Abstract
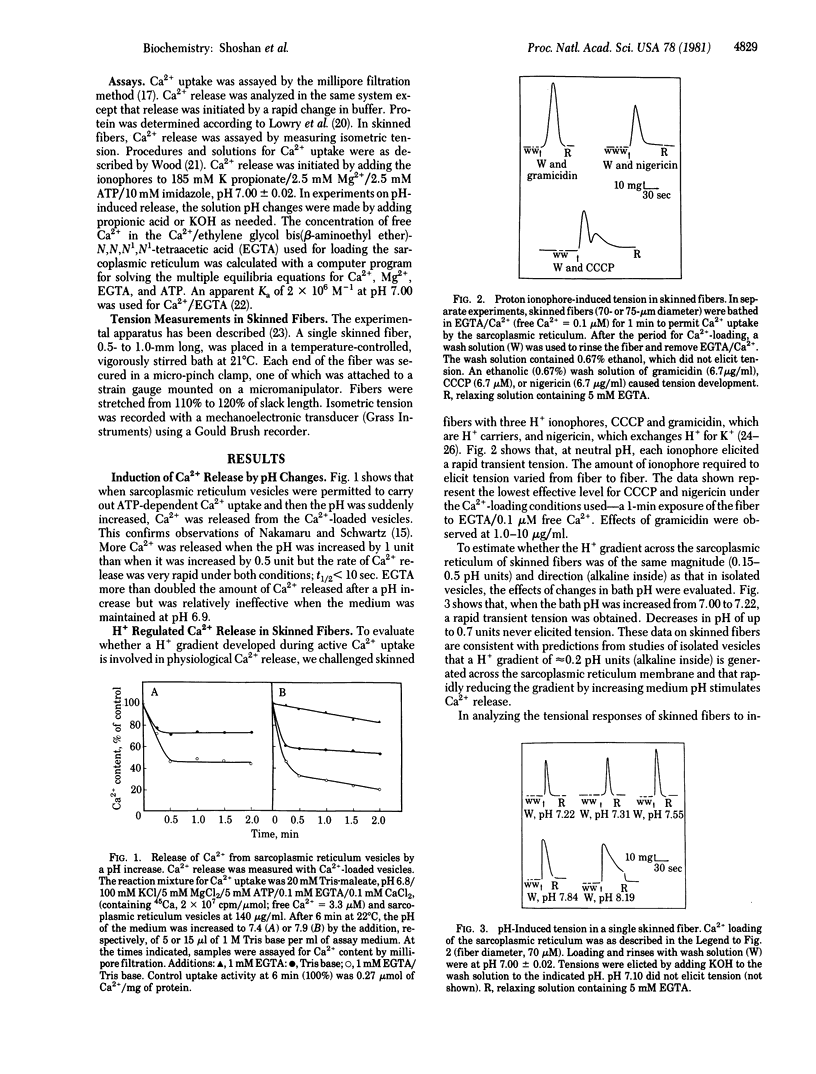
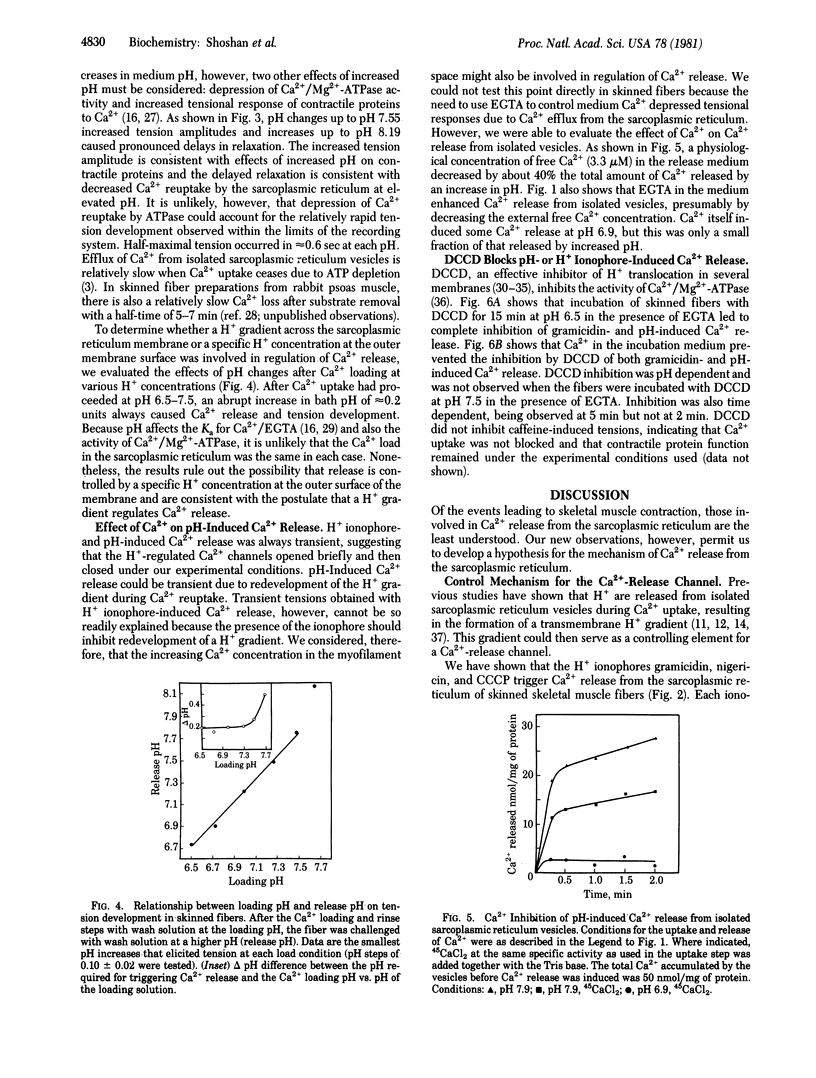
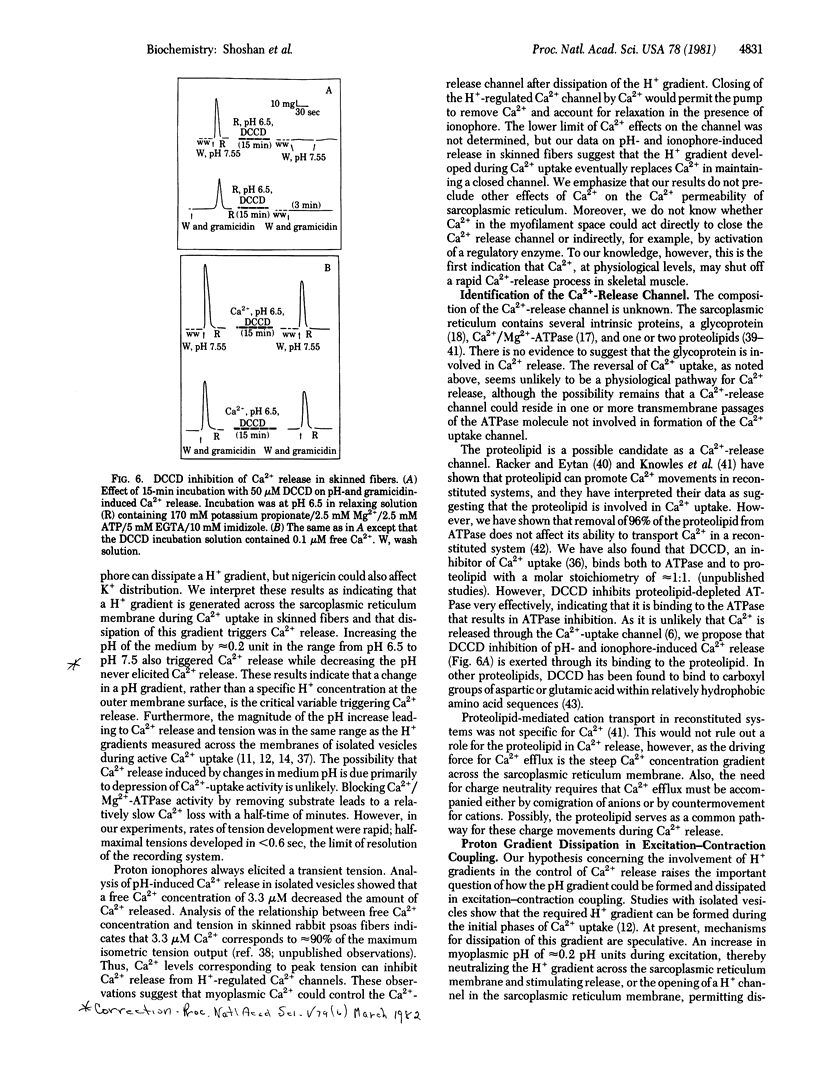
Sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles from mammalian skeletal muscle have previously been shown to develop a proton gradient (alkaline inside) of 0.15-0.5 pH units during active Ca2+ uptake. We found that dissipation of this gradient by the proton ionophores gramicidin, nigericin, and carbonyl cyanide p-trichloromethoxyphenylhydrazone caused a rapid transient tension in skinned rabbit psoas muscle fibers. Increases, but not decreases, in medium pH of approximately 0.2 units over the range from pH 6.5 to pH 7.5 also elicited transient tensions. In isolated vesicles, physiological levels of Ca2+ (3.3 microM), inhibited pH-induced Ca2+ release. Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide blocked pH- and ionophore-induced Ca2+ release under conditions in which it could bind to sarcoplasmic reticulum proteins but did not inhibit Ca2+ uptake. We propose that a proton gradient generated across sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes during Ca2+ uptake maintains a Ca2+ release channel in a closed conformation and that dissipation of this gradient permits the Ca2+ release channel to open. We further propose that elevated myoplasmic Ca2+ also causes the Ca2+ channel to close, permitting Ca2+ uptake through Ca2+/Mg2+-ATPase to function effectively. As the proteolipids of sarcoplasmic reticulum bind dicyclohexylcarbodiimide under conditions in which Ca2+ release is blocked and as they have previously been shown to have Ca2+ ionophoric activity, we propose that the Ca2+-release channel either resides in the proteolipids or is controlled by H+ fluxes through the proteolipids.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brandt P. W., Cox R. N., Kawai M. Can the binding of Ca2+ to two regulatory sites on troponin C determine the steep pCa/tension relationship of skeletal muscle? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4717–4720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiesi M., Inesi G. Adenosine 5'-triphosphate dependent fluxes of manganese and and hydrogen ions in sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 24;19(13):2912–2918. doi: 10.1021/bi00554a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Célis H. 1-Butanol extracted proteolipid. Proton conducting properties. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 15;92(1):26–31. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91514-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degani H., Shavit N. Ion movements in isolated chloroplasts. 