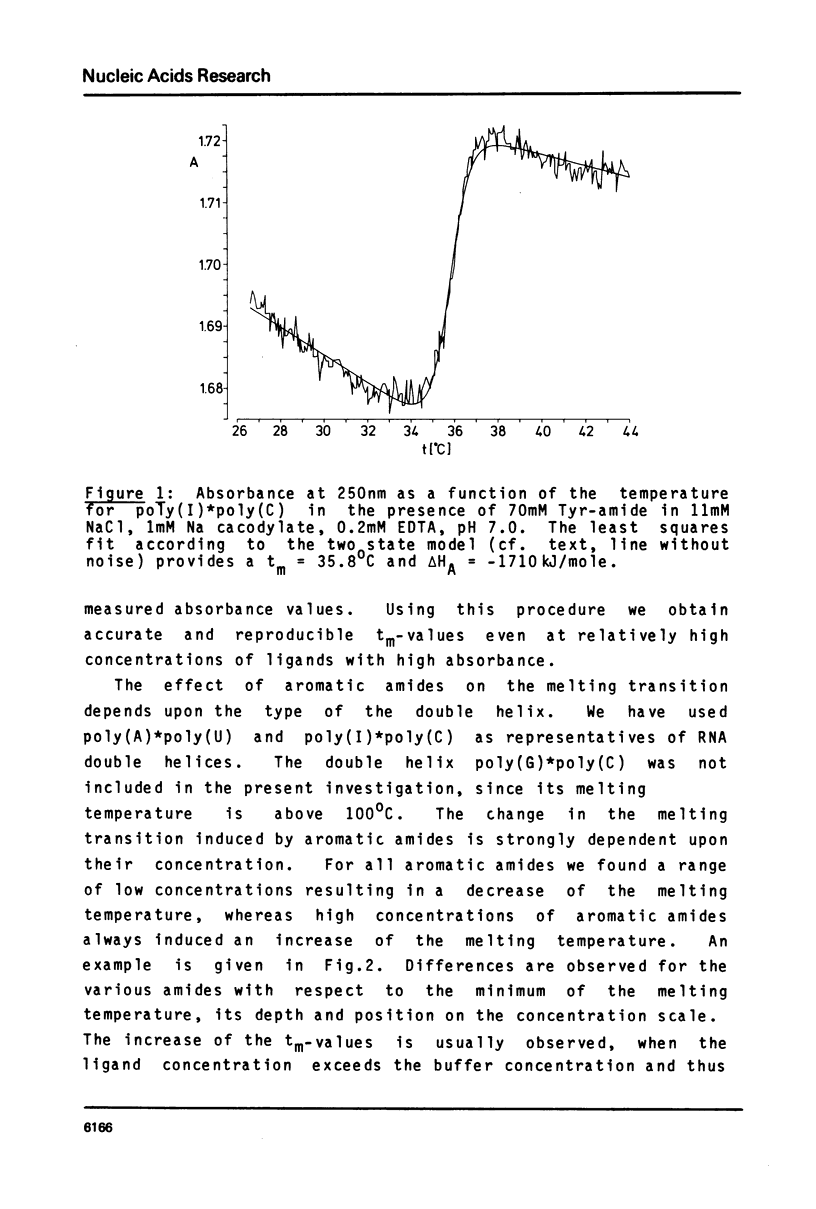
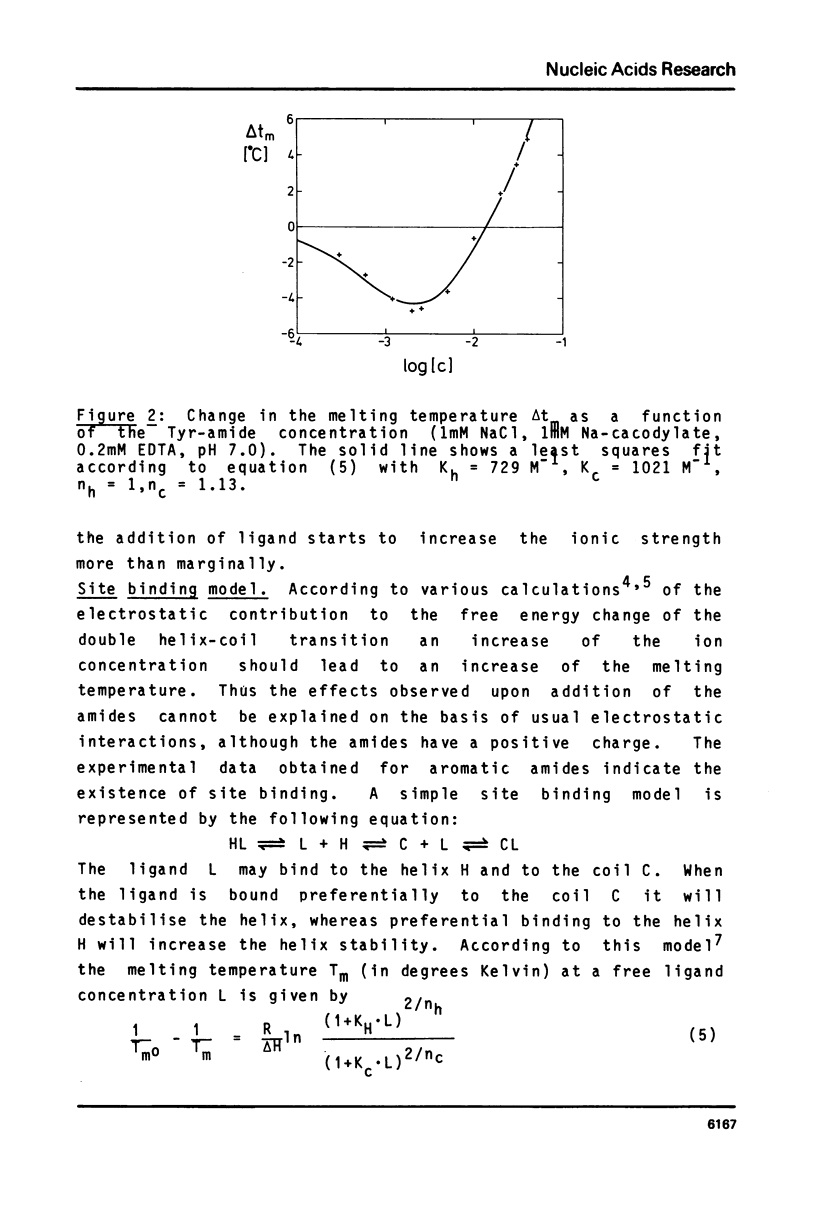
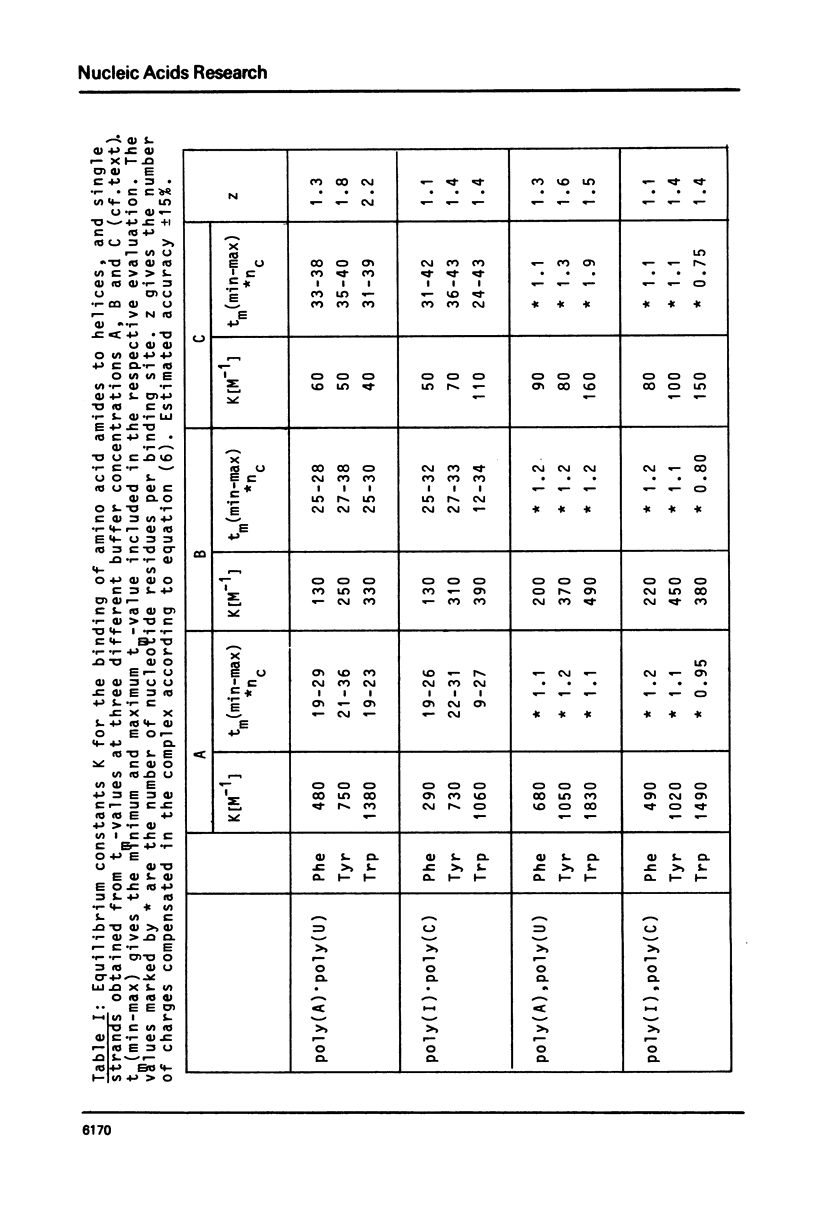
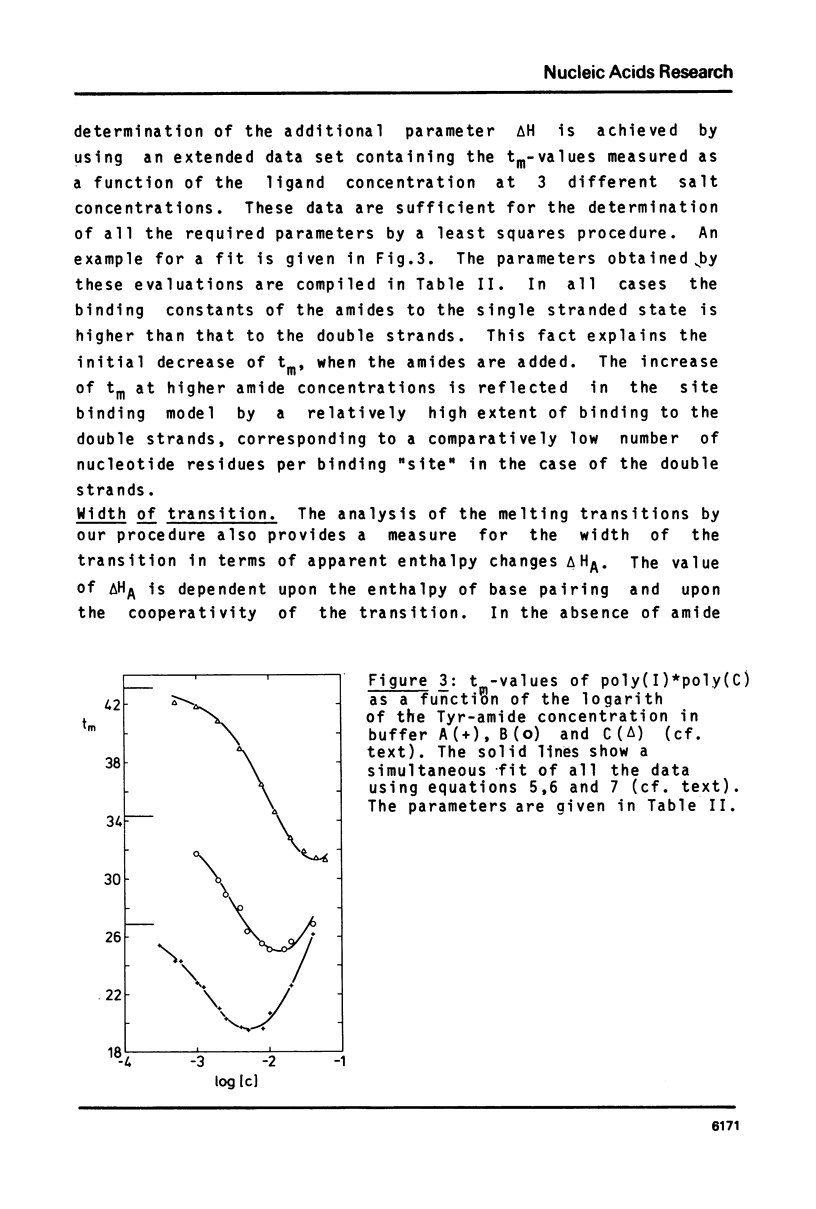
Abstract
The amides of L-phenylalanine, L-tyrosine and L-tryptophane decrease the melting temperatures tm of poly(A)*poly(U) and poly(I)*poly(C) double helices at low concentrations (1 mM), whereas high concentrations finally lead to an increase of tm. This dependence of the tm-values upon the ligand concentration can be represented quantitatively by a simple site binding model, providing binding parameters for the interaction between the amides and the nucleic acids both in the double- and the single-stranded conformation. According to these data the affinity to the single strands is higher than that to the double strands and increases in the series Phe less than Tyr less than Trp. The binding constants decrease with increasing salt concentration as expected for an interaction driven by electrostatic attraction. However, part of the interaction is also due to stacking between the aromatic amides and the nucleic acid bases. The present results