Abstract
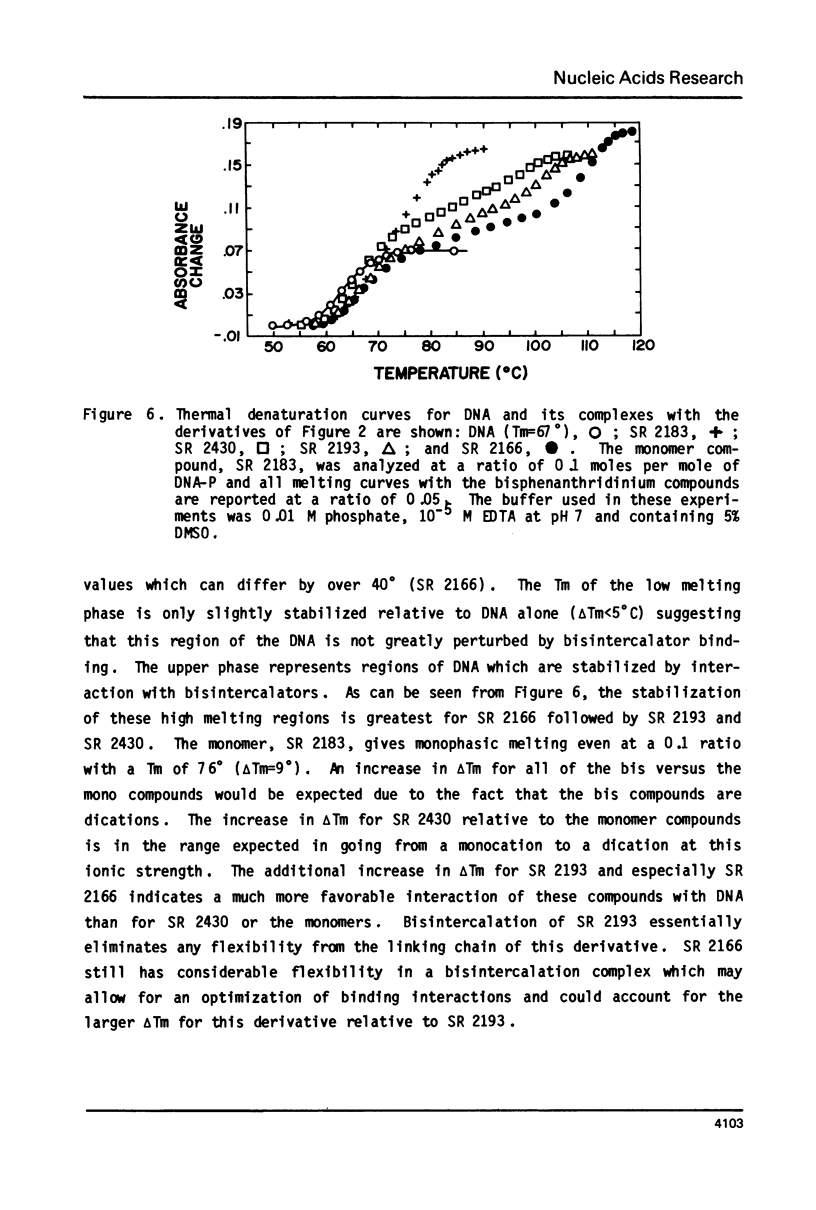
The interaction with closed circular supercoiled and linear DNA of bisphenanthridinium compounds substituted through both the meta and para positions of the 6-phenyl group, along with appropriate monomer intercalators as controls, has been investigated by viscometric titration. When CPK models for the phenanthridinium rings of the three bis-compounds are oriented in a parallel manner as a model for intercalation, their ring plane to ring plane distances are approximately 7 to 8 A (SR 2430), 11 A (SR 2193), and 15 A (SR 2166). In SR 2430 the two phenanthridines are linked through the para positions of the 6-phenyl group; this chain allows intercalation of the two rings at adjacent binding sites in DNA, but is not long enough to accommodate an excluded site. The viscometric titrations with both superhelical and linear DNA clearly indicate that SR 2430 gives results close to those of the monomer control compounds while SR 2193 and SR 2166 have approximately twice the unwinding angle and DNA length increase on binding to DNA as the monomer compounds. These phenanthridinium compounds, therefore, are capable of bisintercalation only if their linking groups are of sufficient length to allow an excluded binding site between base pairs. This conclusion is supported by DNA thermal denaturation experiments in the presence of these compounds.
