Abstract
The structure and function of the genes encoding the polypeptide components of plasma lipoproteins are of interest because of the central role they play in the regulation of lipid metabolism. We have now completed our previous studies on the human apoAI gene and furthermore isolated and sequenced cDNA clones for apoAII , CII and CIII. The nucleotide sequences show the signal peptides of apoAII , CII and CIII to be 18, 22 and 20 amino acids in length, respectively, and in addition that prepro apoAII bears a classical propeptide structure of 5 amino acids. The amino acid homology detected between apoCII and pro- apoAI is discussed, as is the gene arrangement of the 5' non-coding region of apoAI mRNA. The relative liver mRNA levels of the 4 apolipoproteins analysed in this study have been estimated and compared with their corresponding plasma products. The data reported here provide an essential basis for further studies of structural and functional alleles of apo AI, AII, CII and CIII genes.
Full text
PDF

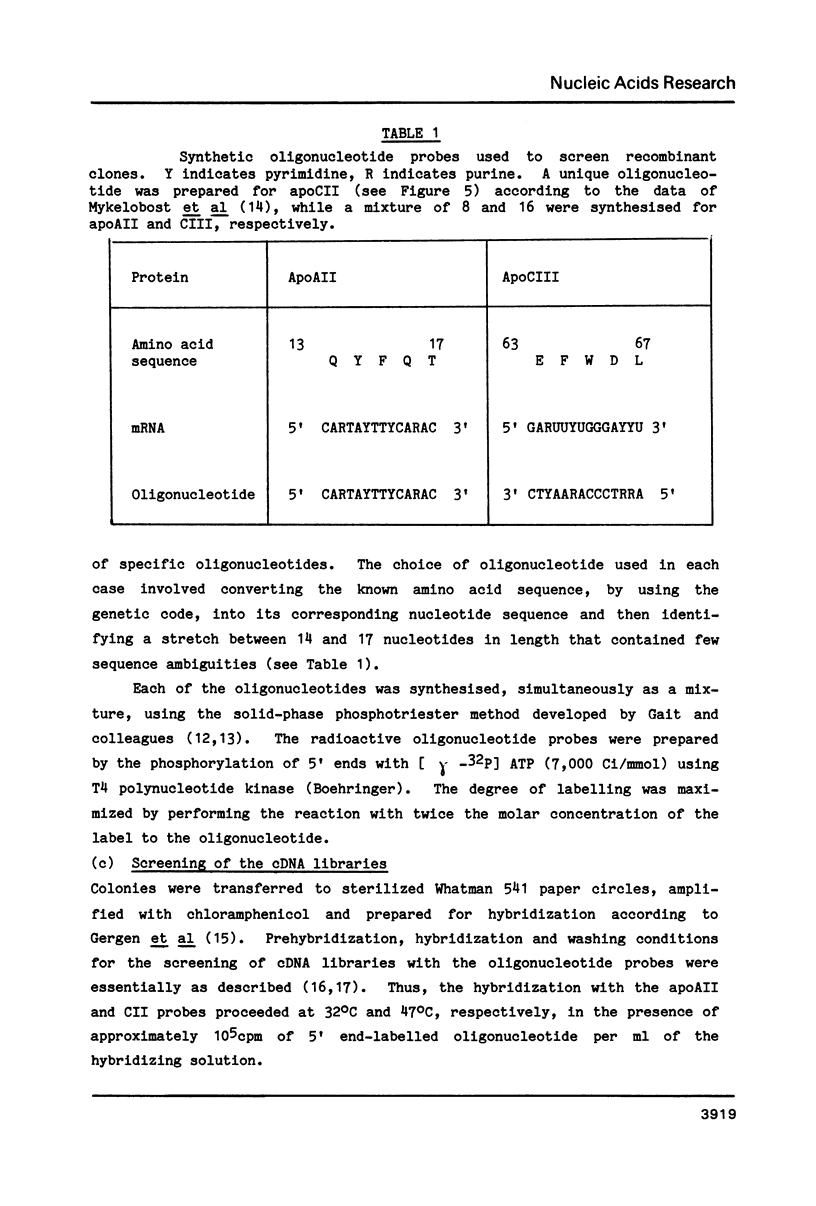







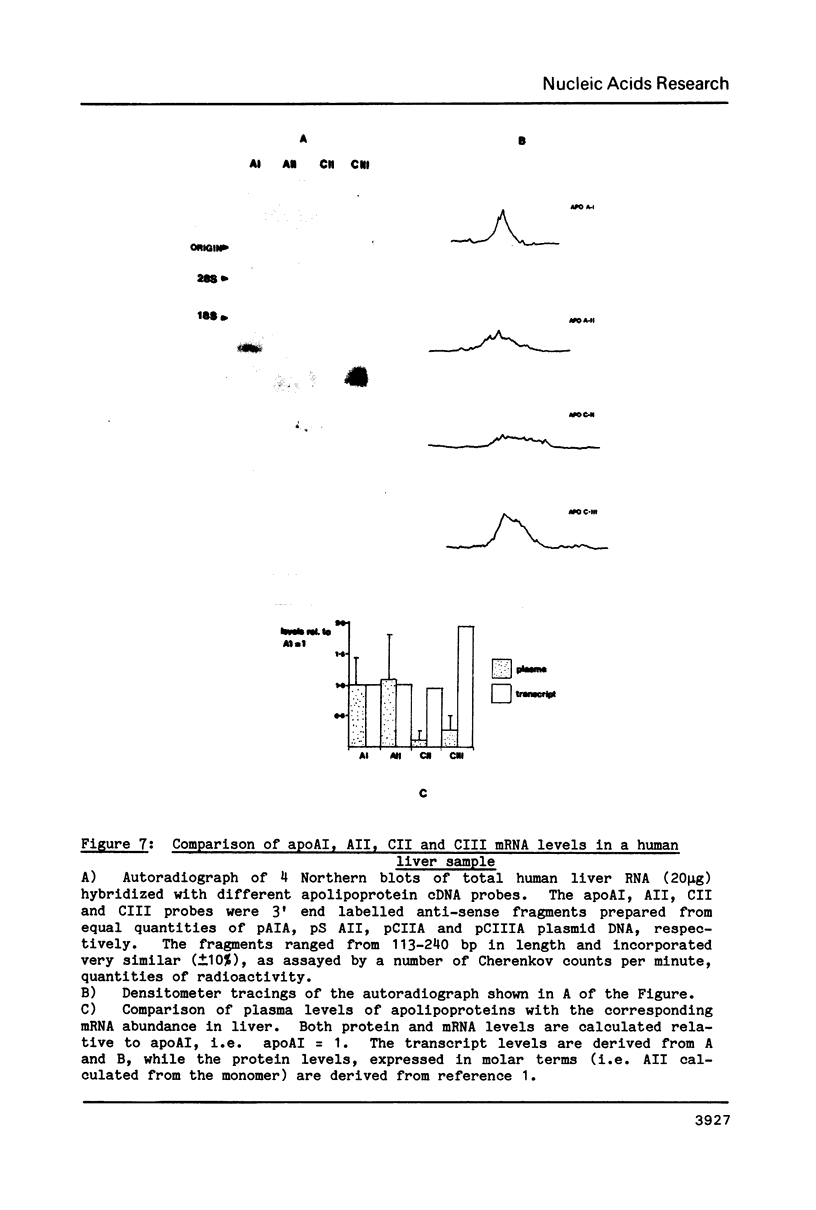





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan M., Lanyon W. G., Paul J. Multiple origins of transcription in the 4.5 Kb upstream of the epsilon-globin gene. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):187–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90221-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breckenridge W. C., Little J. A., Steiner G., Chow A., Poapst M. Hypertriglyceridemia associated with deficiency of apolipoprotein C-II. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jun 8;298(23):1265–1273. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197806082982301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer H. B., Jr, Lux S. E., Ronan R., John K. M. Amino acid sequence of human apoLp-Gln-II (apoA-II), an apolipoprotein isolated from the high-density lipoprotein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1304–1308. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer H. B., Jr, Shulman R., Herbert P., Ronan R., Wehrly K. The complete amino acid sequence of alanine apolipoprotein (apoC-3), and apolipoprotein from human plasma very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4975–4984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson D. P., Ross J. Human beta-globin promoter and coding sequences transcribed by RNA polymerase III. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):857–864. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90543-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth M. L., Gait M. J., Goelet P., Hong G. F., Singh M., Titmas R. C. Rapid synthesis of oligodeoxyribonucleotides VI. Efficient, mechanised synthesis of heptadecadeoxyribonucleotides by an improved solid phase phosphotriester route. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 10;9(7):1691–1706. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.7.1691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Posakony J. W., Maniatis T., Lawn R. M., O'Connell C., Spritz R. A., DeRiel J. K., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M., Slightom J. L. The structure and evolution of the human beta-globin gene family. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):653–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90429-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidge N., Nestel P., Ishikawa T., Reardon M., Billington T. Turnover of apoproteins A-I and A-II of high density lipoprotein and the relationship to other lipoproteins in normal and hyperlipidemic individuals. Metabolism. 1980 Jul;29(7):643–653. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(80)90109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman S. A., Deininger P. L., LaPorte P., Friedmann T., Geiduschek E. P. Analysis of transcription of the human Alu family ubiquitous repeating element by eukaryotic RNA polymerase III. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6439–6456. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gait M. J., Singh M., Sheppard R. C., Edge M. D., Greene A. R., Heathcliffe G. R., Atkinson T. C., Newton C. R., Markham A. F. Rapid synthesis of oligodeoxyribonucleotides. IV. Improved solid phase synthesis of oligodeoxyribonucleotides through phosphotriester intermediates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 11;8(5):1081–1096. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.5.1081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gergen J. P., Stern R. H., Wensink P. C. Filter replicas and permanent collections of recombinant DNA plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2115–2136. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girvitz S. C., Bacchetti S., Rainbow A. J., Graham F. L. A rapid and efficient procedure for the purification of DNA from agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Aug;106(2):492–496. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90553-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Dana S. E., Brunschede G. Y., Brown M. S. Genetic heterogeneity in familial hypercholesterolemia: evidence for two different mutations affecting functions of low-density lipoprotein receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1092–1096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. I., Bisgaier C. L., Sims H. F., Sachdev O. P., Glickman R. M., Strauss A. W. Biosynthesis of human preapolipoprotein A-IV. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):468–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. I., Budelier K. A., Sims H. F., Edelstein C., Scanu A. M., Strauss A. W. Biosynthesis of human preproapolipoprotein A-II. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):14054–14059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. I., Smith D. P., Alpers D. H., Strauss A. W. Proteolytic processing of the primary translation product of rat intestinal apolipoprotein A-IV mRNA. Comparison with preproapolipoprotein A-I processing. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8418–8423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. I., Smith D. P., Andy R., Alpers D. H., Schonfeld G., Strauss A. W. The primary translation product of rat intestinal apolipoprotein A-I mRNA is an unusual preproprotein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):971–978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hospattankar A. V., Fairwell T., Ronan R., Brewer H. B., Jr Amino acid sequence of human plasma apolipoprotein C-II from normal and hyperlipoproteinemic subjects. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):318–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. L., Baker H. N., Gilliam E. B., Gotto A. M., Jr Primary structure of very low density apolipoprotein C-II of human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):1942–1945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins P. J., Harper R. W., Nestel P. J. Severity of coronary atherosclerosis related to lipoprotein concentration. Br Med J. 1978 Aug 5;2(6134):388–391. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6134.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karathanasis S. K., McPherson J., Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L. Linkage of human apolipoproteins A-I and C-III genes. 1983 Jul 28-Aug 3Nature. 304(5924):371–373. doi: 10.1038/304371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karathanasis S. K., Norum R. A., Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L. An inherited polymorphism in the human apolipoprotein A-I gene locus related to the development of atherosclerosis. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):718–720. doi: 10.1038/301718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karathanasis S. K., Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L. Isolation and characterization of the human apolipoprotein A-I gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6147–6151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis B., Chait A., Wootton I. D., Oakley C. M., Krikler D. M., Sigurdsson G., February A., Maurer B., Birkhead J. Frequency of risk factors for ischaemic heart-disease in a healthy British population. With particular reference to serum-lipoprotein levels. Lancet. 1974 Feb 2;1(7849):141–146. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92438-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestel P. J., Fidge N. H. Apoprotein C metabolism in man. Adv Lipid Res. 1982;19:55–83. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-024919-0.50008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. Sequence at the 3' end of globin mRNA shows homology with immunoglobulin light chain mRNA. Nature. 1974 Nov 29;252(5482):359–362. doi: 10.1038/252359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees A., Shoulders C. C., Stocks J., Galton D. J., Baralle F. E. DNA polymorphism adjacent to human apoprotein A-1 gene: relation to hypertriglyceridaemia. Lancet. 1983 Feb 26;1(8322):444–446. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91440-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoulders C. C., Baralle F. E. Isolation of the human HDL apoprotein A1 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 25;10(16):4873–4882. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.16.4873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoulders C. C., Kornblihtt A. R., Munro B. S., Baralle F. E. Gene structure of human apolipoprotein A1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 11;11(9):2827–2837. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.9.2827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer-Sam J., Simmer R. L., Keith D. H., Shively L., Teplitz M., Itakura K., Gartler S. M., Riggs A. D. Isolation of a cDNA clone for human X-linked 3-phosphoglycerate kinase by use of a mixture of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotides as a detection probe. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):802–806. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoffel W., Krüger E., Deutzmann R. Cell-free translation of human liver apolipoprotein AI and AII mRNA. Processing of primary translation products. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1983 Mar;364(3):227–237. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1983.364.1.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss A. W., Zimmerman M., Mumford R. A., Alberts A. W. Processing of pre-proalbumin and pre-placental lactogen. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;343:168–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb47250.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suggs S. V., Wallace R. B., Hirose T., Kawashima E. H., Itakura K. Use of synthetic oligonucleotides as hybridization probes: isolation of cloned cDNA sequences for human beta 2-microglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6613–6617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Johnson M. J., Hirose T., Miyake T., Kawashima E. H., Itakura K. The use of synthetic oligonucleotides as hybridization probes. II. Hybridization of oligonucleotides of mixed sequence to rabbit beta-globin DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 25;9(4):879–894. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.4.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]