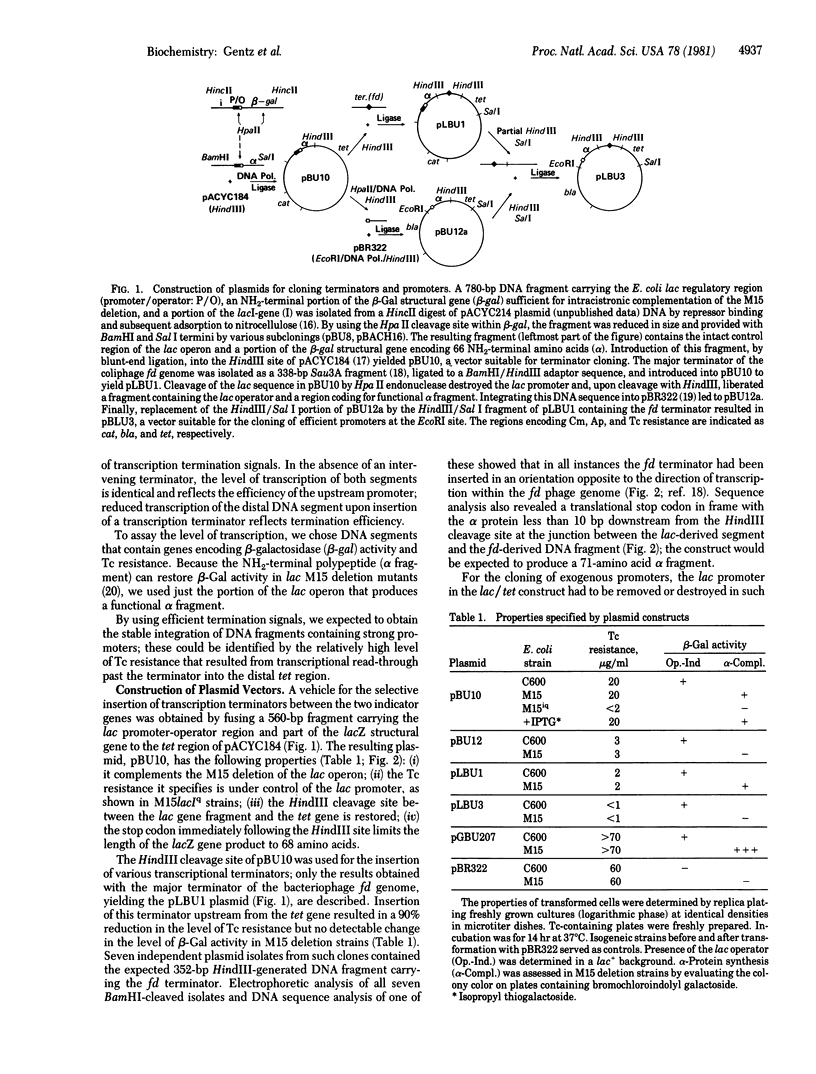
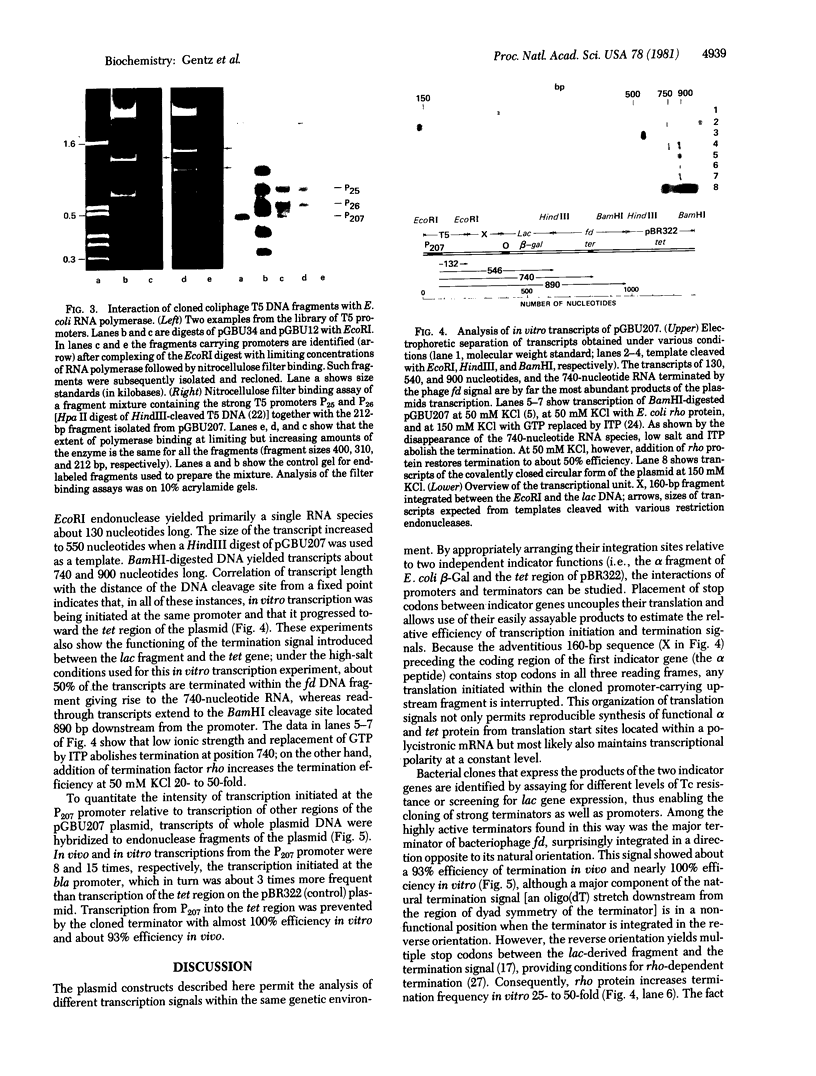
Abstract
Downstream placement of a strong transcriptional termination signal has made possible the cloning of bacteriophage T5 promoters known to exhibit high signal strength. The cloning system constructed contains two easily assayable indicator functions whose expression is controlled by the integration of promoters and terminators, respectively. By assessing transcription within the indicator regions, the efficiency of promoters as well as termination signals can be determined in vitro and in vivo.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Gottesman M. Control of transcription termination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:967–996. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.004535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backman K., Ptashne M., Gilbert W. Construction of plasmids carrying the cI gene of bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4174–4178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck E., Sommer R., Auerswald E. A., Kurz C., Zink B., Osterburg G., Schaller H., Sugimoto K., Sugisaki H., Okamoto T. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage fd DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Dec;5(12):4495–4503. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.12.4495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabello F., Timmis K., Cohen S. N. Replication control in a composite plasmid constructed by in vitro linkage of two distinct replicons. Nature. 1976 Jan 29;259(5541):285–290. doi: 10.1038/259285a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopf K., Bujard H. Structure and function of the genome of coliphage T5. Transcription in vitro of the "nicked" and "nick-free" T5+ DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1975 May 6;53(2):371–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04077.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landy A., Olchowski E., Ross W., Reiness G. Isolation of a functional lac regulatory region. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;133(4):273–281. doi: 10.1007/BF00332703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neff N. F., Chamberlin M. J. Termination of transcription by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase in vitro is affected by ribonucleoside triphosphate base analogs. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2455–2460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Bourgeois S., Newby R. F., Cohn M. DNA binding of the lac repressor. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 14;34(2):365–368. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90261-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Simpson R. B., Gilbert W. E. coli RNA polymerase interacts homologously with two different promoters. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):269–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stüber D., Bujard H. Organization of transcriptional signals in plasmids pBR322 and pACYC184. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):167–171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stüber D., Delius H., Bujard H. Electron microscopic analysis of in vitro transcriptional complexes: mapping of promoters of the coliphage T5 genome. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Oct 30;166(2):141–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00285916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West R. W., Jr, Rodriguez R. L. Construction and characterization of E. coli promoter-probe plasmid vectors. II. RNA polymerase binding studies on antibiotic-resistance promoters. Gene. 1980 May;9(3-4):175–193. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90321-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Gabain A., Bujard H. Interaction of E. coli RNA polymerase with promotors of coliphage T5: the rates of complex formation and decay and their correlation with in vitro and in vivo transcriptional activity. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Dec 9;157(3):301–311. doi: 10.1007/BF00268667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Gabain A., Bujard H. Interaction of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase with promoters of several coliphage and plasmid DNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):189–193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]