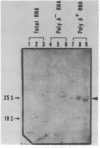
Abstract
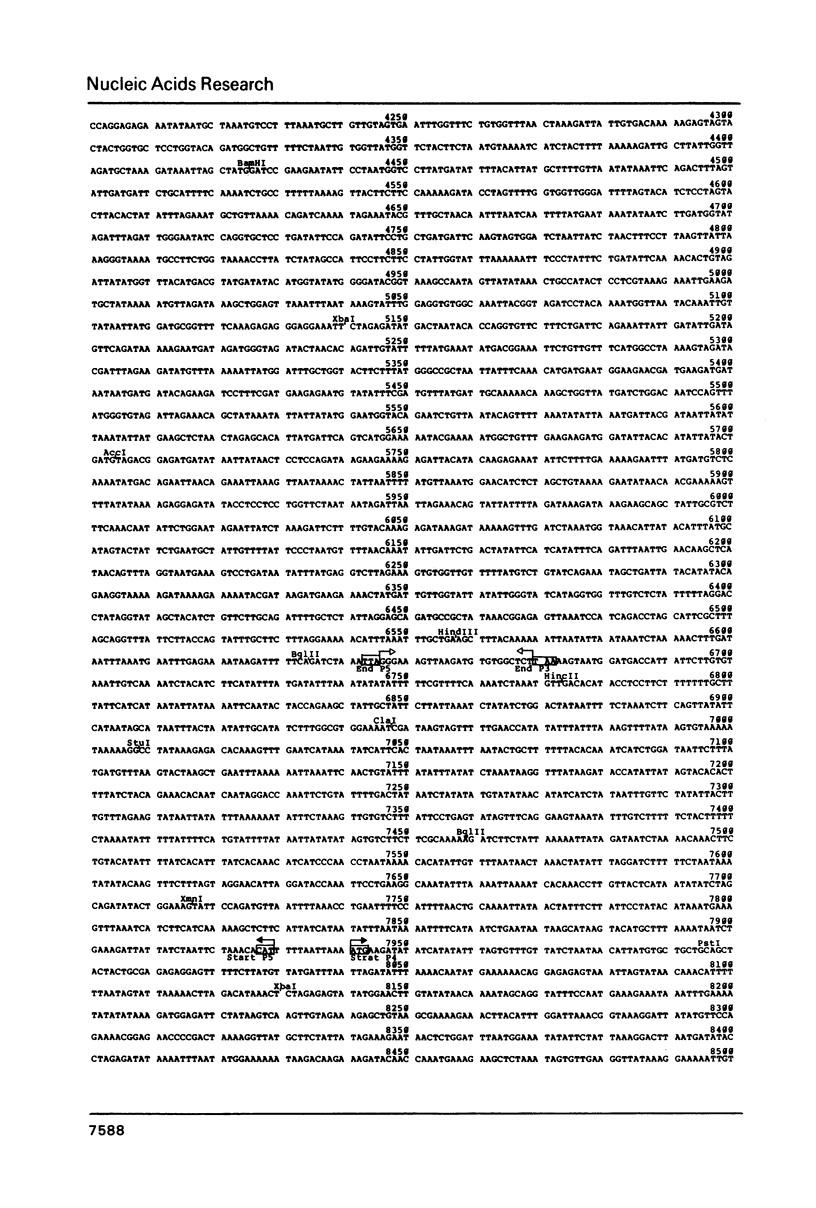
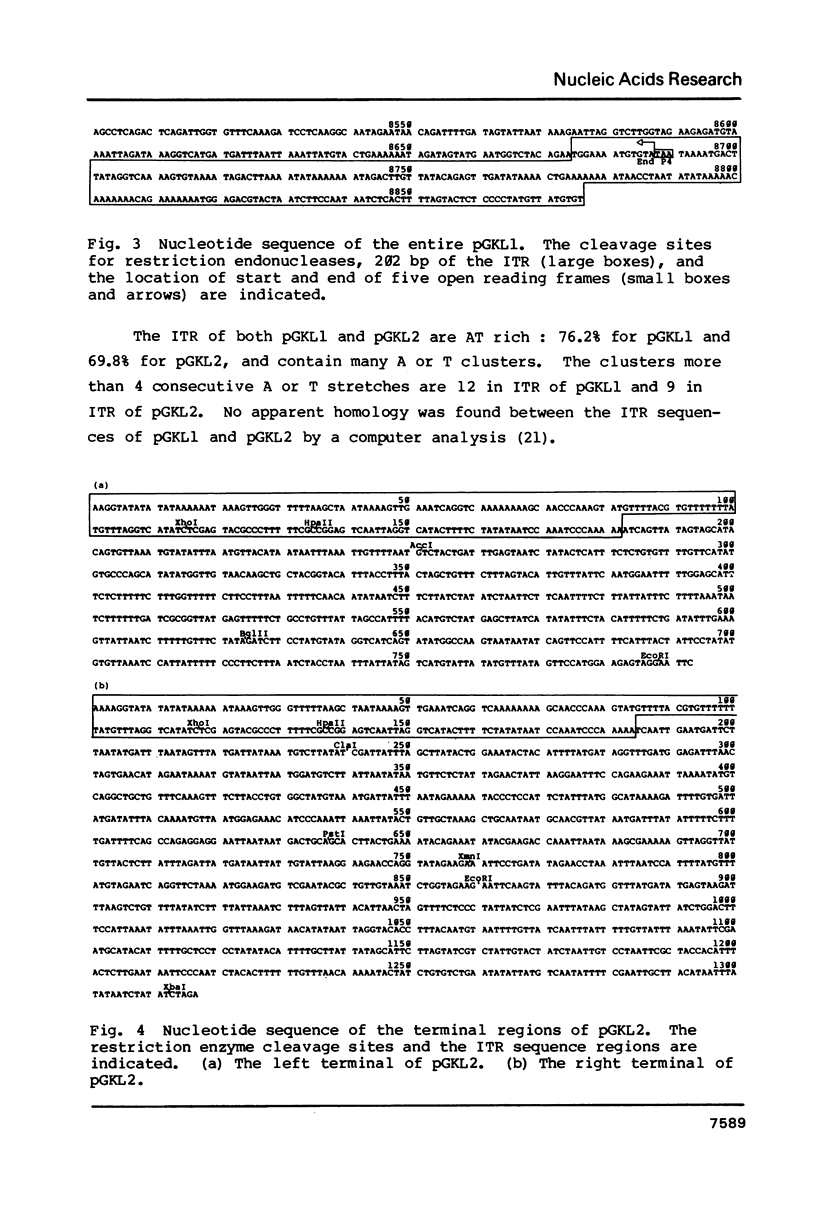
The linear DNA killer plasmids (pGKL1 and pGKL2) isolated from a Kluyveromyces lactis killer strain are also maintained and expressed its killer character in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. After these killer plasmid DNAs isolated from S. cerevisiae were treated with alkali, four terminal fragments from each plasmid DNAs were cloned separately. Using these and other cloned DNA fragments, the terminal nucleotide sequences of pGKL2 and the complete nucleotide sequence of pGKL1 were determined. The inverted terminal repetitions of 202 bp and 182 bp were found in pGKL1 and pGKL2, respectively. The pGKL1 sequence showed an extremely high A + T content of 73.2% and it contained five large open reading frames. The largest of these open reading frame was suggested to code for a membrane-bound precursor of glycoprotein subunit of the killer toxin.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aleström P., Stenlund A., Li P., Pettersson U. A common sequence in the inverted terminal repetitions of human and avian adenoviruses. Gene. 1982 May;18(2):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90117-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Parker B. A., Reiser J., Renart J., Stark G. R., Wahl G. M. Detection of specific RNAs or specific fragments of DNA by fractionation in gels and transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:220–242. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergold P. J., Campbell G. R., Littau V. C., Johnson E. M. Sequence and hairpin structure of an inverted repeat series at termini of the Physarum extrachromosomal rDNA molecule. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1287–1299. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90310-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H., Gall J. G. A tandemly repeated sequence at the termini of the extrachromosomal ribosomal RNA genes in Tetrahymena. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):33–53. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90294-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostian K. A., Elliott Q., Bussey H., Burn V., Smith A., Tipper D. J. Sequence of the preprotoxin dsRNA gene of type I killer yeast: multiple processing events produce a two-component toxin. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):741–751. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90354-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broach J. R., Li Y. Y., Feldman J., Jayaram M., Abraham J., Nasmyth K. A., Hicks J. B. Localization and sequence analysis of yeast origins of DNA replication. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):1165–1173. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Taussig R., Kustu S., Botstein D. The secreted form of invertase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is synthesized from mRNA encoding a signal sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;3(3):439–447. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.3.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael G. G., McMaster G. K. The analysis of nucleic acids in gels using glyoxal and acridine orange. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):380–391. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escarmís C., Salas M. Nucleotide sequence at the termini of the DNA of Bacillus subtilis phage phi 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1446–1450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein D. B., Strausberg S., McAlister L. Alterations of transcription during heat shock of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8405–8411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunge N., Murata K., Sakaguchi K. Transformation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae with linear DNA killer plasmids from Kluyveromyces lactis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):462–464. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.462-464.