Abstract
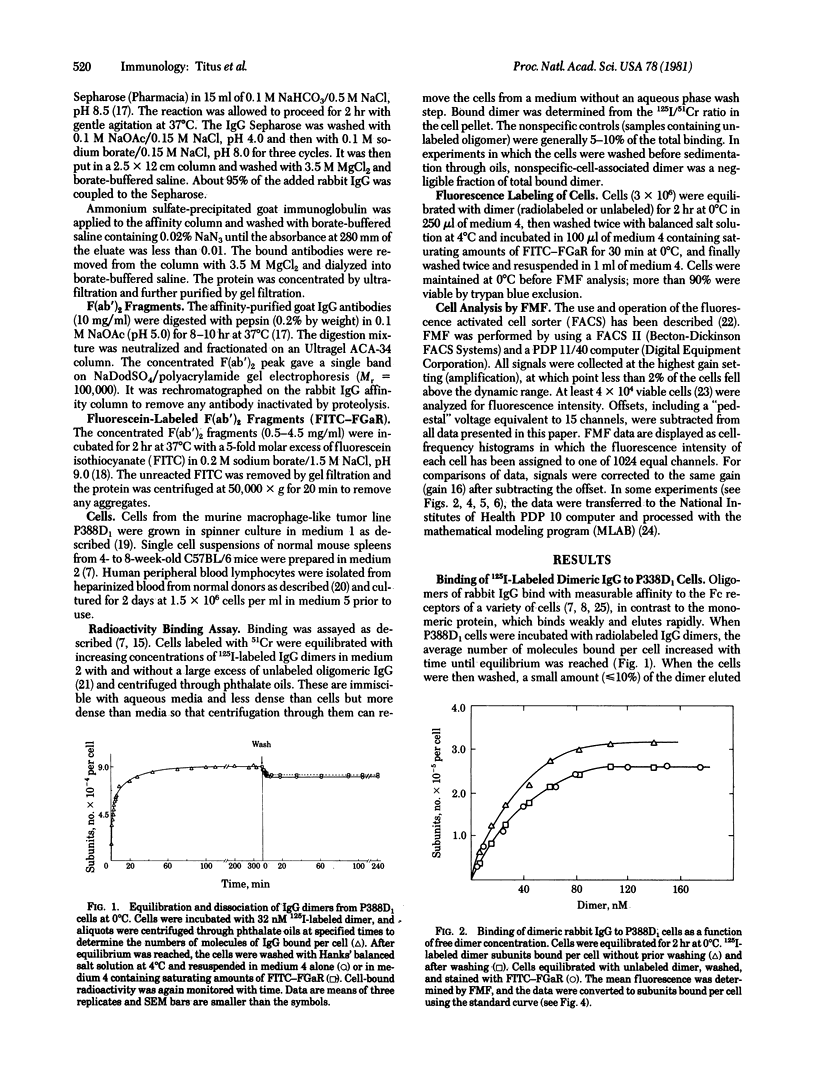
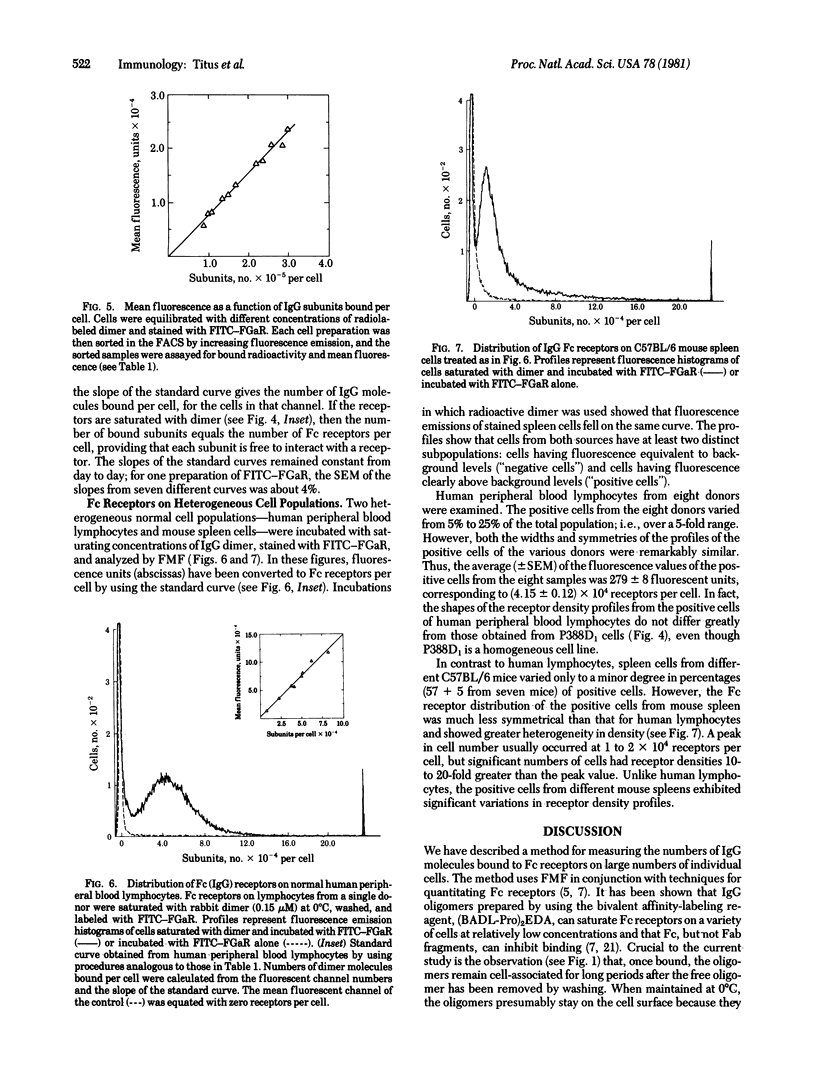
A flow microfluorometric method has been developed for quantitating the numbers of Fc receptors on individual cells. The cells were equilibrated at 0 degrees C with radiolabeled, affinity-crosslinked rabbit IgG dimers, washed, and treated with fluorescent antibodies against rabbit IgG. The stained cells were analyzed for fluorescence emission by using a fluorescence-activated cell sorter and for bound dimer molecules by using a gamma counter. Standard curves relating fluorescence emission to numbers of dimer molecules bound to cells were used to determine Fc receptor distributions on P388D1 cells, human peripheral blood lymphocytes, and normal mouse spleen cells. Essentially all of the P388D1 cells bore Fc receptors, distributed in a skewed Gaussian profile having a peak at 2 X 10(5) receptors per cell. Human peripheral blood lymphocytes and mouse spleen cells contained positive and negative subpopulations. The percentage of positive cells in human lymphocytes from different donors ranged from 50 to 25; the receptor distributions of these cells were symmetrical and similar in all donors in shape and average receptor density (4.2 X 10(4) receptors per cell). Mouse spleen cells contained 55% positive cells with nonsymmetrical heterogeneous distributions of receptor densities. These cells peaked at 1 to 2 X 10(4) receptors per cell, but significant numbers of cells had receptor densities 10- to 20-fold greater.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander E. L., Titus J. A., Segal D. M. Human leukocyte Fc (IgG) receptors: quantitation and affinity with radiolabeled affinity cross-linked rabbit IgG. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):295–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander E. L., Titus J. A., Segal D. M. Quantitation of Fc receptors and surface immunoglobulin is affected by cell isolation procedures using plasmagel and ficoll-hypaque. J Immunol Methods. 1978;22(3-4):263–272. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90034-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerottini J. C., Brunner K. T. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity, allograft rejection, and tumor immunity. Adv Immunol. 1974;18:67–132. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60308-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly J. M., Wunderlich J. R. The cellular nature of concanavalin A-stimulated antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1980 Apr;124(4):1917–1923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickler H. B., Kubicek M. T., Arbeit R. D., Sharrow S. O. Studies on the nature of the relationship between Ia antigens and Fc receptors on murine B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):348–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickler H. B. Lymphocyte receptors for immunoglobulin. Adv Immunol. 1976;24:167–214. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60330-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyer R. L., Koshland M. E., Knopf P. M. Immunoglobulin binding by mouse intestinal epithelial cell receptors. J Immunol. 1976 Aug;117(2):587–593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzenberg L. A., Sweet R. G., Herzenberg L. A. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Sci Am. 1976 Mar;234(3):108–117. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0376-108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. F., Plotz P. H., Segal D. M. Complement and cell-mediated lysis of haptenated erythrocytes sensitized with oligomers of rabbit IgG antibody. Mol Immunol. 