Abstract
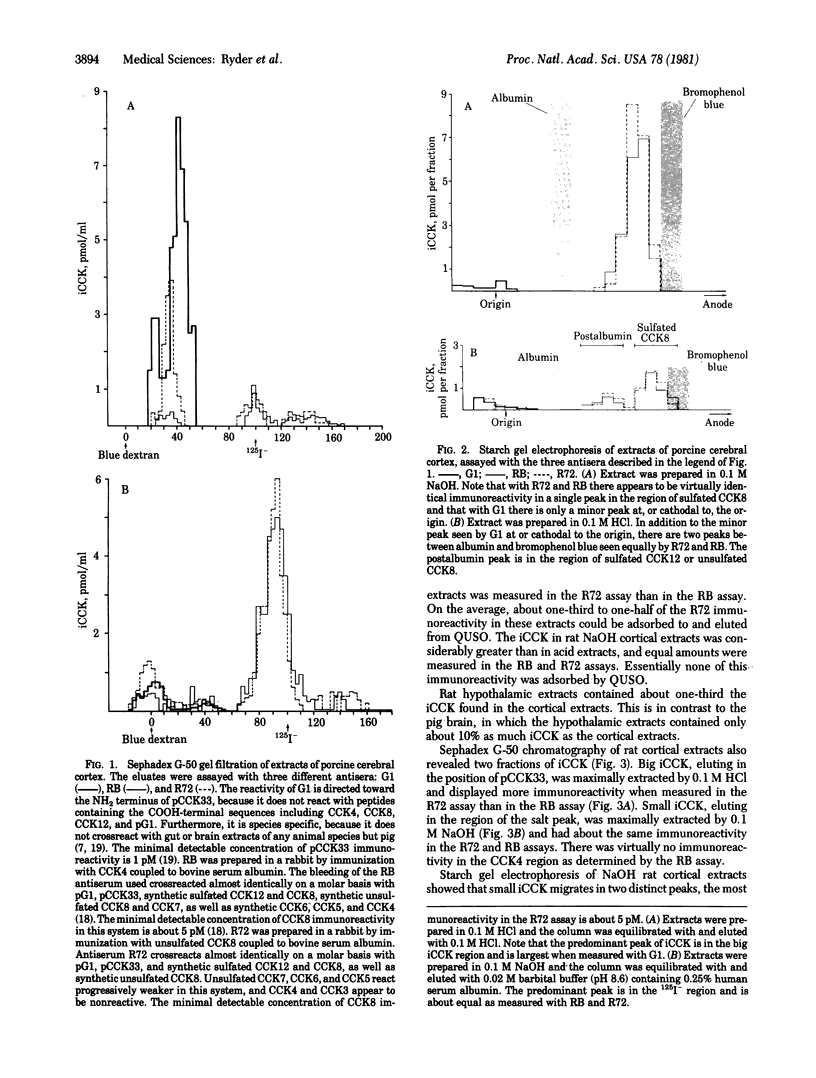
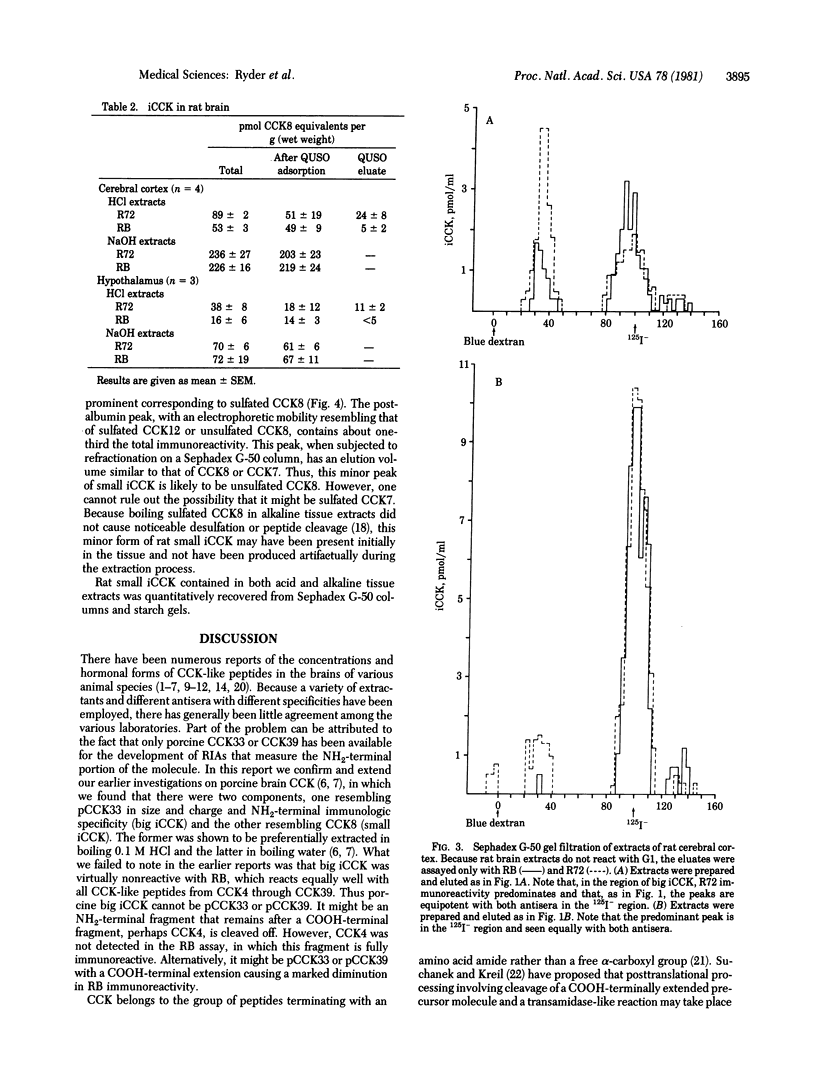
Two major classes of immunoreactive cholecystokinin peptides (iCCK) have been identified in rat and pig brains: (i) large basic peptides (big iCCK) resembling the 33-amino acid porcine cholecystokinin (pCCK33) in size and charge; (ii) small acidic peptides (small iCCK) resembling the COOH-terminal fragments of CCK. Boiling 0.1 M HCl maximally extracts big iCCK; boiling 0.1 M NaOH maximally extracts small iCCK. The differences in hormonal forms removed by these extractants are not likely to be due to enzymatic conversion during the extraction procedures. Fractionation on Sephadex G-50 and starch gel electrophoresis combined with radioimmunoassay using three antisera of different specificities--(i) directed towards the NH2 terminus of pCCK33, (ii) produced by immunization with COOH-terminal fragment CCK8, (iii) produced by immunization with COOH-terminal fragment CCK4--are consistent with the hypothesis that a major fraction of big iCCK may represent intact cholecystokinin with a COOH-terminal extension, as has recently been suggested for gastrin, a molecule having a COOH-terminal pentapeptide identical with that of cholecystokinin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beinfeld M. C., Meyer D. K., Brownstein M. J. Cholecystokinin octapeptide in the rat hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):376–378. doi: 10.1038/288376a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dockray G. J. Cholecystokinin-like peptides in avian brain and gut. Experientia. 1979 May 15;35(5):628–630. doi: 10.1007/BF01960363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dockray G. J. Cholecystokinins in rat cerebral cortex: identification, purification and characterization by immunochemical methods. Brain Res. 1980 Apr 21;188(1):155–165. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90564-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dockray G. J., Gregory R. A., Hutchison J. B., Harris J. I., Runswick M. J. Isolation, structure and biological activity of two cholecystokinin octapeptides from sheep brain. Nature. 1978 Aug 17;274(5672):711–713. doi: 10.1038/274711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dockray G. J. Immunochemical evidence of cholecystokinin-like peptides in brain. Nature. 1976 Dec 9;264(5586):568–570. doi: 10.1038/264568a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glowinski J., Iversen L. L. Regional studies of catecholamines in the rat brain. I. The disposition of [3H]norepinephrine, [3H]dopamine and [3H]dopa in various regions of the brain. J Neurochem. 1966 Aug;13(8):655–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb09873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist A. L., Dockray G. J., Rosenquist G. L., Walsh J. H. Immunochemical characterization of cholecystokinin-like peptides in lamprey gut and brain. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1979 Apr;37(4):474–481. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(79)90028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamers C. B., Morley J. E., Poitras P., Sharp B., Carlson H. E., Hershman J. M., Walsh J. H. Immunological and biological studies on cholecystokinin in rat brain. Am J Physiol. 1980 Sep;239(3):E232–E235. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.239.3.E232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller J. E., Straus E., Yalow R. S. Cholecystokinin and its COOH-terminal octapeptide in the pig brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3035–3037. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noyes B. E., Mevarech M., Stein R., Agarwal K. L. Detection and partial sequence analysis of gastrin mRNA by using an oligodeoxynucleotide probe. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1770–1774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehfeld J. F., Goltermann N. R. Immunochemical evidence of cholecystokinin tetrapeptides in hog brain. J Neurochem. 1979 Apr;32(4):1339–1341. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb11065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehfeld J. F. Immunochemical studies on cholecystokinin. II. Distribution and molecular heterogeneity in the central nervous system and small intestine of man and hog. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):4022–4030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robberecht P., Deschodt-Lanckman M., Vanderhaeghen J. J. Demonstration of biological activity of brain gastrin-like peptidic material in the human: its relationship with the COOH-terminal octapeptide of cholecystokinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):524–528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder S. W., Eng J., Straus E., Yalow R. S. Alkaline extraction of cholecystokinin-immunoreactivity from rat brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 May 30;94(2):704–709. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91289-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider B. S., Monahan J. W., Hirsch J. Brain cholecystokinin and nutritional status in rats and mice. J Clin Invest. 1979 Nov;64(5):1348–1356. doi: 10.1172/JCI109591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus E., Malesci A., Pinget M., Yalow R. S. Fractionation of immunoreactive cholecystokinin by adsorption to QUSO or talc. Life Sci. 1979 Jul 23;25(4):343–346. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90265-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus E., Malesci A., Yalow R. S. Characterization of a nontrypsin cholecystokinin converting enzyme in mammalian brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5711–5714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus E. Special problems of the radioimmunoassay for gut hormones. Clin Gastroenterol. 1980 Sep;9(3):555–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus E., Yalow R. S. Species specificity of cholecystokinin in gut and brain of several mammalian species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):486–489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suchanek G., Kreil G. Translation of melittin messenger RNA in vitro yields a product terminating with glutaminylglycine rather than with glutaminamide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):975–978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderhaeghen J. J., Signeau J. C., Gepts W. New peptide in the vertebrate CNS reacting with antigastrin antibodies. Nature. 1975 Oct 16;257(5527):604–605. doi: 10.1038/257604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





