Abstract
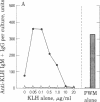
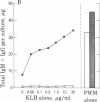
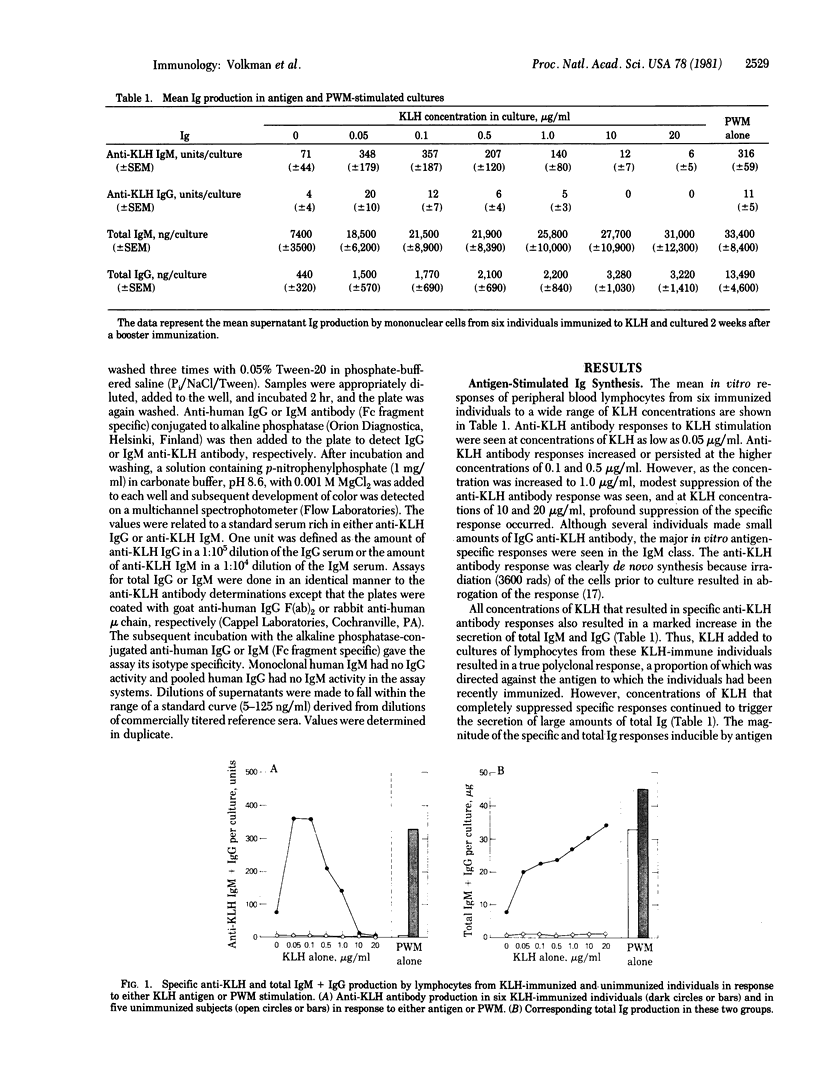
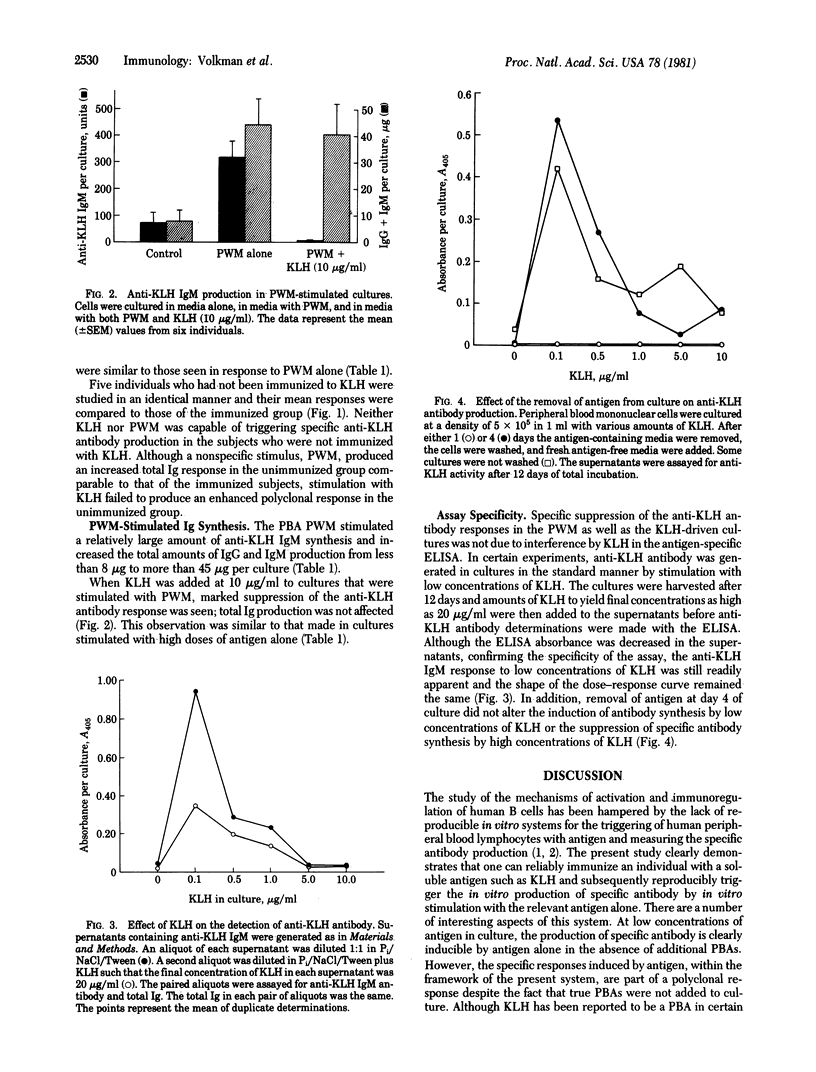
The precise events associated with B cell activation in humans are a subject of intense investigation. It has been difficult to develop an in vitro model of antigen-specific triggering of antibody synthesis by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells that is independent of exogenous mitogens. In the present study a sensitive and reproducible culture system and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay have been established wherein antigen alone is used to trigger antigen-specific antibody synthesis by mononuclear cells from subjects immunized to keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH). The in vitro antigen-induced anti-KLH response is comparable in magnitude to that induced by pokeweed mitogen, is predominantly IgM in isotype, and is accompanied by a simultaneous increase in polyclonal antibody production. Anti-KLH responses were seen at in vitro KLH concentrations as low as 0.05 microgram/ml. However, concentrations of KLH greater than 5 microgram/ml resulted in profound suppression of the anti-LHL response while continuing to trigger large amounts of total polyclonal immunoglobulin synthesis. This suppression by high concentrations of antigen was also observed in pokeweed mitogen-driven anti-KLH production. These observations are consistent with previous results from the mouse model showing a close association between antigen-specific and polyclonal responses and the phenomenon of antigen-induced, antigen-specific suppression. Thus, an in vitro model of antigen induction of antigen-specific antibody synthesis in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells has been demontrated and should prove useful in exploring the mechanism of human B cell activation and immunoregulation.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burke G. P., Smith K. A., Stocking R. I., Ferm M., McIntyre O. R. Anti-keyhole limpet hemocyanin antibody in normal unsensitized individuals. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1977 Apr;59(4):309–313. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(77)90052-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callard R. E. Specific in vitro antibody response to influenza virus by human blood lymphocytes. Nature. 1979 Dec 13;282(5740):734–736. doi: 10.1038/282734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. D., Lawton A. R., Bockman D. E. Agammaglobulinaemia with B lymphocytes. Specific defect of plasma-cell differentiation. Lancet. 1971 Oct 9;2(7728):791–794. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92742-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho A., Möller G. Thymus-independent B-cell induction and paralysis. Adv Immunol. 1975;21:113–236. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60220-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delfraissy J. F., Galanaud P., Dormont J., Wallon C. Primary in vitro antibody response from human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):630–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dosch H. M., Gelfand E. W. In vitro induction and measurement of hemolytic plaque forming cells in man. J Immunol Methods. 