1979 Nov;16(11):889–897. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90087-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kekwick R. A. The serum proteins in multiple myelomatosis. Biochem J. 1940 Sep;34(8-9):1248–1257. doi: 10.1042/bj0341248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knott G. D. Mlab--a mathematical modeling tool. Comput Programs Biomed. 1979 Dec;10(3):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(79)90075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koren H. S., Handwerger B. S., Wunderlich J. R. Identification of macrophage-like characteristics in a cultured murine tumor line. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):894–897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loken M. R., Parks D. R., Herzenberg L. A. Identification of cell asymmetry and orientation by light scattering. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977 Jul;25(7):790–795. doi: 10.1177/25.7.330730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plotz P. H., Kimberly R. P., Guyer R. L., Segal D. M. Stable model immune complexes produced by bivalent affinity labeling haptens: in-vivo survival. Mol Immunol. 1979 Sep;16(9):721–729. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal D. M., Hurwitz E. Binding of affinity cross-linked oligomers of IgG to cells bearing Fc receptors. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1338–1337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal D. M., Hurwitz E. Dimers and trimers of immunoglobulin G covalently cross-linked with a bivalent affinity label. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 30;15(24):5253–5258. doi: 10.1021/bi00669a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal D. M., Titus J. A. The subclass specificity for the binding of murine myeloma proteins to macrophage and lymphocyte cell lines and to normal spleen cells. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1395–1403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S. C., Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Endocytosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:669–722. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout R. D., Herzenberg L. A. The Fc receptor on thymus-derived lymphocytes. I. Detection of a subpopulation of murine T lymphocytes bearing the Fc receptor. J Exp Med. 1975 Sep 1;142(3):611–621. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.3.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout R. D., Herzenberg L. A. The Fc receptor on thymus-derived lymphocytes: II. Mitogen responsiveness of T lymphocytes bearing the Fc receptor. J Exp Med. 1975 Nov 1;142(5):1041–1051. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.5.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout R. D., Murphy D. B., McDevitt H. O., Herzenberg L. A. The Fc receptor on thymus-derived lymphocytes. IV. Inhibition of binding of antigen-antibody complexes to Fc receptor-positive T cells by anti-Ia sera. J Exp Med. 1977 Jan 1;145(1):187–203. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.1.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout R. D., Waksal S. D., Herzenberg L. A. The Fc receptor on thymus-derived lymphocytes. III. Mixed lymphocyte reactivity and cell-mediated lympholytic activity of Fc- and Fc+ T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Jul 1;144(1):54–68. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


