Abstract
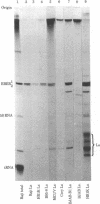
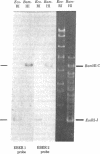
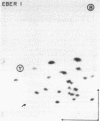
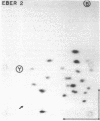
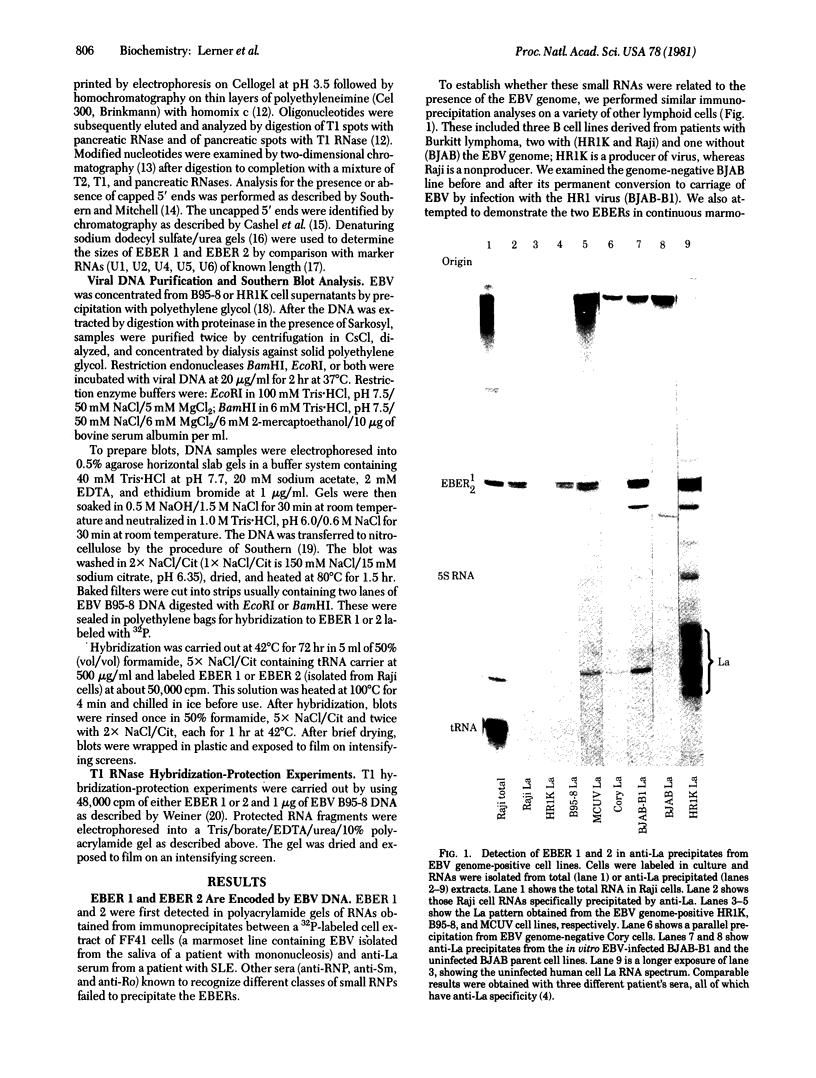
Primate cells harboring the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genome synthesize large amounts of two small RNAs:EBER 1 and EBER 2 (EBV-encoded RNA). These RNAs are approximately 180 nucleotides long, possess 5' pppA termini, and lack poly(A). They have different T1 and pancreatic RNase digestion fingerprints. They are not found in normal B lymphocytes, in transformed B lymphocytes that lack EBV DNA, in T lymphocytes transformed by Herpesvirus ateles, or in a variety of other nonlymphoid mammalian cells. Hybridization analyses indicate that EBER 1 and EBER 2 are encoded by the EcoRI-J fragment of EBV (B95-8) DNA. In vivo both RNAs are associated with protein(s), allowing their specific precipitation by the systemic lupus erythematosus-associated antibody anti-La. The La antigen in uninfected mammalian cells consists of a heterogeneous class of small ribonucleoprotein particles, some of whose RNA components exhibit sequence homology with a highly repetitive, interspersed class of human DNA designated the Alu family. Possible functions for EBER 1 and EBER 2 in infection and cell transformation by EBV and their potential relationship to the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus are discussed.
