Abstract
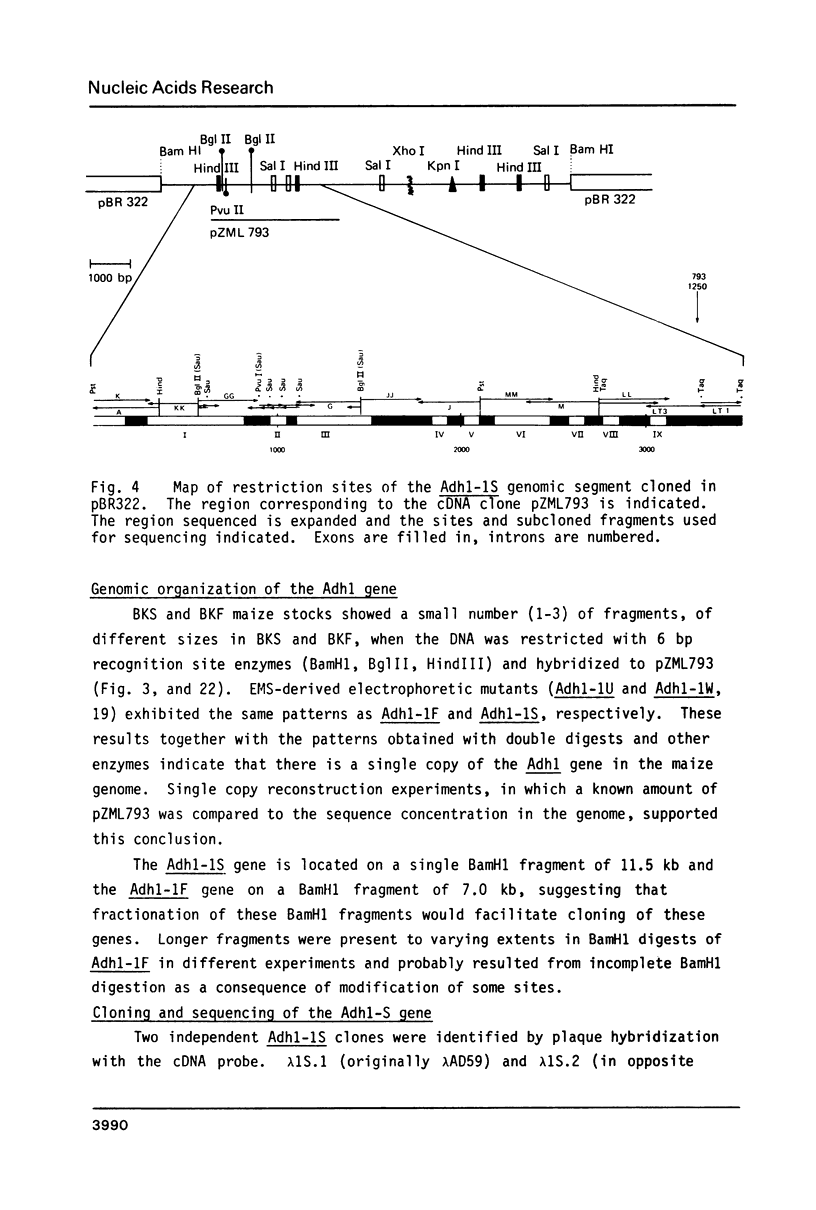
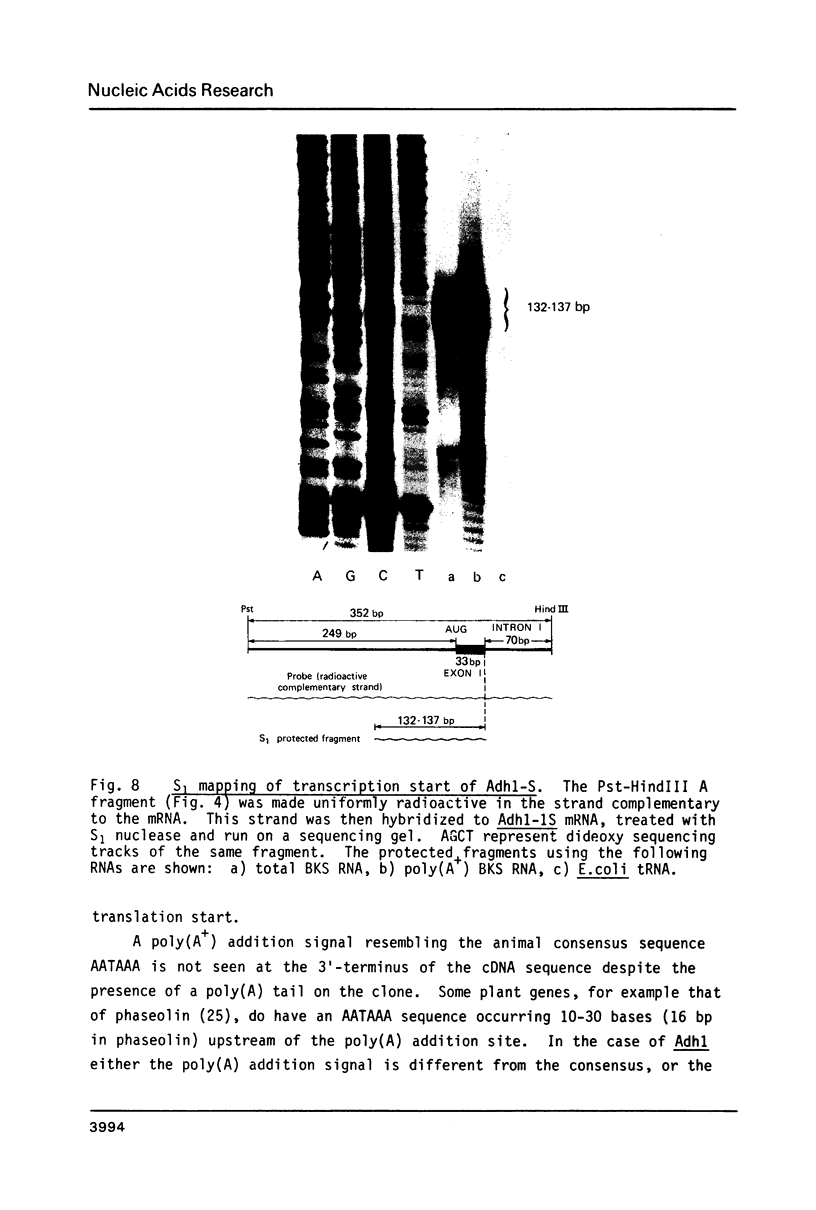
A cDNA clone of maize Adh1 which contains the entire protein coding region of the gene has been constructed. The protein sequence predicted from the nucleotide sequence is in agreement with limited protein sequencing data for the ADH1 enzyme. An 11.5 kb genomic fragment containing the Adh1 gene has been isolated using the cDNA clone as a probe, and the gene region fully sequenced. The gene is interrupted by 9 introns, their junction sequences fitting the animal gene consensus sequence. Within the gene there is a triplication of a segment (104 bp) spanning an intron-exon junction. Presumptive promoter elements have been identified and are similar in nucleotide sequence and location, relative to the start of transcription, to those of other plant and animal genes. No recognizable poly(A+) addition signal is evident. Comparison of the nucleotide sequences of the cDNA (derived from an Adh1 -F allele) and genomic (derived from an Adh1 -S allele) clones has identified an amino acid difference consistent with the observed difference in electrophoretic mobility of the two enzymes. The maize ADH1 amino acid sequence is 50% homologous to that of horse liver ADH but is only 20% homologous to yeast ADH.
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler P. M., Rimkus D., Davidson N. Gel electrophoretic fractionation of RNAs by partial denaturation with methylmercuric hydroxide. Anal Biochem. 1979 Oct 15;99(1):200–206. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund H., Brändén C. I., Jörnvall H. Structural comparisons of mammalian, yeast and bacillar alcohol dehydrogenases. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 25;102(1):61–73. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund H., Nordström B., Zeppezauer E., Söderlund G., Ohlsson I., Boiwe T., Söderberg B. O., Tapia O., Brändén C. I., Akeson A. Three-dimensional structure of horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase at 2-4 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 25;102(1):27–59. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeling M. Allelic variation at the level of intragenic recombination. Genetics. 1978 May;89(1):211–224. doi: 10.1093/genetics/89.1.