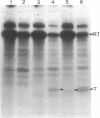
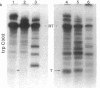
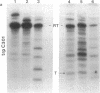
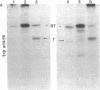
Abstract
Termination of transcription by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase in vitro appears to depend primarily on two structural features of the termination site--a G+C-rich region of dyad symmetry and a series of terminal uridine residues in the transcript. To determine whether these two features are sufficient to specify rho-independent termination in vitro, we have introduced new sequences within a tryptophan (trp) operon structural gene to create two sites with these characteristics. Transcription with wild-type RNA polymerase in vitro demonstrates that discrete termination occurs at one of these new sites, although at a low level. Use of the mutant RNA polymerase rpo203, which is more sensitive to certain weak terminators than is the wild-type enzyme, increases termination at both sites. We have compared the activity of our synthetic terminators with those of several termination sites in the E. coli trp operon. Under normal conditions of transcription in vitro, termination becomes more efficient with an increase in the length of the stem in the RNA hairpin or an increase in the number of consecutive uridine residues. Transcription with the rpo203 polymerase and with ribonucleotide analogs gives changes consistent with these general trends. These results support a model for termination involving separate but essential roles for the RNA hairpin and the stretch of uridines in the transcript.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Gottesman M. Control of transcription termination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:967–996. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.004535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adhya S., Sarkar P., Valenzuela D., Maitra U. Termination of transcription by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: influence of secondary structure of RNA transcripts on rho-independent and rho-dependent termination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1613–1617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand K., Korn L. J., Lee F., Yanofsky C. The attenuator of the tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli. Heterogeneous 3'-OH termini in vivo and deletion mapping of functions. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov 25;117(1):227–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90032-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Jendrisak J. J. A procedure for the rapid, large-scall purification of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase involving Polymin P precipitation and DNA-cellulose chromatography. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4634–4638. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie G. E., Platt T. A functional hybrid ribosome binding site in tryptophan operon messenger RNA of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Nov 5;143(3):335–341. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90195-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie G. E., Platt T. Gene structure in the tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli. Nucleotide sequence of trpC and the flanking intercistronic regions. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 5;142(4):519–530. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90261-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnham P. J., Platt T. A model for transcription termination suggested by studies on the trp attenuator in vitro using base analogs. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):739–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90320-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnham P. J., Platt T. Rho-independent termination: dyad symmetry in DNA causes RNA polymerase to pause during transcription in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 11;9(3):563–577. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.3.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. P., Beckwith J. Mutant RNA polymerase of Escherichia coli terminates transcription in strains making defective rho factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):294–297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F., Yanofsky C. Transcription termination at the trp operon attenuators of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: RNA secondary structure and regulation of termination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4365–4369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin F. H., Tinoco I., Jr DNA-RNA hybrid duplexes containing oligo(dA:rU) sequences are exceptionally unstable and may facilitate termination of transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2295–2299. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neff N. F., Chamberlin M. J. Termination of transcription by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase in vitro is affected by ribonucleoside triphosphate base analogs. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2455–2460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. W. Termination factor for RNA synthesis. Nature. 1969 Dec 20;224(5225):1168–1174. doi: 10.1038/2241168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D., Shimatake H., Brady C., Wulff D. L. The relationship between function and DNA sequence in an intercistronic regulatory region in phage lambda. Nature. 1978 Mar 30;272(5652):414–423. doi: 10.1038/272414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler M. E., Yanofsky C. Pausing of RNA polymerase during in vitro transcription of the tryptophan operon leader region. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 23;20(13):3738–3744. doi: 10.1021/bi00516a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu A. M., Christie G. E., Platt T. Tandem termination sites in the tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2913–2917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski G., Yanofsky C. Escherichia coli tryptophan operon leader mutations, which relieve transcription termination, are cis-dominant to trp leader mutations, which increase transcription termination. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 5;142(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90210-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]