Abstract
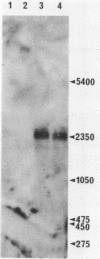
A rare cDNA coding for most of the alpha subunit of the Torpedo nicotinic acetylcholine receptor has been cloned into bacteria. The use of a mismatched oligonucleotide primer of reverse transcriptase facilitated the design of an efficient, specific probe for recombinant bacteria. DNA sequence analysis has enabled the elucidation of a large part of the polypeptide primary sequence which is discussed in relation to its acetylcholine binding activity and the location of receptor within the plasma membrane. When used as a radioactive probe, the cloned cDNA binds specifically to a single Torpedo mRNA species of about 2350 nucleotides in length but fails to show significant cross-hybridisation with alpha subunit mRNA extracted from cat muscle.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal K. L., Brunstedt J., Noyes B. E. A general method for detection and characterization of an mRNA using an oligonucleotide probe. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):1023–1028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. J., Blobel G. In vitro synthesis, glycosylation, and membrane insertion of the four subunits of Torpedo acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5598–5602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballivet M., Patrick J., Lee J., Heinemann S. Molecular cloning of cDNA coding for the gamma subunit of Torpedo acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4466–4470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnard E. A., Miledi R., Sumikawa K. Translation of exogenous messenger RNA coding for nicotinic acetylcholine receptors produces functional receptors in Xenopus oocytes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 May 22;215(1199):241–246. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emtage J. S., Tacon W. C., Catlin G. H., Jenkins B., Porter A. G., Carey N. H. Influenza antigenic determinants are expressed from haemagglutinin genes cloned in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):171–174. doi: 10.1038/283171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habener J. F., Rosenblatt M., Kemper B., Kronenberg H. M., Rich A., Potts J. T., Jr Pre-proparathyroid hormone; amino acid sequence, chemical synthesis, and some biological studies of the precursor region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2616–2620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Meselson M. Plasmid screening at high colony density. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghton M., Stewart A. G., Doel S. M., Emtage J. S., Eaton M. A., Smith J. C., Patel T. P., Lewis H. M., Porter A. G., Birch J. R. The amino-terminal sequence of human fibroblast interferon as deduced from reverse transcripts obtained using synthetic oligonucleotide primers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 10;8(9):1913–1931. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.9.1913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving R. A., Toneguzzo F., Rhee S. H., Hofmann T., Ghosh H. P. Synthesis and assembly of membrane glycoproteins: presence of leader peptide in nonglycosylated precursor of membrane glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):570–574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Ike Y., Ikuta S., Itakura K. Solid phase synthesis of polynucleotides. VI. Further studies on polystyrene copolymers for the solid support. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1755–1769. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Merlie J., Yogeeswaran G. Biochemical properties of acteylcholine receptor subunits from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4465–4470. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyddiatt A., Sumikawa K., Wolosin J. M., Dolly J. O., Barnard E. A. Affinity labelling by bromoacetylcholine of a characteristic subunit in the acetylcholine receptor from muscle and Torpedo electric organ. FEBS Lett. 1979 Dec 1;108(1):20–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81169-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. D. Glycoproteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41:673–702. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.003325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendez B., Valenzuela P., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. Cell-free synthesis of acetylcholine receptor polypeptides. Science. 1980 Aug 8;209(4457):695–697. doi: 10.1126/science.7394526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlie J. P., Hofler J. G., Sebbane R. Acetylcholine receptor synthesis from membrane polysomes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6995–6999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlie J. P., Sebbane R., Tzartos S., Lindstrom J. Inhibition of glycosylation with tunicamycin blocks assembly of newly synthesized acetylcholine receptor subunits in muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2694–2701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery M. A., Hunkapiller M. W., Strader C. D., Hood L. E. Acetylcholine receptor: complex of homologous subunits. Science. 1980 Jun 27;208(4451):1454–1456. doi: 10.1126/science.7384786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soreq H., Bartfeld D., Parvari R., Fuchs S. Increase in the translatable mRNA for acetylcholine receptor during embryonic development of Torpedo ocellata electric organ. FEBS Lett. 1982 Mar 8;139(1):32–40. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80480-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumikawa K., Houghton M., Emtage J. S., Richards B. M., Barnard E. A. Active multi-subunit ACh receptor assembled by translation of heterologous mRNA in Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1981 Aug 27;292(5826):862–864. doi: 10.1038/292862a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twigg A. J., Sherratt D. Trans-complementable copy-number mutants of plasmid ColE1. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):216–218. doi: 10.1038/283216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandlen R. L., Wu W. C., Eisenach J. C., Raftery M. A. Studies of the composition of purified Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor and of its subunits. Biochemistry. 1979 May 15;18(10):1845–1854. doi: 10.1021/bi00577a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Schold M., Johnson M. J., Dembek P., Itakura K. Oligonucleotide directed mutagenesis of the human beta-globin gene: a general method for producing specific point mutations in cloned DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3647–3656. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]