Abstract
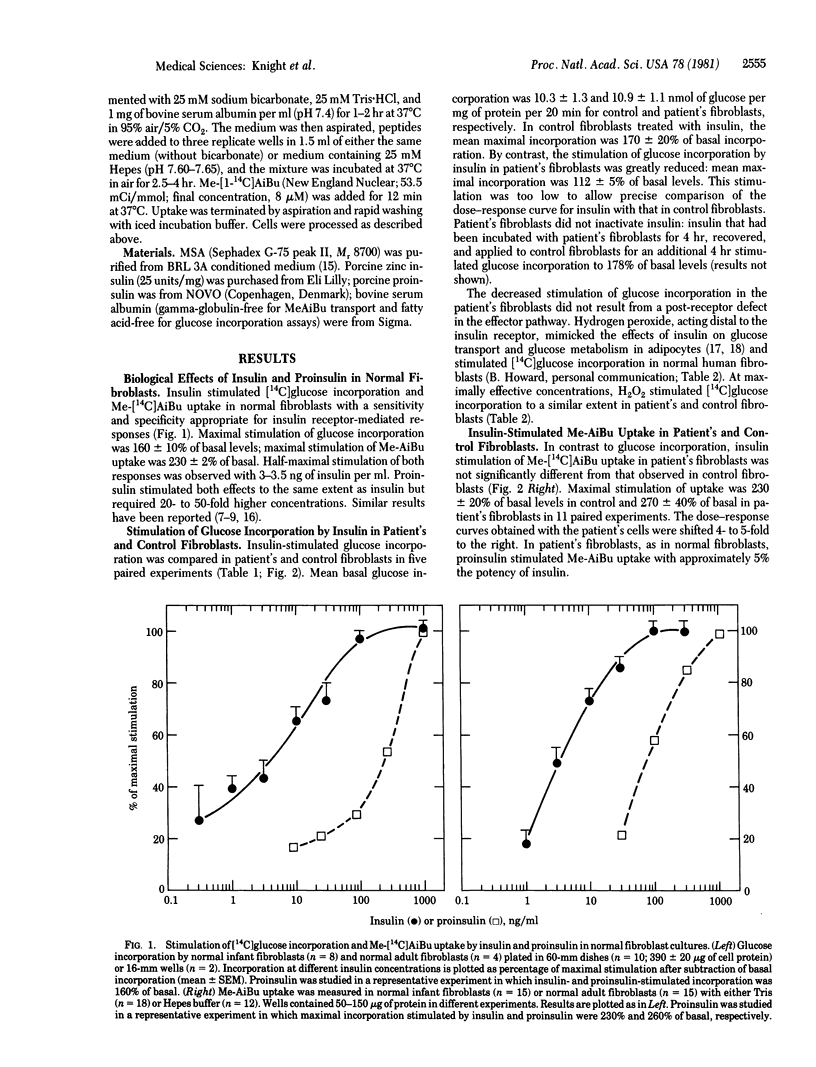
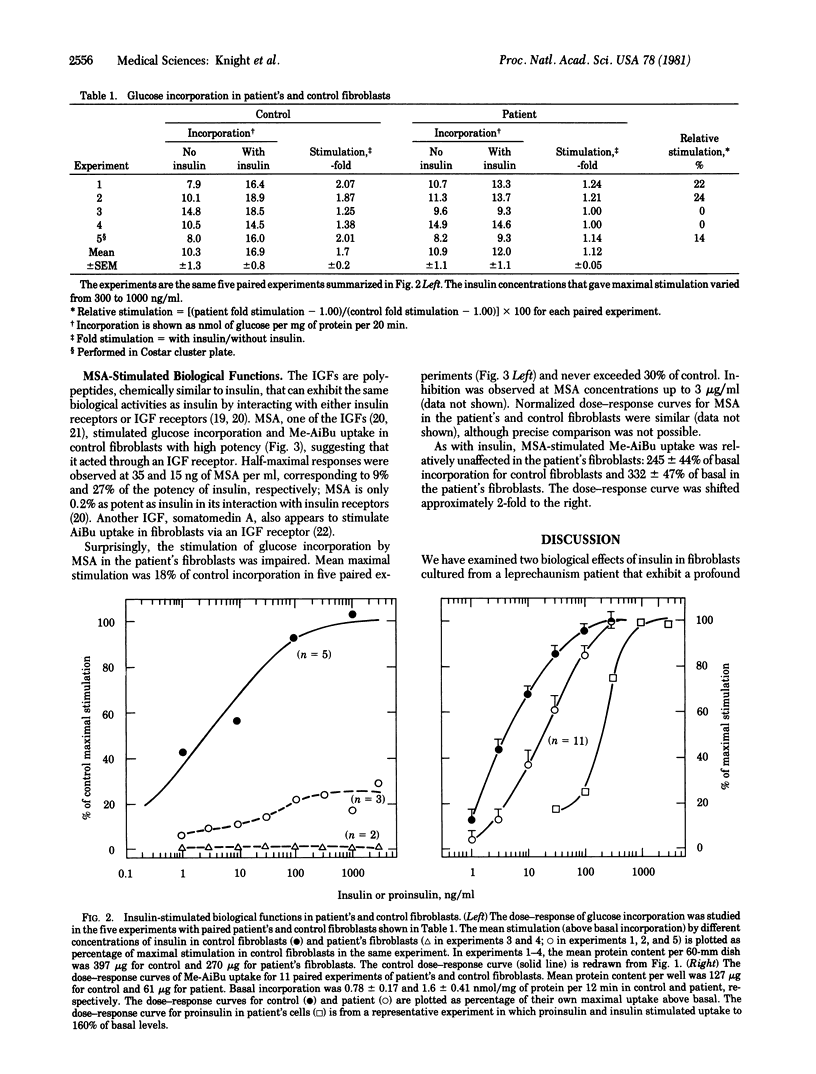
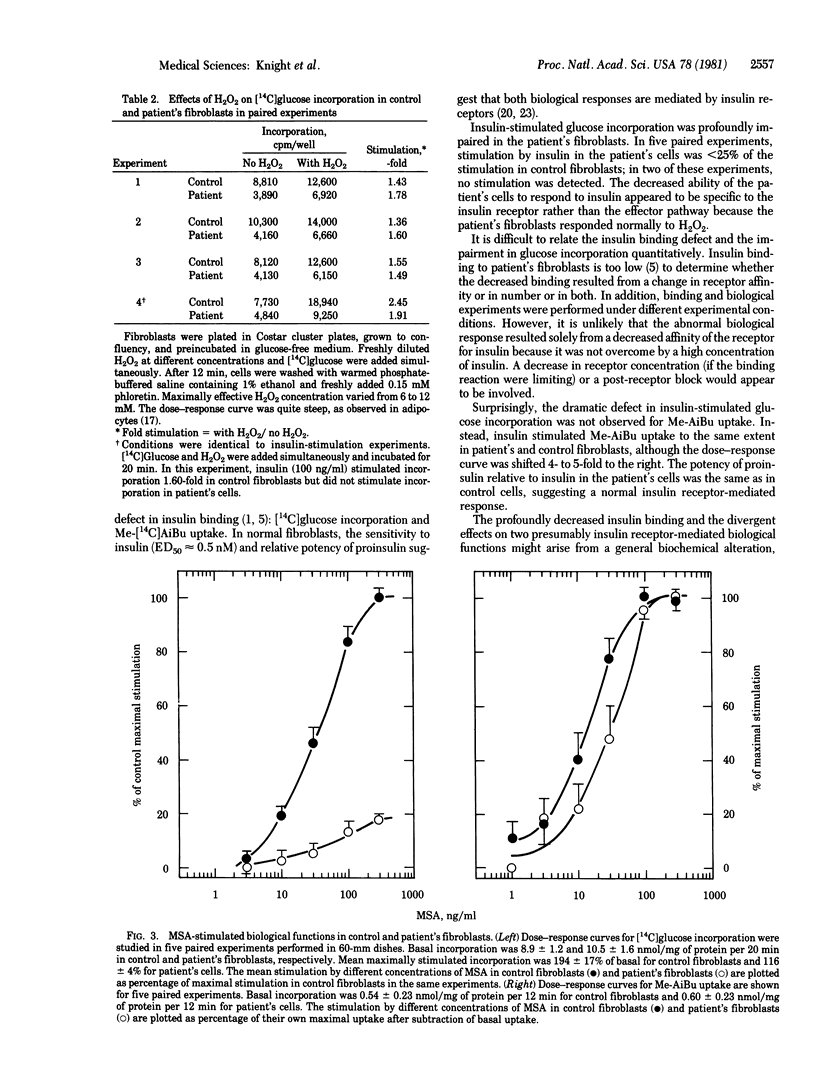
Fibroblasts cultured from an infant with leprechaunism and insulin resistance have been reported to exhibit profound, selective defect in insulin binding. We now examine the effect of this defect on two acute metabolic actions of insulin thought to be mediated by the insulin receptor, glucose incorporation and N-methyl-alpha-aminoisobutyric acid (Me-AiBu) uptake. In the patient's fibroblasts, maximal insulin-stimulated glucose incorporation was less than 25% of that in control fibroblasts, whereas stimulation by hydrogen peroxide, an insulinomimetic agent that acts distal to the insulin receptor, was normal. By contrast, insulin stimulated Me-AiBu uptake to the same extent in patient's and control fibroblasts. Impaired glucose incorporation and relatively normal Me-AiBu uptake also were observed in the patient's cells with multiplication-stimulating activity, an insulin-like growth factor, despite the fact that multiplication-stimulating activity appeared to stimulate both responses in normal fibroblasts via an insulin-like growth factor receptor. The divergent effects on two hormone-stimulated functions in the patient's cells suggests differences in the coupling of a receptor to different effectors. The same coupling mechanisms appear to be used by insulin receptors and receptors for insulin-like growth factors.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bar R. S., Levis W. R., Rechler M. M., Harrison L. C., Siebert C., Podskalny J., Roth J., Muggeo M. Extreme insulin resistance in ataxia telangiectasia: defect in affinity of insulin receptors. N Engl J Med. 1978 May 25;298(21):1164–1171. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197805252982103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P., Lawrence J. C., Jr, Lynn W. S. Evidence for electron transfer reactions involved in the Cu2+ -dependent thiol activation of fat cell glucose utilization. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 25;249(4):1001–1006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P., Lawrence J. C., Jr, Lynn W. S. Hexose transport in isolated brown fat cells. A model system for investigating insulin action on membrane transport. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 10;249(17):5421–5427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ercole A. J., Underwood L. E., Groelke J., Plet A. Leprechaunism: studies of the relationship among hyperinsulinism, insulin resistance, and growth retardation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Mar;48(3):495–502. doi: 10.1210/jcem-48-3-495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon J. T., Kahn C. R., Kempner E. S., Schlegel W. Characterization of the insulin receptor in its membrane environment by radiation inactivation. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3412–3419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. E. Effect of insulin on fetal growth. Semin Perinatol. 