Abstract
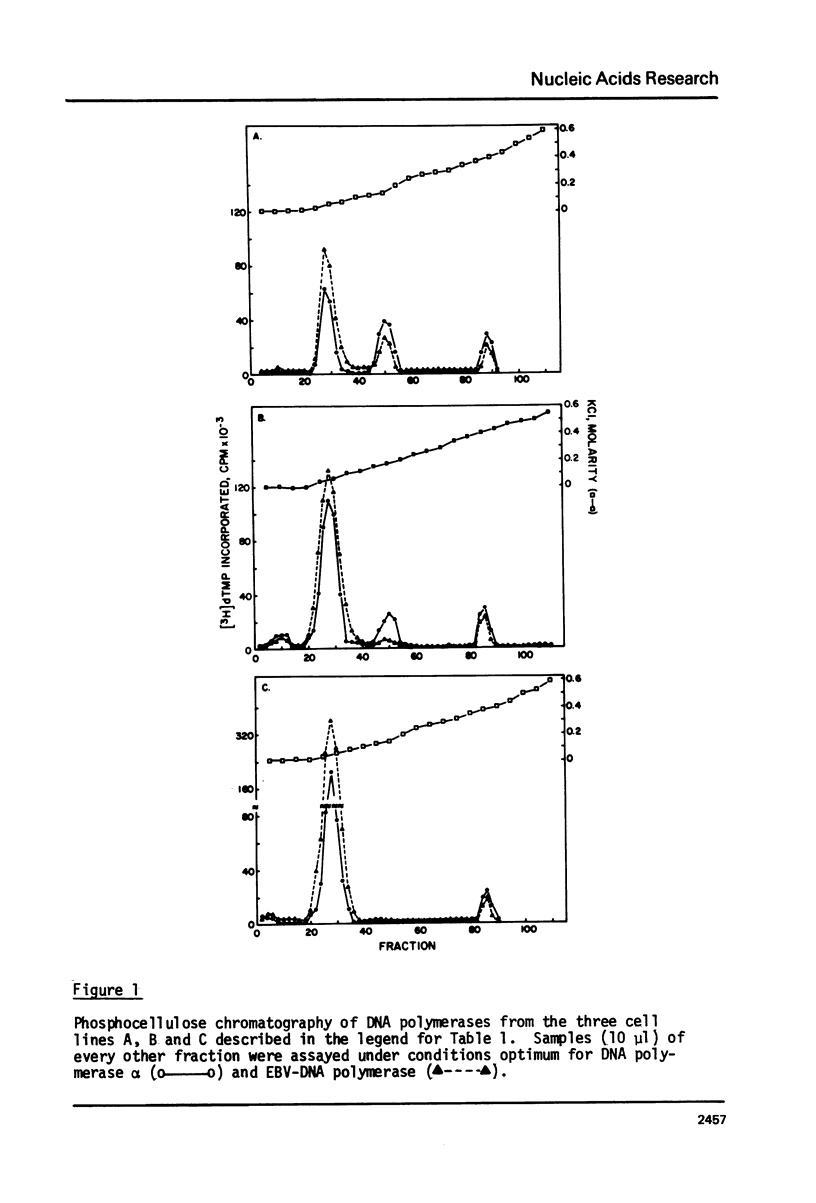
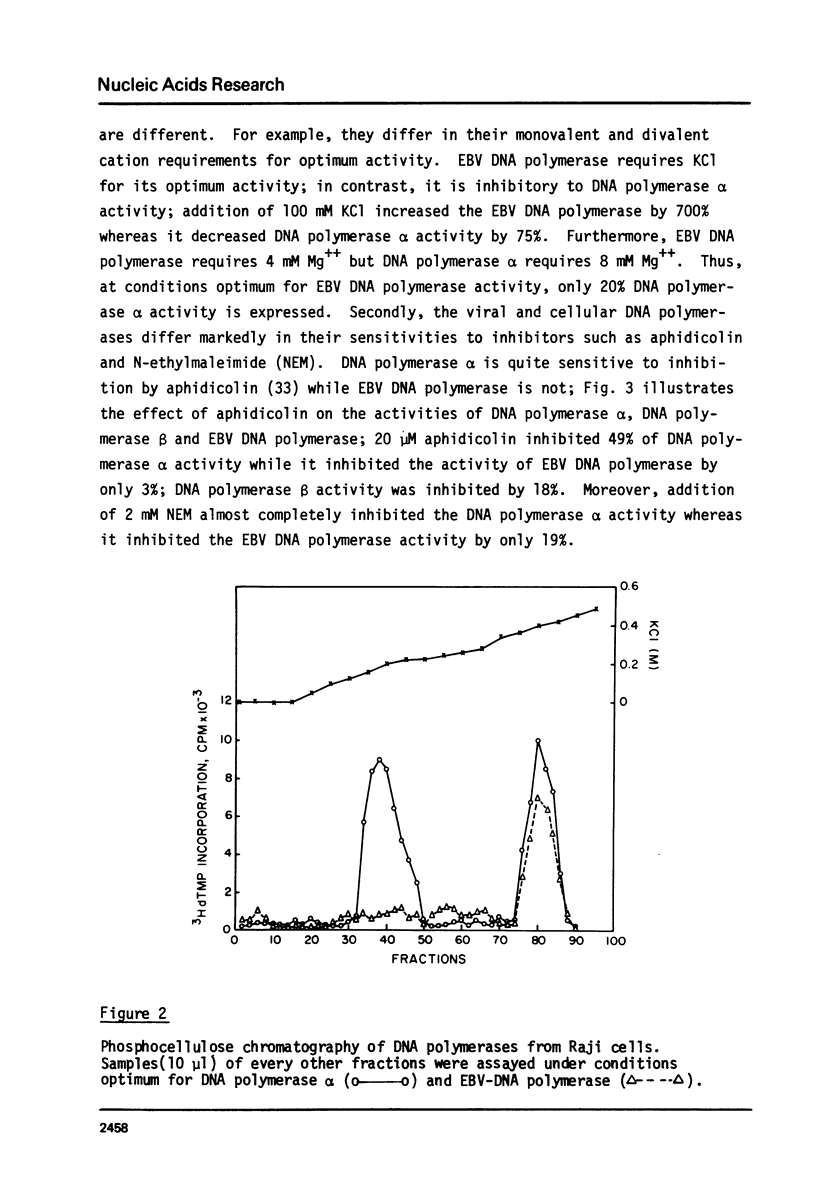
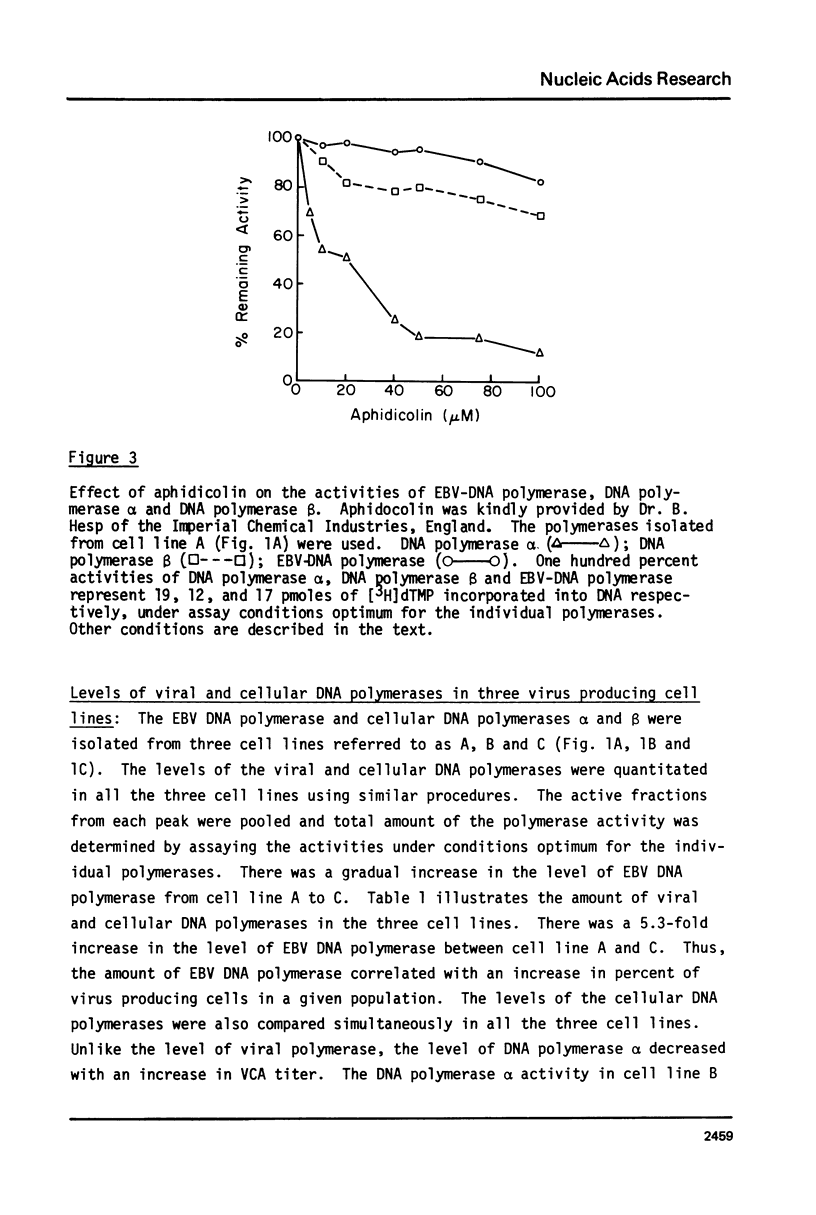
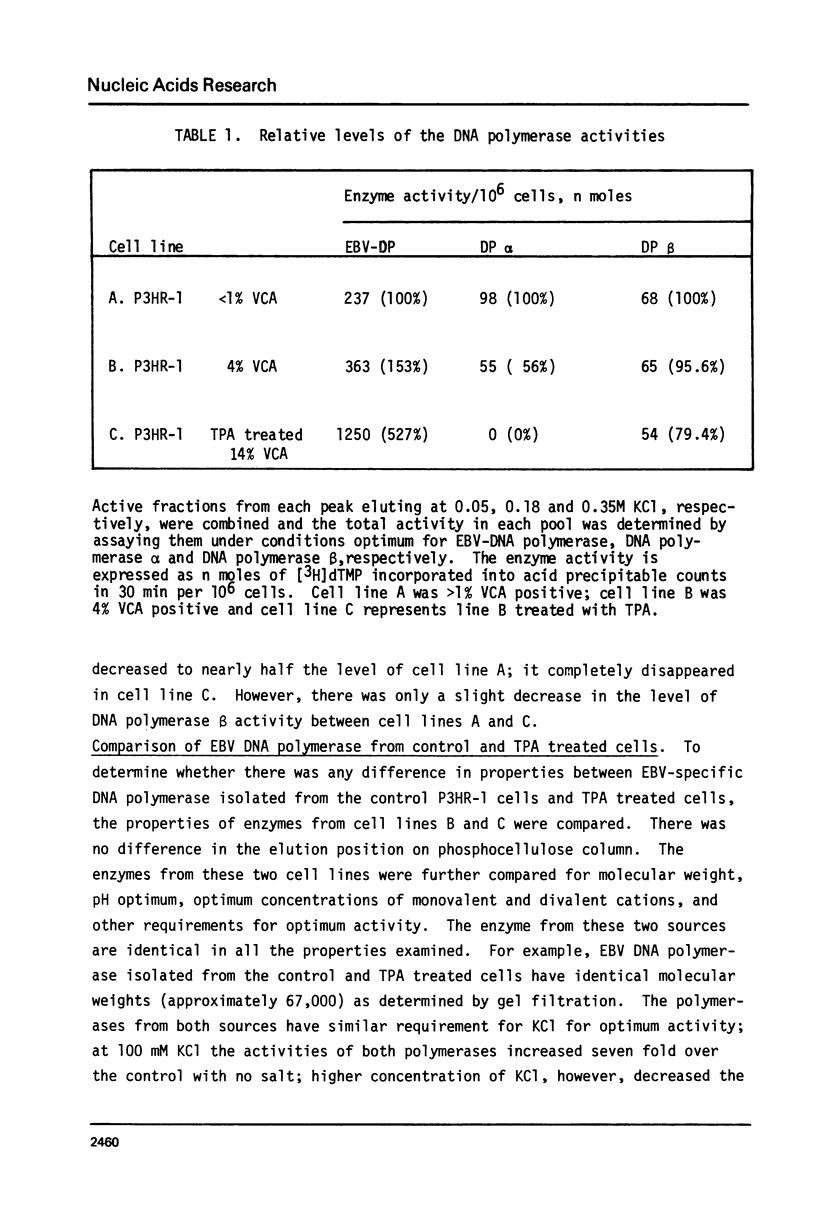
We have determined the levels of cellular DNA polymerases and Epstein-Barr virus specific DNA polymerase in three Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines producing varying amounts of EBV, one of which was induced by 12-0-tetra-decanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA). There was a proportional increase in the level of EBV-DNA polymerase with an increase in the percent of virus-producing cells. However, there was a reciprocal relationship between the levels of EBV-DNA polymerase and DNA polymerase alpha i.e., in cell line containing the highest level of EBV-DNA polymerase, activity of DNA polymerase alpha, but not of DNA polymerase beta, was reduced to an insignificantly low level. TPA does not have any direct effect on activities of either EBV-DNA polymerase or DNA polymerase alpha. EBV-DNA polymerases isolated from cells grown with or without TPA are indistinguishable in their properties such as elution position on phosphocellulose column, molecular weight, mono and divalent cation requirements, pH optimum, and other requirements for optimum activity. Addition of crude extracts of cells grown in presence of TPA to the purified DNA polymerase alpha did not inhibit its activity indicating that the observed loss was not due to any specific inhibitor present in TPA treated cells. Raji, a nonproducer cell line, did not contain EBV-DNA polymerase. There was no induction of EBV-DNA polymerase when Raji cells were grown in presence of TPA. The phenomenon of reduction in the levels of DNA polymerase alpha in cells induced to produce EBV may represent a mechanism by which the host DNA replication is shut off following virus infection.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allaudeen H. S., Bertino J. R. Isolation of a herpesvirus-specific DNA polymerase from tissues of an American patient with Burkitt lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4504–4508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allaudeen H. S. Inhibition of deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases of human leukemic leukocytes by 2',3'-dideoxythymidine triphosphate. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Apr 15;29(8):1149–1153. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90410-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aron G. M., Purifoy D. J., Schaffer P. A. DNA synthesis and DNA polymerase activity of herpes simplex virus type 1 temperature-sensitive mutants. J Virol. 1975 Sep;16(3):498–507. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.3.498-507.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. C., Bohn E. W., Planck S. R., Wilson S. H. Mouse DNA polymerase alpha. Subunit structure and identification of a species with associated exonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11678–11687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta A. K., Feighny R. J., Pagano J. S. Induction of Epstein-Barr virus-associated DNA polymerase by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5120–5125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein M. A., Achong B. G. Recent progress in Epstein-Barr virus research. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:421–445. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.002225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feighny R. J., Henry B. E., 2nd, Datta A. K., Pagano J. S. Induction of DNA polymerase activity after superinfection of Raji cells with Epstein-Barr virus. Virology. 1980 Dec;107(2):415–423. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90308-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. R., Prezyna C., Benz W. C. Two Epstein-Barr virus-associated DNA polymerase activities. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 10;253(23):8617–8628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampar B., Derge J. G., Martos L. M., Walker J. L. Synthesis of Epstein-Barr virus after activation of the viral genome in a "virus-negative" human lymphoblastoid cell (Raji) made resistant to 5-bromodeoxyuridine (thymidine kinase-virus antigen-immunofluorescence-herpesvirus fingerprints). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):78–82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W. Immunofluorescence in cells derived from Burkitt's lymphoma. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1248–1256. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1248-1256.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Henle G., Zajac B. A., Pearson G., Waubke R., Scriba M. Differential reactivity of human serums with early antigens induced by Epstein-Barr virus. Science. 1970 Jul 10;169(3941):188–190. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3941.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudewentz J., Bornkamm G. W., Zur Hausen H. Effect of the diterpene ester TPA on Epstein-Barr virus antigen- and DNA synthesis in producer and nonproducer cell lines. Virology. 1980 Jan 15;100(1):175–178. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90563-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Dombos L., Gothoskar B. Sensitivity of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) producer and non-producer human lymphoblastoid cell lines to superinfection with EB-virus. Int J Cancer. 1972 Jul 15;10(1):44–57. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910100108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luka J., Kallin B., Klein G. Induction of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) cycle in latently infected cells by n-butyrate. Virology. 1979 Apr 15;94(1):228–231. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90455-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magrath I. T., Pizzo P. A., Novikovs L., Levine A. S. Enhancement of Epstein-Barr virus replication in producer cell lines by a combination of low temperature and corticosteroids. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):477–481. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90360-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Lipman M. Release of infectious Epstein-Barr virus by transformed marmoset leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):190–194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. L., Glaser R., Rapp F. Studies of an Epstein-Barr virus-induced DNA polymerase. Virology. 1977 Feb;76(2):494–502. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90232-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonoyama M., Pagano J. S. Detection of Epstein-Barr viral genome in nonproductive cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 22;233(38):103–106. doi: 10.1038/newbio233103a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooka T., Lenoir G., Daillie J. Characterization of an Epstein-Barr virus-induced DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):1–10. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.1-10.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedrali-Noy G., Spadari S. Effect of aphidicolin on viral and human DNA polymerases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jun 27;88(4):1194–1202. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purifoy D. J., Benyesh-Melnick M. DNA polymerase induction by DNA-negative temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 2. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):374–386. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90280-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radsak K. Effect of herpes simplex virus type 1 infection on the cellular DNA polymerase activities of mouse cell cultures. J Gen Virol. 1978 Dec;41(3):479–491. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-41-3-479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovey M. G., Lenoir G., Begon-Lours J. Activation of latent Epstein-Barr virus by antibody to human IgM. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):270–272. doi: 10.1038/276270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissbach A. Eukaryotic DNA polymerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:25–47. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.000325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissbach A., Hong S. C., Aucker J., Muller R. Characterization of herpes simplex virus-induced deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6270–6277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto N., zur Hausen H. Effect of inhibition of DNA synthesis on Epstein--Barr virus induction by tumor promoters. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):104–110. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90487-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto N., zur Hausen H. Tumour promoter TPA enhances transformation of human leukocytes by Epstein-Barr virus. Nature. 