Abstract
Temperature-sensitive (ts) RNA polymerase mutants of a picornavirus are reported. Two foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) mutants designated ts 22 and ts 115 have been characterized. As judged by isoelectric focusing, both have charge alterations in P56a, the FMDV RNA polymerase protein. Virus RNA synthesis in cells infected with the mutants is severely impaired at the nonpermissive temperature. RNA polymerase purified from baby hamster kidney cells infected with these mutants exhibits a marked ts transcribing activity in vitro. Spontaneous revertants of both mutants have P56a polypeptides that are indistinguishable from the parental proteins on the basis of charge. The revertants regain the ability to synthesize virus RNA in vivo at the nonpermissive temperature. RNA polymerase purified from the revertants remains transcriptionally active at the nonpermissive temperature.
Full text
PDF

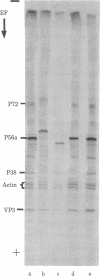
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Doel T. R., Sangar D. V., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. A re-appraisal of the biochemical map of foot-and-mouth disease virus RNA. J Gen Virol. 1978 Nov;41(2):395–404. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-41-2-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Baltimore D. Poliovirus-specific primer-dependent RNA polymerase able to copy poly(A). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3677–3680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. M., Newman J. W. Temperature-sensitive mutants of foot-and-mouth disease virus with altered structural polypeptides. I. Identification by electrofocusing. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):59–66. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.59-66.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. M., Slade W. R., Newman J. W., McCahon D. Temperature-sensitive mutants of foot-and-mouth disease virus with altered structural polypeptides. II. Comparison of recombination and biochemical maps. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):67–72. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.67-72.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Torre J. L., Grubman M. J., Baxt B., Bachrach H. L. The structural polypeptides of aphthovirus are phosphoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7444–7447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake J. R., Priston A. J., Slade W. R. A genetic recombination map of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1975 Jun;27(3):355–367. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-27-3-355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake J., Mackenzie J. S. Improved technique for the isolation of temperature-sensitive mutants of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):665–668. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.665-668.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe P. A., Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Purification and properties of the sigma subunit of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 3;18(7):1344–1352. doi: 10.1021/bi00574a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCahon D., Slade W. R., Priston R. A., Lake J. R. An extended genetic recombination map for foot-and-mouth diseases virus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jun;35(3):555–565. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-35-3-555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J. F., Cartwright B., Doel T. R., Brown F. Purification and identification of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1979 Nov;45(2):497–507. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-45-2-497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polatnick J. Isolation of a foot-and-mouth disease polyuridylic acid polymerase and its inhibition by antibody. J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):774–779. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.774-779.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radloff R. J. Isolation and preliminary characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of encephalomyocarditis virus. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):182–192. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.182-192.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sangar D. V., Black D. N., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. Biochemical mapping of the foot-and-mouth disease virus genome. J Gen Virol. 1977 May;35(2):281–297. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-35-2-281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sangar D. V. The replication of picornaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1979 Oct;45(1):1–13. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-45-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]