1978 Oct;2(4):319–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg M. D. Action of insulin analogues on cultured human fibroblasts reflects biological potency. Life Sci. 1976 Mar 1;18(5):521–527. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90330-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg M. D., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin and epidermal growth factor. Human fibroblast receptors related to deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis and amino acid uptake. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):3845–3853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg M. D., Fryklund L. Insulin and somatomedins A and B: comparisons of biological activities in cultured human skin-derived fibroblasts. Life Sci. 1977 Oct 1;21(7):943–950. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90260-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard B. V., Mott D. M., Fields R. M., Bennett P. H. Insulin stimulation of glucose entry in cultured human fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Oct;101(1):129–138. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041010115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P. The mobile receptor hypothesis and "cooperativity" of hormone binding. Application to insulin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 21;433(3):482–495. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90275-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Hazum E., Shechter Y., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin receptor: covalent labeling and identification of subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4918–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Baird K. L., Jarrett D. B., Flier J. S. Direct demonstration that receptor crosslinking or aggregation is important in insulin action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4209–4213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Olefsky J. M., Elders J., Mako M. E., Given B. D., Schedwie H. K., Fiser R. H., Hintz R. L., Horner J. A., Rubenstein A. H. Insulin resistance due to a defect distal to the insulin receptor: demonstration in a patient with leprechaunism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3469–3473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Cam A., Freychet P. Effect of insulin on amino acid transport in isolated rat hepatocytes. Diabetologia. 1978 Aug;15(2):117–123. doi: 10.1007/BF00422256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. S., Pohl S. L. Insulin-induced insulin resistance of alpha-aminoisobutyric acid transport in cultured human skin fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):9976–9978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maturo J. M., 3rd, Hollenberg M. D. Insulin receptor: interaction with nonreceptor glycoprotein from liver cell membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3070–3074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minton A. P. The bivalent ligand hypothesis. A quantitative model for hormone action. Mol Pharmacol. 