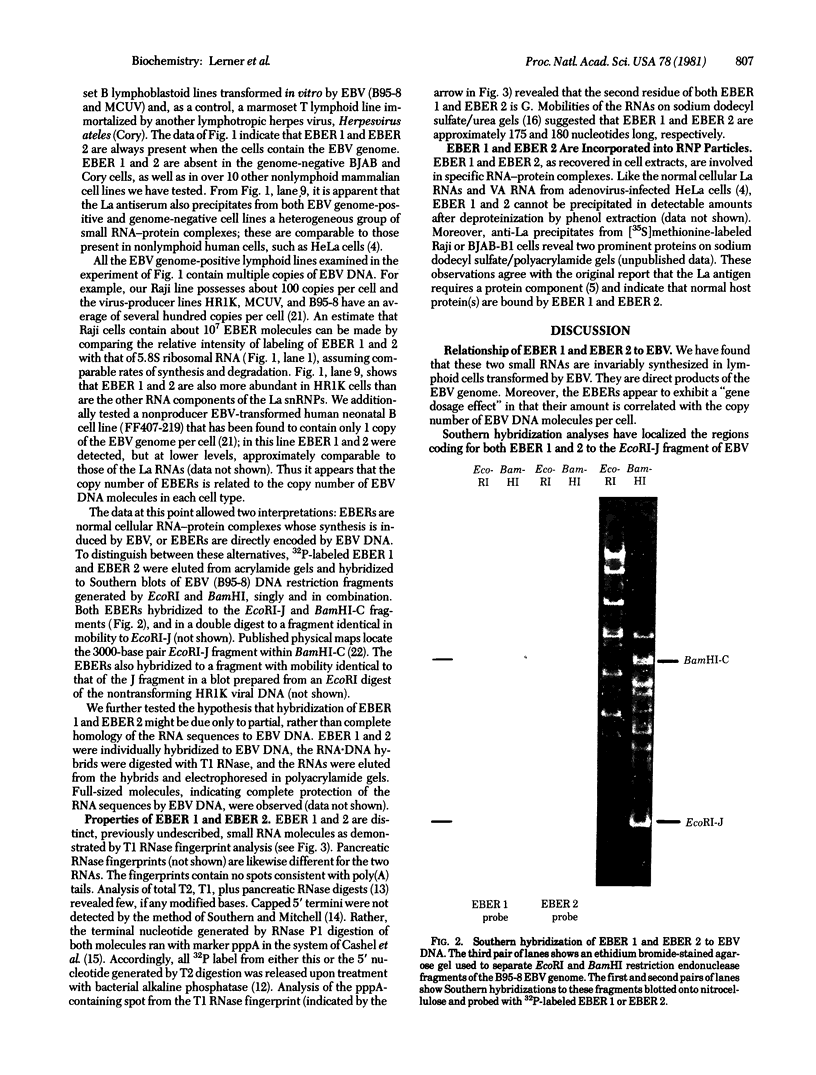
Full text
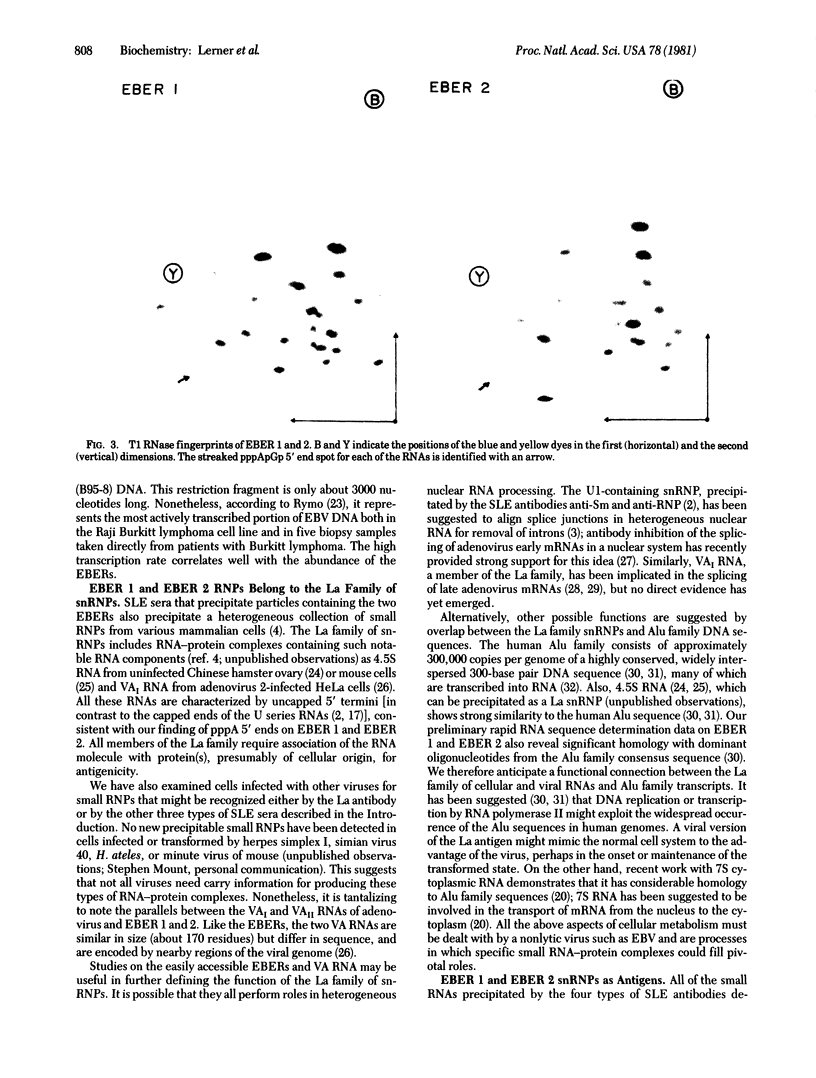
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akusjärvi G., Mathews M. B., Andersson P., Vennström B., Pettersson U. Structure of genes for virus-associated RNAI and RNAII of adenovirus type 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alspaugh M., Maddison P. Resolution of the identity of certain antigen-antibody systems in systemic lupus erythematosus and Sjögren's syndrome: an interlaboratory collaboration. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Jul;22(7):796–798. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandsma J., Miller G. Nucleic acid spot hybridization: rapid quantitative screening of lymphoid cell lines for Epstein-Barr viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6851–6855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashel M., Lazzarini R. A., Kalbacher B. An improved method for thin-layer chromatography of nucleotide mixtures containing 32P-labelled orthophosphate. J Chromatogr. 1969 Mar 11;40(1):103–109. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)96624-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C., Biro P. A., Choudary P. V., Elder J. T., Wang R. R., Forget B. G., de Riel J. K., Weissman S. M. RNA polymerase III transcriptional units are interspersed among human non-alpha-globin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5095–5099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada F., Kato N. Nucleotide sequences of 4.5S RNAs associated with poly(A)-containing RNAs of mouse and hamster cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 25;8(6):1273–1285. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.6.1273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Toomey T. P., Leinwand L., Duncan C. H., Biro P. A., Choudary P. V., Weissman S. M., Rubin C. M., Houck C. M., Deininger P. L. Ubiquitous, interspersed repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1398–1402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W., Leinwand L. Low molecular weight RNAs hydrogen-bonded to nuclear and cytoplasmic poly(A)-terminated RNA from cultured Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90095-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Boyle J. A., Mount S. M., Wolin S. L., Steitz J. A. Are snRNPs involved in splicing? Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):220–224. doi: 10.1038/283220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Antibodies to small nuclear RNAs complexed with proteins are produced by patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5495–5499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B. Binding of adenovirus VA RNA to mRNA: a possible role in splicing? Nature. 1980 Jun 19;285(5766):575–577. doi: 10.1038/285575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattioli M., Reichlin M. Heterogeneity of RNA protein antigens reactive with sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Description of a cytoplasmic nonribosomal antigen. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Jul-Aug;17(4):421–429. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray V., Holliday R. Mechanism for RNA splicing of gene transcripts. FEBS Lett. 1979 Oct 1;106(1):5–7. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80682-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provost T. T. Subsets in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Invest Dermatol. 1979 Mar;72(3):110–113. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12530348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. M., Houck C. M., Deininger P. L., Friedmann T., Schmid C. W. Partial nucleotide sequence of the 300-nucleotide interspersed repeated human DNA sequences. Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):372–374. doi: 10.1038/284372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rymo L. Identification of transcribed regions of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in Burkitt lymphoma-derived cells. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):8–18. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.8-18.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberklang M., Gillum A. M., RajBhandary U. L. Use of in vitro 32P labeling in the sequence analysis of nonradioactive tRNAs. Methods Enzymol. 1979;59:58–109. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)59072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skare J., Strominger J. L. Cloning and mapping of BamHi endonuclease fragments of DNA from the transforming B95-8 strain of Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3860–3864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M., Mitchell A. R. Chromatography of nucleic acid digests on thin layers of cellulose impregnated with polyethyleneimine. Biochem J. 1971 Jul;123(4):613–617. doi: 10.1042/bj1230613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B., Phelps M., Domoradzki J. Epstein-Barr virus DNA is amplified in transformed lymphocytes. J Virol. 1979 Sep;31(3):590–595. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.3.590-595.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M. An abundant cytoplasmic 7S RNA is complementary to the dominant interspersed middle repetitive DNA sequence family in the human genome. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):209–218. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuki A., Brimacombe R. Nucleotide sequences of Escherichia coli 16-S RNA associated with ribosomal proteins S7, S9, S10, S14 and S19. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 1;56(1):23–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02203.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H. Oncogenic Herpes viruses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 20;417(1):25–53. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(75)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]