Abstract
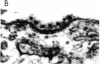
We have developed a method for conjugating low density lipoproteins (LDL) with colloidal gold. Conjugation, complete after 1 min, occurs by electrostatic adsorption of the LDL to the negatively charged gold particle. Each conjugate consists of approximately eight biologically active LDL molecules clustered around a central 19-nm gold granule. Acidic (pH 4), alkaline (pH 9), or high ionic (600 milliosmolar NaCl) environments do not dissociate the conjugate. Colloidal gold is an electron-dense, nondegradable marker that is easily identified within the cell and serves as a valuable probe for studying receptor binding and endocytosis. By using a modified method of ruthenium red staining, the LDL molecules of the conjugate can be directly visualized when they are bound to the cell surface receptor. Receptor binding (4 degrees C) of the conjugate by cultured human fibroblasts reveals that the gold granule is positioned 18-21 nm from the coated pit region of the membrane. This distance, similar to the diameter of LDL, suggests concomitant internalization of the receptor during vesicular endocytosis and early lysosomal incorporation (10 min at 37 degrees C). Continued internalization (30-60 min at 37 degrees C) results in the formation of free pools of gold within the lysosome.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. G., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Role of the coated endocytic vesicle in the uptake of receptor-bound low density lipoprotein in human fibroblasts. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):351–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. G., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Localization of low density lipoprotein receptors on plasma membrane of normal human fibroblasts and their absence in cells from a familial hypercholesterolemia homozygote. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2434–2438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Familial hypercholesterolemia: defective binding of lipoproteins to cultured fibroblasts associated with impaired regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):788–792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J., Iacovides A., Winlove C. P. The interactions of colloidal gold with plasma macromolecules and its uptake by the arterial wall in the rabbit [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:28P–28P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierichs R. Ruthenium red as a stain for electron microscopy. Some new aspects of its application and mode of action. Histochemistry. 1979 Nov;64(2):171–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00490097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Basu S. K., Brunschede G. Y., Brown M. S. Release of low density lipoprotein from its cell surface receptor by sulfated glycosaminoglycans. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90258-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handley D. A., Olsen B. R. Butvar B-98 as a thin support film. Ultramicroscopy. 1979;4(4):479–480. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3991(79)80025-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horisberger M. Agglutination of erythrocytes using lectin-labeled spacers. Experientia. 1978 Jun 15;34(6):721–722. doi: 10.1007/BF01947280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger M., Smith L. C., Anderson R. G., Goldstein J. L., Kao Y. J., Pownall H. J., Gotto A. M., Jr, Brown M. S. Reconstituted low density lipoprotein: a vehicle for the delivery of hydrophobic fluorescent probes to cells. J Supramol Struct. 1979;10(4):467–478. doi: 10.1002/jss.400100409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft J. H. Ruthenium red and violet. II. Fine structural localization in animal tissues. Anat Rec. 1971 Nov;171(3):369–415. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091710303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. B. Labeling of high density lipoproteins with [3H] acetic anhydride. J Lipid Res. 1978 Jan;19(1):107–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKanna J. A., Haigler H. T., Cohen S. Hormone receptor topology and dynamics: morphological analysis using ferritin-labeled epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5689–5693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman R. C., Green S. R., Attie A. D., Steinberg D. Radiolabeled sucrose covalently linked to protein. A device for quantifying degradation of plasma proteins catabolized by lysosomal mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):6876–6879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sata T., Havel R. J., Jones A. L. Characterization of subfractions of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins separated by gel chromatography from blood plasma of normolipemic and hyperlipemic humans. J Lipid Res. 1972 Nov;13(6):757–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte L. D., Cornicelli J. A. Platelet-derived growth factor stimulates low density lipoprotein receptor activity in cultured human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5962–5966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte L. D., Kaplan K. L., Nossel H. L., Lages B. A., Weiss H. J., Goodman D. S. Studies of the release from human platelets of the growth factor for cultured human arterial smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 1978 Mar;42(3):402–409. doi: 10.1161/01.res.42.3.402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]