indicate a direct correlation between the presence of aromatic amino acids at the binding site of helix destabilising proteins and the properties of simple derivatives of these amino acids. Furthermore the results suggest that very simple peptides containing aromatic amino acids served as a starting point for the evolution of helix destabilising proteins.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Durand M., Borazan H. N., Maurizot J. C., Dimicoli J. L., Hélène C. Nucleic acids-protein interactions. Conformational changes induced by the binding of aromatic amines to polyadenylic acid. Biochimie. 1976;58(4):395–402. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(76)80248-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand M., Maurizot J. C., Helene C. Calorimetric investigation of 5-methoxytryptamine binding to DNA and poly (A). FEBS Lett. 1976 Nov 15;72(1):9–12. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80886-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helene C., Maurizot J. C. Interactions of oligopeptides with nucleic acids. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1981;10(3):213–258. doi: 10.3109/10409238109113600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinz H. J., Haar W., Ackermann T. Experimental thermodynamics of the helix--random coil transition. 3. Determination of the transition enthalpies of the helical complexes poly(I+C) and poly I in solution. Biopolymers. 1970;9(8):923–936. doi: 10.1002/bip.1970.360090806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakauer H., Sturtevant J. M. Heats of the helix-coil transitions of the poly A-poly U complexes. Biopolymers. 1968 Apr;6(4):491–512. doi: 10.1002/bip.1968.360060406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning G. S. The molecular theory of polyelectrolyte solutions with applications to the electrostatic properties of polynucleotides. Q Rev Biophys. 1978 May;11(2):179–246. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D. Theoretical calculations of the helix-coil transition of DNA in the presence of large, cooperatively binding ligands. Biopolymers. 1976 Jul;15(7):1345–1375. doi: 10.1002/bip.1976.360150710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pörschke D., Ronnenberg J. The reaction of aromatic peptides with double helical DNA. Quantitative characterisation of a two step reaction scheme. Biophys Chem. 1981 Aug;13(4):283–290. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(81)85002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pörschke D. Structure and dynamics of a tryptophanepeptide-polynucleotide complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Apr 11;8(7):1591–1612. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.7.1591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Record M. T., Jr, Anderson C. F., Lohman T. M. Thermodynamic analysis of ion effects on the binding and conformational equilibria of proteins and nucleic acids: the roles of ion association or release, screening, and ion effects on water activity. Q Rev Biophys. 1978 May;11(2):103–178. doi: 10.1017/s003358350000202x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schildkraut C. Dependence of the melting temperature of DNA on salt concentration. Biopolymers. 1965;3(2):195–208. doi: 10.1002/bip.360030207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