1979 Jul 19;280(5719):244–245. doi: 10.1038/280244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yefenof E., Klein G., Ben-Bassat H., Lundin L. Differences in the ConA-induced redistribution and agglutination patterns of EBV genome-free and EBV-carrying human lymphoma lines. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Aug;108(1):185–190. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(77)80024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zur Hausen H., Schulte-Holthausen H. Presence of EB virus nucleic acid homology in a "virus-free" line of Burkitt tumour cells. Nature. 1970 Jul 18;227(5255):245–248. doi: 10.1038/227245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de-Thé G., Geser A., Day N. E., Tukei P. M., Williams E. H., Beri D. P., Smith P. G., Dean A. G., Bronkamm G. W., Feorino P. Epidemiological evidence for causal relationship between Epstein-Barr virus and Burkitt's lymphoma from Ugandan prospective study. Nature. 1978 Aug 24;274(5673):756–761. doi: 10.1038/274756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de-Thé G., Geser A., Day N. E., Tukei P. M., Williams E. H., Beri D. P., Smith P. G., Dean A. G., Bronkamm G. W., Feorino P. Epidemiological evidence for causal relationship between Epstein-Barr virus and Burkitt's lymphoma from Ugandan prospective study. Nature. 1978 Aug 24;274(5673):756–761. doi: 10.1038/274756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de-Thé G., Geser A., Day N. E., Tukei P. M., Williams E. H., Beri D. P., Smith P. G., Dean A. G., Bronkamm G. W., Feorino P. Epidemiological evidence for causal relationship between Epstein-Barr virus and Burkitt's lymphoma from Ugandan prospective study. Nature. 1978 Aug 24;274(5673):756–761. doi: 10.1038/274756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H., Bornkamm G. W., Schmidt R., Hecker E. Tumor initiators and promoters in the induction of Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):782–785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H. Oncogenic Herpes viruses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 20;417(1):25–53. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(75)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


