Abstract
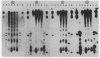
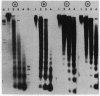
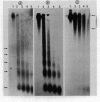
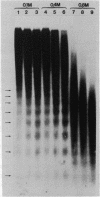
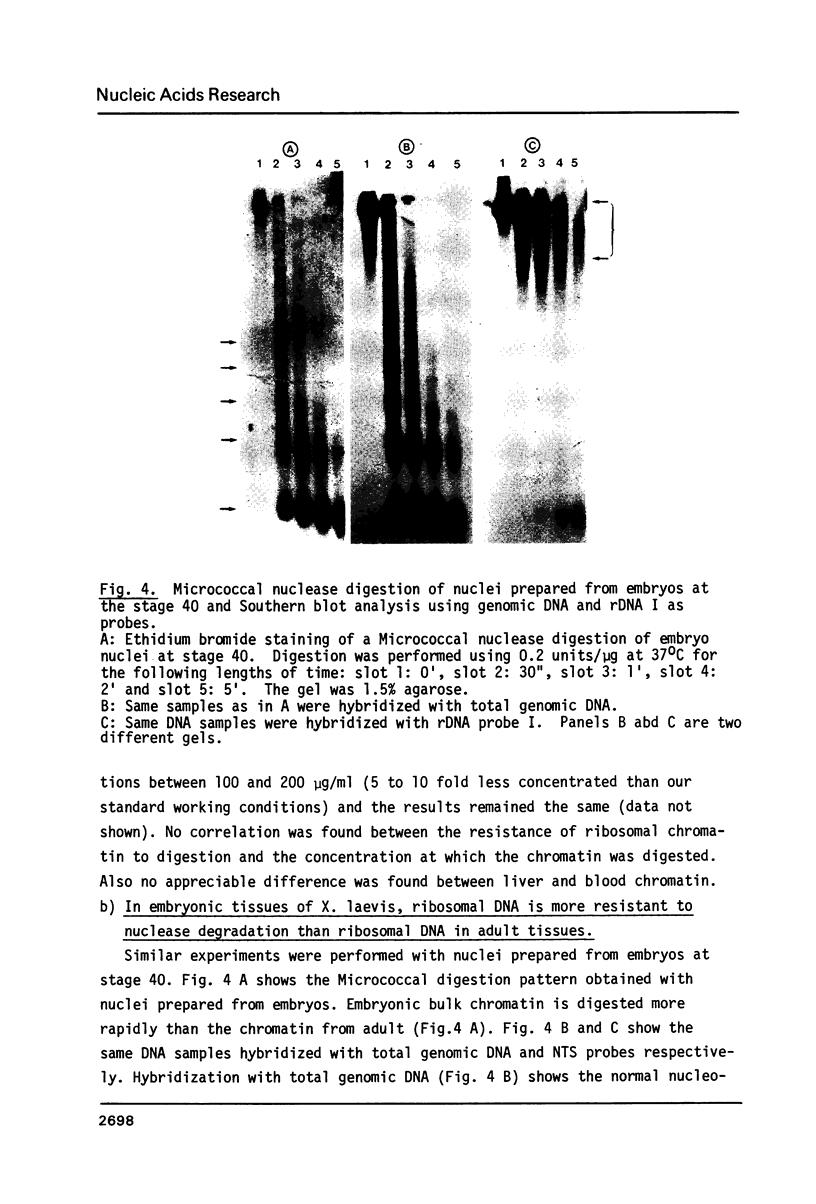
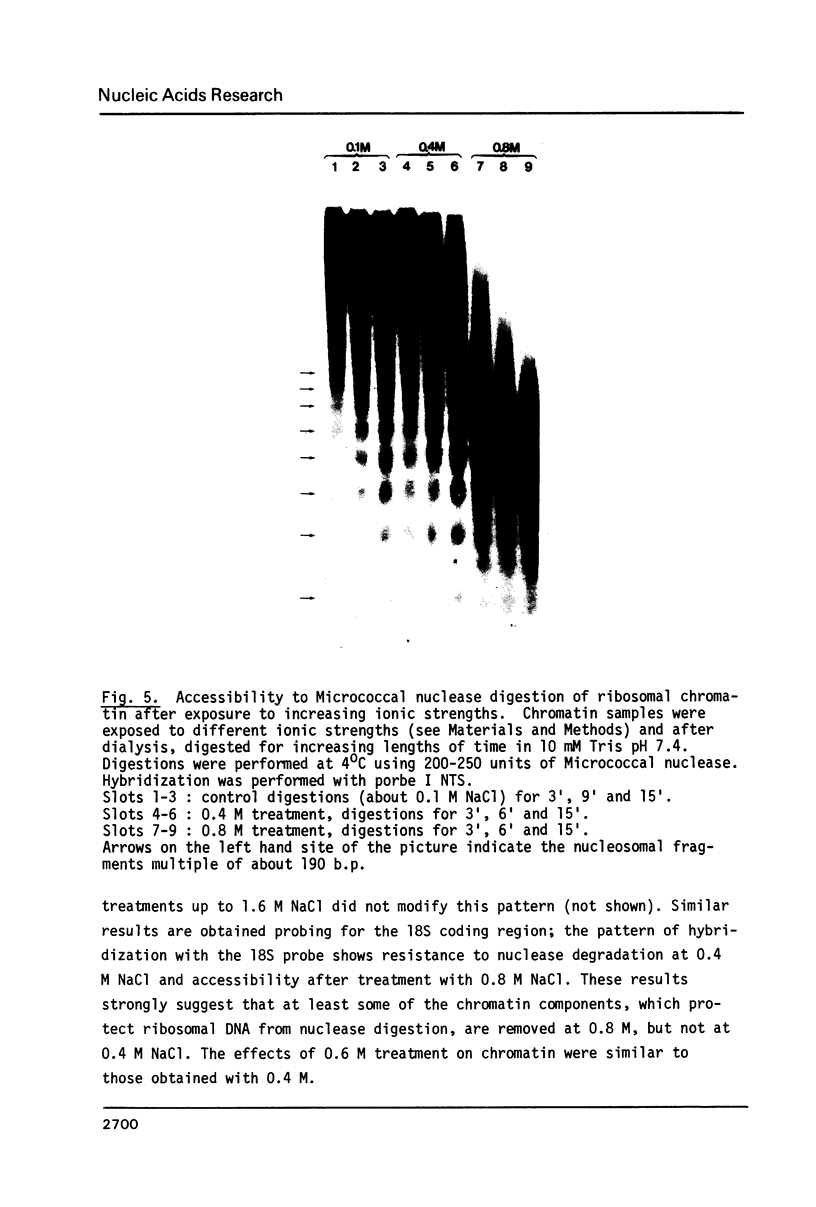
Micrococcal nuclease digestion was used as a tool to study the organization of the ribosomal chromatin in liver, blood and embryo cells of X. laevis. It was found that in liver and blood cells, ribosomal DNA is efficiently protected from nuclease attack in comparison to bulk chromatin. Although ribosomal chromatin is fragmented in a typical nucleosomal pattern, a considerable portion of ribosomal DNA retains a high molecular weight even after extensive digestion. A greater accessibility of the coding region in comparison to the non-coding spacer was found. In embryos, when ribosomal DNA is fully transcribed, these genes are even more highly protected than in adult tissues: in fact, the nucleosomal ladder can hardly be detected and rDNA is preserved in high molecular weight. Treatment of chromatin with 0.8 M NaCl abolishes the specific resistance of the ribosomal chromatin to digestion. The ribosomal chromatin, particularly in its active state, seems to be therefore tightly complexed with chromosomal proteins which protect its DNA from nuclease degradation.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellard M., Dretzen G., Bellard F., Oudet P., Chambon P. Disruption of the typical chromatin structure in a 2500 base-pair region at the 5' end of the actively transcribed ovalbumin gene. EMBO J. 1982;1(2):223–230. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01151.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boseley P., Moss T., Mächler M., Portmann R., Birnstiel M. Sequence organization of the spacer DNA in a ribosomal gene unit of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):19–31. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90291-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne L. A., Hewish D. R., Mobbs J. Mammalian chromatin substructure studies with the calcium-magnesium endonuclease and two-dimensional polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1974 Oct;143(1):67–72. doi: 10.1042/bj1430067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerini-Otero R. D., Zasloff M. A. Nucleosomal packaging of the thymidine kinase gene of herpes simplex virus transferred into mouse cells: an actively expressed single-copy gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5079–5083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giri C. P., Gorovsky M. A. DNase I sensitivity of ribosomal genes in isolated nucleosome core particles. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):197–214. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.197-e. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igo-Kemenes T., Hörz W., Zachau H. G. Chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:89–121. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Koller T. Structure of the active nucleolar chromatin of Xenopus laevis Oocytes. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):279–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90346-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy A., Noll M. Chromatin fine structure of active and repressed genes. Nature. 