Abstract
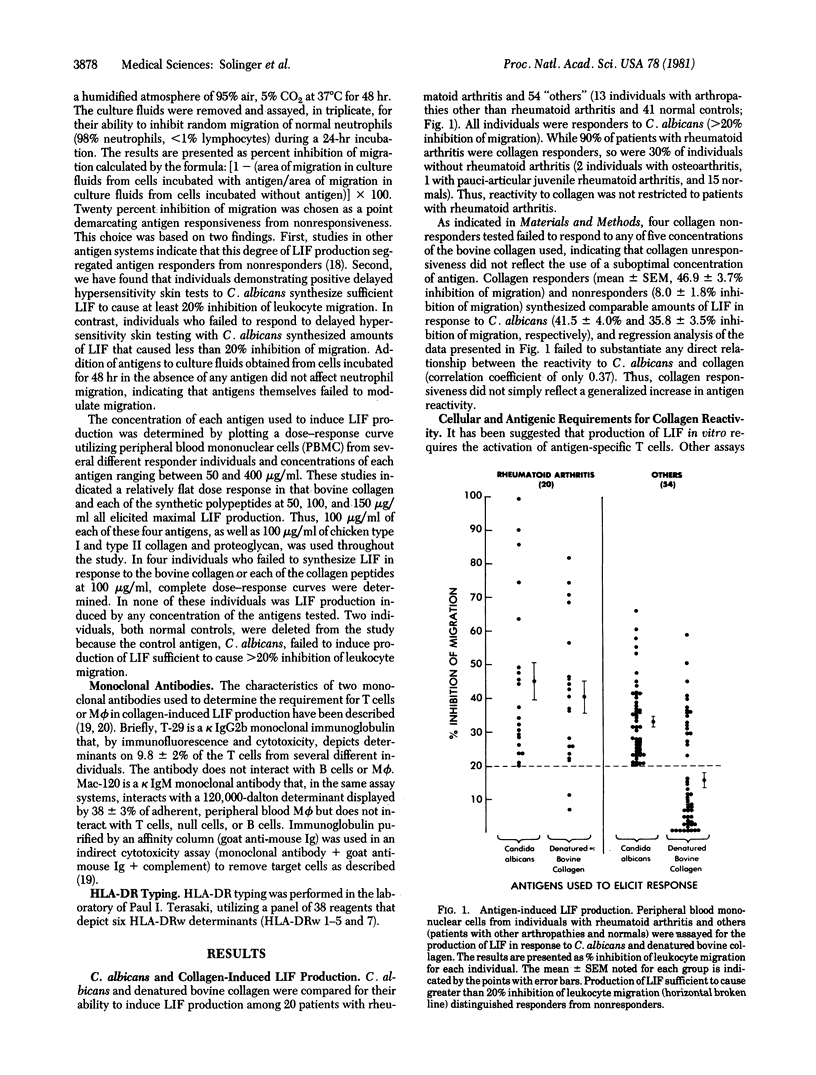
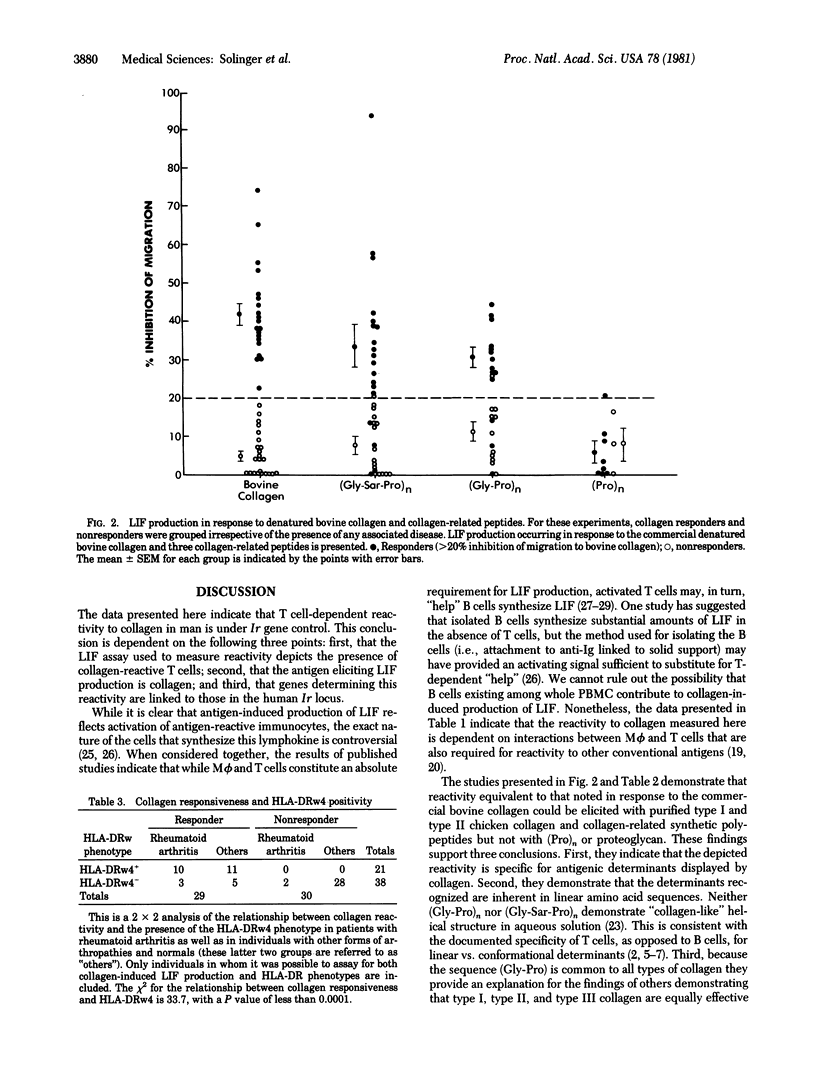
Rheumatoid arthritis is significantly associated with the HLA determinant HLA-DRw4 and cell-mediated reactivity to collagen. To determine if genes linked to those coding for HLA-DRw4 constituted immune response genes for collagen reactivity, peripheral blood mononuclear cells from 20 individuals with rheumatoid arthritis, 13 individuals with other arthropathies, and 41 normal individuals were compared for their ability to synthesize the lymphokine leukocyte inhibition factor in response to denatured bovine collagen. All individuals were responsive to the control antigen Candida albicans. While 90% of the patients with rheumatoid arthritis responded to collagen, so did 30% of the individuals without rheumatoid arthritis. This included 15 normal individuals without any evidence of arthritis. Collagen responsiveness was dependent on interactions between T cells and macrophages was dependent on interactions between T cells and macrophages and was directed against determinants expressed by primary amino acid sequences in the synthetic polypeptide (Gly-Pro)n. HLA-DRw typing of 59 individuals revealed a highly significant relationship (P less than 0.0001, chi 2 = 33.7) between HLA-DRw4 and collagen responsiveness, irrespective of whether or not rheumatoid arthritis was present. All normal individuals who were HLA-DRw4-positive were collagen responders. These studies demonstrate that the cellular, molecular, and genetic characteristics of collagen reactivity in man parallel those documented for the T cell-dependent response to antigens under immune response gene control in rodents.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adorini L., Harvey M. A., Miller A., Sercarz E. E. Fine specificity of regulatory T cells. II. Suppressor and helper T cells are induced by different regions of hen egg-white lysozyme in a genetically nonresponder mouse strain. J Exp Med. 1979 Aug 1;150(2):293–306. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.2.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ananthanarayanan V. S., Brahmachari S. K., Rapaka R. S., Bhatnagar R. S. Polypeptide models of collagen. Solution properties of (Gly-Pro-Sar)n and (Gly-Sar-Pro)n. Biopolymers. 1976 Apr;15(4):707–716. doi: 10.1002/bip.1976.360150409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chess L., Rocklin R. E., MacDermott R. P., David J. R., Schlossman S. F. Leukocyte inhibitory factor (LIF): production by purified human T and B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):315–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibofsky A., Winchester R., Hansen J., Patarroyo M., Dupont B., Paget S., Lahita R., Halper J., Fotino M., Yunis E. Contrasting patterns of newer histocompatibility determinants in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Jun;21(5 Suppl):S134–S138. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffing W. L., Moore S. B., Luthra H. S., McKenna C. H., Fathman C. G. Associations of antibodies to native DNA with HLA-DRw3. A possible major histocompatibility complex-linked human immune response gene. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2 Pt 2):319s–325s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausman P. B., Raff H. V., Gilbert R. C., Picker L. J., Stobo J. D. T cells and macrophages involved in the autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction are required for the response to conventional antigen. