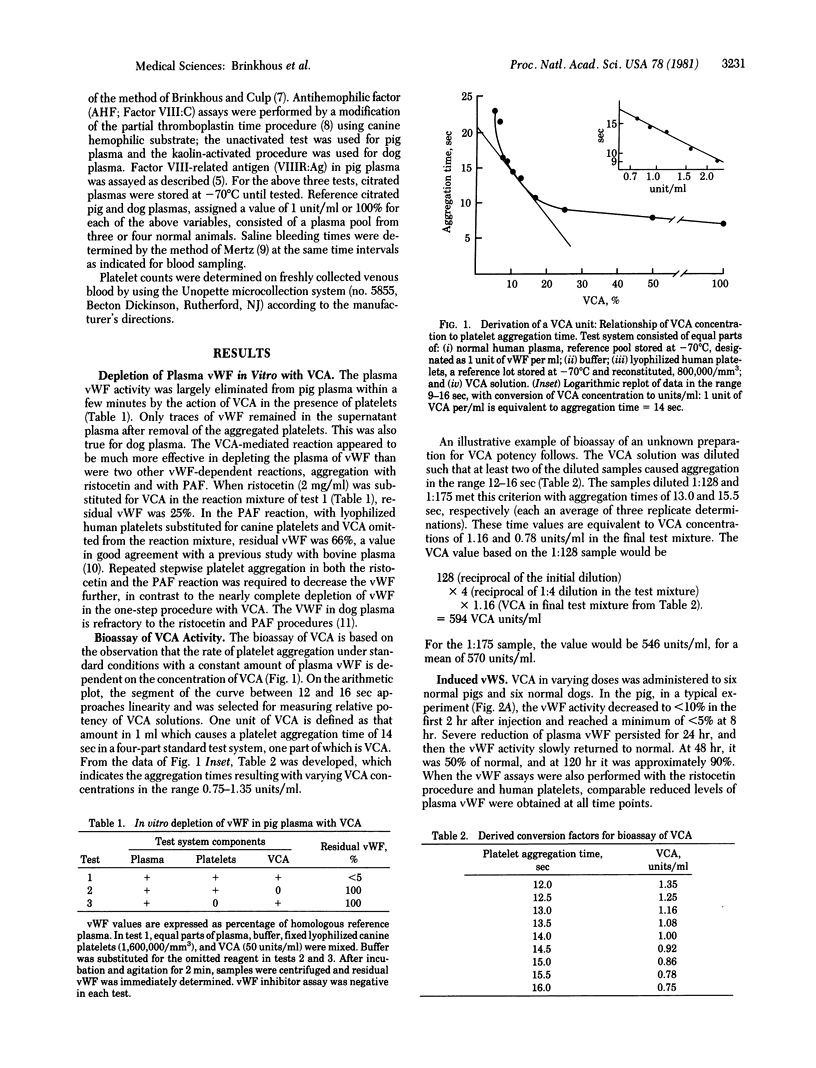
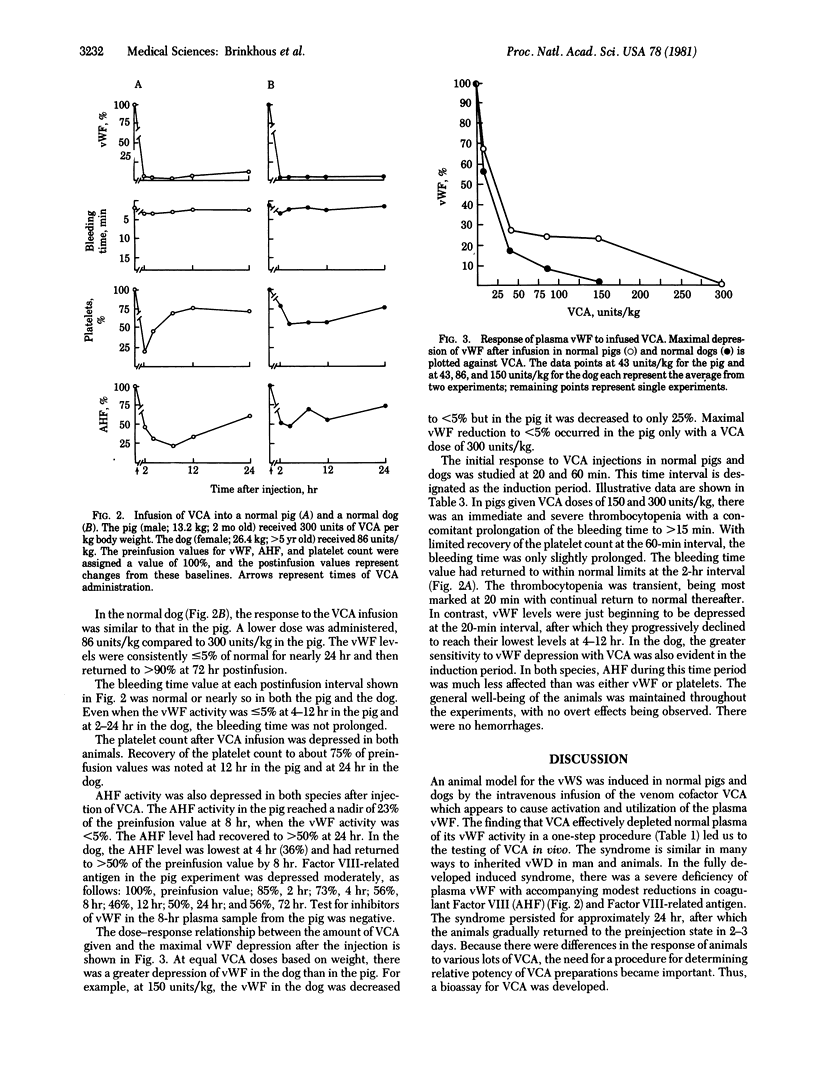
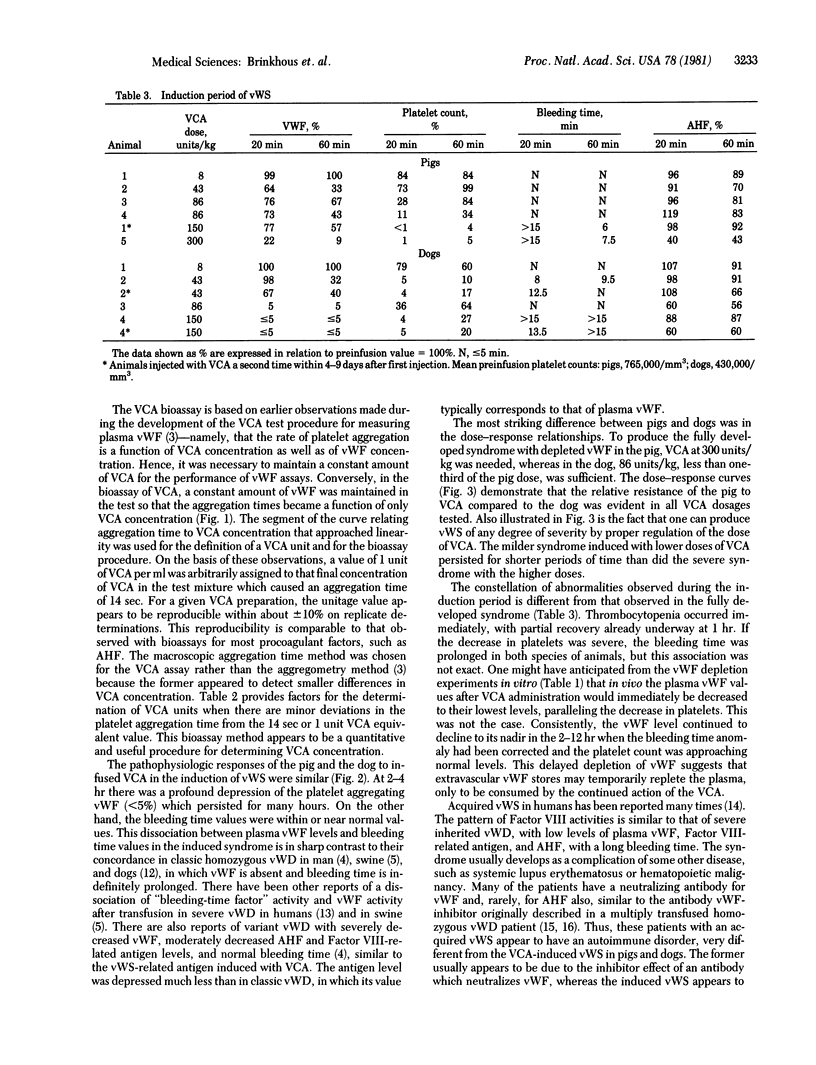
Abstract
Hereditary deficiency of the macromolecular Factor VIII complex results in classic von Willebrand disease in man and animals, a bleeder state characterized by loss of the multiple biologic activities associated with the Factor VIII complex, including the platelet-aggregating von Willebrand factor. The bleeding time is also long. Venom coagglutinin, a Bothrops factor that causes platelet aggregation in vitro, depletes the plasma of its von Willebrand factor. The rate of platelet aggregation is a function of the amount of the coagglutinin present. Based on this observation, a sensitive and quantitative assay for the venom coagglutinin was developed. We administered the purified Bothrops factor to normal pigs and dogs and induced a von Willebrand syndrome similar to the inherited disease. The plasma von Willebrand factor was severely depleted; the antihemophilic factor and the Factor VIII-related antigen were not depleted as much. The bleeding time was normal. During the induction phase of the syndrome, transient thrombocytopenia with a long bleeding time occurred. The pig was less sensitive than the dog to the effect of coagglutinin. The severity of the syndrome is determined by the amount of venom coagglutinin administered. It is suggested that the syndrome could be induced in any mammalian species because the plasma of all mammals tested in vitro is sensitive to the venom factor. This model provides another avenue for the study of the heterogeneity of the Factor VIII complex and the pathophysiology of its components.