Abstract
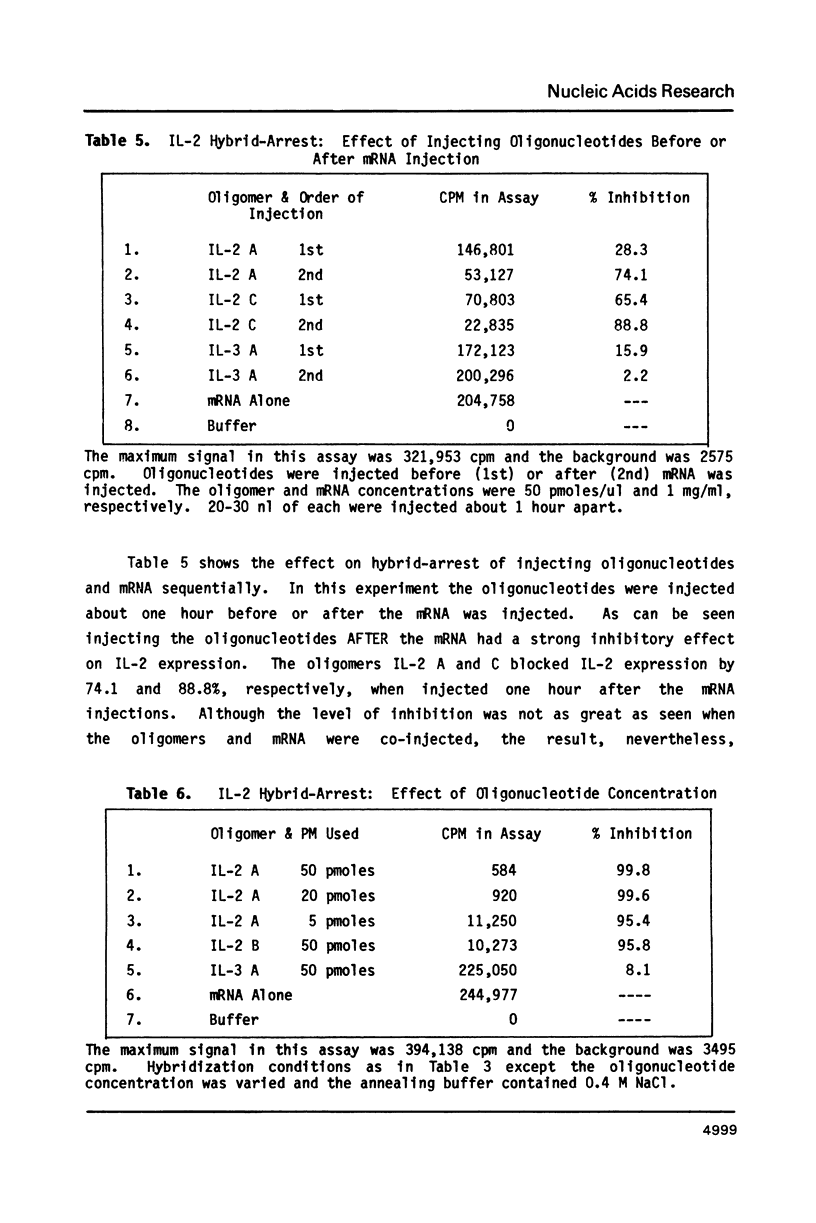
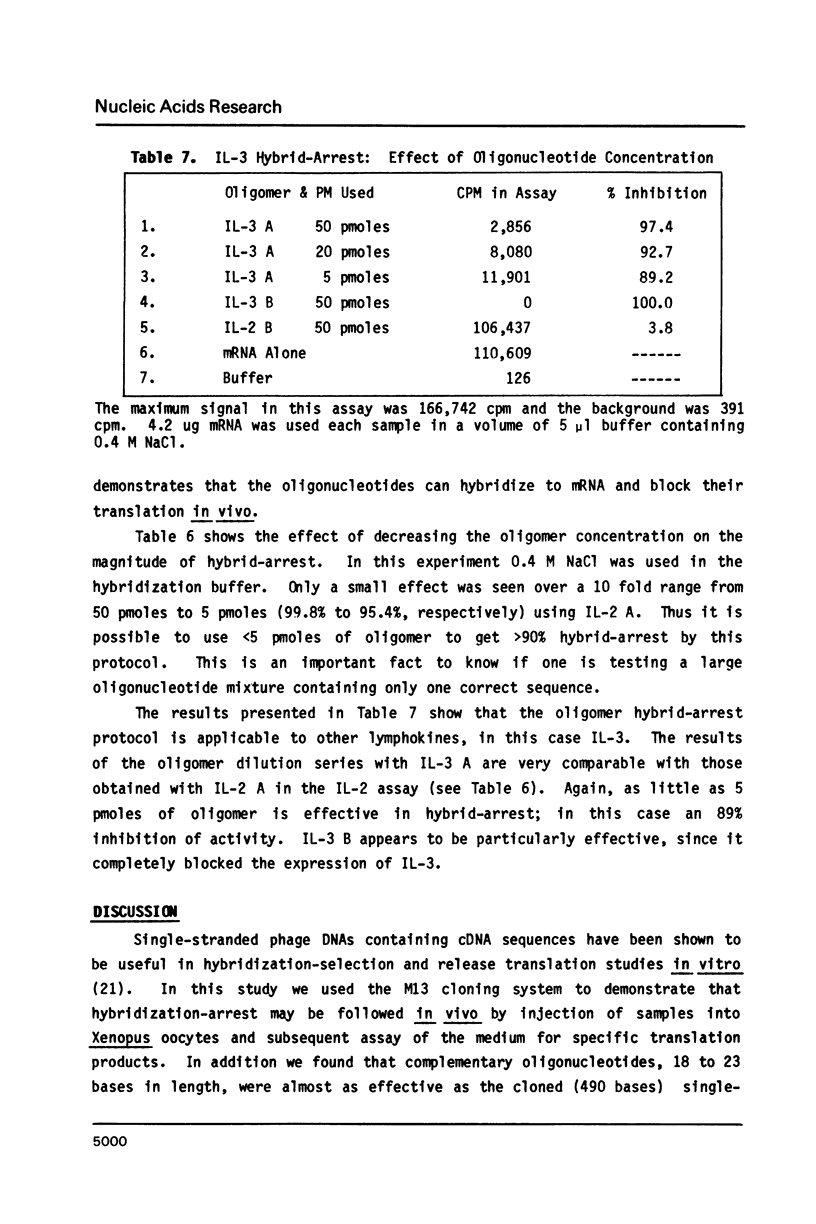
The expression of heterologous mRNA in Xenopus oocytes was quantitatively inhibited by coinjection of single-stranded complementary DNA or synthetic complementary oligonucleotides. The lymphokines Interleukin-2 (IL-2) and Interleukin-3 (IL-3) were used as model systems to test the effectiveness of this procedure. Messenger RNA samples were hybridized to single stranded complementary DNA or oligonucleotides, injected into oocytes and the oocyte incubation medium assayed for the presence or absence of specific translation products 48 hours later. When IL-2 mRNA was hybridized to a large excess of long (490 bases) single stranded complementary DNA, the expression of IL-2 was effectively blocked (greater than 98%). Complementary oligonucleotides (18-23 bases) were almost as effective as the polynucleotide in inhibiting IL-2 activity (greater than 95%). Oligonucleotides derived from the 5' end, middle or 3' end of the coding sequence were all effective in arresting IL-2 mRNA translation. Oligonucleotide hybrid-arrest was effective even when no NaCl was present in the hybridization buffer, indicating that the annealing reaction could occur within the oocyte after injection. Definite proof that hybrid-arrest could occur in vivo was shown by the fact that oligonucleotides injected before or after mRNA injection, while not as effective as co-injection, still showed substantial inhibition of specific mRNA translation. The oligonucleotide hybrid-arrest method was equally effective in the case of IL-3, demonstrating its general applicability.
