Abstract
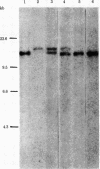
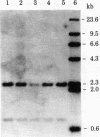
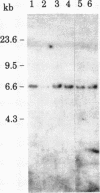
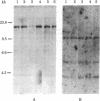
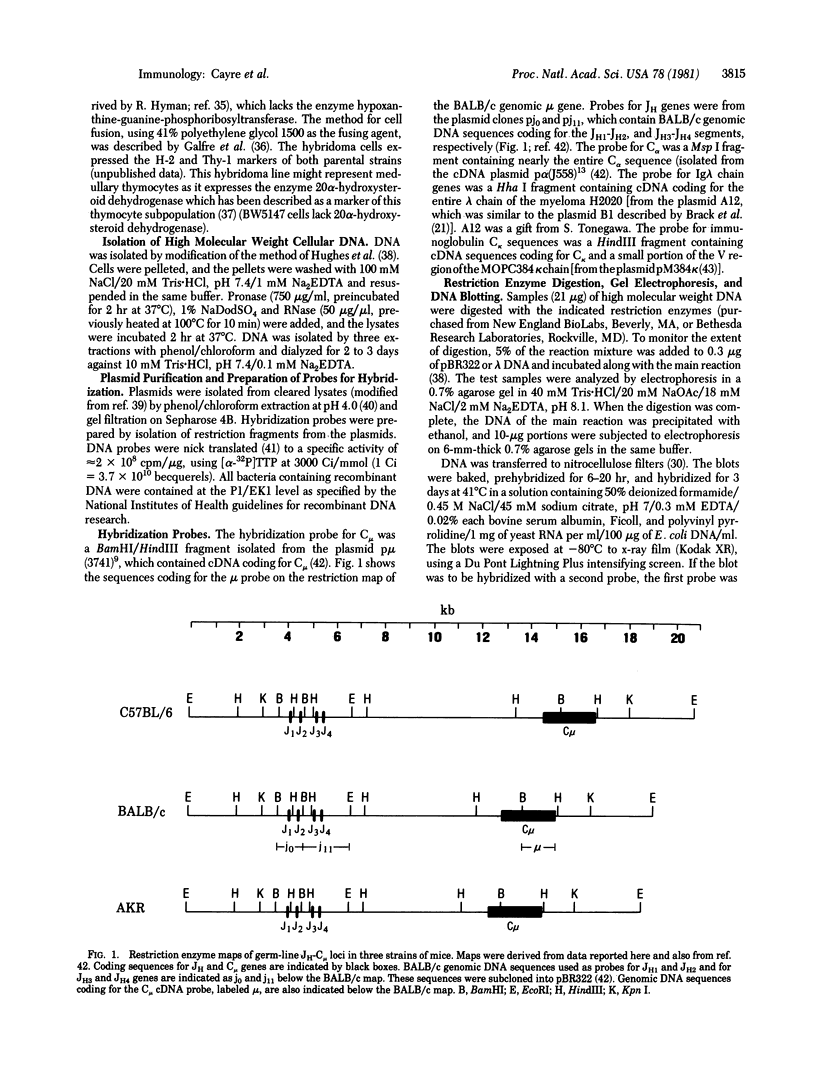
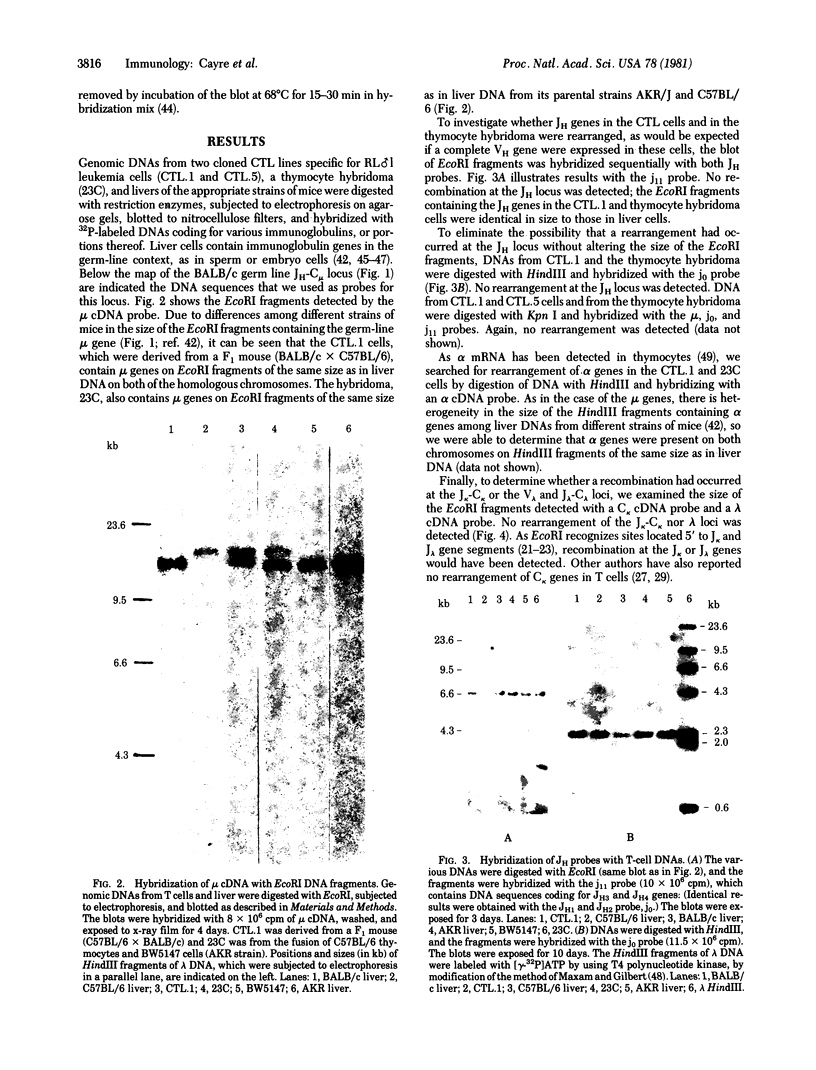
Considerable evidence has accumulated suggesting that the antigen receptor(s) on T cells is coded for by genes for the variable (V) region of the immunoglobulin heavy (H) chains. In B cells, a complete gene for the immunoglobulin VH region is formed by somatic recombination of VH and joining region heavy chain (JH) gene segments [through an intermediate diversity(D) region gene segment]. In an attempt to determine whether a complete immunoglobulin VH region is expressed on T cells that bear an antigen receptor, we analyzed the restriction map of the JH-C mu locus in genomic DNA from two cloned murine cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) lines specific for the x-ray-induced leukemia RL male 1. We found no rearrangement of the JH C mu locus in the CTL lines, indicating that the T-cell antigen receptor(s) in these CTLs is not coded for by a complete immunoglobulin VH gene formed by joining of VH, (DH), and JH genes. In addition, we determined that C mu genes on both chromosomes were present and that there was no rearrangement of the C alpha, C kappa, or lambda chain genes in these CTL cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernard O., Gough N. M. Nucleotide sequence of immunoglobulin heavy chain joining segments between translocated VH and mu constant regions genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3630–3634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binz H., Wigzell H. Antigen-binding, idiotypic T-lymphocyte receptors. Contemp Top Immunobiol. 1977;7:113–177. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3054-7_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binz H., Wigzell H., Bazin H. T-cell idiotypes are linked to immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Nature. 1976 Dec 16;264(5587):639–642. doi: 10.1038/264639a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binz H., Wigzell H. Shared idiotypic determinants on B and T lymphocytes reactive against the same antigenic determinants. II. Determination of frequency and characteristics of idiotypic T and B lymphocytes in normal rats using direct visualization. J Exp Med. 1975 Nov 1;142(5):1218–1230. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.5.1218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brack C., Hirama M., Lenhard-Schuller R., Tonegawa S. A complete immunoglobulin gene is created by somatic recombination. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerottini J. C., Nordin A. A., Brunner K. T. Specific in vitro cytotoxicity of thymus-derived lymphocytes sensitized to alloantigens. Nature. 1970 Dec 26;228(5278):1308–1309. doi: 10.1038/2281308a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cory S., Adams J. M. Deletions are associated with somatic rearrangement of immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):37–51. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90386-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cory S., Adams J. M., Kemp D. J. Somatic rearrangements forming active immunoglobulin mu genes in B and T lymphoid cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4943–4947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. M., Calame K., Early P. W., Livant D. L., Joho R., Weissman I. L., Hood L. An immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene is formed by at least two recombinational events. Nature. 1980 Feb 21;283(5749):733–739. doi: 10.1038/283733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early P., Huang H., Davis M., Calame K., Hood L. An immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region gene is generated from three segments of DNA: VH, D and JH. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):981–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90089-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster A., Hobart M., Hengartner H., Rabbitts T. H. An immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene is altered in two T-cell clones. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):897–899. doi: 10.1038/286897a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfre G., Howe S. C., Milstein C., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. Antibodies to major histocompatibility antigens produced by hybrid cell lines. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):550–552. doi: 10.1038/266550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Smith K. A. In vitro generation of tumor-specific cytotoxic lymphocytes. Secondary allogeneic mixed tumor lymphocyte culture of normal murine spleen cells. J Exp Med. 1977 Aug 1;146(2):468–482. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.2.468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman J. W., Lewis G. K., Primi D., Hornbeck P., Ruddle N. H. Antigen-specific molecules from murine T lymphocytes and T cell hybridomas. Mol Immunol. 1980 Jul;17(7):933–945. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Shank P. R., Spector D. H., Kung H. J., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E., Vogt P. K., Breitman M. L. Proviruses of avian sarcoma virus are terminally redundant, co-extensive with unintegrated linear DNA and integrated at many sites. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1397–1410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman R., Stallings V. Complementation patterns of Thy-1 variants and evidence that antigen loss variants "pre-exist" in the parental population. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Feb;52(2):429–436. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.2.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hämmerling G. J., Black S. J., Berek C., Eichmann K., Rajewsky K. Idiotypic analysis of lymphocytes in vitro. II. Genetic control of T-helper cell responsiveness to anti-idiotypic antibody. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):861–869. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack R. S., Imanishi-Kari T., Rajewsky K. Idiotypic analysis of the response of C57BL/6 mice to the (4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)acetyl group. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Aug;7(8):559–565. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830070813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joho R., Weissman I. L., Early P., Cole J., Hood L. Organization of kappa light chain genes in germ-line and somatic tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1106–1110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karjalainen K., Mäkelä O. A mendelian idiotype is demonstrable in the heteroclitic anti-NP antibodies of the mouse. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Feb;8(2):105–111. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Harris A. W., Cory S., Adams J. M. Expression of the immunoglobulin C mu gene in mouse T and B lymphoid and myeloid cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2876–2880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawinkel U., Cramer M., Imanishi-Kari T., Jack R. S., Rajewsky K., Mäkelä O. Isolated hapten-binding receptors of sensitized lymphocytes. I. Receptors from nylon wool-enriched mouse T lymphocytes lack serological markers of immunoglobulin constant domains but express heavy chain variable portions. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Aug;7(8):566–573. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830070814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawinkel U., Cramer M., Kindred B., Rajewsky K. Isolated hapten-binding receptors of sensitized lymphocytes. V. Cellular origin of receptor molecules. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Oct;9(10):815–820. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830091013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronenberg M., Davis M. M., Early P. W., Hood L. E., Watson J. D. Helper and killer T cells do not express B cell immunoglobulin joining and constant region gene segments. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1745–1761. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonai P., Ben-Neriah Y., Steinman L., Givol D. Selective participation of immunoglobulin V region and major histocompatibility complex products in antigen binding by T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Dec;8(12):827–832. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830081202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J. Surface immunoglobulins of B and T lymphocytes: molecular properties, association with the cell membrane, and a unified model of antigen recognition. Contemp Top Mol Immunol. 1976;5:125–160. