Abstract
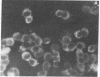
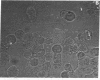
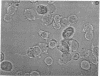
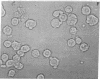
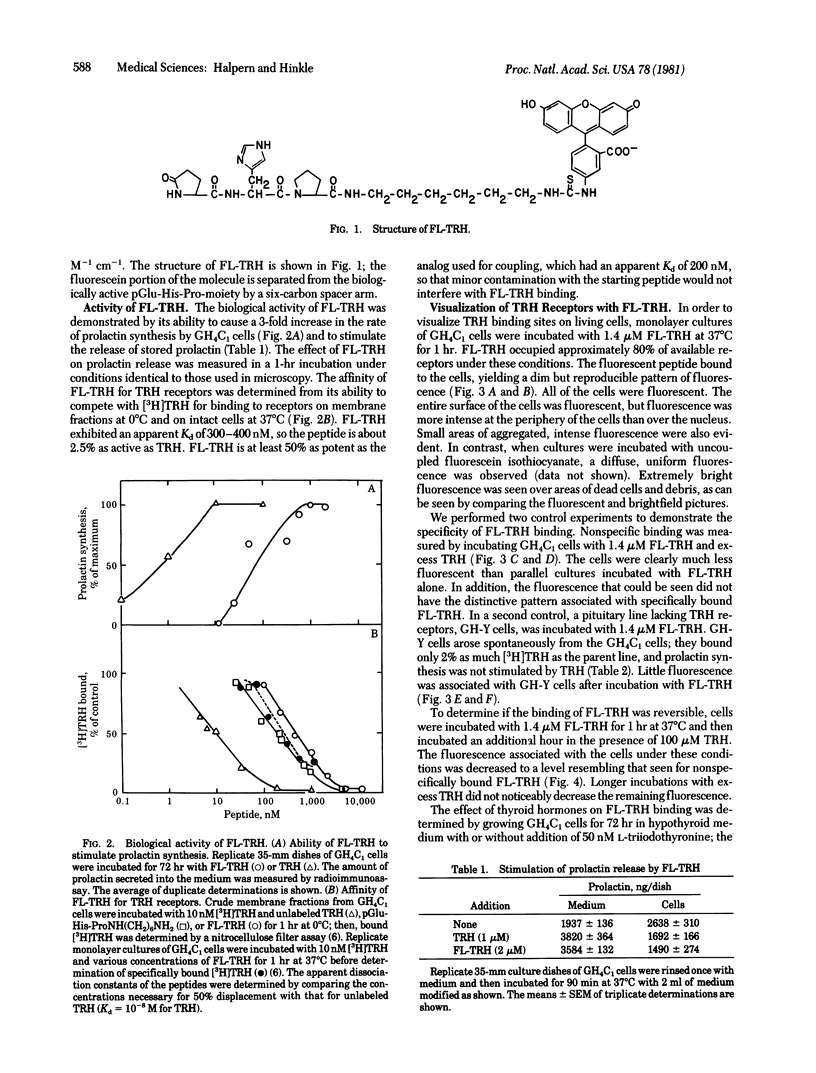
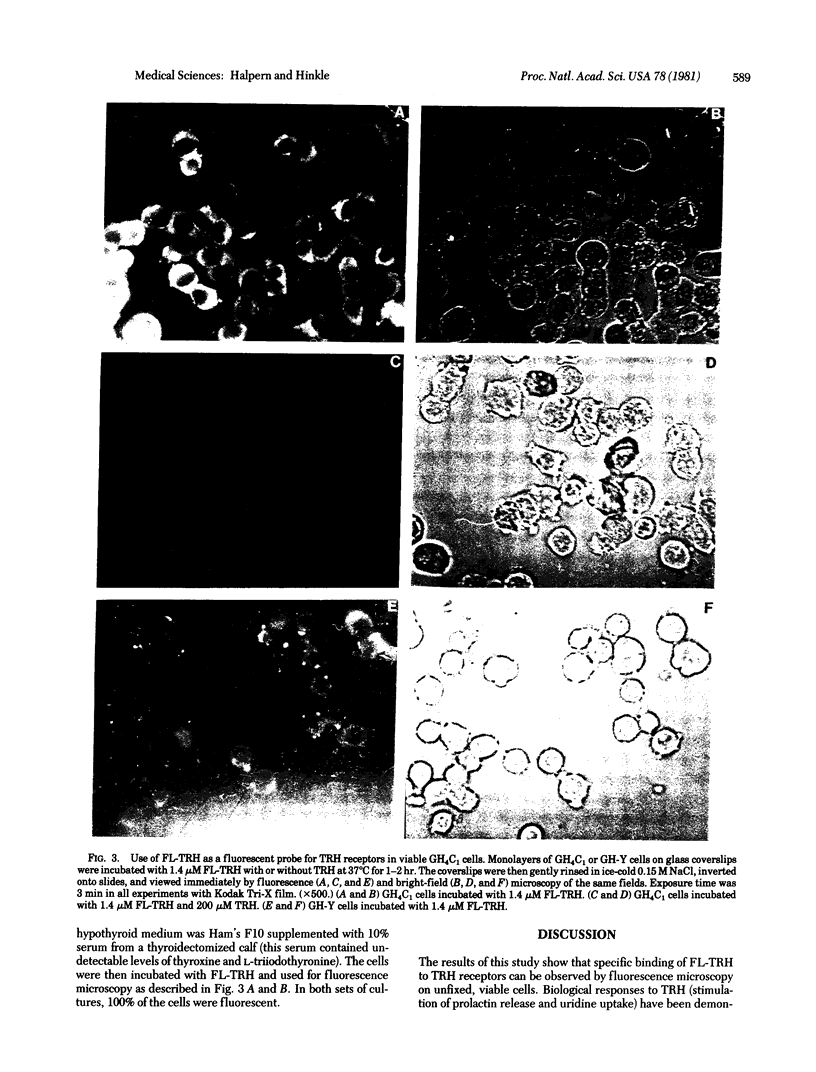
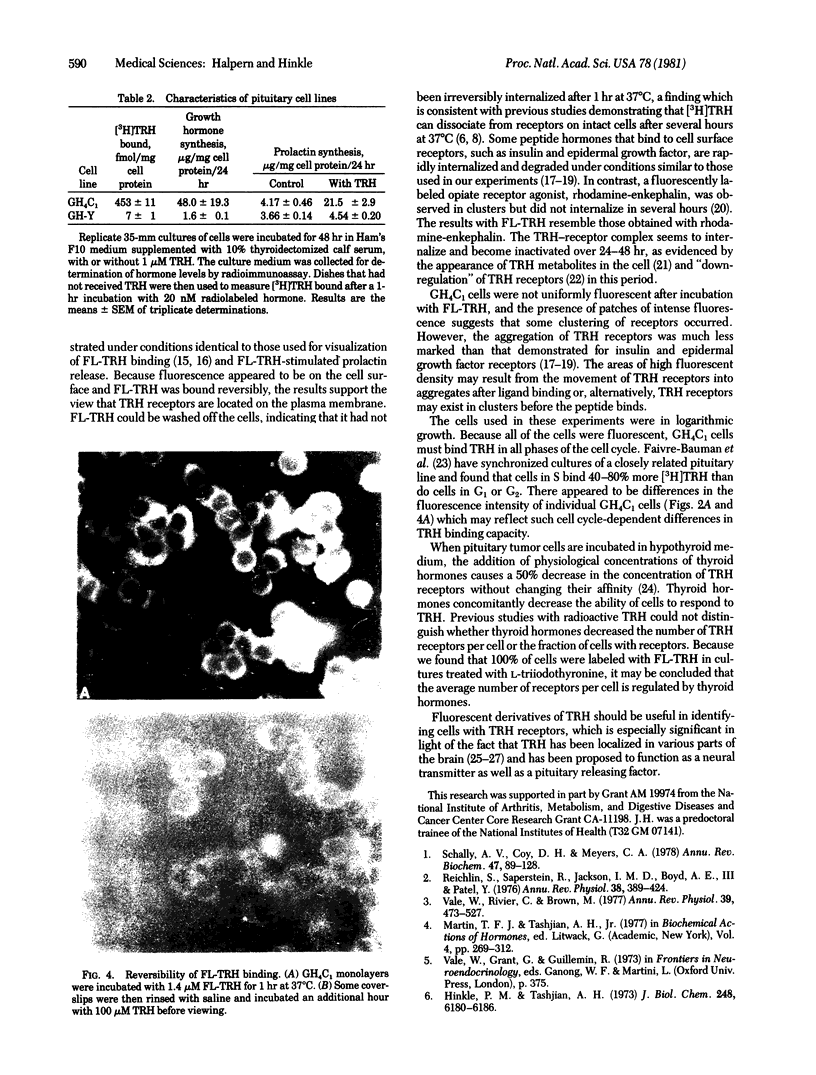
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) binds to specific receptors on GH4C1 pituitary tumor cells. A fluorescently labeled analog of TRH was synthesized by coupling pGlu-His-ProNH(CH2)6NH2 to fluorescein isothiocyanate. The fluorescein-labeled peptide (FL-TRH) stimulated prolactin synthesis and release by GH4C1 cultures and bound to TRH receptors with an apparent Kd of 400 nM. Binding of FL-TRH to unfixed, viable GH4C1 cells was followed by fluorescence microscopy. After incubation with 1.4 microM FL-TRH for 1 hr at 37 degrees C, the surface of all cells was fluorescent and patches of intense fluorescence were evident. Control cultures incubated with FL-TRH and excess TRH were not fluorescent, and a line of pituitary tumor cells which lacks TRH receptors displayed little fluorescence after incubation with FL-TRH. When GH4C1 cells were incubated with FL-TRH for 1 hr at 37 degrees C and then with excess TRH for an additional 1 hr, the fluorescence associated with the cells was diminished to control levels. The results demonstrate that the fluorescein-labeled peptide labels specific TRH receptors.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bournaud F., Gourdji D., Mongongu S., Tixier-Vidal A. [3H]-Thyroliberin (TRH) binding to nuclei isolated from a pituitary clonal cell line (GH3). Neuroendocrinology. 1977;24(3-4):183–194. doi: 10.1159/000122760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dannies P. S., Tasjian A. H., Jr Release and synthesis of prolactin by rat pituitary cell strains are regulated independently by thyrotropin-releasing hormone. Nature. 1976 Jun 24;261(5562):707–710. doi: 10.1038/261707a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faivre-Bauman A., Gourdji D., Grouselle D., Tixier-Vidal A. Binding of thyrotropin releasing hormone and prolactin release by synchronized GH3 rat pituitary cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 3;67(1):50–57. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90281-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler H., Ash J. F., Singer S. J., Cohen S. Visualization by fluorescence of the binding and internalization of epidermal growth factor in human carcinoma cells A-431. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3317–3321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazum E., Chang K. J., Cuatrecasas P. Opiate (Enkephalin) receptors of neuroblastoma cells: occurrence in clusters on the cell surface. Science. 1979 Nov 30;206(4422):1077–1079. doi: 10.1126/science.227058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle P. M., Lewis D. G., Greer T. L. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone-receptor interaction in GH3 pituitary cells. Endocrinology. 1980 Mar;106(3):1000–1005. doi: 10.1210/endo-106-3-1000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle P. M., Lewis D. G. Solubilization of pituitary receptors for thyrotropin-releasing hormone. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 3;541(3):347–359. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90194-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle P. M., Tashjian A. H., Jr Degradation of thyrotropin-releasing hormone by the GH3 strain of pituitary cells in culture. Endocrinology. 1975 Aug;97(2):324–331. doi: 10.1210/endo-97-2-324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle P. M., Tashjian A. H., Jr Receptors for thyrotropin-releasing hormone in prolactin producing rat pituitary cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):6180–6186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle P. M., Tashjian A. H., Jr Thyrotropin-releasing hormone regulates the number of its own receptors in the GH3 strain of pituitary cells in culture. Biochemistry. 1975 Aug 26;14(17):3845–3851. doi: 10.1021/bi00688a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle P. M., Woroch E. L., Tashjian A. H., Jr Receptor-binding affinities and biological activities of analogs of thyrotropin-releasing hormone in prolactin-producing pituitary cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3085–3090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson I. M., Reichlin S. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH): distribution in hypothalamic and extrahypothalamic brain tissues of mammalian and submammalian chordates. Endocrinology. 1974 Sep;95(3):854–862. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-3-854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrie F., Barden N., Poirier G., De Lean A. Binding of thyrotropin-releasing hormone to plasma membranes of bovine anterior pituitary gland (hormone receptor-adenylate cyclase-equilibrium constant-( 3 H)thyrotropin). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):283–287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. F., Tashjian A. H., Jr Thyrotropin-releasing hormone modulation of uridine uptake in rat pituitary cells. Evidence that uridine phosphorylation is regulated. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 10;253(1):106–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxfield F. R., Schlessinger J., Shechter Y., Pastan I., Willingham M. C. Collection of insulin, EGF and alpha2-macroglobulin in the same patches on the surface of cultured fibroblasts and common internalization. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):805–810. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90336-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrone M. H., Hinkle P. M. Regulation of pituitary receptors for thyrotropin-releasing hormone by thyroid hormones. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 25;253(14):5168–5173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier G., Labrie F., Barden N., Lemaire S. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor: Its partial purification from bovine anterior pituitary gland and its close association with adenyl cyclase. FEBS Lett. 1972 Feb 15;20(3):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80087-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichlin S., Saperstein R., Jackson I. M., Boyd A. E., 3rd, Patel Y. Hypothalamic hormones. Annu Rev Physiol. 1976;38:389–424. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.38.030176.002133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schally A. V., Coy D. H., Meyers C. A. Hypothalamic regulatory hormones. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:89–128. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Shechter Y., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Direct visualization of binding, aggregation, and internalization of insulin and epidermal growth factor on living fibroblastic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2659–2663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashjian A. H., Jr, Yasumura Y., Levine L., Sato G. H., Parker M. L. Establishment of clonal strains of rat pituitary tumor cells that secrete growth hormone. Endocrinology. 1968 Feb;82(2):342–352. doi: 10.1210/endo-82-2-342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale W., Rivier C., Brown M. Regulatory peptides of the hypothalamus. Annu Rev Physiol. 1977;39:473–527. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.39.030177.002353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winokur A., Utiger R. D. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone: regional distribution in rat brain. Science. 1974 Jul 19;185(4147):265–267. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4147.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]