Full text
PDF


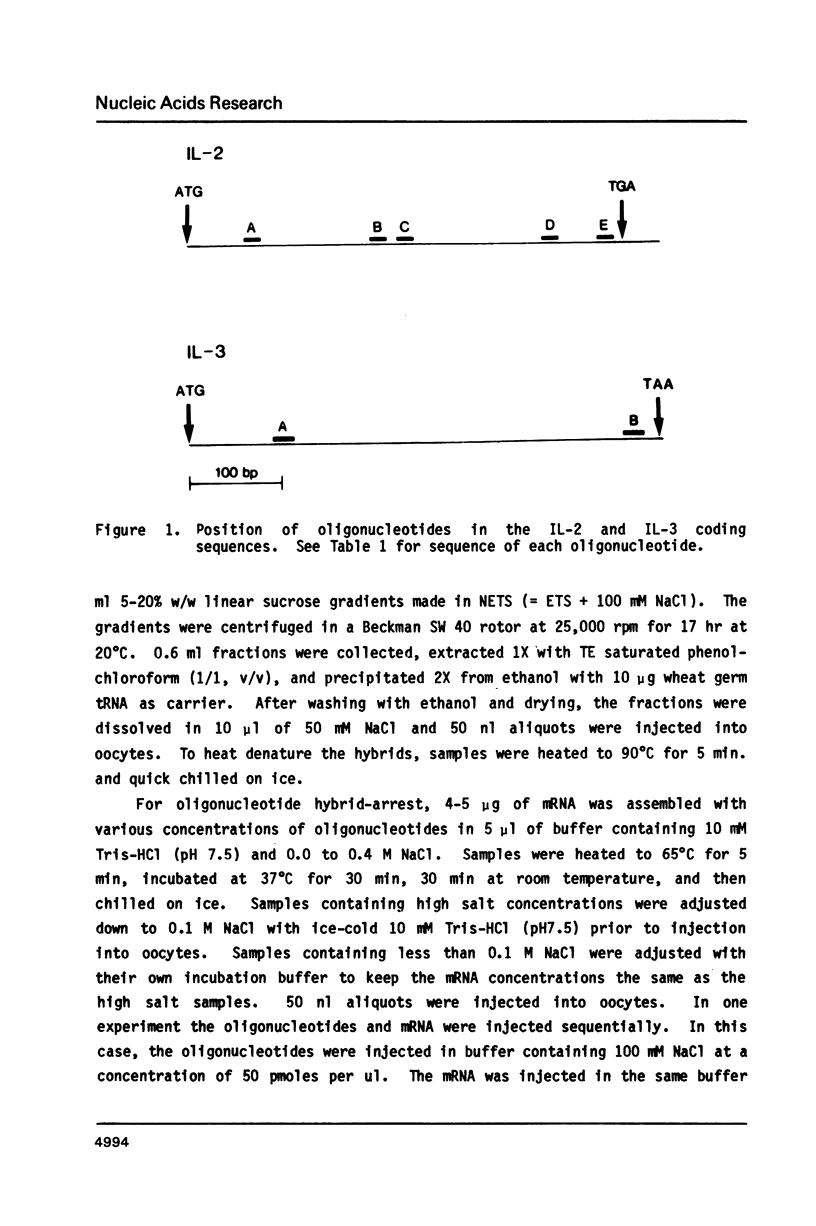

