Abstract
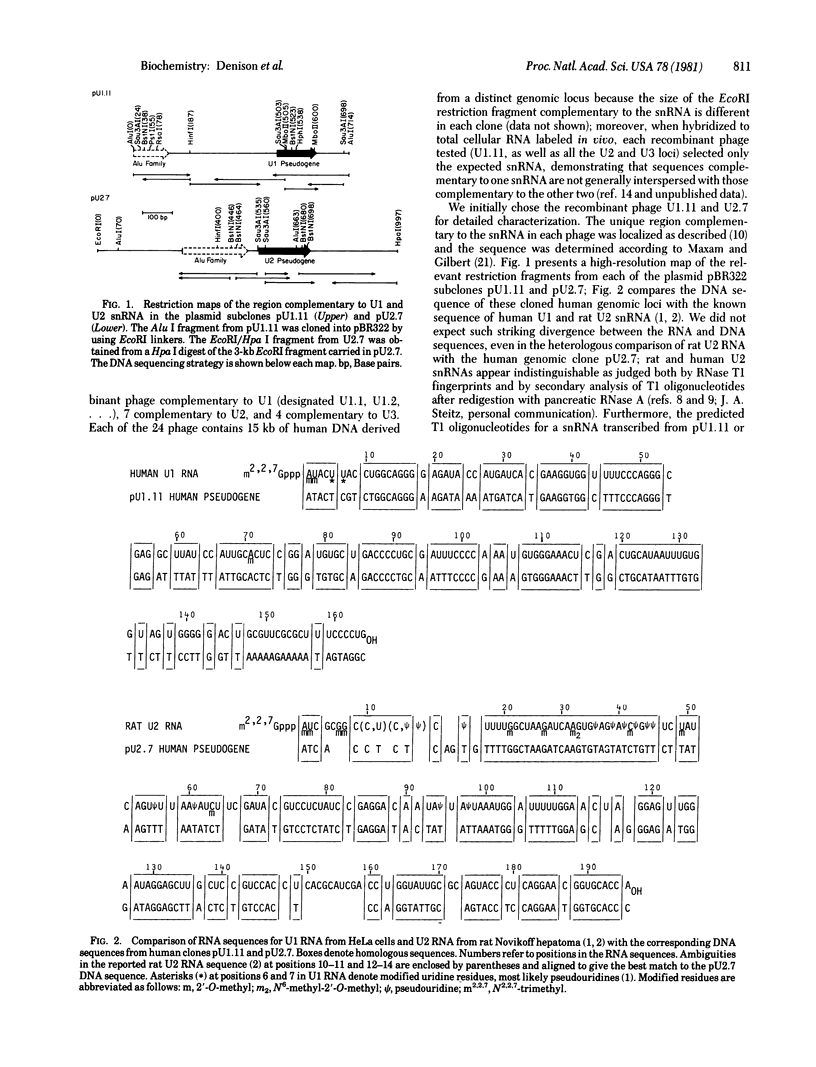
We have cloned and partially characterized 24 loci from the human genome which are complementary to U1, U2, or U3, the three major species of small nuclear RNA (snRNA) in HeLa cells. When compared to the known U1 (human) and U2 (rat) snRNA sequences, the DNA sequences we report here for the complementary regions from two of the clones, U1.11 and U2.7, reveal the presence of truncated and divergent gene copies. Furthermore, most if not all of the 24 cloned loci contain gene copies that are significantly divergent from the homologous HeLa snRNA species because DNA from every recombinant phage except U1.7 and U1.15 proved unable to form snRNA.DNA hybrids which protect full-length HeLa snRNA from ild digestion with ribonuclease T1. Hence, we refer to these loci as snRNA pseudogenes. In both clones U1.11 and U2.7, an element of the dominant middle repetitive DNA sequence family in the human genome, the Alu family, is located upstream from the snRNA pseudogene and in the same orientation. Alu elements in the same location and orientation relative to bona fide genes have previously been found in the human beta-globin gene cluster [Duncan, C. H., Biro, P. A., Choudary, P. V., Elder, J. T., Wang, R. C., Forget, G. B., deRiel, J. K. & Weissman, S. M. (1979) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76, 5095-5099]. We discuss the significance of these findings in relation to the nature of snRNA multigene families and other reported examples of pseudogenes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Richards J. E., Slightom J. L., Tucker P. W., Smithies O. Cloning human fetal gamma globin and mouse alpha-type globin DNA: preparation and screening of shotgun collections. Science. 1978 Dec 22;202(4374):1279–1284. doi: 10.1126/science.725603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Williams B. G., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Furlong L., Grunwald D. J., Kiefer D. O., Moore D. D., Schumm J. W. Charon phages: safer derivatives of bacteriophage lambda for DNA cloning. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):161–169. doi: 10.1126/science.847462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branlant C., Krol A., Ebel J. P., Lazar E., Gallinaro H., Jacob M., Sri-Widada J., Jeanteur P. Nucleotide sequences of nuclear U1A RNAs from chicken, rat and man. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 25;8(18):4143–4154. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.18.4143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary M. L., Haynes J. R., Schon E. A., Lingrel J. B. Identification by nucleotide sequence analysis of a goat pseudoglobin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 24;8(20):4791–4802. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.20.4791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Britten R. J. Regulation of gene expression: possible role of repetitive sequences. Science. 1979 Jun 8;204(4397):1052–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.451548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C., Biro P. A., Choudary P. V., Elder J. T., Wang R. R., Forget B. G., de Riel J. K., Weissman S. M. RNA polymerase III transcriptional units are interspersed among human non-alpha-globin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5095–5099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliceiri G. L. Sensitivity of low molecular weight RNA synthesis to UV radiation. Nature. 1979 May 3;279(5708):80–81. doi: 10.1038/279080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engberg J., Hellung-Larsen P., Frederiksen S. Isolation and DNA-RNA hybridization properties of small-molecular-weight nuclear RNA components from baby-hamster-kidney cells. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jan 16;41(2):321–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein P., Reddy R., Henning D., Busch H. The nucleotide sequence of nuclear U6 (4.7 S) RNA. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8901–8906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firtel R. A., Timm R., Kimmel A. R., McKeown M. Unusual nucleotide sequences at the 5' end of actin genes in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6206–6210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada F., Kato N. Nucleotide sequences of 4.5S RNAs associated with poly(A)-containing RNAs of mouse and hamster cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 25;8(6):1273–1285. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.6.1273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn C. L., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Phillips S. J., Weaver S., Haigwood N. L., Voliva C. F., Edgell M. H. DNA sequence organization of the beta-globin complex in the BALB/c mouse. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):159–168. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90123-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Toomey T. P., Leinwand L., Duncan C. H., Biro P. A., Choudary P. V., Weissman S. M., Rubin C. M., Houck C. M., Deininger P. L. Ubiquitous, interspersed repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1398–1402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen E. G., Hellung-Larsen P., Frederiksen S. Synthesis of low molecular weight RNA components A, C and D by polymerase II in alpha-amanitin-resistant hamster cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jan;6(1):321–330. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.1.