Abstract
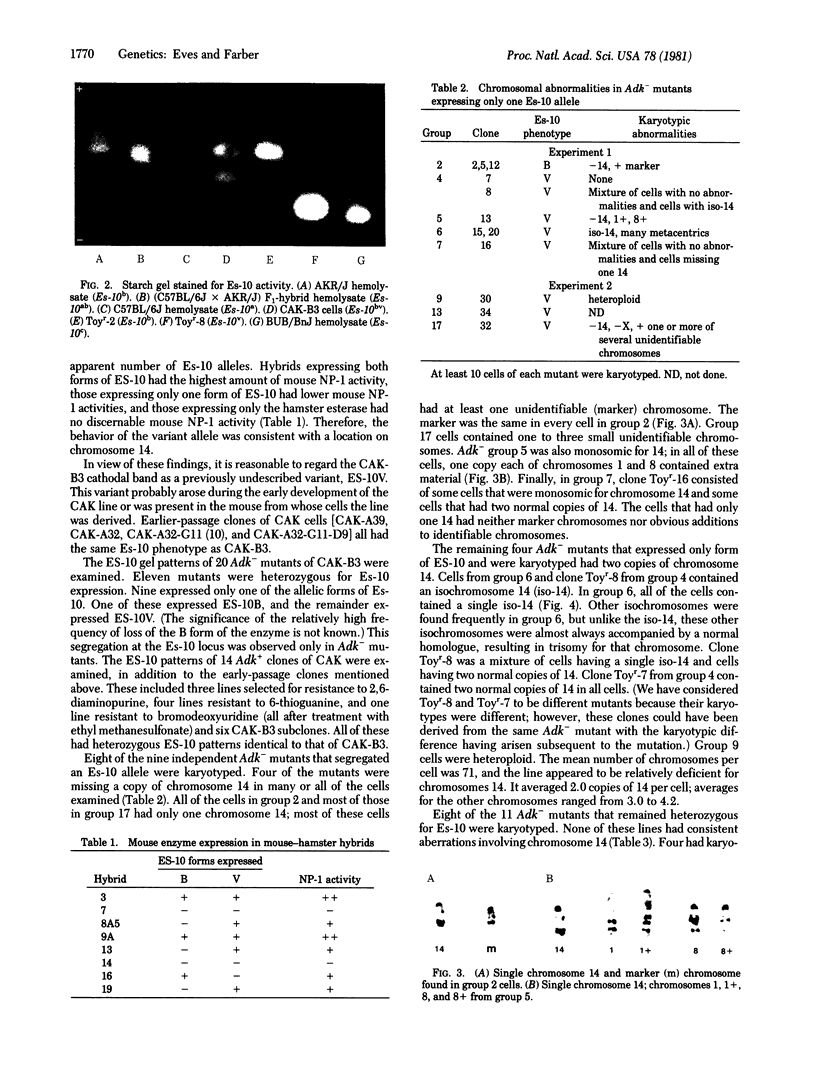
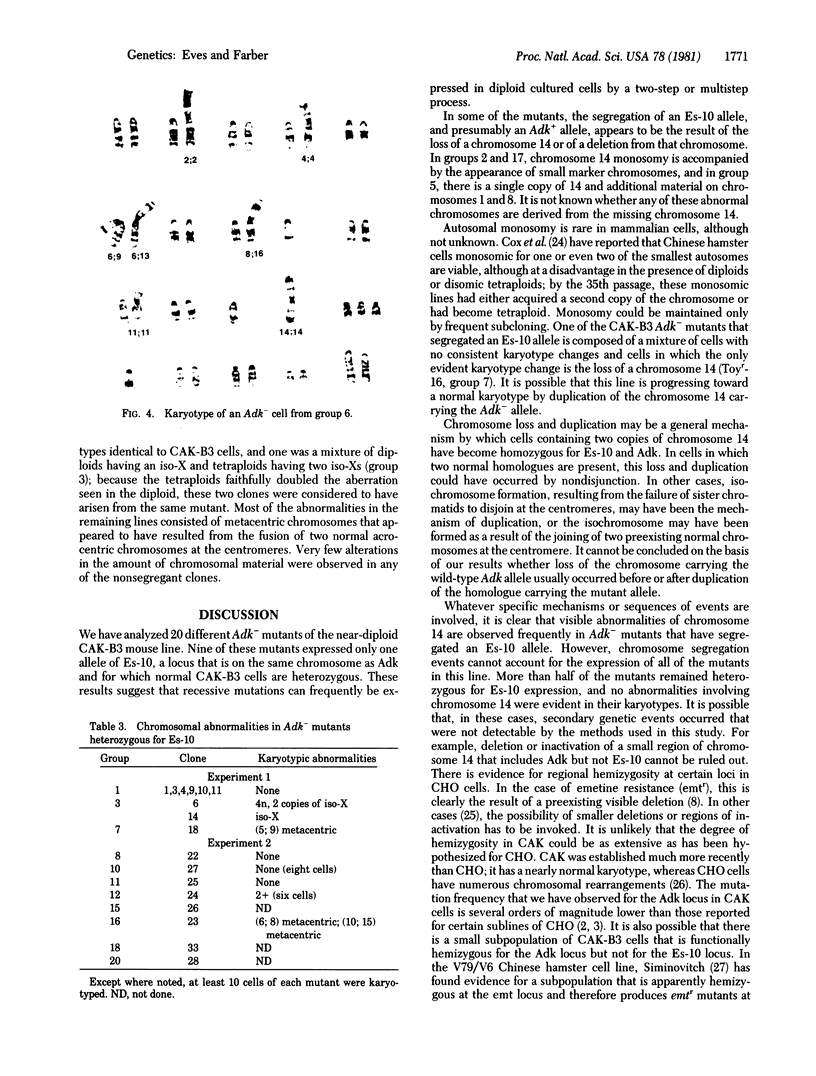
The genes coding for adenosine kinase (ADK; ATP:adenosine 5'-phosphotransferase, EC 2.7.1.20) and esterase-10 (ES-10; carboxylesterase, carboxylic-ester hydrolase, EC 3.1.1.1) are both located on chromosome 14 in the mouse. The near-diploid mouse cell line CAK is heterozygous for two electrophoretic variants of ES-10. Recessive Adk- mutants of CAK have been isolated and analyzed for Es-10 phenotype and karyotypic abnormalities. Two classes of mutants were found with approximatley equal frequencies: those that remained heterozygous in the expression of Es-10 and those that expressed only one Es-10 allele. Of the mutants that lacked one form of ES-10, approximately half were missing most or all of one copy of chromosome 14; the other contained two copies of 14, frequently in the form of an isochromosome. There were no abnormalities of this chromosome found among the mutants that were Es-10 heterozygotes. These results suggest that the expression of an autosomal recessive mutation in near-diploid mouse cells is frequently associated with events that result in the segregation of a physically linked marker and part or all of a chromosome.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Campbell C. E., Worton R. G. Linkage of genetic markers emt and chr in Chinese hamster cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1980 Mar;6(2):215–224. doi: 10.1007/BF01538797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan T. S., Creagan R. P., Reardon M. P. Adenosine kinase as a new selective marker in somatic cell genetics: isolation of adenosine kinase--deficient mouse cell lines and human--mouse hybrid cell lines containing adenosine kinase. Somatic Cell Genet. 1978 Jan;4(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF01546489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasin L. A. The effect of ploidy on chemical mutagenesis in cultured Chinese hamster cells. J Cell Physiol. 1973 Oct;82(2):299–307. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040820218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasin L. A., Urlaub G. Chromosome-wide event accompanies the expression of recessive mutations in tetraploid cells. Science. 1975 Mar 21;187(4181):1091–1093. doi: 10.1126/science.1167702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. M., Birnie S., Tucker D. N. The in vitro isolation and characterization of monosomic sublines derived from a Colcemid-treated Chinese hamster cell population. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1976;17(1):18–25. doi: 10.1159/000130683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson R. L., Gerald P. S. Improved techniques for the induction of mammalian cell hybridization by polyethylene glycol. Somatic Cell Genet. 