1981 Jan 15;289(5794):198–203. doi: 10.1038/289198a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohr D. E. Detailed analysis of the nucleosomal organization of transcribed DNA in yeast chromatin. Biochemistry. 1981 Oct 13;20(21):5966–5972. doi: 10.1021/bi00524a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D. J., Gorovsky M. A. Subunit structure of rDNA-containing chromatin. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 24;15(4):750–755. doi: 10.1021/bi00649a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ness P. J., Labhart P., Banz E., Koller T., Parish R. W. Chromatin structure along the ribosomal DNA of Dictyostelium. Regional differences and changes accompanying cell differentiation. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 25;166(3):361–381. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper P. W., Celis J., Kaltoft K., Leer J. C., Nielsen O. F., Westergaard O. Tetrahymena ribosomal RNA gene chromatin is digested by micrococcal nuclease at sites which have the same regular spacing on the DNA as corresponding sites in the bulk nuclear chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Feb;3(2):493–505. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.2.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruitt S. C., Grainger R. M. A mosaicism in the higher order structure of Xenopus oocyte nucleolar chromatin prior to and during ribosomal gene transcription. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):711–720. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90434-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R. Ribosomal genes of Xenopus laevis: evidence of nucleosomes in transcriptionally active chromatin. Science. 1976 Oct 29;194(4264):529–532. doi: 10.1126/science.973136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheer U. Structural organization of spacer chromatin between transcribed ribosomal RNA genes in amphibian oocytes. Eur J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;23(1):189–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spadafora C., Oudet P., Chambon P. Rearrangement of chromatin structure induced by increasing ionic strength and temperature. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct;100(1):225–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb02053.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinelli G., Albanese I., Anello L., Ciaccio M., Di Liegro I. Chromatin structure of histone genes in sea urchin sperms and embryos. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):7977–7991. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.7977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weischet W. O., Glotov B. O., Zachau H. G. Protection of expressed immunoglobulin genes against nuclease cleavage. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 11;11(11):3593–3612. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.11.3593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Wong Y. C., Elgin S. C. The chromatin structure of specific genes: II. Disruption of chromatin structure during gene activity. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):807–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]