Abstract
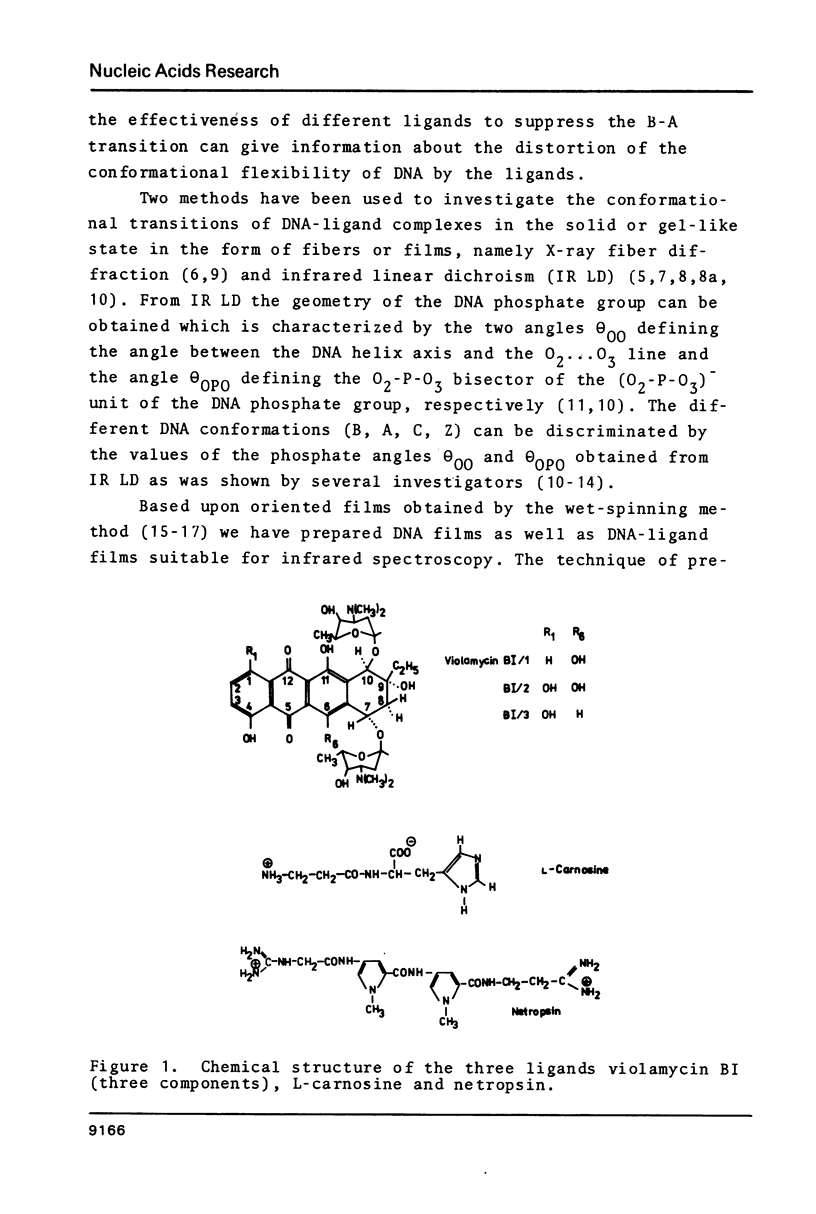
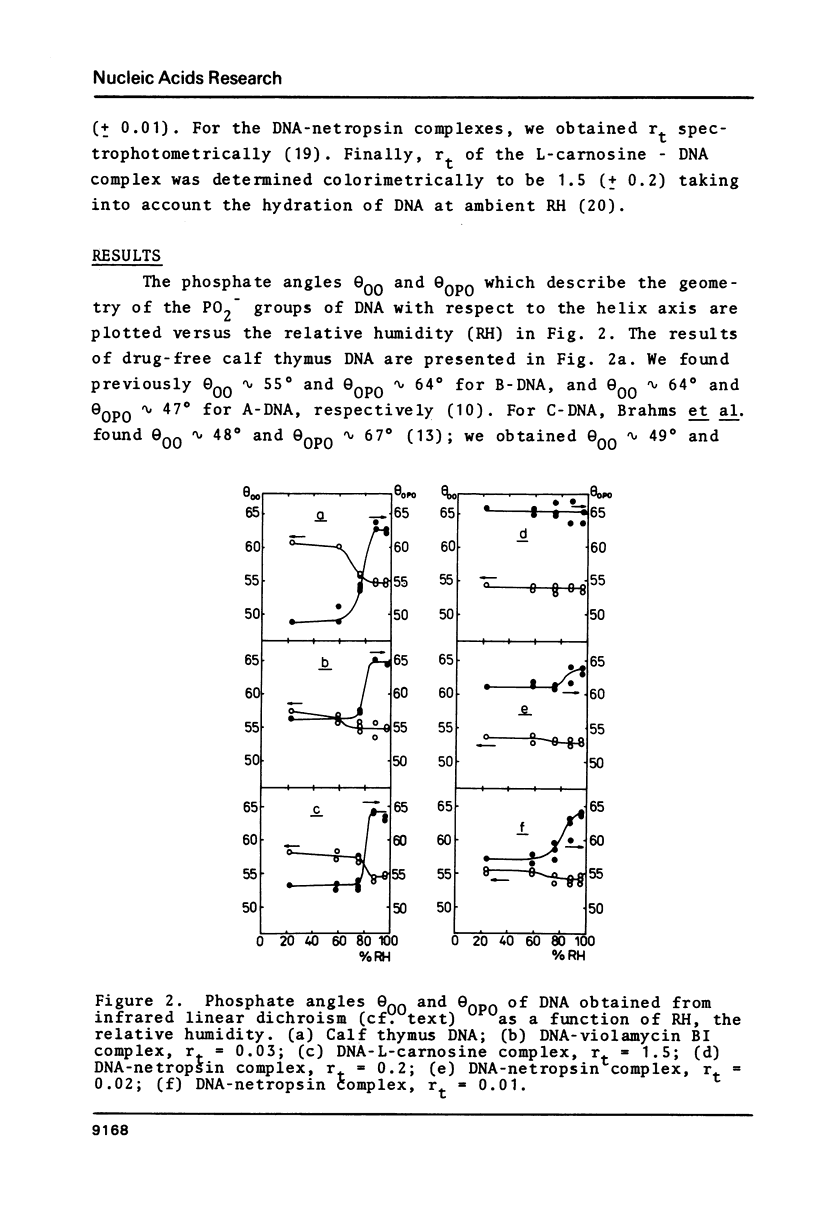
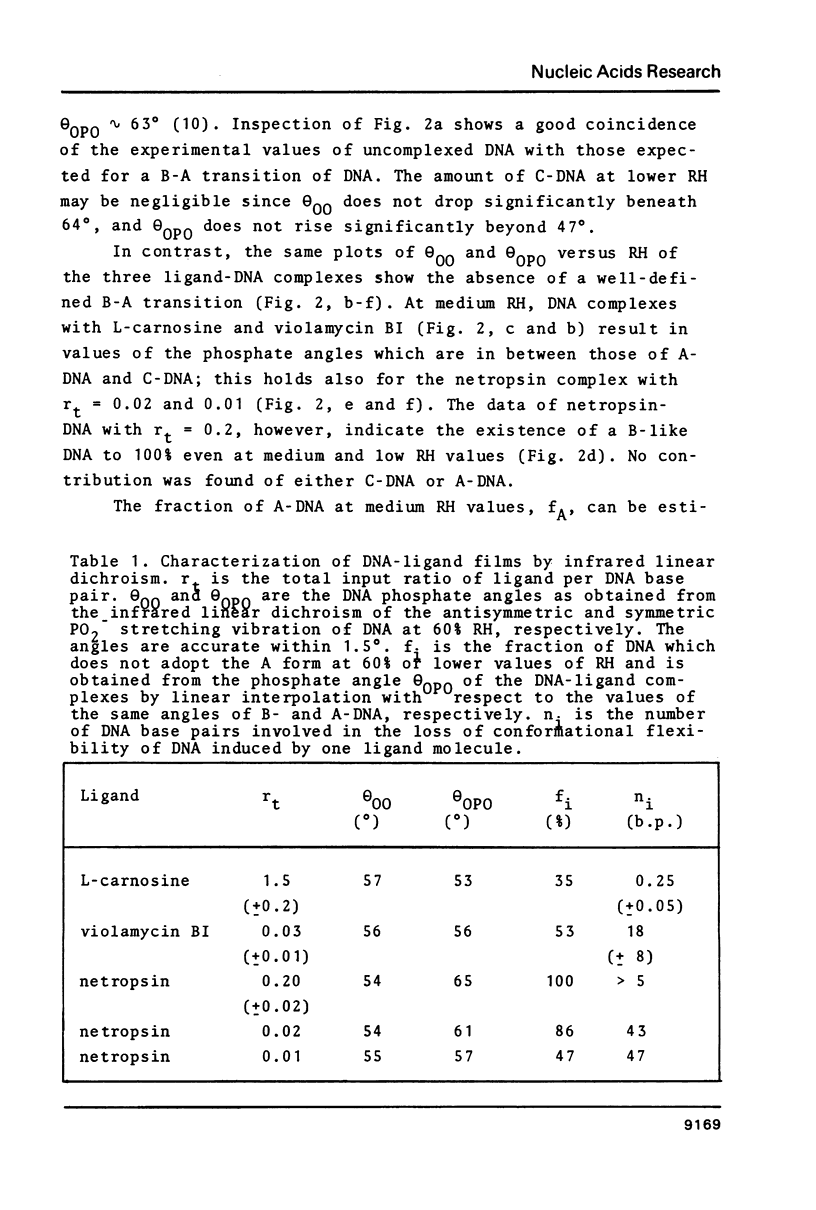
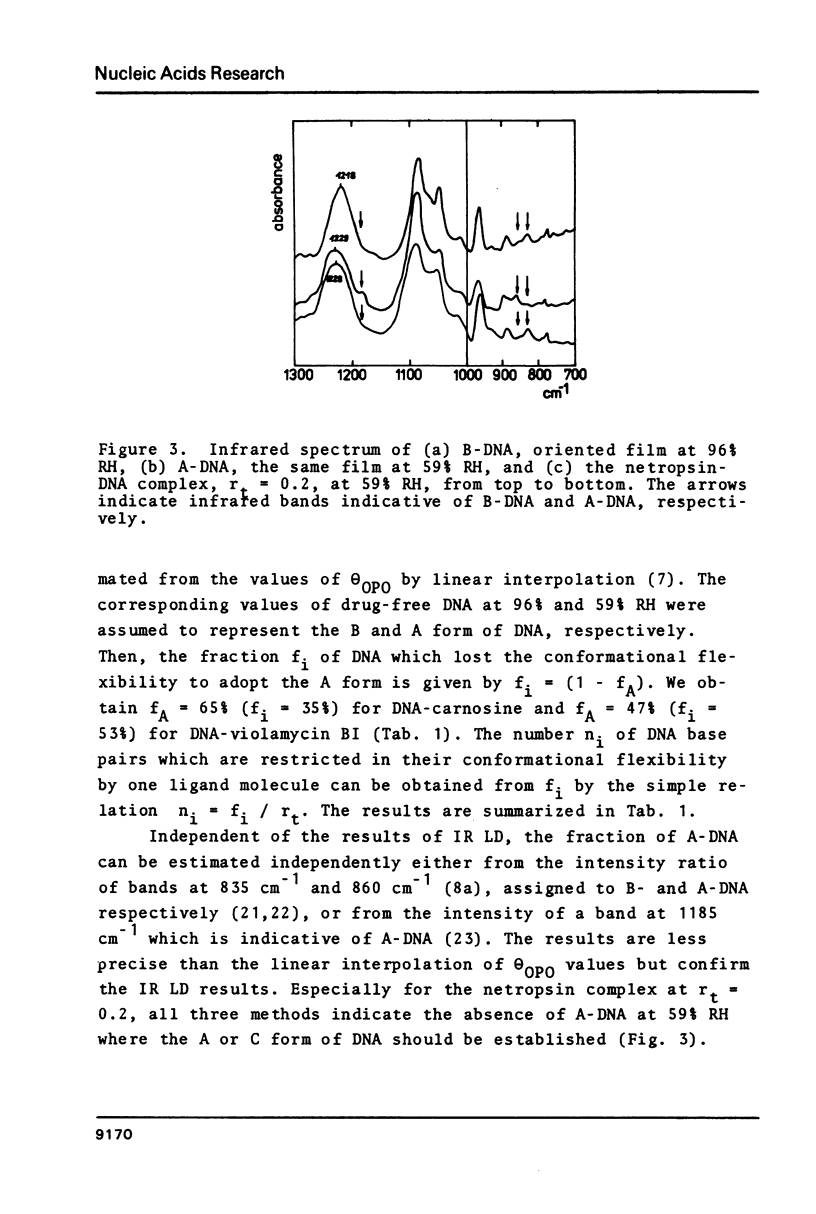
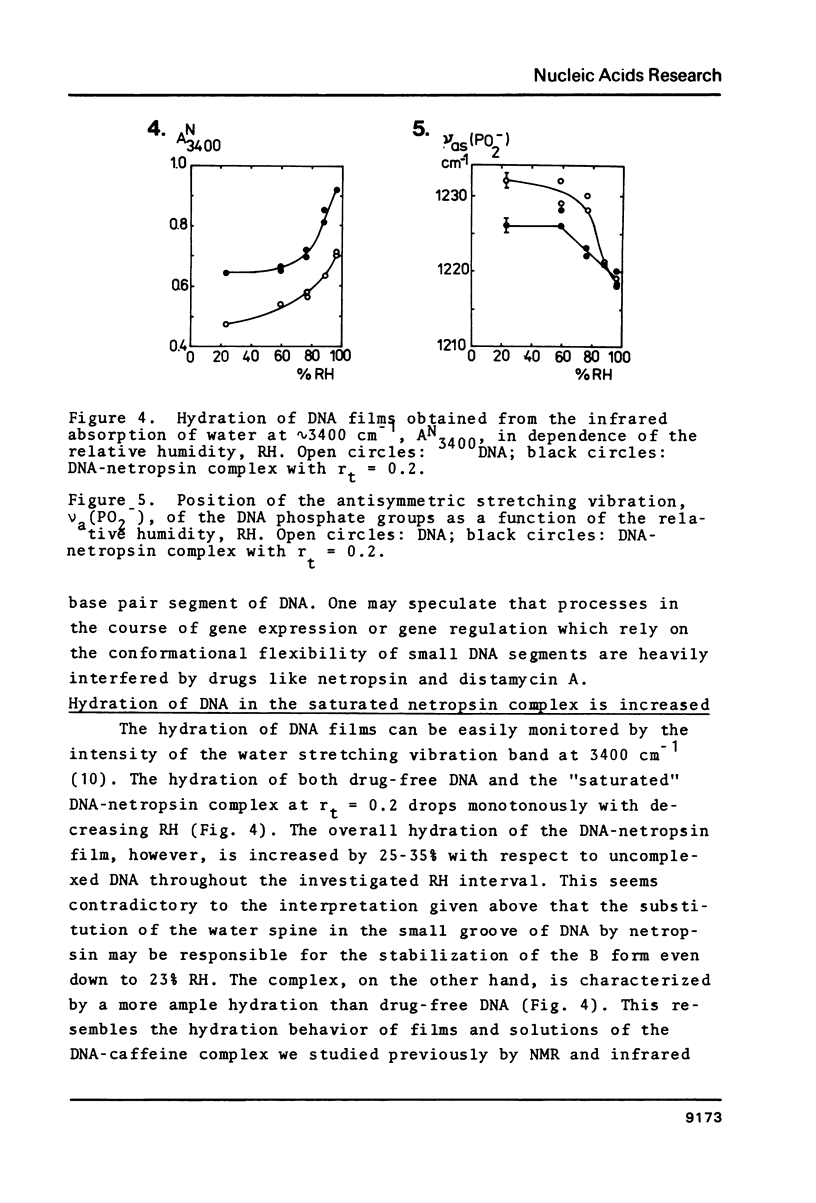
Oriented DNA films prepared by the wet-spinning technique have been complexed with several ligands: the anthracycline antibiotic violamycin BI, the dipeptide L-carnosine, and the oligopeptide antibiotic netropsin. The formation of the DNA-ligand complexes is accompanied by dramatic changes of the conformational flexibility of DNA. The B-A transition which occurs usually between 80% and 70% relative humidity (RH) is more or less suppressed by the ligands. Violamycin BI at a total ligand per DNA base pair ratio, rt, of approximately 0.03 and L-carnosine at rt approximately 1.5 inhibit the B-A transition of approximately 18 and approximately 0.25 base pairs per ligand molecule, respectively. Netropsin at rt = 0.2 induces a very stable B-DNA even at rather low RH (23%). The total hydration of this complex is significantly higher than for a drug-free DNA film. Netropsin-DNA complexes at rt of 0.02 and 0.01 result in an inhibition of approximately 45 base pairs per drug molecule with respect to the B-A transition.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alden C. J., Kim S. H. Solvent-accessible surfaces of nucleic acids. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 15;132(3):411–434. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90268-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahms J., Pilet J., Phuong Lan T. T., Hill L. R. Direct evidence of the C-like form of sodium deoxyribonucleate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3352–3355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champeil P., Tran T. P., Brahms J. A new approach to the characterization of the B and A forms of DNA by I.R. spectroscopy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Dec 10;55(3):881–887. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91226-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P. J., Hamilton L. D. The A-B conformational change in the sodium salt of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1966 Apr;16(2):562–563. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80193-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Drew H. R., Conner B. N., Wing R. M., Fratini A. V., Kopka M. L. The anatomy of A-, B-, and Z-DNA. Science. 1982 Apr 30;216(4545):475–485. doi: 10.1126/science.7071593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fita I., Campos J. L., Puigjaner L. C., Subirana J. A. X-ray diffraction study of DNA complexes with arginine peptides and their relation to nucleoprotamine structure. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 15;167(1):157–177. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleck W., Strauss D., Koch W., Prauser H. Violamycin, a new red-pigment antibiotic. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1974;14(7):551–558. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3630140702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritzsche H., Lang H., Sprinz H., Pohle W. On the interaction of caffeine with nucleic acids. IV. Studies of the caffeine-DNA interaction by infrared and ultraviolet linear dichroism, proton and deuteron nuclear magnetic resonance. Biophys Chem. 1980 Feb;11(1):121–131. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(80)85014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan M., Dattagupta N., Crothers D. M. Transmission of allosteric effects in DNA. Nature. 1979 Apr 5;278(5704):521–524. doi: 10.1038/278521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov V. I., Minchenkova L. E., Minyat E. E., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D., Schyolkina A. K. The B to A transition of DNA in solution. J Mol Biol. 1974 Aug 25;87(4):817–833. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90086-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov V. I., Minchenkova L. E., Schyolkina A. K., Poletayev A. I. Different conformations of double-stranded nucleic acid in solution as revealed by circular dichroism. Biopolymers. 1973;12(1):89–110. doi: 10.1002/bip.1973.360120109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liquier J., Gadenne M. C., Taillandier E., Defer N., Favatier F., Kruh J. Conformation of DNA in chromatin protein-DNA complexes studied by infrared spectroscopy. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Apr;6(4):1479–1493. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.4.1479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liquier J., Taboury J., Taillandier E., Brahms J. Infrared linear dichroism investigations of deoxyribonucleic complexes with histones H2B and H3. Biochemistry. 