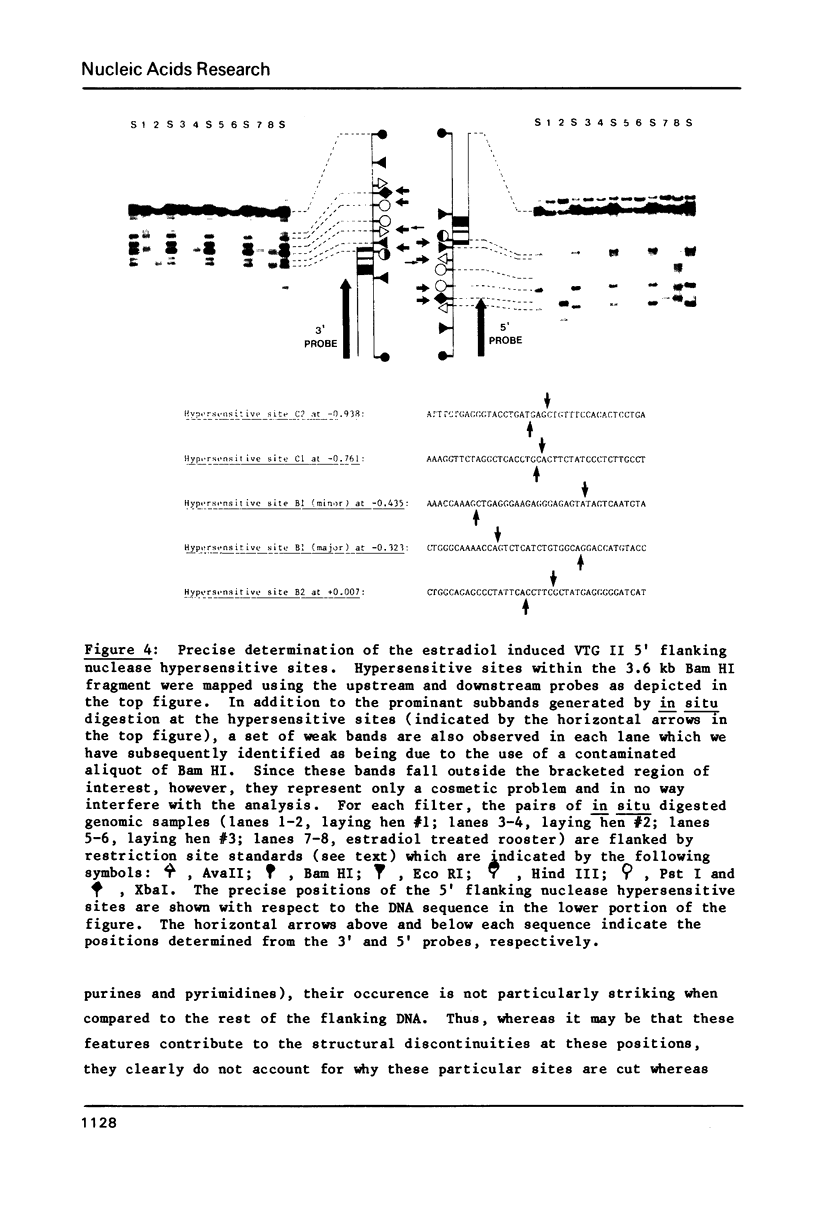
We have precisely determined the positions of the first three exons for the major chicken vitellogenin gene (VTG II) by a combination of S1 nuclease protection, primer extension and DNA sequencing experiments. In addition, we have determined the nucleotide sequences of the 5' flanking nuclease hypersensitive sites that we have previously shown are induced during the estrogen mediated activation of the VTG II gene in liver (1). One of these sites is found to be nearly identical to the enhancer core sequence of SV40. A computer assisted analysis of the DNA sequences upstream from the VTG II gene has revealed four short (7 to 9 base pair) sequence elements that are present in similar positions flanking the other major estrogen inducible gene for liver, very low density apolipoprotein II (apoVLDL II). For VTG II, these sequences are located between two of the induced nuclease hypersensitive sites that are liver specific. Sequences homologous to one element, located approximately 100 base pairs upstream from the mRNA cap sites of the VTG II and apoVLDL II genes, are also observed for three estrogen inducible genes that are expressed in the oviduct, although for each of these genes the sequence falls further upstream, between -220 and -200. We suggest that these conserved sequences may be important in mediating the tissue specific responses of these genes to estrogen.
