Abstract
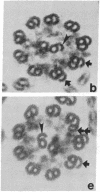
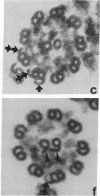
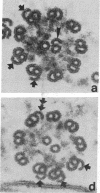
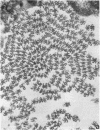
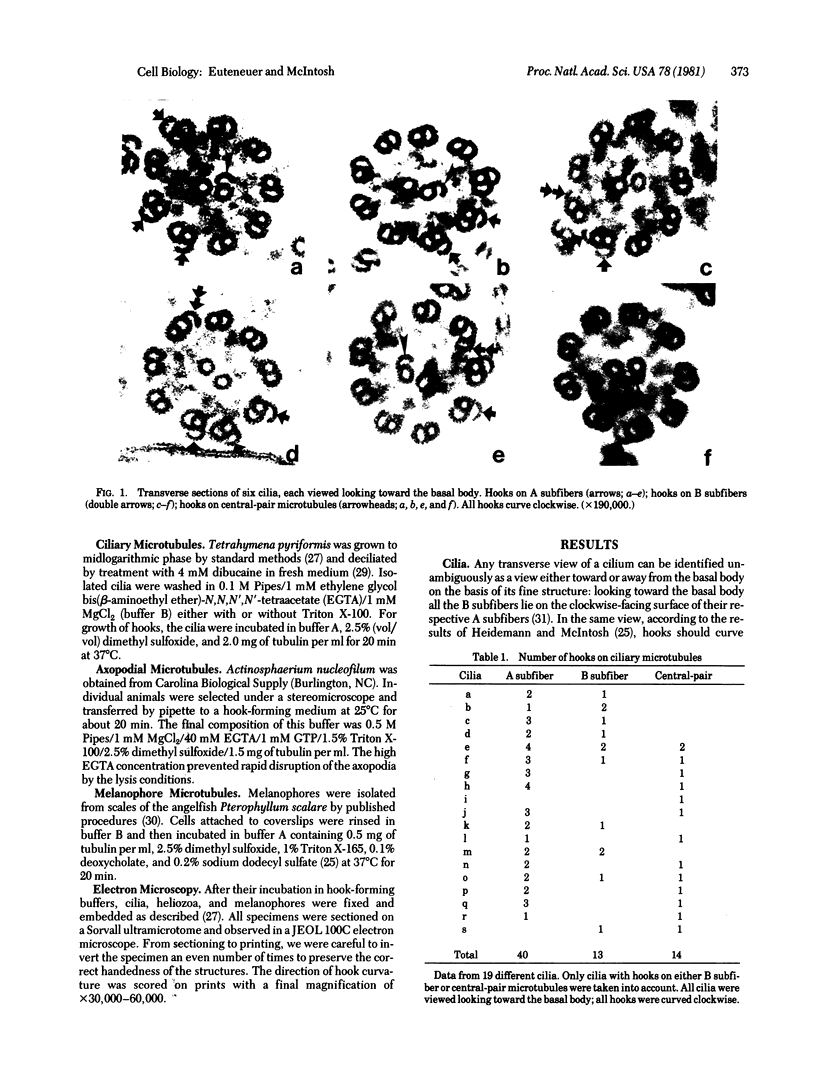
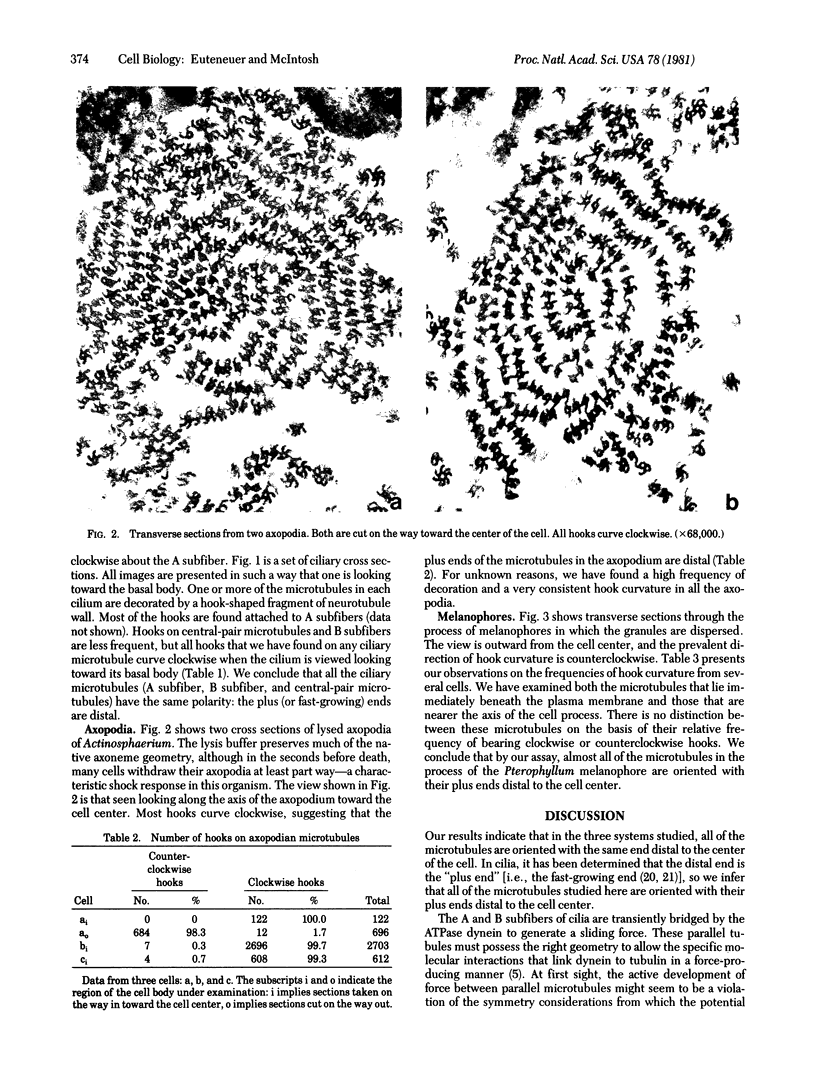
We have investigated the structural polarity of microtubules from several systems in which these fibers are thought to contribute to cell motility. By using a method for displaying microtubule polarity in the electron microscope, we find that both the A and B subfibers of Tetrahymena ciliary outer doublets and the inner pair of single microtubules are all oriented with their plus ends (i.e., their fast-growing ends) distal to the basal body. All of the microtubules in the axopodia of the heliozoan Actinosphaerium and all of the microtubules in the processes of melanophores from the angelfish Pterophyllum are likewise oriented with their plus ends distal to the cell centers. These results suggest that cellular systems for motility, and even those capable of bidirectional motility, can be constructed from microtubules of a single polarity.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen C., Borisy G. G. Structural polarity and directional growth of microtubules of Chlamydomonas flagella. J Mol Biol. 1974 Dec 5;90(2):381–402. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90381-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergen L. G., Borisy G. G. Head-to-tail polymerization of microtubules in vitro. Electron microscope analysis of seeded assembly. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jan;84(1):141–150. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergen L. G., Kuriyama R., Borisy G. G. Polarity of microtubules nucleated by centrosomes and chromosomes of Chinese hamster ovary cells in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jan;84(1):151–159. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borisy G. G. Polarity of microtubules of the mitotic spindle. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 25;124(3):565–570. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90188-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton P. R., Himes R. H. Electron microscope studies of pH effects on assembly of tubulin free of associated proteins. Delineation of substructure by tannic acid staining. J Cell Biol. 1978 Apr;77(1):120–133. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.1.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers H. R., Porter K. R. Transformations in the structure of the cytoplasmic ground substance in erythrophores during pigment aggregation and dispersion. I. A study using whole-cell preparations in stereo high voltage electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1977 Nov;75(2 Pt 1):541–558. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.2.