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1374–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer B. A., Siwarski D. F., Fischetti G. P., McCoy J. L., Dean J. H., Herberman R. B. Conditions for generating and assaying human leukocyte inhibitory factor (LIF) induced by purified protein derivative (PPD). Immunopharmacology. 1978 Dec;1(1):57–69. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(78)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt H. O., Sela M. Genetic control of the antibody response. I. Demonstration of determinant-specific differences in response to synthetic polypeptide antigens in two strains of inbred mice. J Exp Med. 1965 Sep 1;122(3):517–531. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.3.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A., McDevitt H. The association between the HLA system and disease. Prog Med Genet. 1977;2:39–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J. Biochemical characteristics and biological significance of the genetically-distinct collagens. Mol Cell Biochem. 1976 Dec 10;13(3):165–192. doi: 10.1007/BF01731779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J. Isolation and characterization of a collagen from chick cartilage containing three identical alpha chains. Biochemistry. 1971 Apr 27;10(9):1652–1659. doi: 10.1021/bi00785a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E., Benacerraf B. Functional specificity of thymus- dependent lymphocytes. Science. 1977 Mar 25;195(4284):1293–1300. doi: 10.1126/science.320663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prockop D. J., Kivirikko K. I., Tuderman L., Guzman N. A. The biosynthesis of collagen and its disorders (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1979 Jul 5;301(1):13–23. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197907053010104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff H. V., Picker L. J., Stobo J. D. Macrophage heterogeneity in man. A subpopulation of HLA-DR-bearing macrophages required for antigen-induced T cell activation also contains stimulators for autologous-reactive T cells. J Exp Med. 1980 Sep 1;152(3):581–593. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.3.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapaka R. S., Urry D. W., Ryu R. K., Bhatnagar R. S. Collagen and elastin analogues: snytheses, hydroxylation, calcium binding, and coacervation properties of (pro-Gly)n, (Gly-Pro-Gly)n, and (Pro-Pro-Gly-Gly)n. Ala J Med Sci. 1978 Apr;15(2):196–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocklin R. E. Products of activated lymphocytes: leukocyte inhibitory factor (LIF) distinct from migration inhibitory factor (MIF). J Immunol. 1974 Apr;112(4):1461–1466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A. S., Barcinski M. A., Rosenwasser L. J. Function of macrophages in genetic control of immune responsiveness. Fed Proc. 1978 Jan;37(1):79–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenwasser L. J., Bhatnagar R. S., Stobo J. D. Genetic control of the murine T lymphocyte proliferative response to collagen: analysis of the molecular and cellular contributions to immunogenicity. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2854–2859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Räsänen L., Karhumäki E., Krohn K. Cellular cooperation in mitogen-induced human leukocyte inhibitory factor (LIF) synthesis. Cell Immunol. 1979 May;44(2):395–403. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasazuki T., Kohno Y., Iwamoto I., Tanimura M., Naito S. Association between an HLA haplotype and low responsiveness to tetanus toxoid in man. Nature. 1978 Mar 23;272(5651):359–361. doi: 10.1038/272359b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasazuki T., Ohta N., Kaneoka R., Kojima S. Association between an HLA haplotype and low responsiveness to schistosomal worm antigen in man. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2 Pt 2):314s–318s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. H., Yano A., Paul W. E. Interaction between antigen-presenting cells and primed T lymphocytes: an assessment of Ir gene expression in the antigen-presenting cell. Immunol Rev. 1978;40:153–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb00405.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel R. C. Biosynthesis of collagen crosslinks: increased activity of purified lysyl oxidase with reconstituted collagen fibrils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4826–4830. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver J., Walker L. E., Reisfeld R. A., Pellegrino M. A., Ferrone S. Structural studies of murine I-E and human DR antigens. Mol Immunol. 1979 Jan;16(1):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolen J. S., Menzel E. J., Scherak O., Kojer M., Kolarz G., Steffen C., Mayr W. R. Lymphocyte transformation to denatured type I collagen and B lymphocyte alloantigens in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Apr;23(4):424–431. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solinger A. M., Ultee M. E., Margoliash E., Schwartz R. H. T-lymphocyte response to cytochrome c. I. Demonstration of a T-cell heteroclitic proliferative response and identification of a topographic antigenic determinant on pigeon cytochrome c whose immune recognition requires two complementing major histocompatibility complex-linked immune response genes. J Exp Med. 1979 Oct 1;150(4):830–848. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.4.830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stastny P. HLA-D and Ia antigens in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Jun;21(5 Suppl):S139–S143. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. L., Ewins R. J., Revell P. A., Muir H. Proteoglycans of the intervertebral disc. Homology of structure with laryngeal proteoglycans. Biochem J. 1979 Jun 1;179(3):561–572. doi: 10.1042/bj1790561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart J. M., Postlethwaite A. E., Townes A. S., Kang A. H. Cell-mediated immunity to collagen and collagen alpha chains in rheumatoid arthritis and other rheumatic diseases. Am J Med. 1980 Jul;69(1):13–18. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90494-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. E., Dynesius R. A., Rocklin R. E., David J. R. Cellular sensitivity to collagen in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 1978 Aug 17;299(7):327–332. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197808172990703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbart R. H., Billing R., Golde D. W. Neutrophil migration-inhibition activity produced by a unique T lymphoblast cell line. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Apr;93(4):622–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbart R. H., Yu D. T., Billing R., Fan P. T., Clements P. J., Paulus H. E. Cellular collaboration in the production of human leucocyte migration inhibition factor. Immunology. 1978 May;34(5):815–819. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