Full text
PDF
















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnberg A. C., Meijlink F. C., Mulder J., van Bruggen E. F., Gruber M., Geert A. B. Isolation and characterization of genomic clones covering the chicken vitellogenin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 24;9(14):3271–3286. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.14.3271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., O'Hare K., Breathnach R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene-sequence of putative control regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):127–142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock M. L., Shapiro D. J. Estrogen stabilizes vitellogenin mRNA against cytoplasmic degradation. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):207–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90151-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch J. B., Weintraub H. Temporal order of chromatin structural changes associated with activation of the major chicken vitellogenin gene. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):65–76. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90335-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busslinger M., Portmann R., Irminger J. C., Birnstiel M. L. Ubiquitous and gene-specific regulatory 5' sequences in a sea urchin histone DNA clone coding for histone protein variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 11;8(5):957–977. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.5.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet M., Gannon F., Hen R., Maroteaux L., Perrin F., Chambon P. Organization and sequence studies of the 17-piece chicken conalbumin gene. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):567–574. doi: 10.1038/282567a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremisi C. The appearance of DNase I hypersensitive sites at the 5' end of the late SV40 genes is correlated with the transcriptional switch. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):5949–5964. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.5949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Mulvihill E. R., Egly J. M., Chambon P. Interaction of eukaryotic class-B transcription factors and chick progesterone-receptor complex with conalbumin promoter sequences. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):965–975. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlinger P., Krust A., LeMeur M., Perrin F., Cochet M., Gannon F., Dupret D., Chambon P. Multiple initiation and polyadenylation sites for the chicken ovomucoid transcription unit. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 5;162(2):345–364. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90531-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glikin G. C., Gargiulo G., Rena-Descalzi L., Worcel A. Escherichia coli single-strand binding protein stabilizes specific denatured sites in superhelical DNA. Nature. 1983 Jun 30;303(5920):770–774. doi: 10.1038/303770a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grez M., Land H., Giesecke K., Schütz G., Jung A., Sippel A. E. Multiple mRNAs are generated from the chicken lysozyme gene. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):743–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90182-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronenborn B., Messing J. Methylation of single-stranded DNA in vitro introduces new restriction endonuclease cleavage sites. Nature. 1978 Mar 23;272(5651):375–377. doi: 10.1038/272375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Wasylyk B., Chambon P., Birnstiel M. L. Point mutation in the TATA box curtails expression of sea urchin H2A histone gene in vivo. Nature. 1981 Nov 12;294(5837):178–180. doi: 10.1038/294178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Eisenman R., Weintraub H. Chromatin structure of endogenous retroviral genes and activation by an inhibitor of DNA methylation. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):311–317. doi: 10.1038/292311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haché R. J., Wiskocil R., Vasa M., Roy R. N., Lau P. C., Deeley R. G. The 5' noncoding and flanking regions of the avian very low density apolipoprotein II and serum albumin genes. Homologies with the egg white protein genes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4556–4564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C. Homocopolymer sequences in the spacer of a sea urchin histone gene repeat are sensitive to S1 nuclease. Nature. 1982 Feb 25;295(5851):714–716. doi: 10.1038/295714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley D. E., Coleclough C., Perry R. P. Functional significance and evolutionary development of the 5'-terminal regions of immunoglobulin variable-region genes. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):681–689. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90184-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Gruss P. Enhancer elements. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):313–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90410-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohwi-Shigematsu T., Gelinas R., Weintraub H. Detection of an altered DNA conformation at specific sites in chromatin and supercoiled DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4389–4393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreil G. Transfer of proteins across membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:317–348. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E. C., Roop D. R., Tsai M. J., Woo S. L., O'Malley B. W. Heterogeneous initiation regions for transcription of the chicken ovomucoid gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 25;10(18):5553–5567. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.18.5553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A., Weintraub H. An altered DNA conformation detected by S1 nuclease occurs at specific regions in active chick globin chromatin. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):609–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. The inverted repeat as a recognizable structural feature in supercoiled DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6468–6472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Wood W. I., Dolan M., Engel J. D., Felsenfeld G. A 200 base pair region at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene is accessible to nuclease digestion. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):45–55. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90359-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. S., Lee D. C., Palmiter R. D. Transferrin gene expression. Regulation of mRNA transcription in chick liver by steroid hormones and iron deficiency. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):148–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvihill E. R., LePennec J. P., Chambon P. Chicken oviduct progesterone receptor: location of specific regions of high-affinity binding in cloned DNA fragments of hormone-responsive genes. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):621–632. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Magnesium precipitation of ribonucleoprotein complexes. Expedient techniques for the isolation of undergraded polysomes and messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 13;13(17):3606–3615. doi: 10.1021/bi00714a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotatos N., Wells R. D. Cruciform structures in supercoiled DNA. Nature. 1981 Feb 5;289(5797):466–470. doi: 10.1038/289466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. Enhancer elements activated by steroid hormones? Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):687–688. doi: 10.1038/304687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pustell J., Kafatos F. C. A high speed, high capacity homology matrix: zooming through SV40 and polyoma. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 11;10(15):4765–4782. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.15.4765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storb U., Arp B., Wilson R. The switch region associated with immunoglobulin C mu genes is DNase I hypersensitive in T lymphocytes. Nature. 1981 Nov 5;294(5836):90–92. doi: 10.1038/294090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W., Dawid I. B., Ryffel G. U., Weber R. Vitellogenesis and the vitellogenin gene family. Science. 1981 Apr 17;212(4492):298–304. doi: 10.1126/science.7209528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Derbyshire R., Guy A., Molko D., Roget A., Téoule R., Chambon P. Specific in vitro transcription of conalbumin gene is drastically decreased by single-point mutation in T-A-T-A box homology sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7024–7028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., König M., Gruss P. Multiple point mutations affecting the simian virus 40 enhancer. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):626–631. doi: 10.1126/science.6297005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilks A. F., Cozens P. J., Mattaj I. W., Jost J. P. Estrogen induces a demethylation at the 5' end region of the chicken vitellogenin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4252–4255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilks A., Cato A. C., Cozens P. J., Mattaj I. W., Jost J. P. Isolation and fine structure organisation of an avian vitellogenin gene coding for the major estrogen-inducible mRNA. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):249–259. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90081-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiskocil R., Bensky P., Dower W., Goldberger R. F., Gordon J. I., Deeley R. G. Coordinate regulation of two estrogen-dependent genes in avian liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4474–4478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van het Schip A. D., Meijlink F. C., Strijker R., Gruber M., van Vliet A. J., van de Klundert J. A., Ab G. The nucleotide sequence of the chicken apo very low density lipoprotein II gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 11;11(9):2529–2540. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.9.2529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]