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-8142-6_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K. B., Banerji J., Penncavage N. A., Lang R., Arnheim N. 5' flanking region of immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region genes displays length heterogeneity in germlines of inbred mouse strains. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):187–196. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90167-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max E. E., Seidman J. G., Leder P. Sequences of five potential recombination sites encoded close to an immunoglobulin kappa constant region gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3450–3454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKearn T. J. Antireceptor antiserum causes specific inhibition of reactivity to rat histocompatibility antigens. Science. 1974 Jan 11;183(4120):94–96. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4120.94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama E., Shiku H., Takahashi T., Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. Definition of a unique cell surface antigen of mouse leukemia RL male 1 by cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3486–3490. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Near R. I., Storb U. RNA sequences homologous to the 3' portion of immunoglobulin alpha-chain mRNA in thymus-derived lymphocytes. Biochemistry. 1979 Mar 20;18(6):964–972. doi: 10.1021/bi00573a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor S., Eardley D., Shen F. W., Gershon R. K., Cone R. E. Isolation and partial characterization of antigen-binding molecules produced by in vitro 'educated' T cells. Mol Immunol. 1980 Jul;17(7):913–924. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90040-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajewsky K., Eichmann K. Antigen receptors of T helper cells. Contemp Top Immunobiol. 1977;7:69–112. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3054-7_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin B., Hertel-Wulff B., Kimura A. Alloantigen-specific idiotype-bearing receptors on mouse T lymphocytes. I. Specificity characterization and genetic association with the heavy-chain IgG allotype. J Exp Med. 1979 Aug 1;150(2):307–321. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.2.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano H., Hüppi K., Heinrich G., Tonegawa S. Sequences at the somatic recombination sites of immunoglobulin light-chain genes. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):288–294. doi: 10.1038/280288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman J. G., Nau M. M., Norman B., Kwan S. P., Scharff M., Leder P. Immunoglobulin V/J recombination is accompanied by deletion of joining site and variable region segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6022–6026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shank P. R., Hughes S. H., Kung H. J., Majors J. E., Quintrell N., Guntaka R. V., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Mapping unintegrated avian sarcoma virus DNA: termini of linear DNA bear 300 nucleotides present once or twice in two species of circular DNA. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1383–1395. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Uhr J. W. Immunoglobulin-receptors revisited. Science. 1975 Sep 19;189(4207):964–969. doi: 10.1126/science.1083069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner N. L. Membrane immunoglobulins and antigen receptors on B and T lymphocytes. Adv Immunol. 1974;19(0):67–216. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60252-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein Y. 20alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase: a T lymphocyte-associated enzyme. J Immunol. 1977 Oct;119(4):1223–1229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R., Miller J., Storb U. Rearrangement of immunoglobulin genes. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 30;18(22):5013–5021. doi: 10.1021/bi00589a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M., Ginder G. D., Felsenfeld G. A new method for the purification and identification of covalently closed circular DNA molcules. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Apr;5(4):1139–1152. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.4.1139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]