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunge N., Sakaguchi K. Intergeneric transfer of deoxyribonucleic acid killer plasmids, pGKl1 and pGKl2, from Kluyveromyces lactis into Saccharomyces cerevisiae by cell fusion. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jul;147(1):155–160. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.1.155-160.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunge N., Tamaru A., Ozawa F., Sakaguchi K. Isolation and characterization of linear deoxyribonucleic acid plasmids from Kluyveromyces lactis and the plasmid-associated killer character. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):382–390. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.382-390.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirochika H., Nakamura K., Sakaguchi K. A linear DNA plasmid from Streptomyces rochei with an inverted terminal repetition of 614 base pairs. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):761–766. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01881.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Halegoua S. Secretion and membrane localization of proteins in Escherichia coli. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1980;7(4):339–371. doi: 10.3109/10409238009105465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., Hirai K., Hishinuma F. The yeast linear DNA killer plasmids, pGKL1 and pGKL2, possess terminally attached proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5685–5692. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn L. J., Queen C. L., Wegman M. N. Computer analysis of nucleic acid regulatory sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4401–4405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford C. J., Gallwitz D. Evidence for an intron-contained sequence required for the splicing of yeast RNA polymerase II transcripts. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):519–527. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90433-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAlister L., Finkelstein D. B. Alterations in translatable ribonucleic acid after heat shock of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):603–612. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.603-612.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mostov K. E., Blobel G. A transmembrane precursor of secretory component. The receptor for transcellular transport of polymeric immunoglobulins. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11816–11821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Szostak J. W. Construction of artificial chromosomes in yeast. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):189–193. doi: 10.1038/305189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niwa O., Sakaguchi K., Gunge N. Curing of the killer deoxyribonucleic acid plasmids of Kluyveromyces lactis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Dec;148(3):988–990. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.3.988-990.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Halvorson H. O., Cannon L. E. Presecretory and cytoplasmic invertase polypeptides encoded by distinct mRNAs derived from the same structural gene differ by a signal sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):781–785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippsen P., Thomas M., Kramer R. A., Davis R. W. Unique arrangement of coding sequences for 5 S, 5.8 S, 18 S and 25 S ribosomal RNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae as determined by R-loop and hybridization analysis. J Mol Biol. 1978 Aug 15;123(3):387–404. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90086-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roninson I., Padmanabhan R. Studies on the nature of the linkage between the terminal protein and the adenovirus DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 May 14;94(1):398–405. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80234-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salas M., Mellado R. P., Viñuela E. Characterization of a protein covalently linked to the 5' termini of the DNA of Bacillus subtilis phage phi29. J Mol Biol. 1978 Feb 25;119(2):269–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90438-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sor F., Wésolowski M., Fukuhara H. Inverted terminal repetitions of the two linear DNA associated with the killer character of the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 11;11(15):5037–5044. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.15.5037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Sequence data handling by computer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Nov;4(11):4037–4051. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.11.4037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark M. J., Mileham A. J., Romanos M. A., Boyd A. Nucleotide sequence and transcription analysis of a linear DNA plasmid associated with the killer character of the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 10;12(15):6011–6030. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.15.6011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steenbergh P. H., Maat J., van Ormondt H., Sussenbach J. S. The nucleotide sequence at the termini of adenovirus type 5 DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Dec;4(12):4371–4389. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.12.4371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B. W., Topp W. C., Engler J. A. Conserved sequences at the origin of adenovirus DNA replication. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):530–537. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.530-537.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K., Davis R. W. Transcription of the his3 gene region in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol. 1981 Nov 5;152(3):535–552. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90267-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugisaki Y., Gunge N., Sakaguchi K., Yamasaki M., Tamura G. Characterization of a novel killer toxin encoded by a double-stranded linear DNA plasmid of Kluyveromyces lactis. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jun 1;141(2):241–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08183.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugisaki Y., Gunge N., Sakaguchi K., Yamasaki M., Tamura G. Kluyveromyces lactis killer toxin inhibits adenylate cyclase of sensitive yeast cells. Nature. 1983 Aug 4;304(5925):464–466. doi: 10.1038/304464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Blackburn E. H. Cloning yeast telomeres on linear plasmid vectors. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90109-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipper D. J., Bostian K. A. Double-stranded ribonucleic acid killer systems in yeasts. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Jun;48(2):125–156. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.2.125-156.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolun A., Aleström P., Pettersson U. Sequence of inverted terminal repetitions from different adenoviruses: demonstration of conserved sequences and homology between SA7 termini and SV40 DNA. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):705–713. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90277-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao M. C., Yao C. H. Repeated hexanucleotide C-C-C-C-A-A is present near free ends of macronuclear DNA of Tetrahymena. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7436–7439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa H., Ito J. Terminal proteins and short inverted terminal repeats of the small Bacillus bacteriophage genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2596–2600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Peña P., Barros F., Gascón S., Lazo P. S., Ramos S. Effect of yeast killer toxin on sensitive cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10420–10425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]