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlach W. L., Pryor A. J., Dennis E. S., Ferl R. J., Sachs M. M., Peacock W. J. cDNA cloning and induction of the alcohol dehydrogenase gene (Adh1) of maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2981–2985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Brenner S., Barnett L., Cesareni G. Novel bacteriophage lambda cloning vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5172–5176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J., Freeling M. Purification of maize alcohol dehydrogenase-1 allozymes and comparison of their tryptic peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul 24;624(1):102–110. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90229-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Possible role of flanking nucleotides in recognition of the AUG initiator codon by eukaryotic ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5233–5252. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen K., Devereux J., Wilson D. R., Sheldon E., Larkins B. A. Cloning and sequence analysis reveal structural variation among related zein genes in maize. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):1015–1026. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90465-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. A regulatory upstream promoter element in the Drosophila hsp 70 heat-shock gene. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs M. M., Freeling M., Okimoto R. The anaerobic proteins of maize. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):761–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D., Endo T. Alcohol Dehydrogenase Polymorphism in Maize-simple and Compound Loci. Genetics. 1966 Apr;53(4):709–715. doi: 10.1093/genetics/53.4.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. Genetic control of alcohol dehydrogenase--a competition model for regulation of gene action. Genetics. 1971 Mar;67(3):411–425. doi: 10.1093/genetics/67.3.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B. Diazotizable arylamine cellulose papers for the coupling and hybridization of nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1799–1810. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. Determinant of cistron specificity in bacterial ribosomes. Nature. 1975 Mar 6;254(5495):34–38. doi: 10.1038/254034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieringa B., Meyer F., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Unusual splice sites revealed by mutagenic inactivation of an authentic splice site of the rabbit beta-globin gene. Nature. 1983 Jan 6;301(5895):38–43. doi: 10.1038/301038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






