Abstract
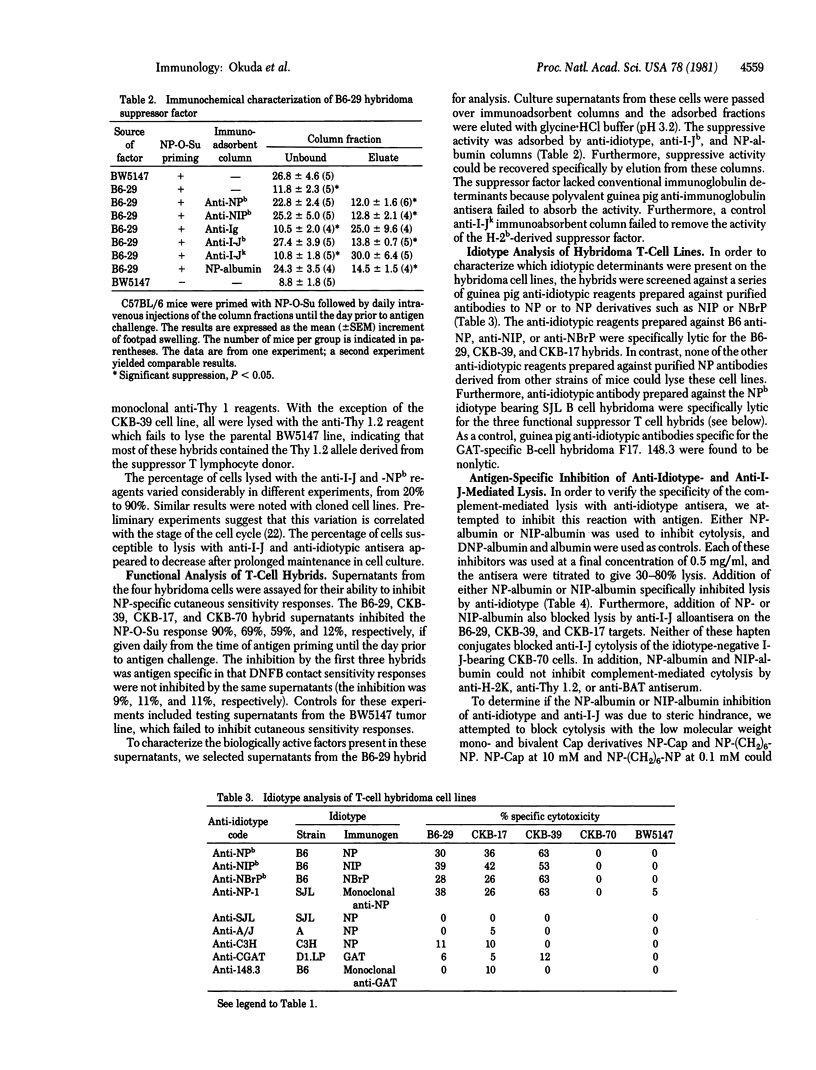
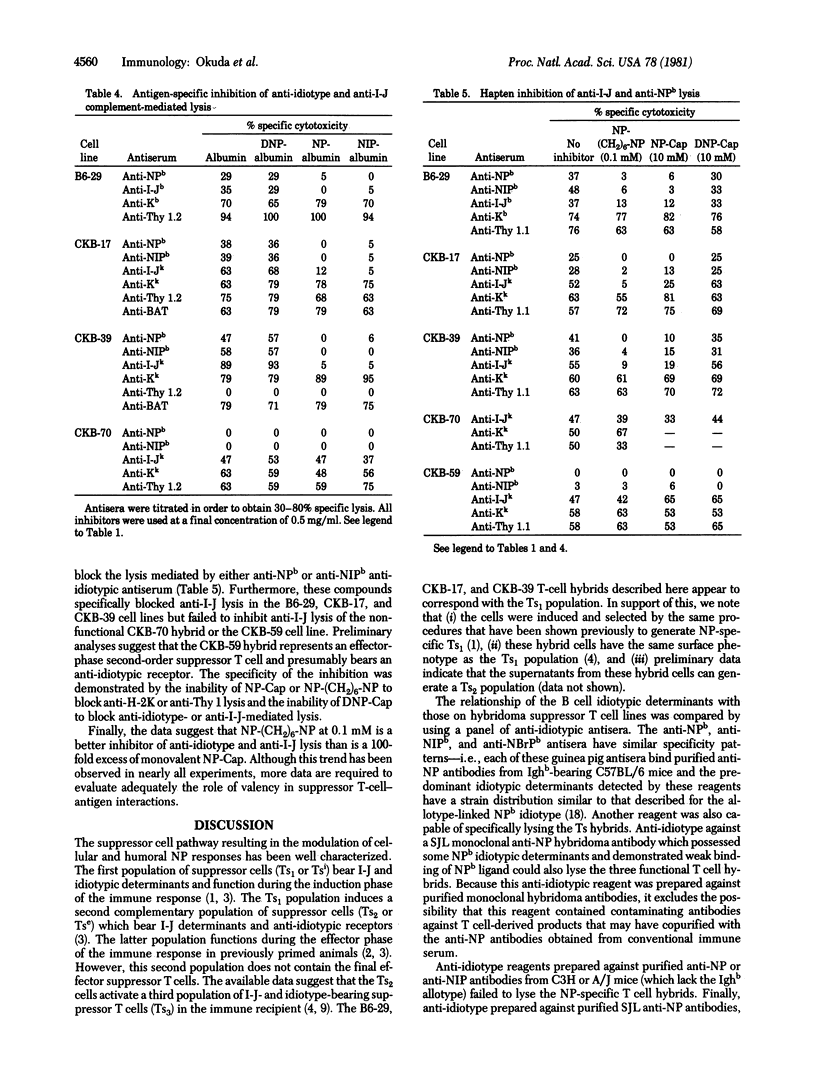
The serological characteristics of the antigen receptor on 4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenylacetyl (NP) specific suppressor T cell hybridomas were analyzed. Three T-cell hybrids could be lysed with anti-idiotype and complement. The reactivity pattern observed from a panel of anti-idiotypic reagents indicated that NPb determinants were detected on all three hybrid lines. NP conjugates with bovine serum albumin or caproic acid specifically inhibited the complement-mediated lysis of these cells by both anti-NPb idiotype and anti-I-J antisera. These hapten conjugates failed to block lysis by anti-Thy 1 or anti-H-2K antisera on the same target cell populations. The data indicate that both I-J and Igh variable region gene products are intimately involved in the recognition of antigen by suppressor T cells. Finally, the suppressor cell hybrids produce soluble factors that mediate antigen-specific suppression. The characteristics of the cells and their factors indicate that the hybrids correspond to the Tsi or first-order suppressor cells in the suppressor cell pathway.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benacerraf B., Germain R. N. A single major pathway of T-lymphocyte interactions in antigen-specific immune suppression. Scand J Immunol. 1981;13(1):1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1981.tb00104.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohi Y., Nisonoff A. Suppression of idiotype and generation of suppressor T cells with idiotype-conjugated thymocytes. J Exp Med. 1979 Oct 1;150(4):909–918. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.4.909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorf M. E., Eguro S. Y., Cabrera G., Yunis E. J., Swanson J., Amos D. B. Detection of cytotoxic non-HL-A antisera. Vox Sang. 1972;22(5):447–456. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1972.tb03992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eardley D. D., Shen F. W., Cantor H., Gershon R. K. Genetic control of immunoregulatory circuits. Genes linked to the Ig locus govern communication between regulatory T-cell sets. J Exp Med. 1979 Jul 1;150(1):44–50. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.1.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golub E. S. Brain-associated theta antigen: reactivity of rabbit anti-mouse brain with mouse lymphoid cells. Cell Immunol. 1971 Aug;2(4):353–361. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(71)90070-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ju S. T., Pierres M., Waltenbaugh C., Germain R. N., Benacerraf B., Dorf M. E. Idiotypic analysis of monoclonal antibodies to poly(Glu60Ala30Tyr10). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2942–2946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapp J. A., Araneo B. A., Clevinger B. L. Suppression of antibody and T cell proliferative responses to L-glutamic acid60-L-alanine30-L-tyrosine10 by a specific monoclonal T cell factor. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):235–240. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä O., Karjalainen K. Inherited immunoglobulin idiotypes of the mouse. Immunol Rev. 1977;34:119–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1977.tb00370.