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dentler W. L., Granett S., Witman G. B., Rosenbaum J. L. Directionality of brain microtubule assembly in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1710–1714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dentler W. L., Rosenbaum J. L. Flagellar elongation and shortening in Chlamydomonas. III. structures attached to the tips of flagellar microtubules and their relationship to the directionality of flagellar microtubule assembly. J Cell Biol. 1977 Sep;74(3):747–759. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.3.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edds K. T. Motility in Echinosphaerium nucleofilum. I. An analysis of particle motions in the axopodia and a direct test of the involvement of the axoneme. J Cell Biol. 1975 Jul;66(1):145–155. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Euteneuer U., McIntosh J. R. Polarity of midbody and phragmoplast microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1980 Nov;87(2 Pt 1):509–515. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.2.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBONS I. R., GRIMSTONE A. V. On flagellar structure in certain flagellates. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Jul;7:697–716. doi: 10.1083/jcb.7.4.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haimo L. T., Telzer B. R., Rosenbaum J. L. Dynein binds to and crossbridges cytoplasmic microtubules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidemann S. R., McIntosh J. R. Visualization of the structural polarity of microtubules. Nature. 1980 Jul 31;286(5772):517–519. doi: 10.1038/286517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa H., Bischoff R., Holtzer H. Formation of arrowhead complexes with heavy meromyosin in a variety of cell types. J Cell Biol. 1969 Nov;43(2):312–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner M. W. Implications of treadmilling for the stability and polarity of actin and tubulin polymers in vivo. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jul;86(1):330–334. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.1.330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis R. L., Wilson L. Opposite end assembly and disassembly of microtubules at steady state in vitro. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90132-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald K. L., Edwards M. K., McIntosh J. R. Cross-sectional structure of the central mitotic spindle of Diatoma vulgare. Evidence for specific interactions between antiparallel microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):443–461. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooseker M. S., Tilney L. G. Organization of an actin filament-membrane complex. Filament polarity and membrane attachment in the microvilli of intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):725–743. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Weihing R. R. Actin and myosin and cell movement. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1974 Jan;2(1):1–65. doi: 10.3109/10409237409105443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringo D. L. Flagellar motion and fine structure of the flagellar apparatus in Chlamydomonas. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jun;33(3):543–571. doi: 10.1083/jcb.33.3.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schliwa M., Euteneuer U. A microtuble-independent component may be involved in granule transport in pigment cells. Nature. 1978 Jun 15;273(5663):556–558. doi: 10.1038/273556a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schliwa M. Stereo high voltage electron microscopy of melanophores. Matrix transformations during pigment movements and the effects of cold and colchicine. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Feb;118(2):323–340. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90157-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelanski M. L., Gaskin F., Cantor C. R. Microtubule assembly in the absence of added nucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):765–768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers K. E., Gibbons I. R. Adenosine triphosphate-induced sliding of tubules in trypsin-treated flagella of sea-urchin sperm. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3092–3096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers K., Kirschner M. W. Characteristics of the polar assembly and disassembly of microtubules observed in vitro by darkfield light microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1979 Oct;83(1):205–217. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.1.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. A., Jr, Baugh L. C., Walker L. F. Nonlethal deciliation of Tetrahymena by a local anesthetic and its utility as a tool for studying cilia regeneration. J Cell Biol. 1974 Apr;61(1):253–257. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.1.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner F. D., Mitchell D. R. Structural conformation of ciliary dynein arms and the generation of sliding forces in Tetrahymena cilia. J Cell Biol. 1978 Feb;76(2):261–277. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witman G. B. The site of in vivo assembly of flagellar microtubules. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;253:178–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb19199.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolosewick J. J., Porter K. R. Stereo high-voltage electron microscopy of whole cells of the human diploid line, WI-38. Am J Anat. 1976 Nov;147(3):303–323. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001470305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]