3. Ionophore-induced ion uptake and its effect on photophosphorylation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Sep;152(1):339–346. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90223-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S., Endo M., Otsuki I. Control of muscle contraction. Q Rev Biophys. 1969 Nov;2(4):351–384. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M. Calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jan;57(1):71–108. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Calcium and cardiac excitation-contraction coupling. Annu Rev Physiol. 1979;41:473–484. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.41.030179.002353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Circ Res. 1977 Feb;40(2):119–129. doi: 10.1161/01.res.40.2.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Calcium-induced release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of skinned cells from adult human, dog, cat, rabbit, rat, and frog hearts and from fetal and new-born rat ventricles. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Apr 28;307:491–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb41979.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Calculator programs for computing the composition of the solutions containing multiple metals and ligands used for experiments in skinned muscle cells. J Physiol (Paris) 1979;75(5):463–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Contractions induced by a calcium-triggered release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of single skinned cardiac cells. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;249(3):469–495. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Effects of pH on the myofilaments and the sarcoplasmic reticulum of skinned cells from cardiace and skeletal muscles. J Physiol. 1978 Mar;276:233–255. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fillingame R. H. Purification of the carbodiimide-reactive protein component of the ATP energy-transducing system of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6630–6637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfer U., Lehninger A. L., Thompson T. E. Protonic conductance across phospholipid bilayer membranes induced by uncoupling agents for oxidative phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):484–490. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles A., Zimniak P., Alfonzo M., Zimniak A., Racker E. Isolation and characterization of proteolipids from sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Membr Biol. 1980 Aug 7;55(3):233–239. doi: 10.1007/BF01869464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama T., Kurebayashi N., Ogawa Y. Heat production and proton release during the ATP-driven Ca uptake by fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum from bullfrog and rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biochem. 