Full text
PDF





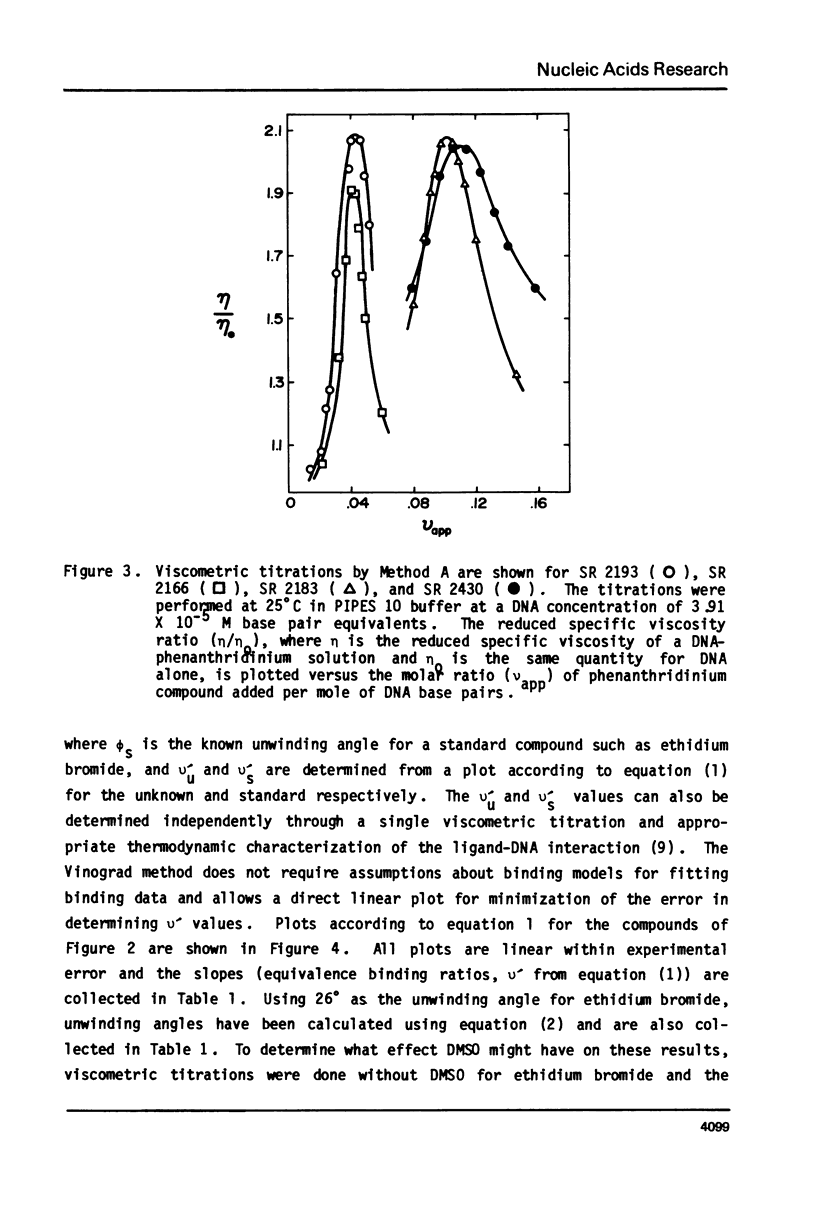
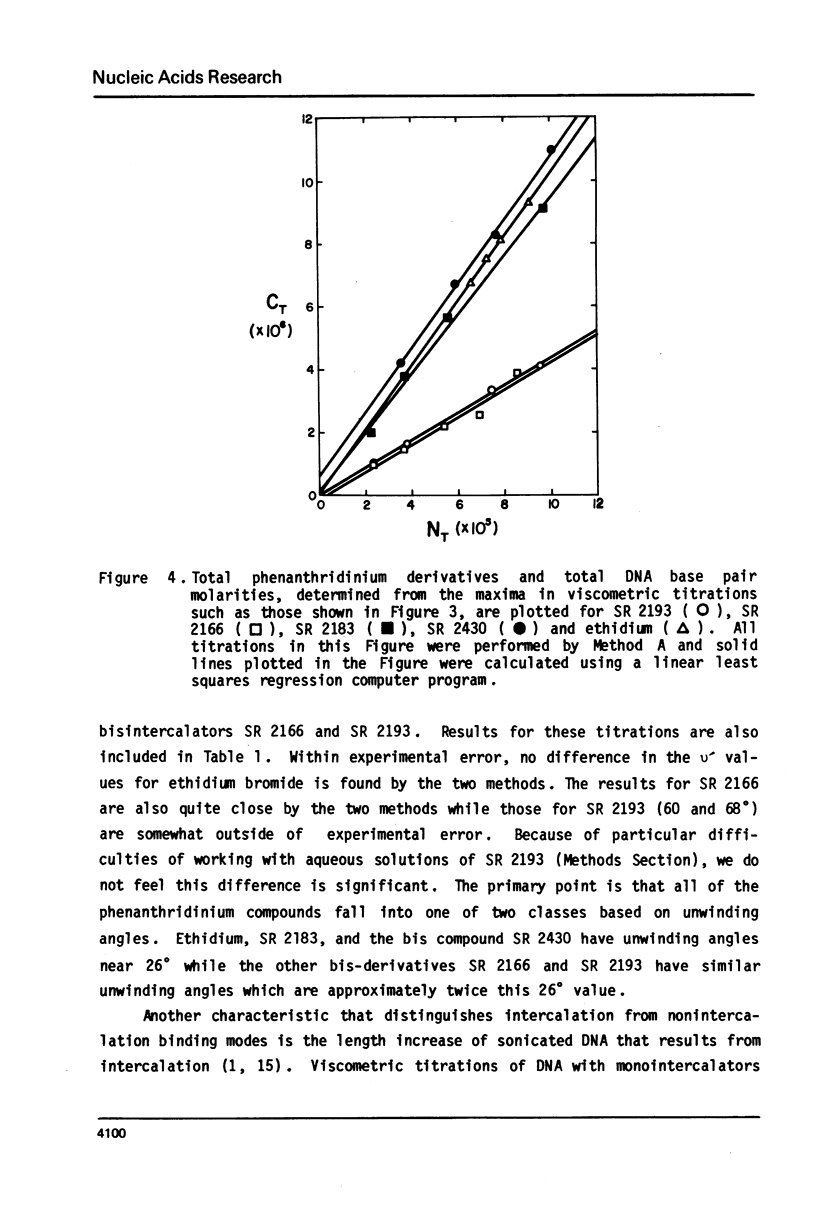
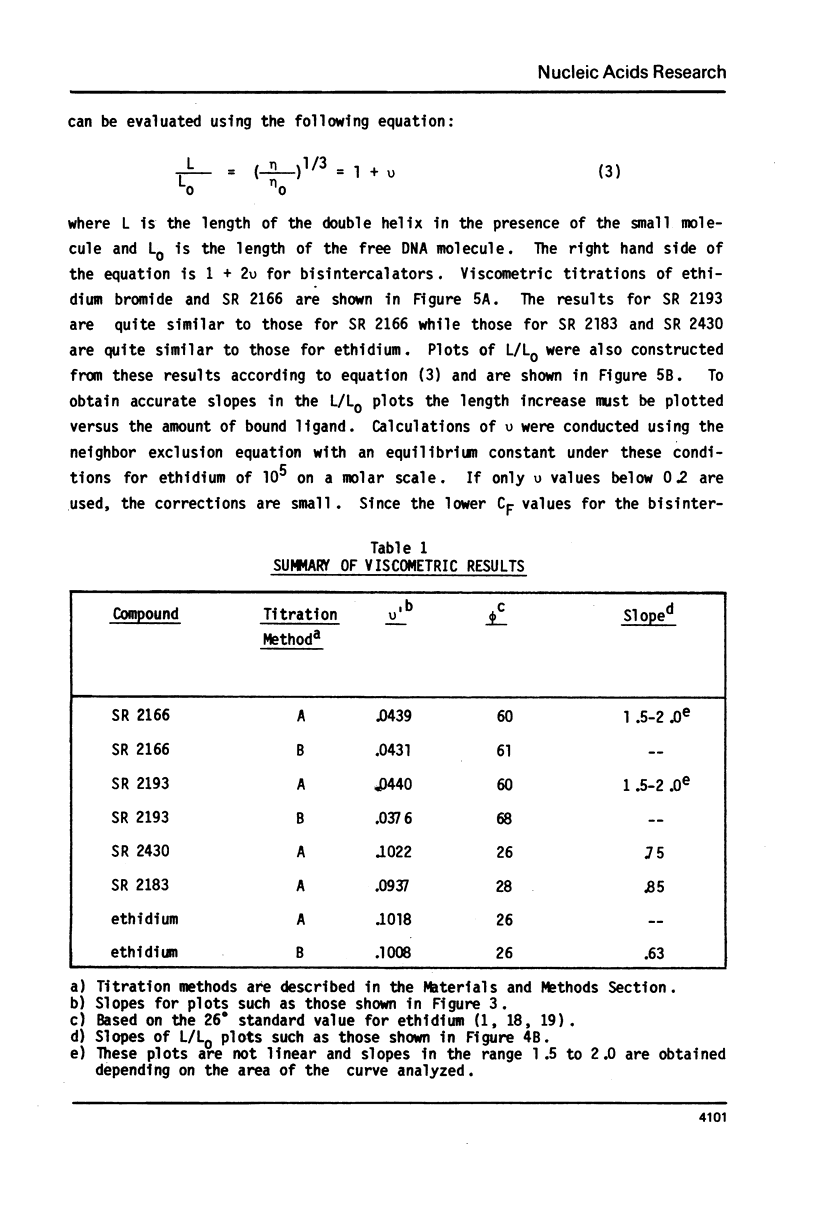
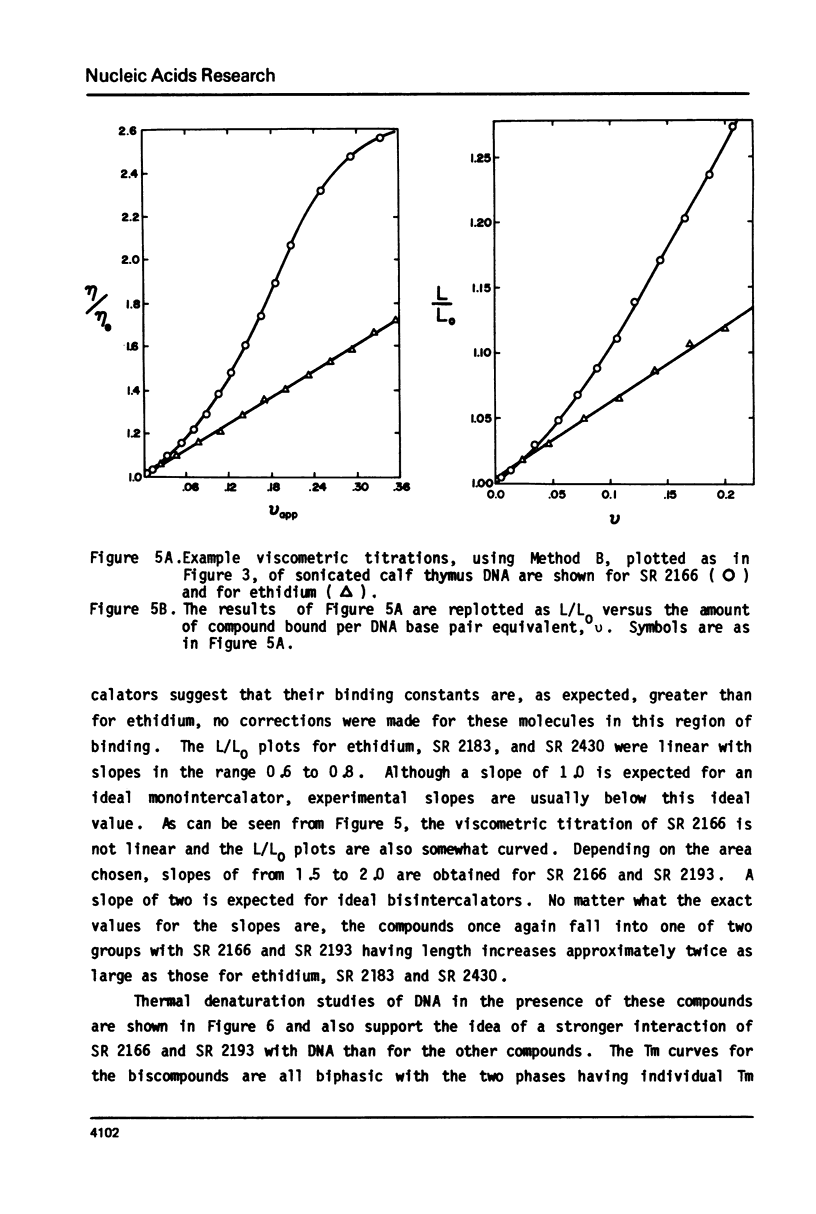



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berman H. M., Young P. R. The interaction of intercalating drugs with nucleic acids. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1981;10:87–114. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.10.060181.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers D. M. Calculation of binding isotherms for heterogenous polymers. Biopolymers. 1968 Apr;6(4):575–584. doi: 10.1002/bip.1968.360060411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaugain B., Barbet J., Capelle N., Roques B. P., Le Pecq J. B. DNA Bifunctional intercalators. 2. Fluorescence properties and DNA binding interaction of an ethidium homodimer and an acridine ethidium heterodimer. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 28;17(24):5078–5088. doi: 10.1021/bi00617a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. L., Lanier A. C., Keel R. A., Wilson W. D. The effect of ionic strength on DNA-ligand unwinding angles for acridine and quinoline derivatives. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Apr 11;8(7):1613–1624. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.7.1613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlmann K. F., Charbeneau N. J., Mosher C. W. Synthesis, DNA-binding and biological activity of a double intercalating analog of ethidium bromide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jul;5(7):2629–2641. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.7.2629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlmann K. F., Mosher C. W., Hammen R. F. Induced circular dichroism as an indicator of double intercalation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Feb 27;92(4):1172–1179. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90410-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlmann K. F., Mosher C. W. New dimeric analogues of ethidium; synthesis, interaction with DNA, and antitumor activity. J Med Chem. 1981 Nov;24(11):1333–1337. doi: 10.1021/jm00143a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Pecq J. B., Le Bret M., Barbet J., Roques B. DNA polyintercalating drugs: DNA binding of diacridine derivatives. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2915–2919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulleyblank D. E., Morgan A. R. The sense of naturally occurring superhelices and the unwinding angle of intercalated ethidium. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 5;91(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90368-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Révet B. M., Schmir M., Vinograd J. Direct determination of the superhelix density of closed circular DNA by viscometric titration. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jan 6;229(1):10–13. doi: 10.1038/newbio229010a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobell H. M., Reddy B. S., Bhandary K. K., Jain S. C., Sakore T. D., Seshadri T. P. Conformational flexibility in DNA structure as revealed by structural studies of drug intercalation and its broader implications in understanding the organization of DNA in chromatin. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):87–102. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelin L. P., Romanos M., Chen T. K., Glaubiger D., Canellakis E. S., Waring M. J. Structural limitations on the bifunctional intercalation of diacridines into DNA. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 14;17(23):5057–5063. doi: 10.1021/bi00616a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring M. J. DNA modification and cancer. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:159–192. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W. D., Jones R. L. Intercalating drugs: DNA binding and molecular pharmacology. Adv Pharmacol Chemother. 1981;18:177–222. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60255-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright R. G., Wakelin L. P., Fieldes A., Acheson R. M., Waring M. J. Effects of ring substituents and linker chains on the bifunctional intercalation of diacridines into deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1980 Dec 9;19(25):5825–5836. doi: 10.1021/bi00566a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