1976 Mar;2(2):165–176. doi: 10.1007/BF01542629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson R. L., O'Malley K. A., Wheeler T. B. Polyethylene glycol-induced mammalian cell hybridization: effect of polyethylene glycol molecular weight and concentration. Somatic Cell Genet. 1976 May;2(3):271–280. doi: 10.1007/BF01538965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deaven L. L., Petersen D. F. The chromosomes of CHO, an aneuploid Chinese hamster cell line: G-band, C-band, and autoradiographic analyses. Chromosoma. 1973;41(2):129–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00319690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber R. A. Gene dosage and the expression of electrophoretic patterns in heteroploid mouse cell lines. Genetics. 1973 Jul;74(3):521–531. doi: 10.1093/genetics/74.3.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber R. A., Liskay R. M. Karyotypic analysis of a near-diploid established mouse cell line. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1974;13(4):384–396. doi: 10.1159/000130288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell S. A., Worton R. G. Chromosome loss is responsible for segregation at the HPRT locus in Chinese hamster cell hybrids. Somatic Cell Genet. 1977 Sep;3(5):539–551. doi: 10.1007/BF01539124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Oliver N. Quantitative analysis of high-resolution trypsin-giemsa bands on human prometaphase chromosomes. Hum Genet. 1978 Dec 18;45(2):137–165. doi: 10.1007/BF00286957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman M. M. Workshop on "mutation and gene transfer in somatic cells". Somatic Cell Genet. 1979 Sep;5(5):665–671. doi: 10.1007/BF01542702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. S., Chan D. Y., Siminovitch L. Evidence for functional hemizygosity at the Emtr locus in CHO cells through segregation analysis. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):1007–1013. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90354-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. S., Siminovitch L. Genetic and biochemical studies with the adenosine analogs toyocamycin and tubercidin: mutation at the adenosine kinase locus in Chinese hamster cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1978 Nov;4(6):715–735. doi: 10.1007/BF01543160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris M. Mutation rates in cells at different ploidy levels. J Cell Physiol. 1971 Oct;78(2):177–184. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040780204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinwand L., Fournier R. E., Nichols E. A., Ruddle F. H. Assignment of the gene for adenosine kinase to chromosome 14 in Mus musculus by somatic cell hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;21(1-2):77–85. doi: 10.1159/000130880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow J., Stocco D., Barron E. Spontaneous mutation rate to thioguanine resistance is decreased in polyploid hamster cells. J Cell Physiol. 1978 Jul;96(1):81–86. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040960110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols E. A., Ruddle F. H. Comparative sensitivities of electrophoretic assays for human enzymes. Biochem Genet. 1979 Feb;17(1-2):127–132. doi: 10.1007/BF00484478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J., Nash H. R. Esterases of Mus musculus: substrate and inhibition characteristics, new isozymes, and homologies with man. Biochem Genet. 1978 Jun;16(5-6):553–569. doi: 10.1007/BF00484219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J., Nash H. R. Polymorphism of esterase-10 in Mus musculus. Biochem Genet. 1976 Feb;14(1-2):119–125. doi: 10.1007/BF00484878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin M. S., Gottesman M. M. High frequency of mutation to tubercidin resistance in CHO cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1979 Sep;5(5):571–583. doi: 10.1007/BF01542695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstraus M. J., Chasin L. A. Separation of linked markers in Chinese hamster cell hybrids: mitotic recombination is not involved. Genetics. 1978 Dec;90(4):735–760. doi: 10.1093/genetics/90.4.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seabright M. A rapid banding technique for human chromosomes. Lancet. 1971 Oct 30;2(7731):971–972. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siminovitch L. On the nature of hereditable variation in cultured somatic cells. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90249-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Womack J. E., Davisson M. T., Eicher E. M., Kendall D. A. Mapping of nucleoside phosphorylase (Np-1) and esterase 10 (Es-10) on mouse chromosome 14. Biochem Genet. 1977 Apr;15(3-4):347–355. doi: 10.1007/BF00484465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Womack J. E., Sharp M. Comparative autosomal linkage in mammals: genetics of esterases in Mus musculus and Rattus norvegicus. Genetics. 1976 Apr;82(4):665–675. doi: 10.1093/genetics/82.4.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worton R. G., Duff C., Campbell C. E. Marker segregation without chromosome loss at the emt locus in Chinese hamster cell hybrids. Somatic Cell Genet. 1980 Mar;6(2):199–213. doi: 10.1007/BF01538796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]