Abstract
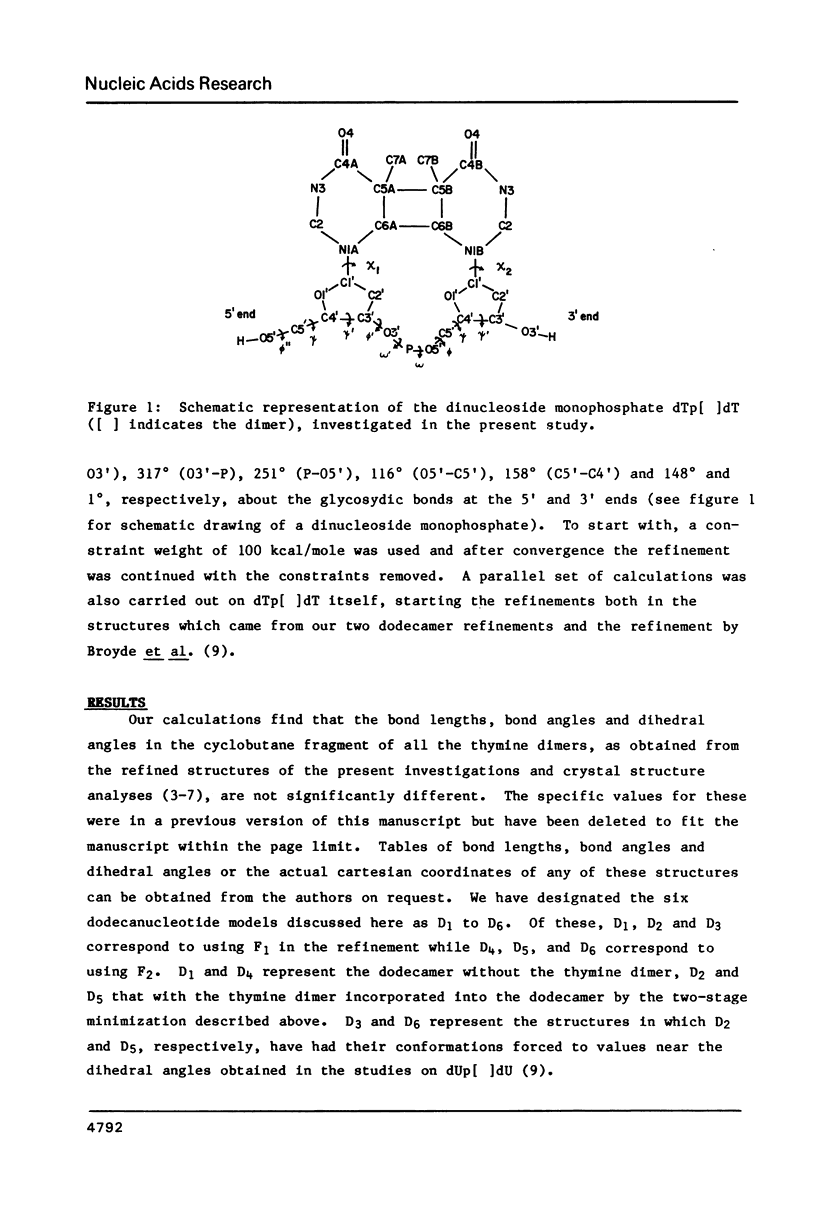
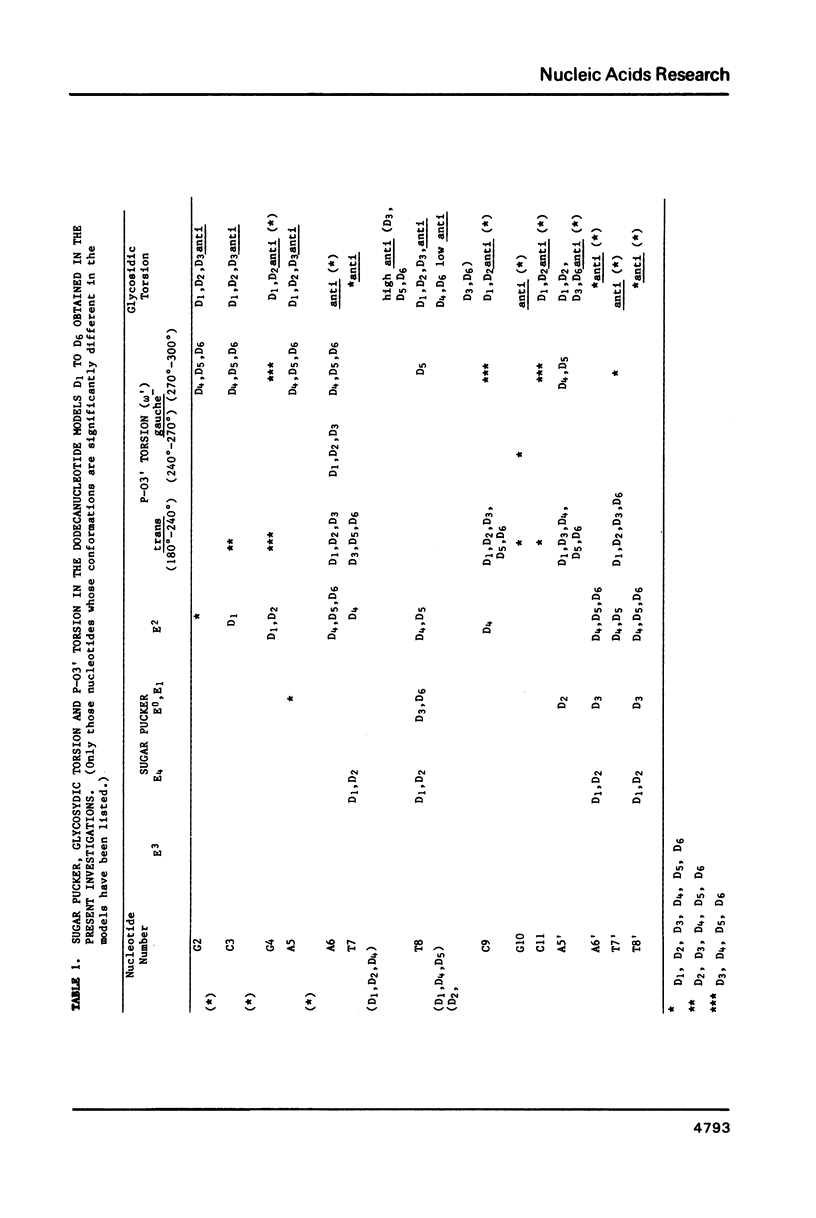
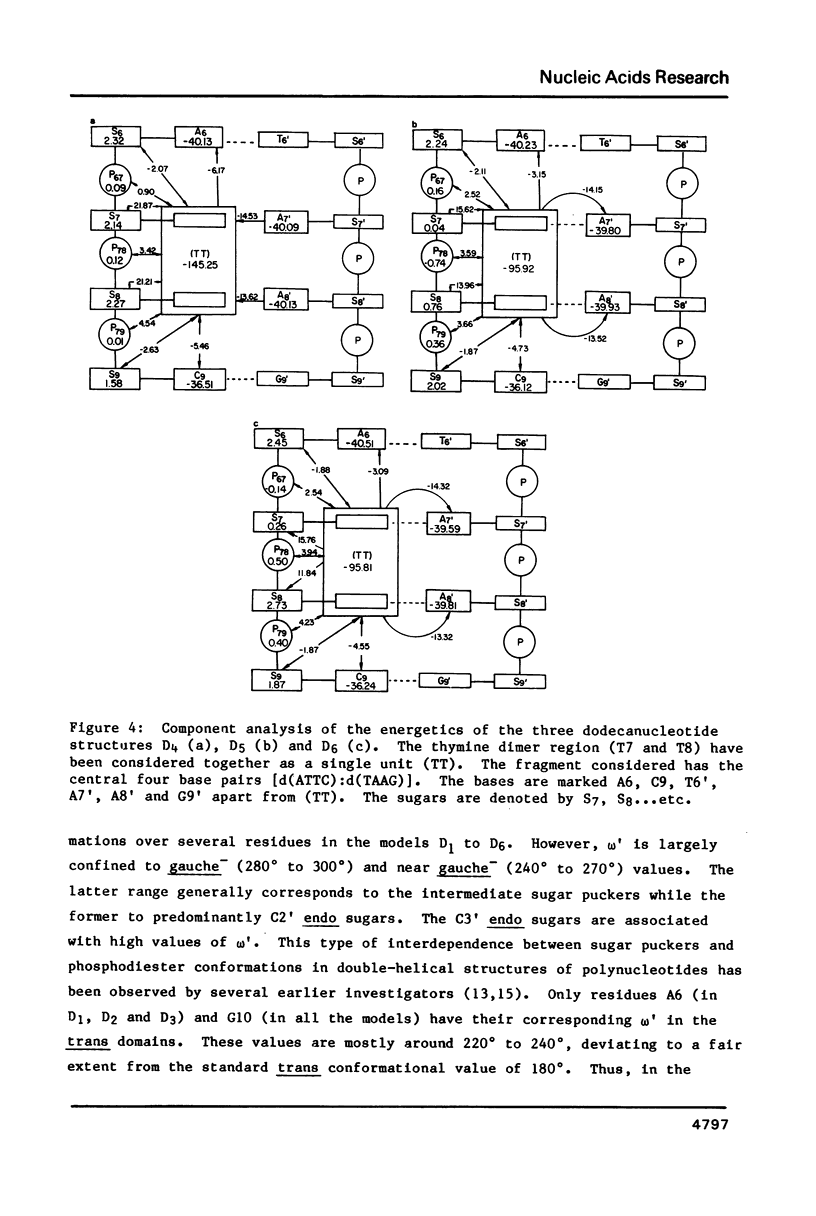
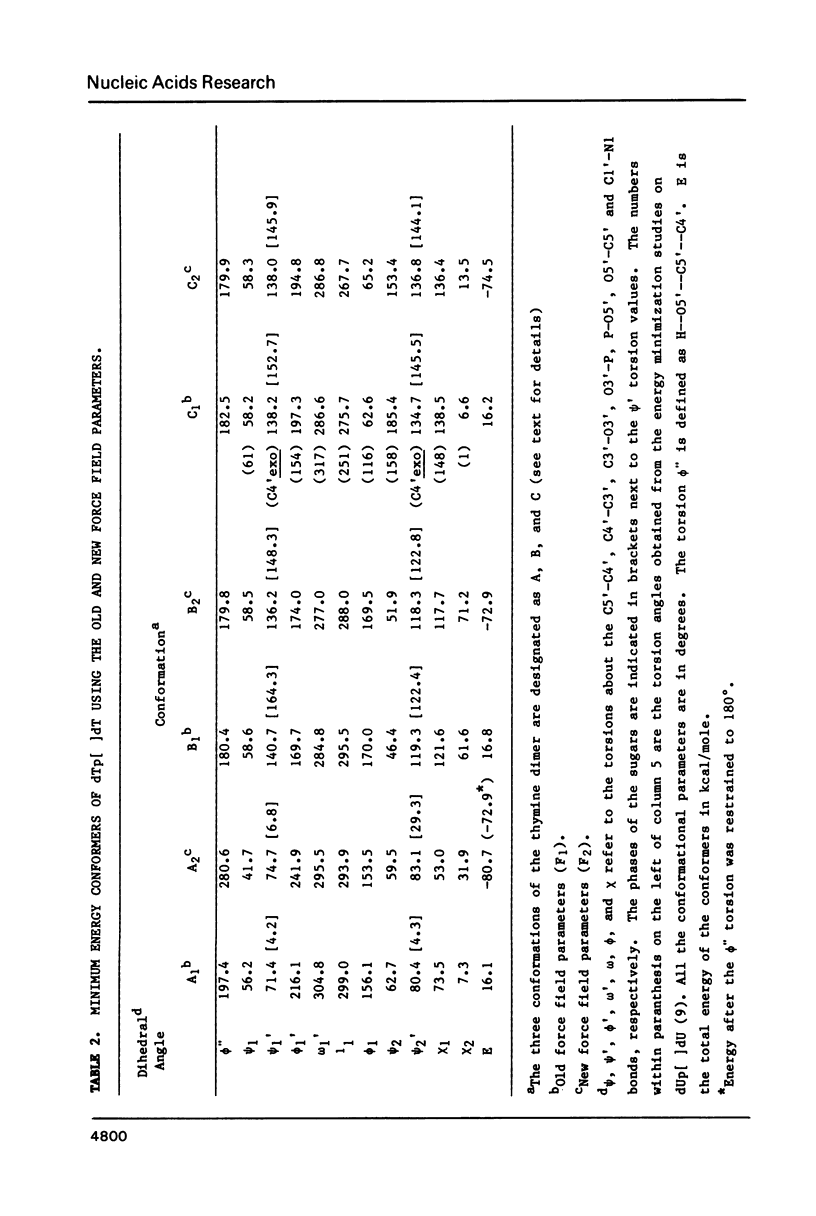
In the light of the biological significance of thymine photodimers , studies of the energetics of the dodecanucleotide fragment d( CGCGAATTCGCG )2 have been carried out using the methods of molecular mechanics, with and without incorporation of a thymine dimer in the cis-syn configuration. The results of the calculations suggest that the thymine dimerized structures show no gross distortion in the double helix with the conformational changes relative to the normal B-DNA double helix restricted largely to the dimer region. The energetics of dTp[]dT reveal a number of conformers which are energetically almost equally favorable and are, as a group, qualitatively consistent with NMR studies on this molecule. The biological implications of the results of the conformational studies, reported here, have been examined vis-a-vis the currently available models for the recognition of DNA "damage" by repair enzymes.
