Abstract
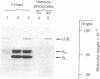
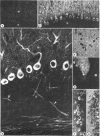
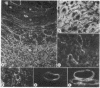
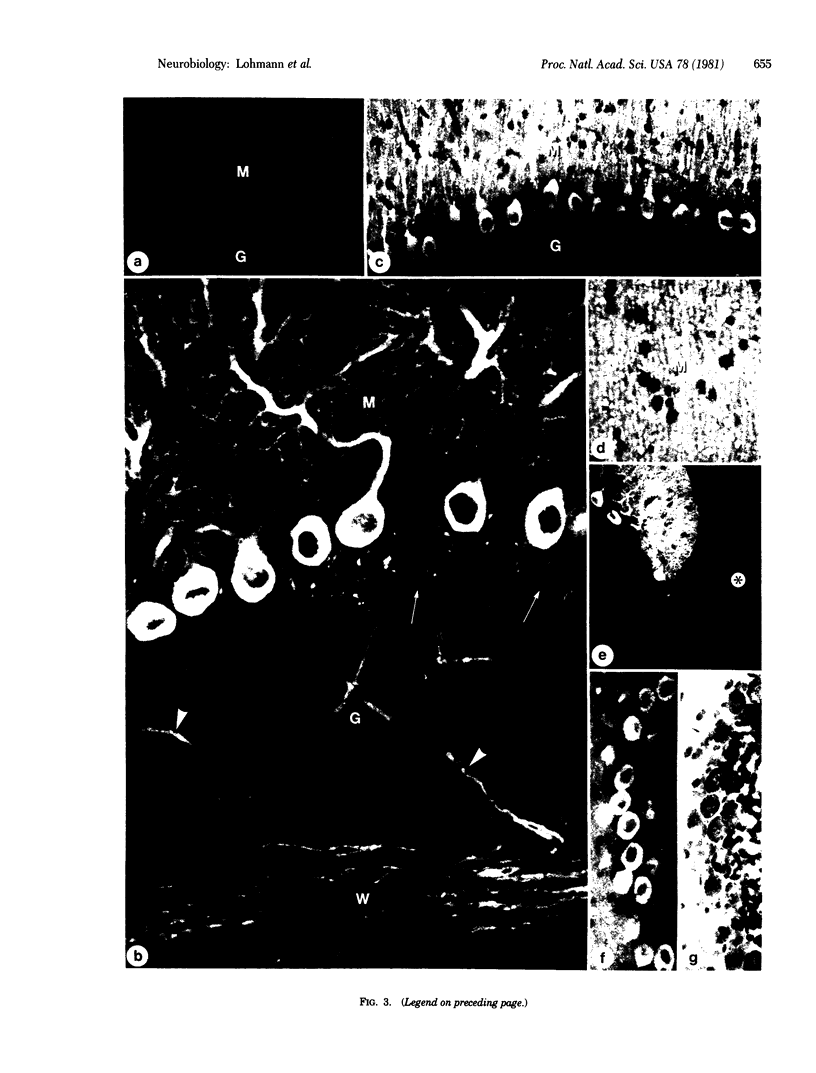
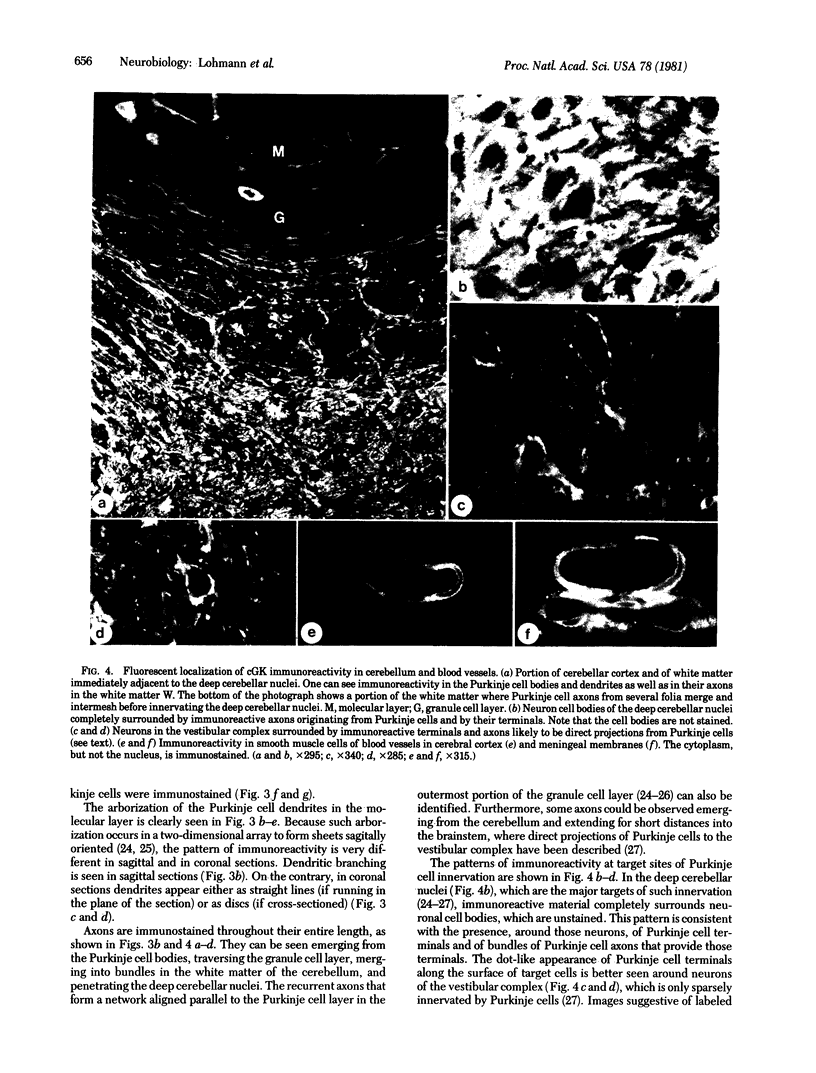
The distribution of cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase in rat brain has been studied by an immunological approach involving radioimmunoassay and fluorescence immunohistochemistry. Data obtained by radioimmunoassay indicate that cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase is 20- to 40-fold more concentrated in cerebellum than in other brain regions. Immunohistochemical experiments demonstrate that the high concentration of immunoreactivity of the protein kinase in cerebellum is attributable to Purkinje cells. Immunoreactivity in these cells is homogeneously distributed throughout the cell (perikarya, dendrites, and axons) with the exception of the nucleus. No other neurons either in the cerebellum or in other brain regions were stained by antiserum to the protein kinase. Immunoreactivity, however, was found throughout the brain on smooth muscle cells of blood vessels.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bandle E., Guidotti A. Studies on the cell location of cyclic 3',5'-guanosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in cerebellum. Brain Res. 1978 Nov 10;156(2):412–416. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90530-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggio G., Brodie B. B., Costa E., Guidotti A. Mechanisms by which diazepam, muscimol, and other drugs change the content of cGMP in cerebellar cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3592–3596. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggio G., Corda M. G., Casu M., Gessa G. L. Striato-cerebellar pathway controlling cyclic GMP content in the cerebellum: role of dopamine, GABA and enkephalins. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1978;18:227–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggio G., Corda M. G., Casu M., Salis M., Gessa G. L. Disappearance of cerebellar cyclic GMP induced by kainic acid. Brain Res. 1978 Oct 6;154(1):203–208. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)91073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom F. E. The role of cyclic nucleotides in central synaptic function. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1975;74:1–103. doi: 10.1007/3-540-07483-x_19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crepel F., Delhaye-Bouchaud N., Dupont J. L., Sotelo C. Dendritic and axonic fields of Purkinje cells in developing and x-irradiated rat cerebellum. A comparative study using intracellular staining with horseradish peroxidase. Neuroscience. 1980;5(2):333–347. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90109-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Ueda T., Bloom F. E., Battenberg E., Greengard P. Widespread distribution of protein I in the central and peripheral nervous systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5977–5981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrendelli J. A. Distribution and regulation of cyclic GMP in the central nervous system. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1978;9:453–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann F., Sold G. A protein kinase activity from rat cerebellum stimulated by guanosine-3':5'-monophosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Nov 15;49(4):1100–1107. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90326-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebabian J. W. Biochemical regulation and physiological significance of cyclic nucleotides in the nervous system. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1977;8:421–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln T. M., Corbin J. D. Adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate- and guanosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate-dependent protein kinases: possible homologous proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3239–3243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln T. M., Corbin J. D. On the role of the cAMP and cGMP-dependent protein kinases in cell function. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1978 Feb;4(1):3–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln T. M., Hall C. L., Park C. R., Corbin J. D. Guanosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate binding proteins in rat tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2559–2563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R. R. The cortex of the cerebellum. Sci Am. 1975 Jan;232(1):56–71. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0175-56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao C. C., Guidotti A., Landis S. Cyclic GMP: reduction of cerebellar concentrations in "nervous" mutant mice. Brain Res. 1975 Jun 13;90(2):335–339. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90316-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathanson J. A. Cyclic nucleotides and nervous system function. Physiol Rev. 1977 Apr;57(2):157–256. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.2.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlichter D. J., Casnellie J. E., Greengard P. An endogenous substrate for cGMP-dependent protein kinase in mammalian cerebellum. Nature. 1978 May 4;273(5657):61–62. doi: 10.1038/273061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlichter D. J., Detre J. A., Aswad D. W., Chehrazi B., Greengard P. Localization of cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase and substrate in mammalian cerebellum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5537–5541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter U., Miller P., Wilson F., Menkes D., Greengard P. Immunological distinction between guanosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3757–3762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]