Abstract
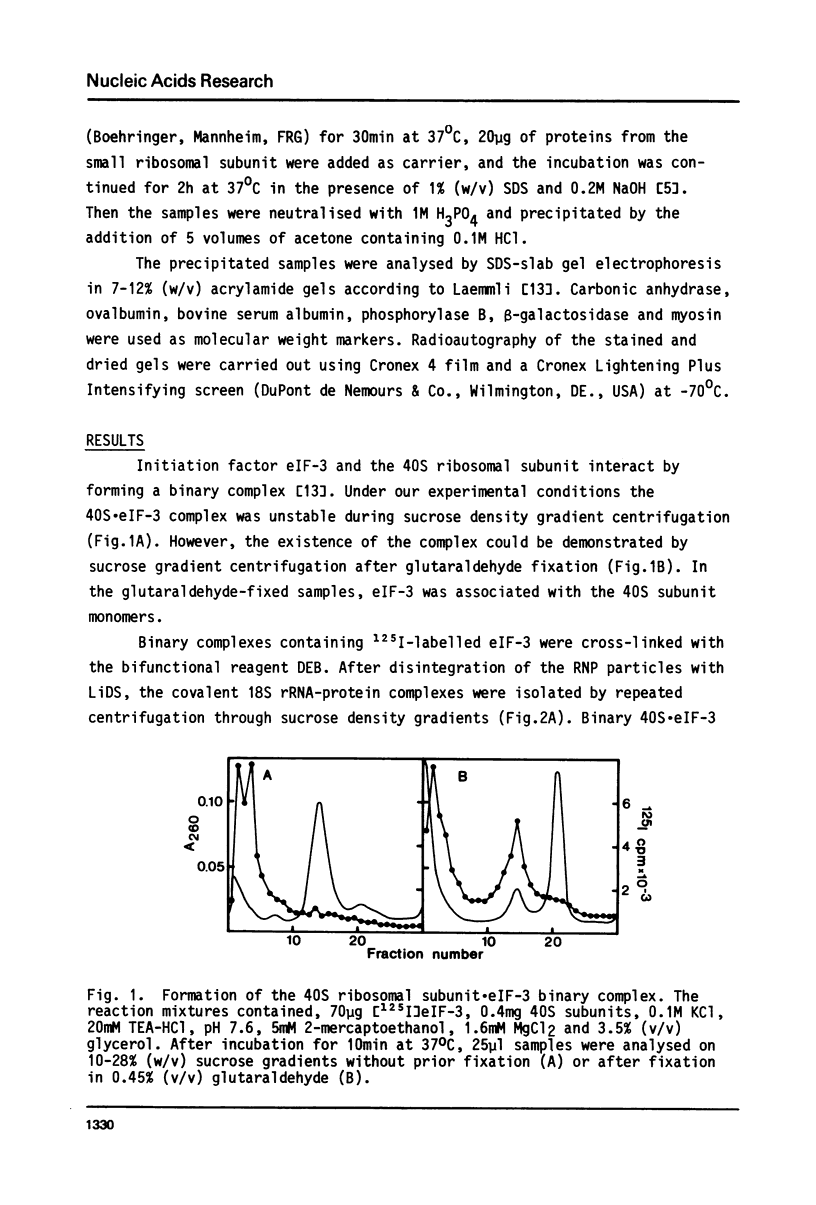
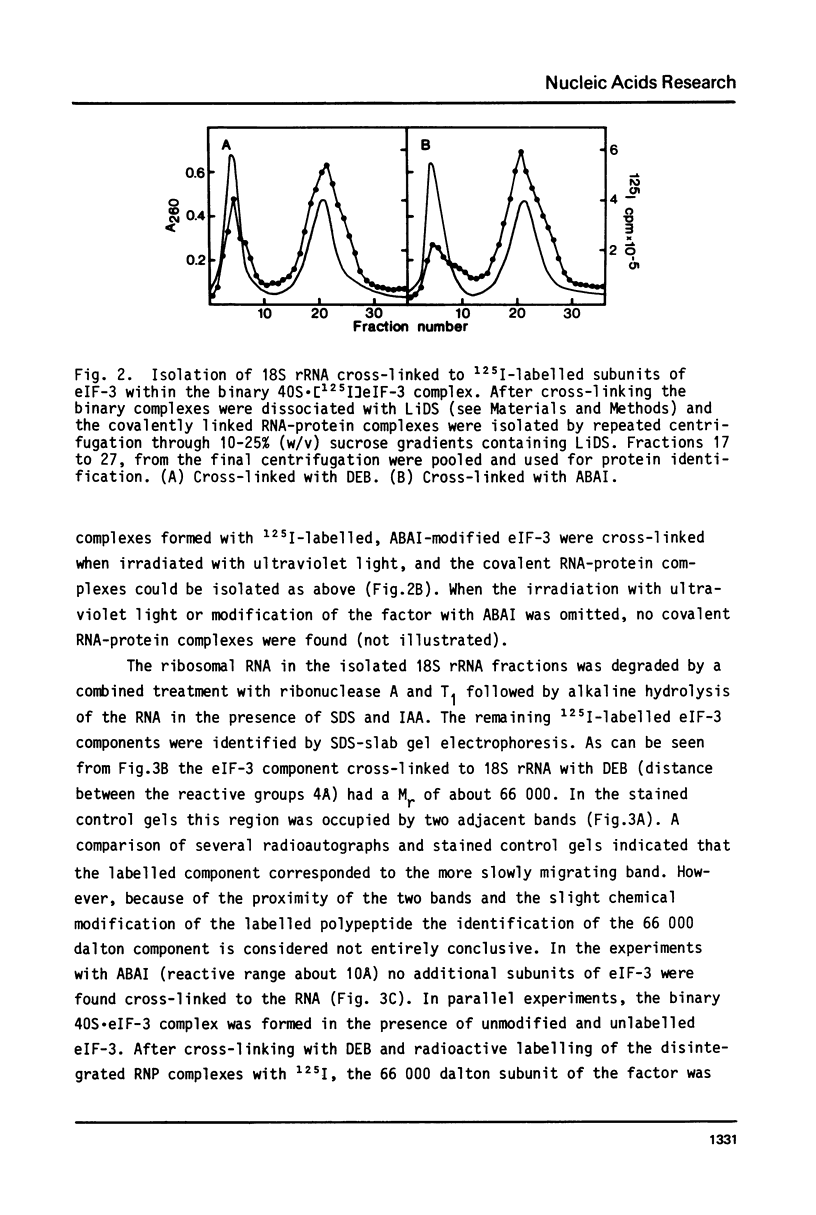
Initiation factor eIF-3 from rat liver forms a binary complex with the small ribosomal subunit. Within this complex, 18S ribosomal RNA can be cross-linked to the 66 000 dalton subunit of eIF-3 by treating the complex with a short bifunctional reagent, diepoxybutane, with a distance of 4A between the reactive groups. In binary complexes containing eIF-3 premodified with the heterobifunctional reagent, methyl-p-azido-benzoylaminoacetimidate (10A), the 66 000 dalton subunit of eIF-3 became covalently bound to 18S rRNA after irradiation of the complex with ultraviolet light. The involvement of only one of the eight eIF-3 subunits in the formation of the covalent RNA-protein complexes indicates a highly specific interaction between 18S rRNA and eIF-3 at the attachment site of the factor on the 40S subunit.
Full text
PDF





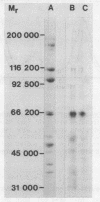
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bommer U. A., Noll F., Lutsch G., Bielka H. Immunochemical detection of proteins in the small subunit of rat liver ribosomes involved in binding of the ternary initiation complex. FEBS Lett. 1980 Feb 25;111(1):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80785-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emanuilov I., Sabatini D. D., Lake J. A., Freienstein C. Localization of eukaryotic initiation factor 3 on native small ribosomal subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1389–1393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagus R., Anderson W. F., Safer B. The regulation of initiation of mammalian protein synthesis. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1981;25:127–185. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60484-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutsch G., Noll F., Theise H., Enzmann G., Bielka H. Localization of proteins S1, S2, S16 and S23 on the surface of small subunits of rat liver ribosomes by immune electron microscopy. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Oct 3;176(2):281–291. doi: 10.1007/BF00273223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nygård O., Westermann P., Hultin T. Met-tRNA-Met-f is located in close proximity to the beta subunit of eIF-2 in the eukaryotic initiation complex, eIF-2 . Met-tRNA-Met-f . GDPCP. FEBS Lett. 1980 Apr 21;113(1):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80510-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nygård O., Westermann P., Hultin T. The use of rRNA-cellulose chromatography in the rapid isolation of homogeneous protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-2 from rat liver microsomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 27;608(1):196–200. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. T., Merrick W. C., Safer B. Binding and release of radiolabeled eukaryotic initiation factors 2 and 3 during 80 S initiation complex formation. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2509–2516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Staehelin T. Initiation of mammalian protein synthesis: the importance of ribosome and initiation factor quality for the efficiency of in vitro systems. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 19;73(3):329–349. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90346-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundkvist I. C., Howard G. A. Comparison of activity and protein content of ribosomal subunits prepared by four different methods from rabbit reticulocytes. FEBS Lett. 1974 May 1;41(2):287–291. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)81231-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundkvist I. C., Staehelin T. Structure and function of free 40 S ribosome subunits: Characterization of initiation factors. J Mol Biol. 1975 Dec 15;99(3):401–418. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trachsel H., Staehelin T. Initiation of mammalian protein synthesis. The multiple functions of the initiation factor eIF-3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 17;565(2):305–314. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90207-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlasik T. N., Domogatsky S. P., Bezlepkina T. A., Ovchinnikov L. P. RNA-binding activity of eukaryotic initiation factors of translation. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jul 11;116(1):8–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80516-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westermann P., Heumann W., Bommer U. A., Bielka H., Nygard O., Hultin T. Crosslinking of initiation factor eIF-2 to proteins of the small subunit of rat liver ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jan 1;97(1):101–104. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westermann P., Nygård O., Bielka H. The alpha and gamma subunits of initiation factor eIF-2 can be cross-linked to 18S ribosomal RNA within the quaternary initiation complex, eIF-2.Met-tRNAf.GDPCP.small ribosomal subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 25;8(14):3065–3071. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.14.3065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]