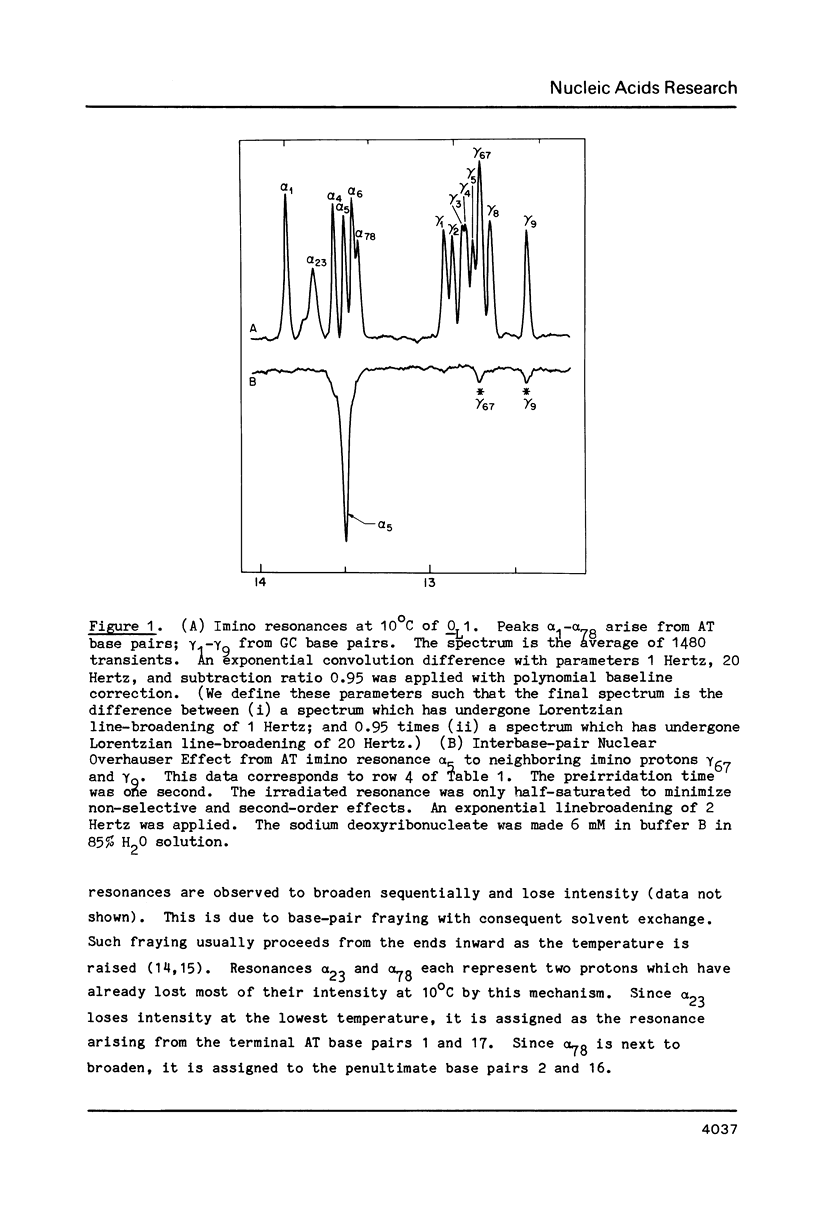
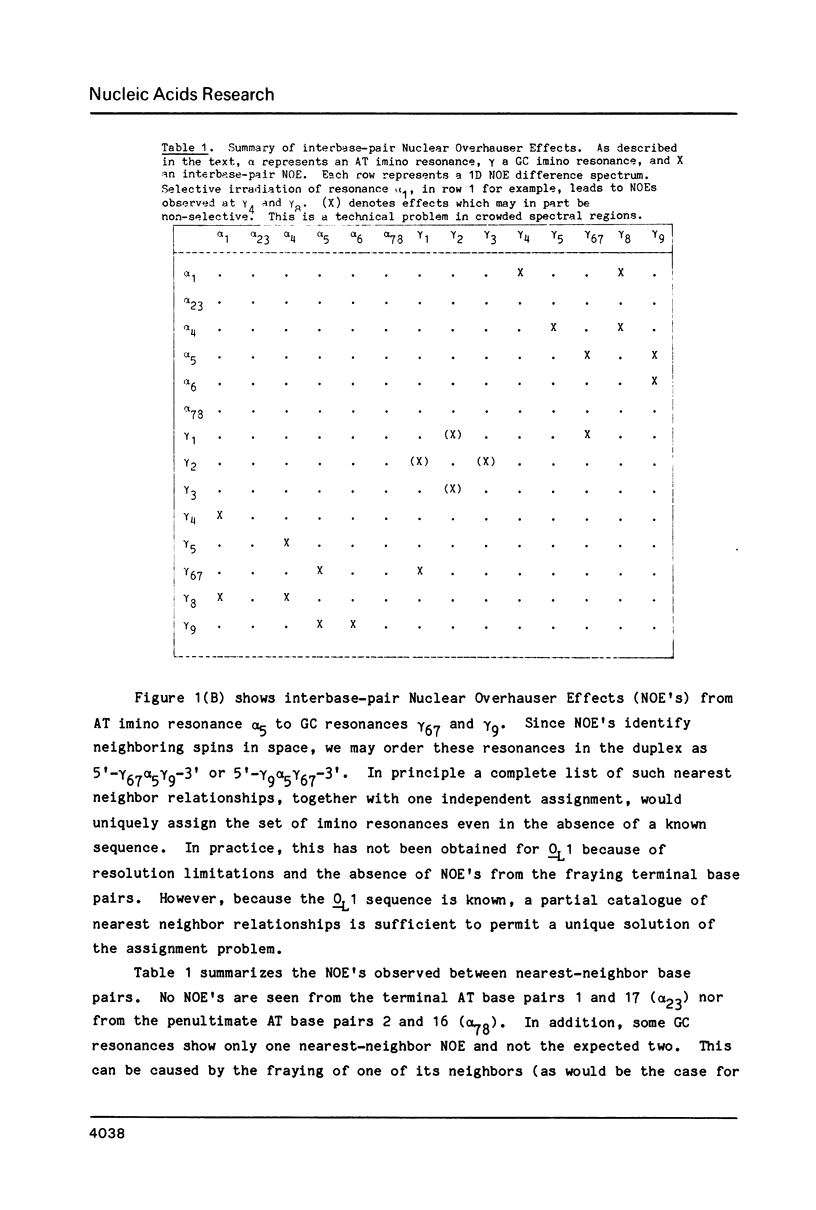
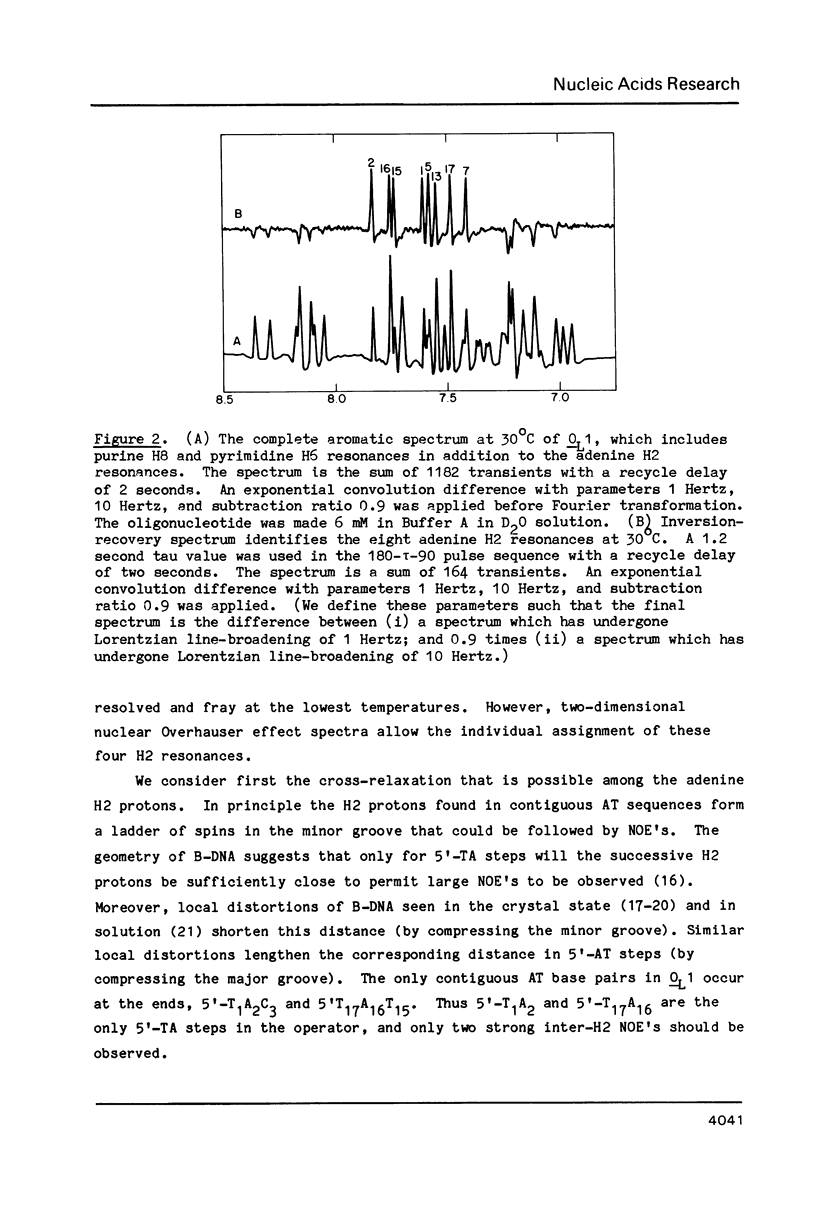
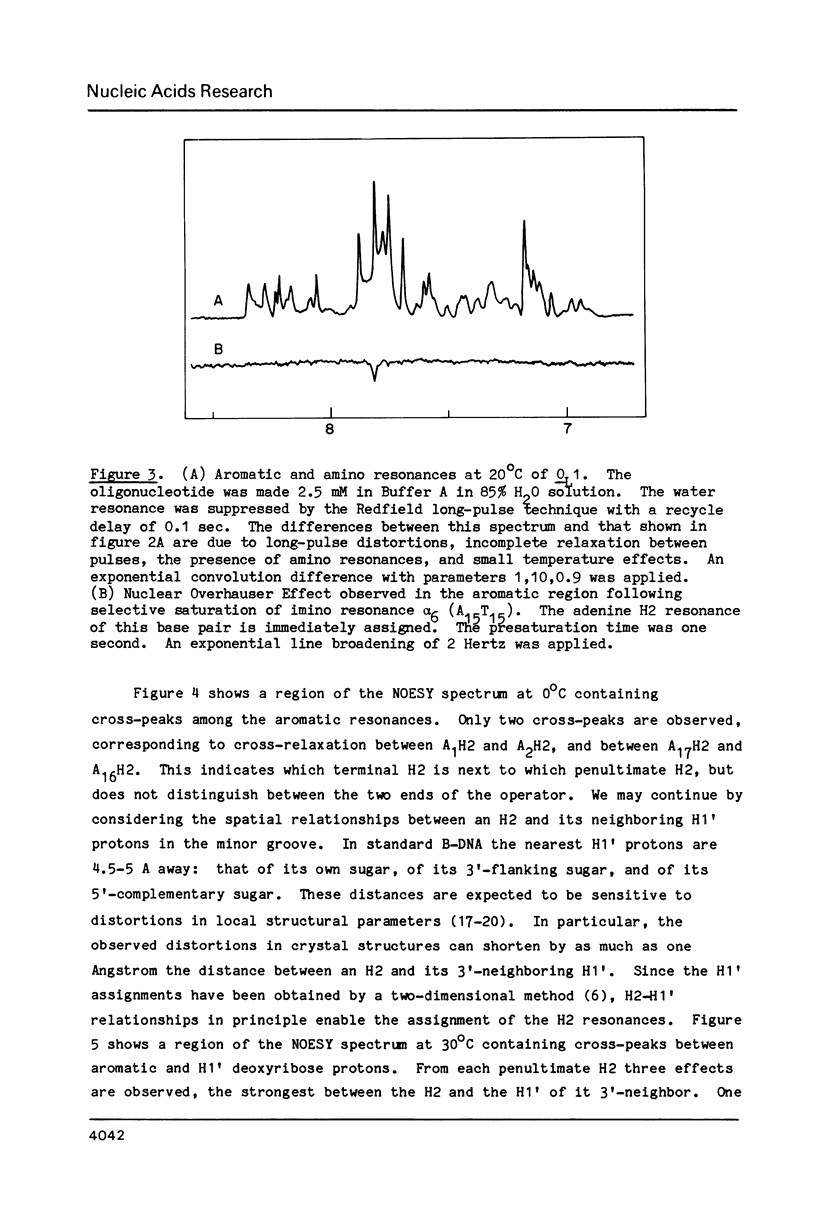
Abstract
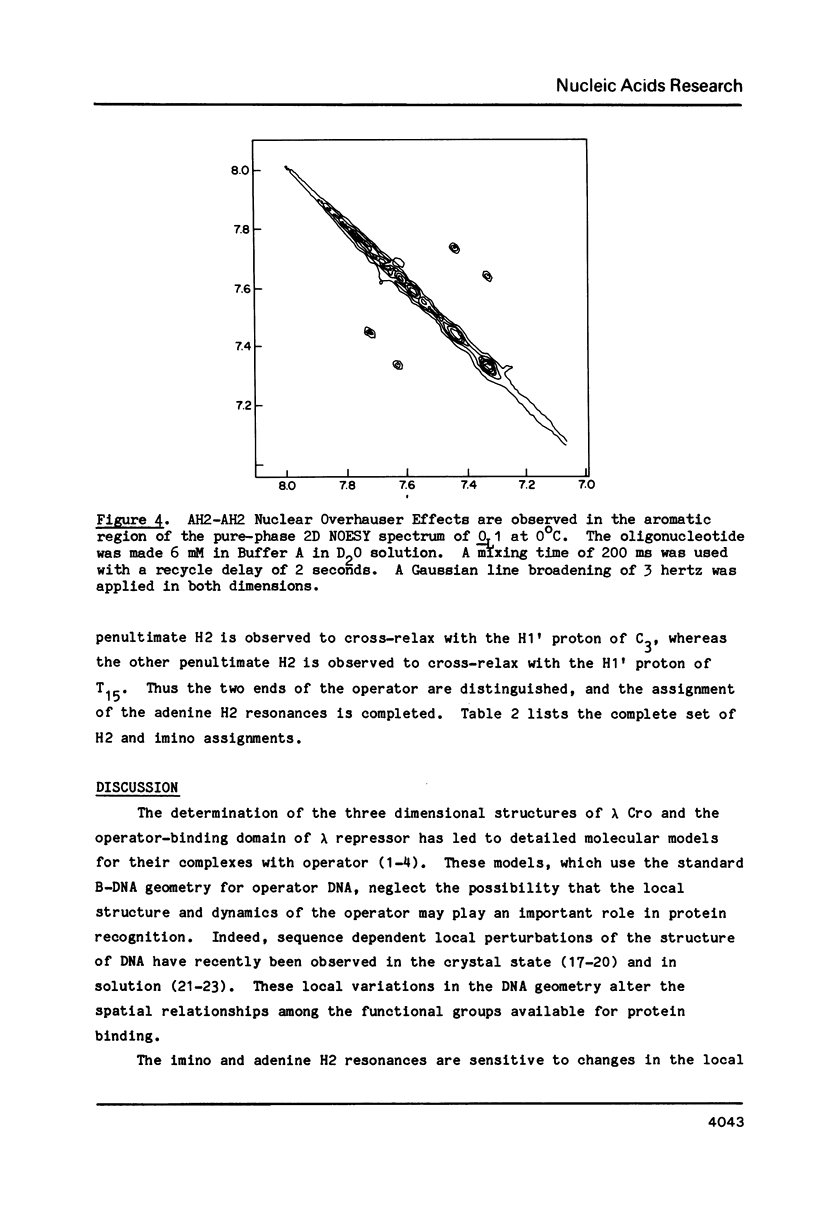
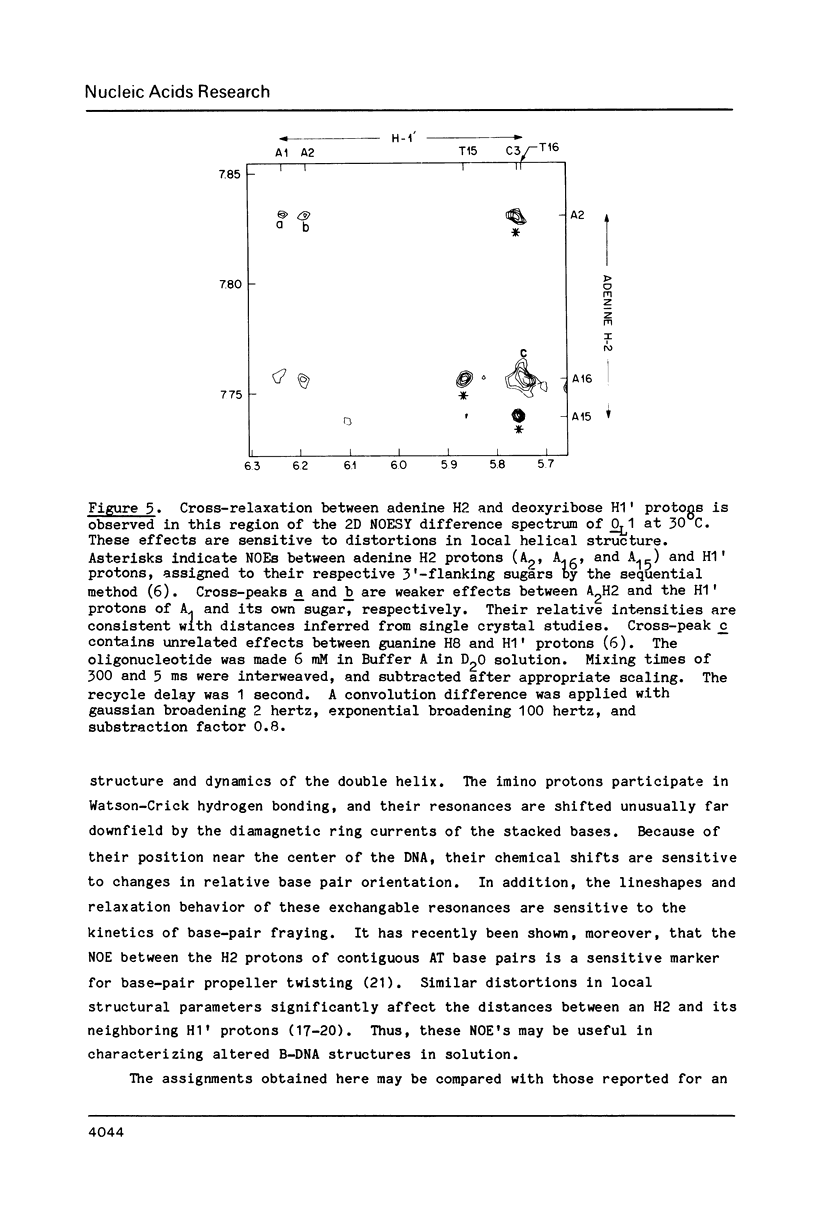
One- and two-dimensional proton NMR methods are being used to study the synthetic lambda operator site O-L1, a 17 base-pair DNA duplex recognized by lambda repressor and Cro protein. The complete assignment of the 17 imino protons, which participate in Watson-Crick hydrogen bonding, and of the eight adenine H2 protons, which lie in the minor groove of the double helix, is presented.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson W. F., Ohlendorf D. H., Takeda Y., Matthews B. W. Structure of the cro repressor from bacteriophage lambda and its interaction with DNA. Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):754–758. doi: 10.1038/290754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou S. H., Hare D. R., Wemmer D. E., Reid B. R. Sequence-specific recognition of deoxyribonucleic acid. Chemical synthesis and nuclear magnetic resonance assignment of the imino protons of lambda OR3 operator deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1983 Jun 21;22(13):3037–3041. doi: 10.1021/bi00282a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E. Base sequence and helix structure variation in B and A DNA. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 25;166(3):419–441. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Drew H. R. Structure of a B-DNA dodecamer. II. Influence of base sequence on helix structure. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 15;149(4):761–786. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Samson S., Dickerson R. E. Structure of a B-DNA dodecamer at 16 K. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4040–4044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. D., Poteete A. R., Lauer G., Sauer R. T., Ackers G. K., Ptashne M. lambda Repressor and cro--components of an efficient molecular switch. Nature. 1981 Nov 19;294(5838):217–223. doi: 10.1038/294217a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston P. D., Redfield A. G. Pulsed FT-NMR double resonance studies of yeast tRNAPhe: specific nuclear Overhauser effects and reinterpretation of low temperature relaxation data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Oct;5(10):3913–3927. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.10.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M., Jeffrey A., Wang J., Ladner R., Ptashne M., Pabo C. O. Structure of the operator-binding domain of bacteriophage lambda repressor: implications for DNA recognition and gene regulation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):435–440. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomonossoff G. P., Butler P. J., Klug A. Sequence-dependent variation in the conformation of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 15;149(4):745–760. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90356-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. W., Ohlendorf D. H., Anderson W. F., Takeda Y. Structure of the DNA-binding region of lac repressor inferred from its homology with cro repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1428–1432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Lewis M. The operator-binding domain of lambda repressor: structure and DNA recognition. Nature. 1982 Jul 29;298(5873):443–447. doi: 10.1038/298443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Kozlowski S. A., Bhatt R. Sequence dependence of base-pair stacking in right-handed DNA in solution: proton nuclear Overhauser effect NMR measurements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3908–3912. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Kozlowski S. A., Marky L. A., Broka C., Rice J. A., Itakura K., Breslauer K. J. Premelting and melting transitions in the d(CGCGAATTCGCG) self-complementary duplex in solution. Biochemistry. 1982 Feb 2;21(3):428–436. doi: 10.1021/bi00532a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Pardi A., Itakura K. DNA conformation, dynamics, and interactions in solution. Science. 1982 May 7;216(4546):581–590. doi: 10.1126/science.6280281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S., Redfield A. G. Nuclear Overhauser effect study and assignment of D stem and reverse-Hoogsteen base pair proton resonances in yeast tRNAAsp. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):7073–7083. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.7073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheek R. M., Zuiderweg E. R., Klappe K. J., van Boom J. H., Kaptein R., Rüterjans H., Beyreuther K. lac Repressor headpiece binds specifically to half of the lac operator: a proton nuclear magnetic resonance study. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 4;22(1):228–235. doi: 10.1021/bi00270a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffler I. E., Elson E. L., Baldwin R. L. Helix formation by dAT oligomers. I. Hairpin and straight-chain helices. J Mol Biol. 1968 Sep 28;36(3):291–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90156-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich E. L., John E. M., Gough G. R., Brunden M. J., Gilham P. T., Westler W. M., Markley J. L. Imino proton assignments in the proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of the lambda phage OR3 deoxyribonucleic acid fragment. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 13;22(19):4362–4365. doi: 10.1021/bi00288a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