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blatt P. M., Brinkhous K. M., Culp H. R., Krauss J. S., Roberts H. R. Antihemophilic factor concentrate therapy in von Willebrand disease. Dissociation of bleeding-time factor and ristocetin-cofactor activities. JAMA. 1976 Dec 13;236(24):2770–2772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkhous K. M., Culp H. R. Plasmatic clotting and/or blood cellular clumping in clinical conditions, experimental animals, and in perfused organs. Thromb Res. 1976 May;8(2 Suppl):125–132. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90055-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkhous K. M., Read M. S. Preservation of platelet receptors for platelet aggregating factor/von Willebrand factor by air drying, freezing, or lyophilization: new stable platelet preparations for von Willebrand factor assays. Thromb Res. 1978 Oct;13(4):591–597. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90148-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkhous K. M., Read M. S. Use of venom coagglutinin and lyophilized platelets in testing for platelet-aggregating von Willebrand factor. Blood. 1980 Mar;55(3):517–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkhous K. M., Thomas B. D., Ibrahim S. A., Read M. S. Plasma levels of platelet aggregating factor/vom Willebrand factor in various species. Thromb Res. 1977 Sep;11(3):345–355. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90186-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper H. A., Wilkins K. W., Jr, Johnson P. R., Jr, Wagner R. H. Platelet-aggregating factor and the aggregation of fixed washed platelets. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 Sep;90(3):512–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griggs T. R., Potter J. S., McClanahan S. B., Webster W. P., Brinkhous K. M. Macromolecular factor VIII complex: functional and structural heterogeneity observed in von Willebrand swine with transfusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):759–763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGDELL R. D., WAGNER R. H., BRINKHOUS K. M. Effect of antihemophilic factor on one-stage clotting tests; a presumptive test for hemophilia and a simple one-stage antihemophilic factor assy procedure. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Apr;41(4):637–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D., Frommel D., Larrieu M. J., Zimmerman T. S. Selective absence of large forms of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor in acquired von Willebrand's syndrome. Response to transfusion. Blood. 1979 Sep;54(3):600–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. H., Graham J. B., Goldin L. R., Elston R. C. Genetics of classic von Willebrand's disease. I. Phenotypic variation within families. Blood. 1979 Jul;54(1):117–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read M. S., Shermer R. W., Brinkhous K. M. Venom coagglutinin: an activator of platelet aggregation dependent on von Willebrand factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4514–4518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussi J. H., Houbouyan L. L., Alterescu R., Franc B., Goguel A. F. Acquired Von Willebrand's syndrome associated with hairy cell leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 1980 Nov;46(3):503–506. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1980.tb06001.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarji K. E., Stratton R. D., Wagner R. H., Brinkhous K. M. Nature of von Willebrand factor: a new assay and a specific inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):2937–2941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.2937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratton R. D., Wagner R. H., Webster W. P., Brinkhous K. M. Antibody nature of circulating inhibitor of plasma von Willebrand factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4167–4171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