1976;11(2):107–116. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90138-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S. Human B cell function in a polyclonally induced plaque forming cell system. Cell triggering and immunoregulation. Immunol Rev. 1979;45:93–116. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S. Immunoregulation in autoimmunity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1980 Jul;66(1):5–17. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(80)90132-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Pratt K. R. Activation of human B lymphocytes. I. Direct plaque-forming cell assay for the measurement of polyclonal activation and antigenic stimulation of human B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):674–684. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Pratt K. R., Whalen G. Activation of human B lymphocytes. VIII. Differential radiosensitivity of subpopulations of lymphoid cells involved in the polyclonally-induced PFC responses of peripheral blood B lymphocytes. Immunology. 1978 Nov;35(5):715–720. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Whalen G., Burch C. Activation of human B lymphocytes XVI. Cellular requirements, interactions, and immunoregulation of pokeweed mitogen-induced total-immunoglobulin producing plaque-forming cells in peripheral blood. Cell Immunol. 1980 Aug 15;54(1):230–240. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90204-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geha R. S. Regulation of human B cell activation. Immunol Rev. 1979;45:275–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00281.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontiainen S., Feldmann M. Suppressor cell induction in vitro. I. Kinetics of induction of antigen-specific suppressor cells. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Apr;6(4):296–301. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molinaro G. A., Dray S. Antibody coated erythrocytes as a manifold probe for antigens. Nature. 1974 Apr 5;248(448):515–517. doi: 10.1038/248515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada T., Taniguchi M., Takemori T. Properties of primed suppressor T cells and their products. Transplant Rev. 1975;26:106–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1975.tb00177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UytdeHaag F., Heynen C. J., Ballieux R. E. Induction of antigen-specific human suppressor T lymphocytes in vitro. Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):556–557. doi: 10.1038/271556a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Durm M., Broder S., Blackman M., Blaese R. M., Strober W. Role of suppressor T cells in pathogenesis of common variable hypogammaglobulinaemia. Lancet. 1974 Sep 14;2(7881):609–613. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91940-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]