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. W., Rosenthal N., Rodakis G. C., Kafatos F. C. Evolution of two major chorion multigene families as inferred from cloned cDNA and protein sequences. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1317–1332. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90242-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krayev A. S., Kramerov D. A., Skryabin K. G., Ryskov A. P., Bayev A. A., Georgiev G. P. The nucleotide sequence of the ubiquitous repetitive DNA sequence B1 complementary to the most abundant class of mouse fold-back RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 25;8(6):1201–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.6.1201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy E., Maniatis T. The nucleotide sequence of a rabbit beta-globin pseudogene. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):545–553. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90492-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Boyle J. A., Mount S. M., Wolin S. L., Steitz J. A. Are snRNPs involved in splicing? Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):220–224. doi: 10.1038/283220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Antibodies to small nuclear RNAs complexed with proteins are produced by patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5495–5499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluff W. F., Jr, White E. L., Benjamin R., Huang R. C. Low molecular weight RNA species from chromatin. Biochemistry. 1975 Aug 12;14(16):3715–3724. doi: 10.1021/bi00687a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. R., Cartwright E. M., Brownlee G. G., Fedoroff N. V., Brown D. D. The nucleotide sequence of oocyte 5S DNA in Xenopus laevis. II. The GC-rich region. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):717–725. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90221-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka Y., Leder A., Leder P. Unusual alpha-globin-like gene that has cleanly lost both globin intervening sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2806–2809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Maniatis T. The structure of a human alpha-globin pseudogene and its relationship to alpha-globin gene duplication. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90491-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C. L., Korn L. J. Computer analysis of nucleic acids and proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):595–609. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R., Henning D., Busch H. Nucleotide sequence of nucleolar U3B RNA. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):11097–11105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R., Ro-Choi T. S., Henning D., Busch H. Primary sequence of U-1 nuclear ribonucleic acid of Novikoff hepatoma ascites cells. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 25;249(20):6486–6494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson H. D., Dickson E., Jelinek W. Determination of nucleotide sequences from double-stranded regions of HeLa cell nuclear RNA. J Mol Biol. 1977 Oct 5;115(4):571–589. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Wall R. A mechanism for RNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1877–1879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. M., Houck C. M., Deininger P. L., Friedmann T., Schmid C. W. Partial nucleotide sequence of the 300-nucleotide interspersed repeated human DNA sequences. Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):372–374. doi: 10.1038/284372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen C. K., Maniatis T. The organization of repetitive sequences in a cluster of rabbit beta-like globin genes. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):379–391. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90512-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata H., Ro-Choi T. S., Reddy R., Choi Y. C., Henning D., Busch H. The primary nucleotide sequence of nuclear U-2 ribonucleic acid. The 5'-terminal portion of the molecule. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):3909–3920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamm I., Kikuchi T., Darnell J. E., Jr, Salditt-Georgieff M. Short capped hnRNA precursor chains in HeLa cells: continued synthesis in the presence of 5,6-dichloro-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 10;19(12):2743–2748. doi: 10.1021/bi00553a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanin E. F., Goldberg G. I., Tucker P. W., Smithies O. A mouse alpha-globin-related pseudogene lacking intervening sequences. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):222–226. doi: 10.1038/286222a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M. An abundant cytoplasmic 7S RNA is complementary to the dominant interspersed middle repetitive DNA sequence family in the human genome. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):209–218. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise J. A., Weiner A. M. Dictyostelium small nuclear RNA D2 is homologous to rat nucleolar RNA U3 and is encoded by a dispersed multigene family. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90159-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve G., Penman S. Small RNA species of the HeLa cell: metabolism and subcellular localization. Cell. 1976 May;8(1):19–31. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90181-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]