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adman E., Jensen L. H. The crystal and molecular structure of the cis-syn photodimer of uracil. Acta Crystallogr B. 1970 Sep 15;26(9):1326–1334. doi: 10.1107/s0567740870004077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerman N., Camerman A. Crystal and molecular structure of photodimer A of 1,3-dimethylthymine (the isomer in irradiated deoxyribonucleic acid). J Am Chem Soc. 1970 Apr 22;92(8):2523–2527. doi: 10.1021/ja00711a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crick F. H., Klug A. Kinky helix. Nature. 1975 Jun 12;255(5509):530–533. doi: 10.1038/255530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flippen J. L., Karle I. L. The crystal structure of a thymine trimer, C15H20N6O7-H2O, a photoproduct of thymine. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 Jun 2;93(11):2762–2768. doi: 10.1021/ja00740a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon L. K., Haseltine W. A. Comparison of the cleavage of pyrimidine dimers by the bacteriophage T4 and Micrococcus luteus UV-specific endonucleases. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):12047–12050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseltine W. A. Ultraviolet light repair and mutagenesis revisited. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):13–17. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90329-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keepers J. W., Kollman P. A., Weiner P. K., James T. L. Molecular mechanical studies of DNA flexibility: coupled backbone torsion angles and base-pair openings. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5537–5541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kollman P. A., Weiner P. K., Dearing A. Studies of nucleotide conformations and interactions. The relative stabilities of double-helical B-DNA sequence isomers. Biopolymers. 1981 Dec;20(12):2583–2621. doi: 10.1002/bip.1981.360201208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx J. L. DNA repair: new clues to carcinogenesis. Science. 1978 May 5;200(4341):518–521. doi: 10.1126/science.200.4341.518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffieux A., Schultz W. Dopaminergic activation of reticulata neurones in the substantia nigra. Nature. 1980 May 22;285(5762):240–241. doi: 10.1038/285240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Rupp W. D. A novel repair enzyme: UVRABC excision nuclease of Escherichia coli cuts a DNA strand on both sides of the damaged region. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):249–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90354-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasisekharan V., Pattabiraman N. Structure of DNA predicted from stereochemistry of nucleoside derivatives. Nature. 1978 Sep 14;275(5676):159–162. doi: 10.1038/275159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