1977 Jul 12;16(14):3262–3266. doi: 10.1021/bi00633a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARVIN D. A., SPENCER M., WILKINS M. H., HAMILTON L. D. The molecular configuration of deoxyribonucleic acid. III. X-ray diffraction study of the C form of the lithium salt. J Mol Biol. 1961 Oct;3:547–565. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilet J., Brahms J. Dependence of B-A conformational change in DNA on base composition. Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 29;236(65):99–100. doi: 10.1038/newbio236099a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilet J., Leng M. Comparison of poly(dG-dC).poly(dG-dC) conformations in oriented films and in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):26–30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohle W., Fritzsche H. A new conformation-specific infrared band of A-DNA in films. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jun 11;8(11):2527–2535. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.11.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUPPRECHT A. Preparation of oriented DNA in large amounts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Jul 18;12:163–168. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90255-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes N. J., Mahendrasingam A., Pigram W. J., Fuller W., Brahms J., Vergne J., Warren R. A. The C conformation is a low salt form of sodium DNA. Nature. 1982 Mar 18;296(5854):267–269. doi: 10.1038/296267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupprecht A. A wet spinning apparatus and auxiliary equipment suitable for preparing samples of oriented DNA. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1970 Jan;12(1):93–121. doi: 10.1002/bit.260120109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupprecht A. Preparation of oriented DNA by wet spinning. Acta Chem Scand. 1966;20(2):494–504. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.20-0494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taillandier E., Fort L., Liquier J., Couppez M., Sautiere P. Role of the protein alpha helixes in histone-DNA interactions studied by vibrational spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1984 Jun 5;23(12):2644–2650. doi: 10.1021/bi00307a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wartell R. M., Larson J. E., Wells R. D. Netropsin. A specific probe for A-T regions of duplex deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 10;249(21):6719–6731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer C. Effects of the antibiotics netropsin and distamycin A on the structure and function of nucleic acids. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1975;15(0):285–318. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60122-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer C., Marck C., Guschlbauer W. Z-DNA and other non-B-DNA structures are reversed to B-DNA by interaction with netropsin. FEBS Lett. 1983 Apr 5;154(1):156–160. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80894-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


