Abstract
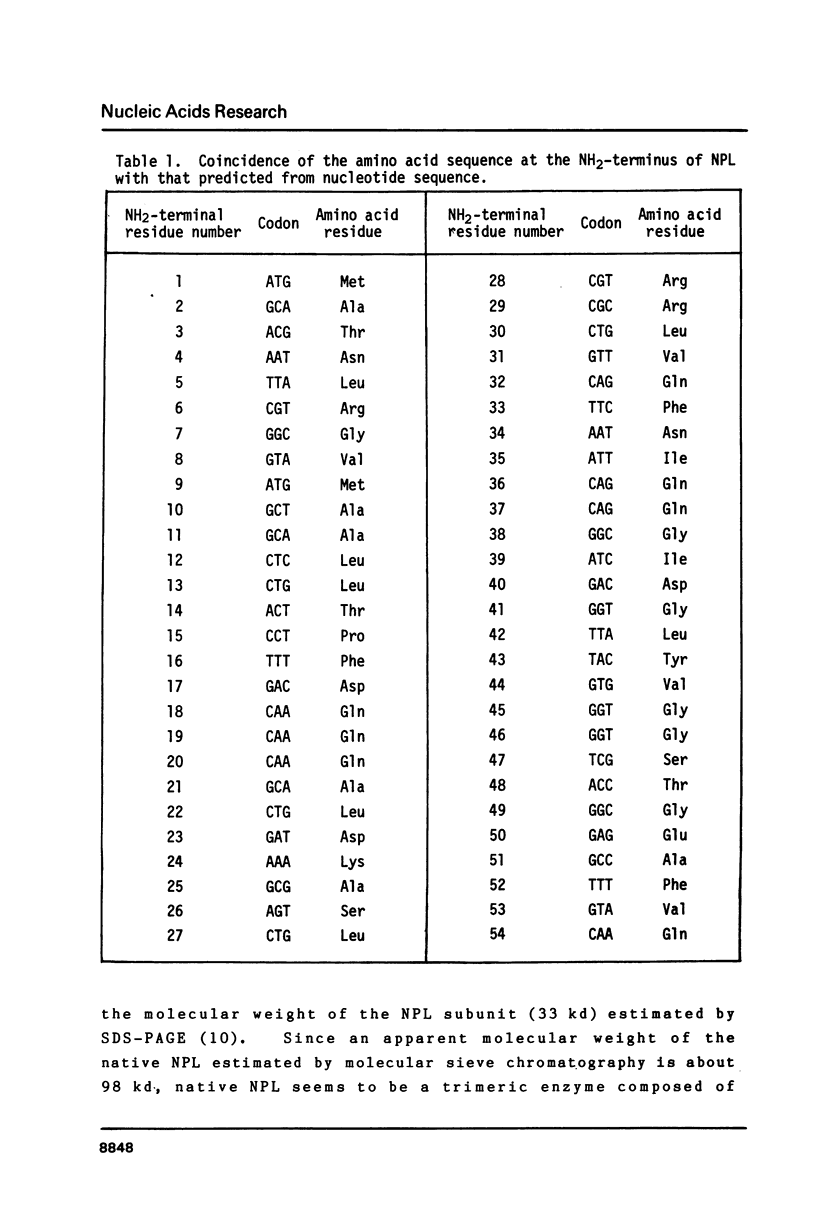
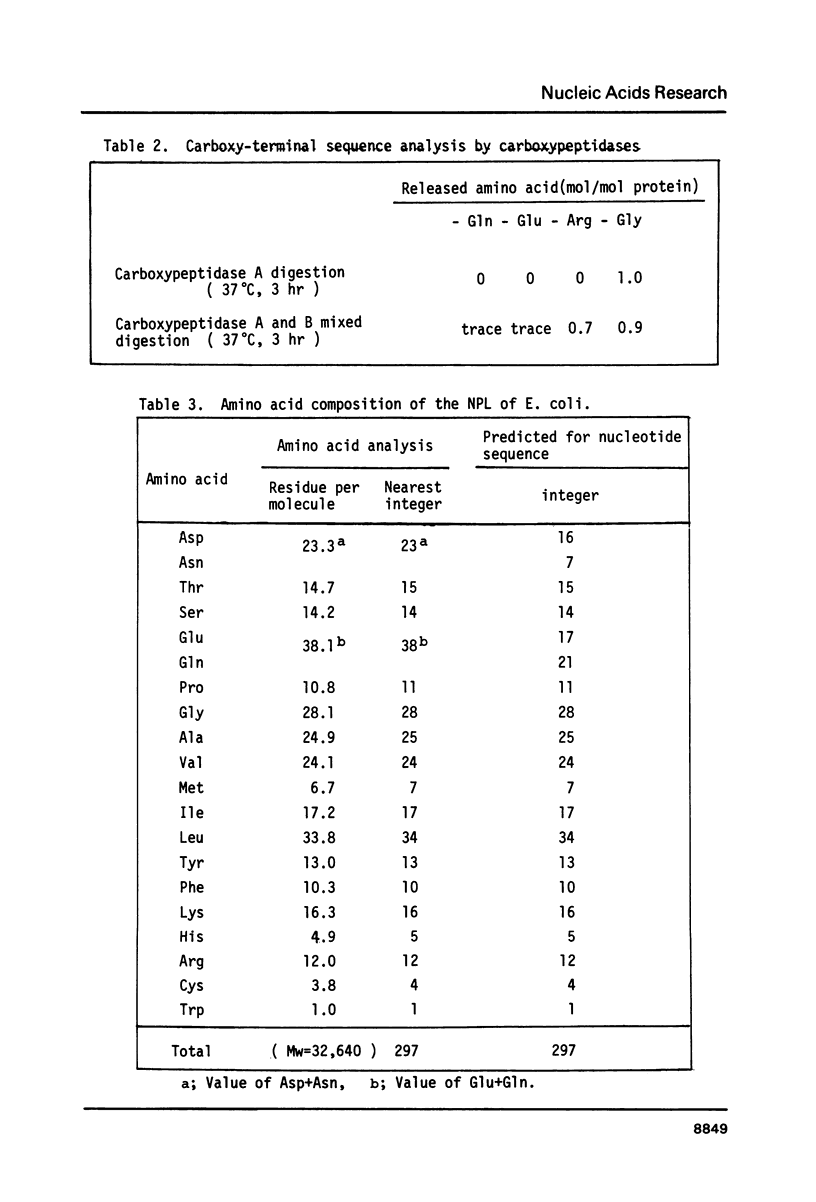
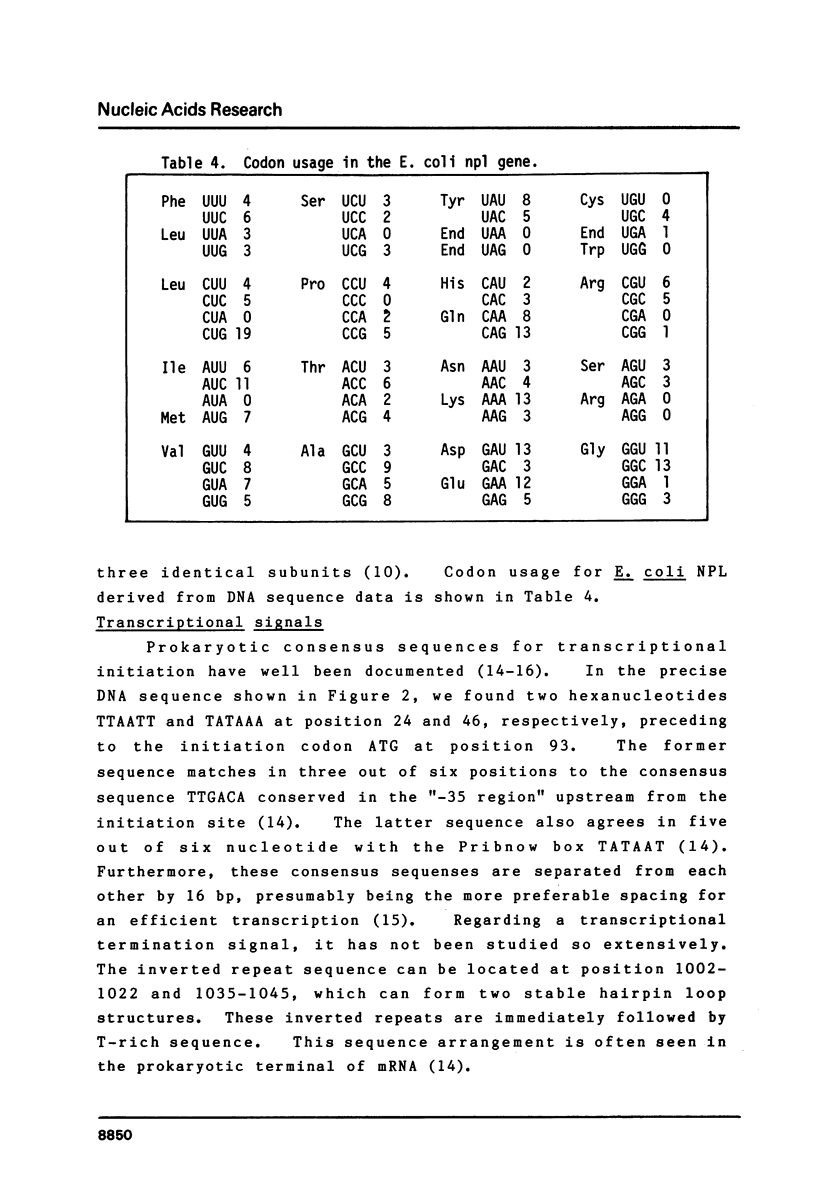
The nucleotide sequence of the cloned DNA, 1,243 bp in length coding for N-acetylneuraminate lyase (N-acetylneuraminate pyruvate lyase; NPL) of Escherichia coli has been determined. Nucleotide sequence and amino acid analysis have assigned the open reading frame for NPL, starting with the ATG near its 5'terminus. The molecular weight calculated from the predicted amino acid sequence was 32,640 daltons, being in good agreement with that of a NPL subunit estimated by the SDS-PAGE method and amino acid composition. Several signal sequences conserved in the promoter regions of E. coli were found in the npl gene. They were the Shine-Dalgarno sequence, the Pribnow box and the sequence coserved in the "-35 region" and they were separated to each other with preferable spacing for an efficient transcription. Downstream from the termination codon, the inverted repeat sequence was present, followed by 4 successive T's.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gaitonde M. K., Dovey T. A rapid and direct method for the quantitative determination of tryptophan in the intact protein. Biochem J. 1970 May;117(5):907–911. doi: 10.1042/bj1170907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimer R., Meyer K. STUDIES ON SIALIC ACID OF SUBMAXILLARY MUCOID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956 Oct;42(10):728–734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.42.10.728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T., Ozeki H. Codon usage and transfer RNA contents: organism-specific codon-choice patterns in reference to the isoacceptor contents. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):1087–1097. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPENOE E. A., DREW R. M. The action of an enzyme of Clostridium perfringens on orosomucoid. J Biol Chem. 1957 Oct;228(2):673–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pribnow D. Nucleotide sequence of an RNA polymerase binding site at an early T7 promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):784–788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Simpson R. B., Gilbert W. E. coli RNA polymerase interacts homologously with two different promoters. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):269–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugahara K., Sugimoto K., Nomura O., Usui T. Enzymatic assay of serum sialic acid. Clin Chim Acta. 1980 Dec 22;108(3):493–498. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(80)90360-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida Y., Tsukada Y., Sugimori T. Purification and properties of N-acetylneuraminate lyase from Escherichia coli. J Biochem. 1984 Aug;96(2):507–522. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


