Abstract
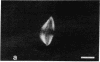
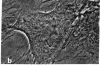
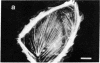
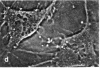
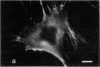
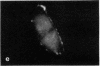
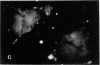
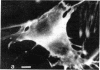
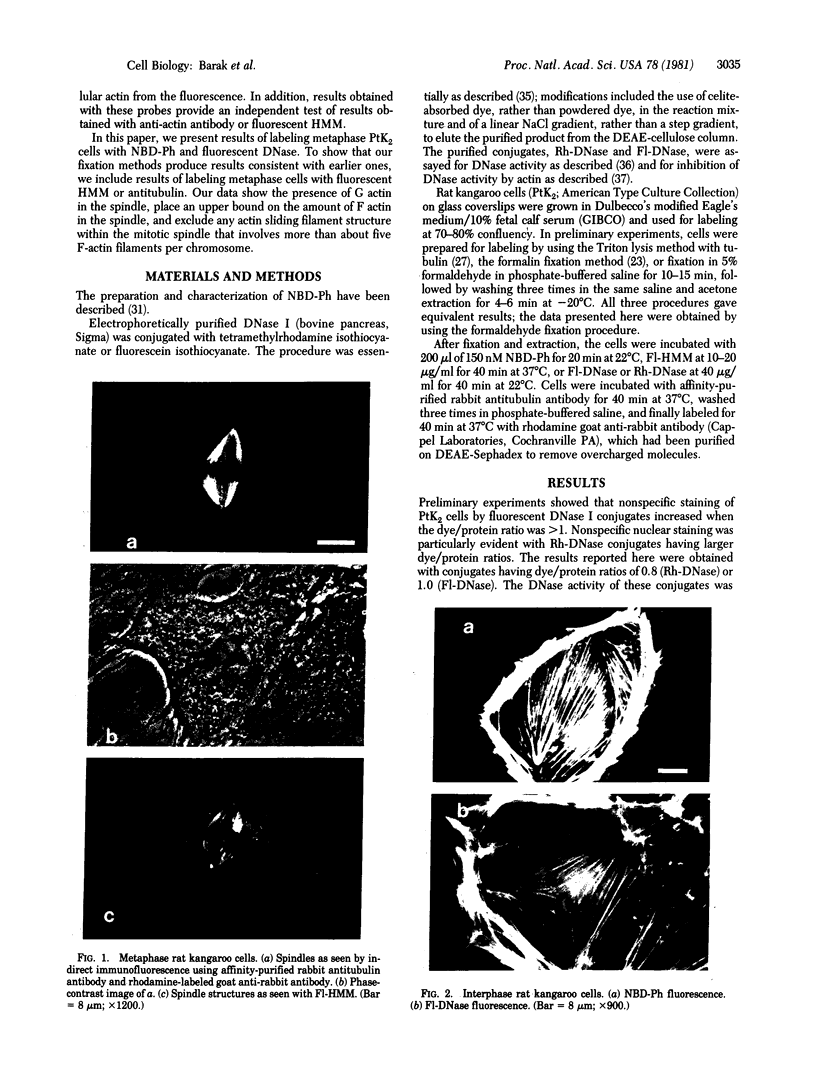
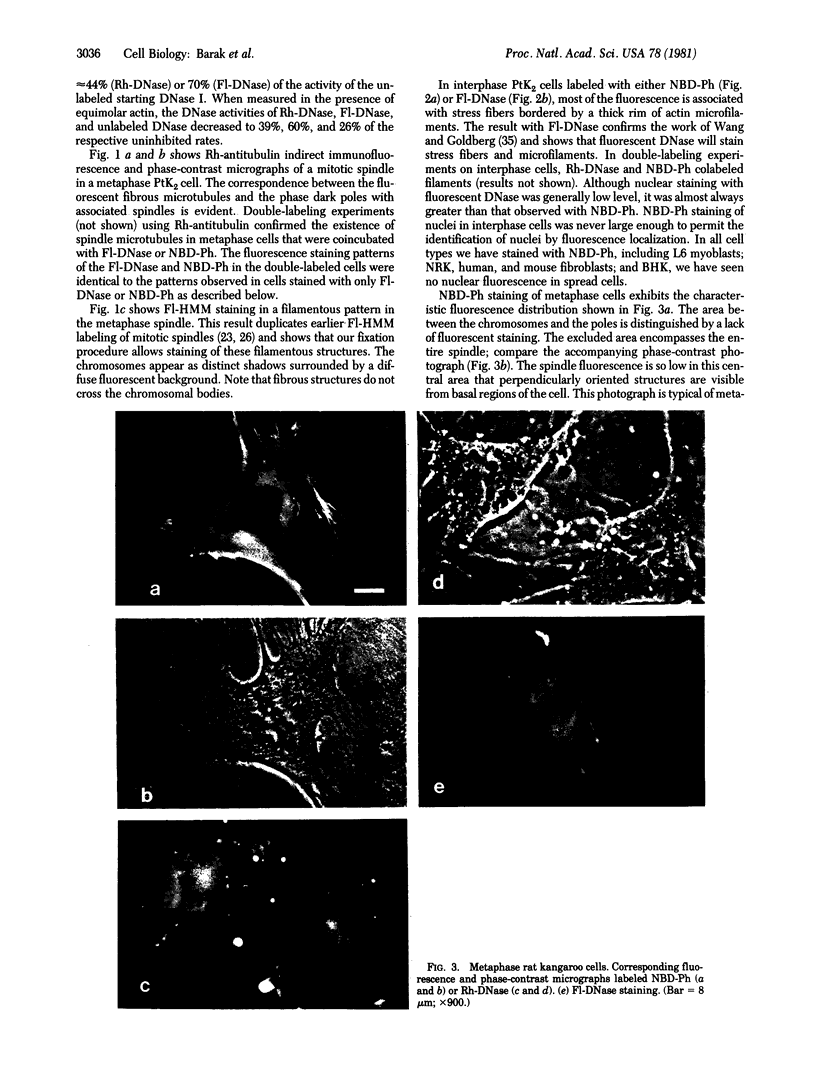
The distribution and polymerization state of actin in metaphase rat kangaroo cells was studied by fluorescence microscopy. Formaldehyde-fixed, acetone-extracted cells were labeled with either of two types of actin probes. The first, 7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazole-phallacidin, has high affinity for F actin and does not bind monomeric G actin. The second was a conjugate of DNase I labeled with either tetramethylrhodamine or fluorescein. DNase binds with high affinity to G actin and with lesser affinity to F actin. The polymerization state of actin was deduced by comparing the fluorescence distribution of the phallacidin derivative with that of the fluorescent DNase. The results indicate that the pole-to-chromosome region of the metaphase spindle contains G actin but little if any conventional F actin. F actin is found concentrated in a diffuse distribution outside the spindle region in metaphase cells and returns to the interzone area between the chromosomes by early telophase. These results exclude spindle models for chromosomal movement that require more than about five F actin filaments per chromosome, support the hypothesis that F actin is involved in force generation for cell cleavage, and are not inconsistent with the possibility that actin outside the spindle may be involved in chromosomal movement.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronson J. F. The use of fluorescein-labeled heavy meromyosin for the cytological demonstration of actin. J Cell Biol. 1965 Jul;26(1):293–298. doi: 10.1083/jcb.26.1.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubin J. E., Weber K., Osborn M. Analysis of actin and microfilament-associated proteins in the mitotic spindle and cleavage furrow of PtK2 cells by immunofluorescence microscopy. A critical note. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Nov;124(1):93–109. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90260-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barak L. S., Yocum R. R. 7-Nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazole (NBD)--phallacidin: synthesis of a fluorescent actin probe. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jan 1;110(1):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90107-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barak L. S., Yocum R. R., Nothnagel E. A., Webb W. W. Fluorescence staining of the actin cytoskeleton in living cells with 7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazole-phallacidin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):980–984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cande W. Z., Lazarides E., McIntosh J. R. A comparison of the distribution of actin and tubulin in the mammalian mitotic spindle as seen by indirect immunofluorescence. J Cell Biol. 1977 Mar;72(3):552–567. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.3.552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comings D. E., Harris D. C. Nuclear proteins. II. Similarity of nonhistone proteins in nuclear sap and chromatin, and essential absence of contractile proteins from mouse liver nuclei. J Cell Biol. 1976 Aug;70(2 Pt 1):440–452. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.2.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R., Morales M. F. Interaction of globular actin with myosin subfragments. J Mol Biol. 1971 Sep 14;60(2):249–261. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90291-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douvas A. S., Harrington C. A., Bonner J. Major nonhistone proteins of rat liver chromatin: preliminary identification of myosin, actin, tubulin, and tropomyosin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3902–3906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forer A., Behnke O. An actin-like component in spermatocytes of a crane fly (Nephrotoma suturalis Loew). I. The spindle. Chromosoma. 1972;39(2):145–173. doi: 10.1007/BF00319840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forer A., Jackson W. T., Engberg A. Actin in spindles of Haemanthus katherinae endosperm. II. Distribution of actin in chromosomal spindle fibres, determined by analysis of serial sections. J Cell Sci. 1979 Jun;37:349–371. doi: 10.1242/jcs.37.1.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara K., Pollard T. D. Fluorescent antibody localization of myosin in the cytoplasm, cleavage furrow, and mitotic spindle of human cells. J Cell Biol. 1976 Dec;71(3):848–875. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.3.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawadi N. Actin in the mitotic spindle. Nature. 1971 Dec 17;234(5329):410–410. doi: 10.1038/234410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D. J., Boyer J. L., Korn E. D. Comparative biochemistry of non-muscle actins. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):8300–8309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi M., Ohnishi K., Hayashi K. Dense precipitate of brain tubulin with skeletal muscle myosin. J Biochem. 1980 May;87(5):1347–1355. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman I. M., Pollard T. D. Actin localization in fixed dividing cells stained with fluorescent heavy meromyosin. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Jun;114(1):15–25. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90030-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman I. M., Pollard T. D. Comparison of purified anti-actin and fluorescent-heavy meromyosin staining patterns in dividing cells. J Cell Biol. 1979 Mar;80(3):509–520. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.3.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkley R., Telser A. Heavy meromyosin-binding filaments in the mitotic apparatus of mammaliam cells. Exp Cell Res. 1974 May;86(1):161–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90662-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiura M., Shibata-Sekiya K., Kato T., Tonomura Y. A chemically modified subfragment-1 of myosin from skeletal muscle as a novel tool for identifying the function of actomyosin in non-muscle cells. J Biochem. 1977 Jul;82(1):105–115. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINBERG U. PURIFICATION OF AN INHIBITOR OF PANCREATIC DEOXYRIBONUCLEASE FROM CALF SPLEEN. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Feb 10;82:237–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Lindberg U. Actin is the naturally occurring inhibitor of deoxyribonuclease I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4742–4746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh J. R., Cande W. Z., Snyder J. A. Structure and physiology of the mammalian mitotic spindle. Soc Gen Physiol Ser. 1975;30:31–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh J. R., McDonald K. L., Edwards M. K., Ross B. M. Three-dimensional structure of the central mitotic spindle of Diatoma vulgare. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):428–442. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. B., Huxley H. E., DeRosier D. J. Three-dimensional reconstruction of F-actin, thin filaments and decorated thin filaments. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 14;50(2):279–295. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICKLAS R. B. CHROMOSOME VELOCITY DURING MITOSIS AS A FUNCTION OF CHROMOSOME SIZE AND POSITION. J Cell Biol. 1965 Apr;25:SUPPL–SUPPL:135. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nothnagel E. A., Barak L. S., Sanger J. W., Webb W. W. Fluorescence studies on modes of cytochalasin B and phallotoxin action on cytoplasmic streaming in Chara. J Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;88(2):364–372. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.2.364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onodera M., Yagi K. Studies on enzymatically active subfragments of myosin-adenosine triphosphatase. I. Preparation using chymotrypsin. J Biochem. 1971 Jan;69(1):145–153. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. L., McConkey E. H. Non-histone chromosomal proteins from HeLa cells. A survey by high resolution, two-dimensional electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 25;251(2):548–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger J. W. Presence of actin during chromosomal movement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2451–2455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schloss J. A., Milsted A., Goldman R. D. Myosin subfragment binding for the localization of actin-like microfilaments in cultured cells. A light and electron microscope study. J Cell Biol. 1977 Sep;74(3):794–815. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.3.794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder T. E. Actin in dividing cells: contractile ring filaments bind heavy meromyosin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1688–1692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimo-Oka T., Hayashi M., Watanabe Y. Tubulin-myosin interaction. Some properties of binding between tubulin and myosin. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 14;19(21):4921–4926. doi: 10.1021/bi00562a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E., Goldberg A. R. Binding of deoxyribonuclease I to actin: a new way to visualize microfilament bundles in nonmuscle cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Sep;26(9):745–749. doi: 10.1177/26.9.361884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland T., Faulstich H. Amatoxins, phallotoxins, phallolysin, and antamanide: the biologically active components of poisonous Amanita mushrooms. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1978 Dec;5(3):185–260. doi: 10.3109/10409237809149870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]