Abstract
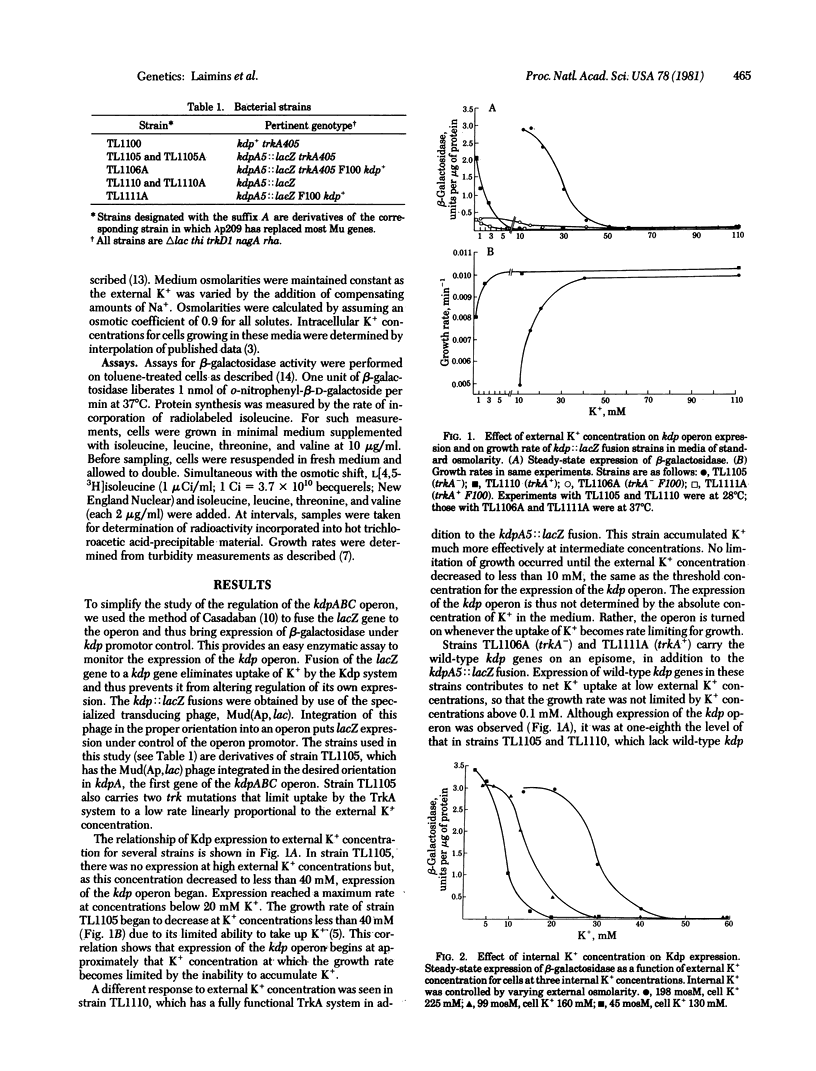
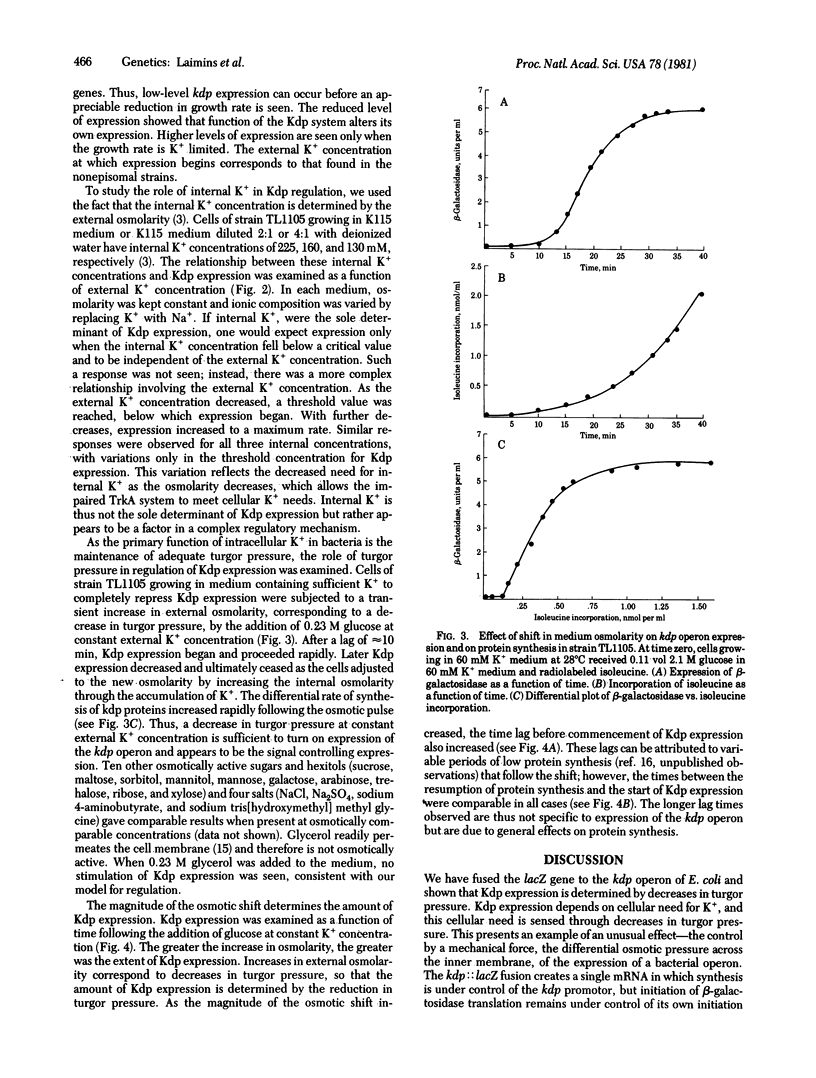
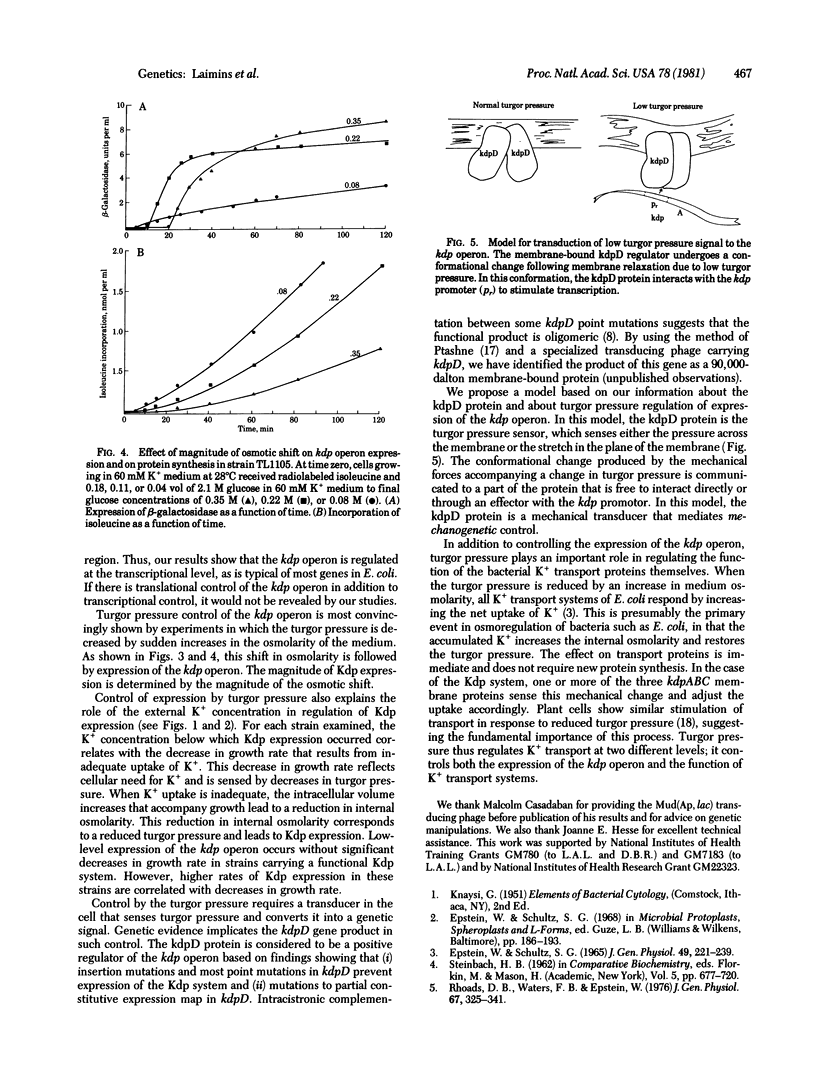
Turgor pressure, the difference in osmotic pressure across the inner membrane, has been found to regulate expression of the kdp operon in Escherichia coli. The kdp operon codes for a high-affinity repressible transport system for the uptake of potassium. We have studied the regulation of Kdp expression in a strain in which the gene for beta-galactosidase, lacZ, was placed under control of the kdp promotor. Neither internal nor external K+ concentrations directly controlled Kdp expression. Only when the external K+ concentration was reduced to the point of limiting growth was the kdp operon expressed. An increase in external osmolarity at constant K+ concentration, a procedure that reduces turgor pressure, caused expression of the kdp operon. As the magnitude of the osmotic shift was increased, corresponding to greater decreases in turgor pressure, the amount of Kdp expression also increased. The kdp operon thus appears to be controlled by changes in a physical force, the turgor pressure.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Lactose genes fused to exogenous promoters in one step using a Mu-lac bacteriophage: in vivo probe for transcriptional control sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4530–4533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W., Davies M. Potassium-dependant mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):836–843. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.836-843.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W., Kim B. S. Potassium transport loci in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):639–644. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.639-644.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W. Transposition of the lac region of Escherichia coli. IV. Escape from repression in bacteriophage-carried lac genes. J Mol Biol. 1967 Dec 28;30(3):529–543. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90366-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutknecht J. Salt transport in Valonia: inhibition of potassium uptake by small hydrostatic pressures. Science. 1968 Apr 5;160(3823):68–70. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3823.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komeda Y., Iino T. Regulation of expression of the flagellin gene (hag) in Escherichia coli K-12: analysis of hag-lac gene fusions. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):721–729. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.721-729.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Rhoads D. B., Altendorf K., Epstein W. Identification of the structural proteins of an ATP-driven potassium transport system in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3216–3219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEntee K., Estein W. Isolation and characterization of specialized transducing bacteriophages for the recA gene of Escherichia coli. Virology. 1977 Mar;77(1):306–318. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90427-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. B., Epstein W. Energy coupling to net K+ transport in Escherichia coli K-12. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1394–1401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. B., Laimins L., Epstein W. Functional organization of the kdp genes of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1978 Aug;135(2):445–452. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.2.445-452.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. B., Waters F. B., Epstein W. Cation transport in Escherichia coli. VIII. Potassium transport mutants. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Mar;67(3):325–341. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.3.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