1981 Jan;19(1):1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses A. C., Nissley S. P., Short P. A., Rechler M. M., Podskalny J. M. Purification and characterization of multiplication-stimulating activity. Insulin-like growth factors purified from rat-liver-cell-conditioned medium. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jan;103(2):387–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04325.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott D. M., Howard B. V., Bennett P. H. Stoichiometric binding and regulation of insulin receptors on human diploid fibroblasts using physiologic insulin levels. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):8762–8767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muggeo M., Kahn C. R., Bar R. S., Rechler M., Flier J. S., Roth J. The underlying insulin receptor in patients with antireceptor autoantibodies: demonstration of normal binding and immunological properties. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Jul;49(1):110–119. doi: 10.1210/jcem-49-1-110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissley S. P., Rechler M. M. Multiplication-stimulating activity (MSA): a somatomedin-like polypeptide from cultured rat liver cells. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1978 May;(48):167–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch P. F., Czech M. P. The subunit structure of the high affinity insulin receptor. Evidence for a disulfide-linked receptor complex in fat cell and liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1722–1731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Podskalny J. M. Insulin receptors in cultured human fibroblasts. Diabetes. 1976 Apr;25(4):250–255. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.4.250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Zapf J., Nissley S. P., Froesch E. R., Moses A. C., Podskalny J. M., Schilling E. E., Humbel R. E. Interactions of insulin-like growth factors I and II and multiplication-stimulating activity with receptors and serum carrier proteins. Endocrinology. 1980 Nov;107(5):1451–1459. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-5-1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M. The role of hormone receptors and GTP-regulatory proteins in membrane transduction. Nature. 1980 Mar 6;284(5751):17–22. doi: 10.1038/284017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. M., Haworth J. C., Degroot G. W., Trevenen C. L., Rechler M. M. A case of leprechaunism with severe hyperinsulinemia. Am J Dis Child. 1980 Feb;134(2):170–175. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1980.02130140044014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilling E. E., Rechler M. M., Grunfeld C., Rosenberg A. M. Primary defect of insulin receptors in skin fibroblasts cultured from an infant with leprechaunism and insulin resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5877–5881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E., Froesch E. R. Nonsuppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA) from human serum: recent accomplishments and their physiologic implications. Metabolism. 1978 Dec;27(12):1803–1828. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(78)90267-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