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry L. L., Dorf M. E., Benacerraf B., Greene M. I. Regulation of immune response to tumor antigen: interference with syngeneic tumor immunity by anti-IA alloantisera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):920–924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunday M. E., Benacerraf B., Dorf M. E. Hapten-specific T cell responses to 4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl acetyl. VIII. Suppressor cell pathways in cutaneous sensitivity responses. J Exp Med. 1981 Apr 1;153(4):811–822. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.4.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunday M. E., Weinberger J. Z., Benacerraf B., Dorf M. E. Hapten-specific T cell responses to 4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl acetyl. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1601–1605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sy M. S., Miller S. D., Moorhead J. W., Claman H. N. Active suppression of 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene-immune T cells. Requirement of an auxiliary T cell induced by antigen. J Exp Med. 1979 May 1;149(5):1197–1207. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.5.1197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada T., Okumura K. The role of antigen-specific T cell factors in the immune response. Adv Immunol. 1979;28:1–87. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60799-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi M., Saito T., Tada T. Antigen-specific suppressive factor produced by a transplantable I-J bearing T-cell hybridoma. Nature. 1979 Apr 5;278(5704):555–558. doi: 10.1038/278555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi M., Takei I., Tada T. Functional and molecular organisation of an antigen-specific suppressor factor from a T-cell hybridoma. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):227–228. doi: 10.1038/283227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger J. Z., Benacerraf B., Dorf M. E. Hapten-specific T cell responses to 4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl acetyl. III. Interaction of effector suppressor T cells is restricted by H-2 and Igh-V genes. J Exp Med. 1980 Jun 1;151(6):1413–1423. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.6.1413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger J. Z., Germain R. N., Benacerraf B., Dorf M. E. Hapten-specific T cell responses to 4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl acetyl. V. Role of idiotypes in the suppressor pathway. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):161–169. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger J. Z., Germain R. N., Ju S. T., Greene M. I., Benacerraf B., Dorf M. E. Hapten-specific T-cell responses to 4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl acetyl. II. Demonstration of idiotypic determinants on suppressor T cells. J Exp Med. 1979 Oct 1;150(4):761–776. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.4.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger J. Z., Greene M. I., Benacerraf B., Dorf M. E. Hapten-specific T-cell responses to 4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl acetyl. I. Genetic control of delayed-type hypersensitivity by VH and I-A-region genes. J Exp Med. 1979 Jun 1;149(6):1336–1348. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.6.1336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