1980 Nov;88(5):1259–1265. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan D. H. Purification and properties of an adenosine triphosphatase from sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 10;245(17):4508–4518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan D. H., Reithmeier R. A., Shoshan V., Campbell K. P., LeBel D., Herrmann T. R., Shamoo A. E. Ion pathways in proteins of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;358:138–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb15392.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madeira V. M. Proton movements across the membranes of sarcoplasmic reticulum during the uptake of calcium ions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Apr 1;200(2):319–325. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90361-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G. Calcium transport and monovalent cation and proton fluxes in sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):636–643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., McKinley D. Permeability of sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane. The effect of changed ionic environments on Ca2+ release. J Membr Biol. 1976 Dec 25;30(1):79–98. doi: 10.1007/BF01869661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., Young R. C. Proton permeability of sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6814–6819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamaru Y., Schwartz A. Possible control of intracellular calcium metabolism by [H+]: sarcoplasmic reticulum of skeletal and cardiac muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Nov 25;41(4):830–836. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90157-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N., Eytan E., Notsani B. E., Sigrist H., Sigrist-Nelson K., Gitler C. Isolation of a chloroplast N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-binding proteolipid, active in proton translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2375–2378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura K., Nakamaru Y. Determination of the intravesicular pH of fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum with 5,5-dimethyl-2,4-oxazolidinedione. J Biochem. 1976 Dec;80(6):1393–1399. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orentlicher M., Reuben J. P., Grundfest H., Brandt P. W. Calcium binding and tension development in detergent-treated muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Feb;63(2):168–186. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.2.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel L., Schuldiner S., Kaback H. R. Reversible effects of chaotropic agents on the proton permeability of Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3387–3391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick U., Racker E. Inhibition of the (Ca2+)ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum by dicyclohexylcarbodiimide: evidence for location of the Ca2+ binding site in a hydrophobic region. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 9;18(1):108–113. doi: 10.1021/bi00568a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressman B. C. Biological applications of ionophores. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:501–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racker E., Eytan E. A coupling factor from sarcoplasmic reticulum required for the translocation of Ca2+ ions in a reconstituted Ca2+ATPase pump. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 25;250(18):7533–7534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racker E., Horstman L. L. Partial resolution of the enzymes catalyzing oxidative phosphorylation. 13. Structure and function of submitochondrial particles completely resolved with respect to coupling factor. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 25;242(10):2547–2551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigekawa M., Finegan J. A., Katz A. M. Calcium transport ATPase of canine cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. A comparison with that of rabbit fast skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 25;251(22):6894–6900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoshan V., Campbell K. P., MacLennan D. H., Frodis W., Britt B. A. Quercetin inhibits Ca2+ uptake but not Ca2+ release by sarcoplasmic reticulum in skinned muscle fibers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4435–4438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. S. Human skeletal muscle: analysis of Ca2+ regulation in skinned fibers using caffeine. Exp Neurol. 1978 Jan 15;58(2):218–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(78)90135-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. S., Zollman J., Reuben J. P., Brandt P. W. Human skeletal muscle: properties of the "chemically skinned%" fiber. Science. 1975 Mar 21;187(4181):1075–1076. doi: 10.1126/science.187.4181.1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Meis L., Vianna A. L. Energy interconversion by the Ca2+-dependent ATPase of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:275–292. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