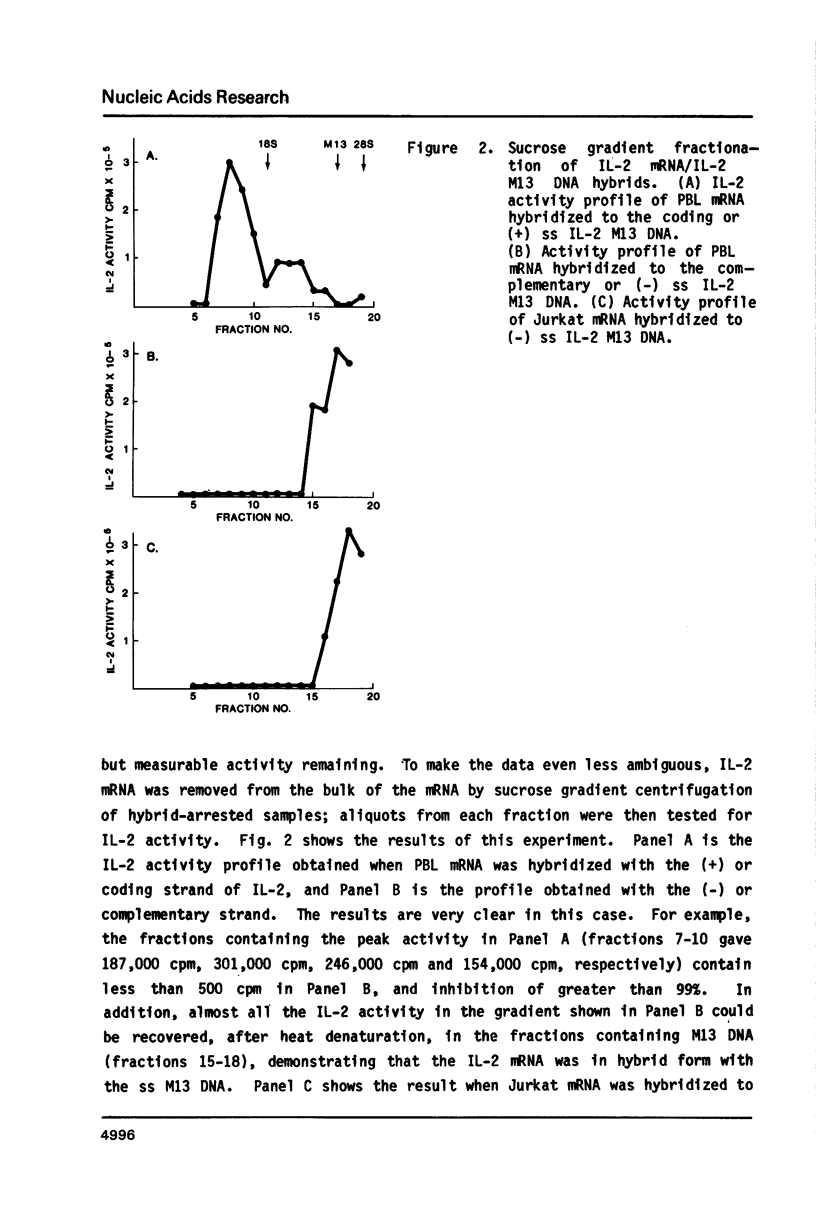
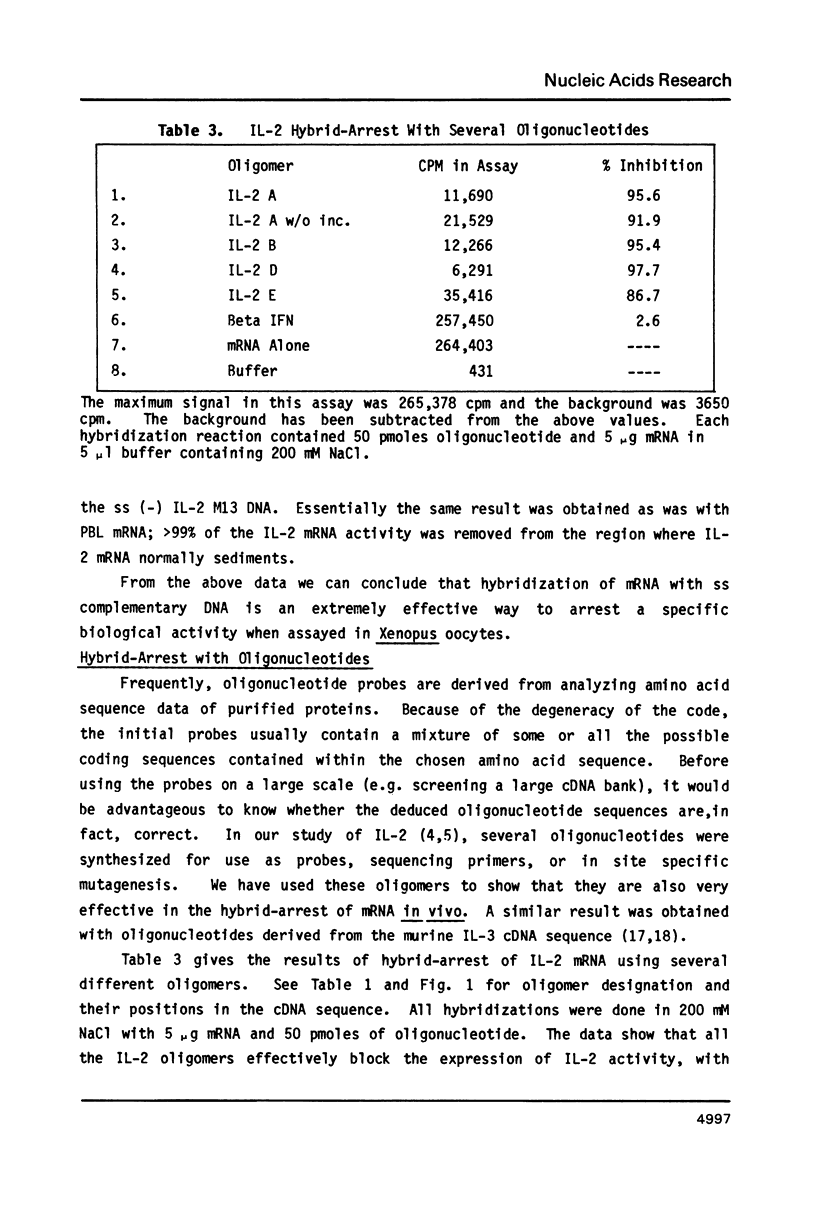
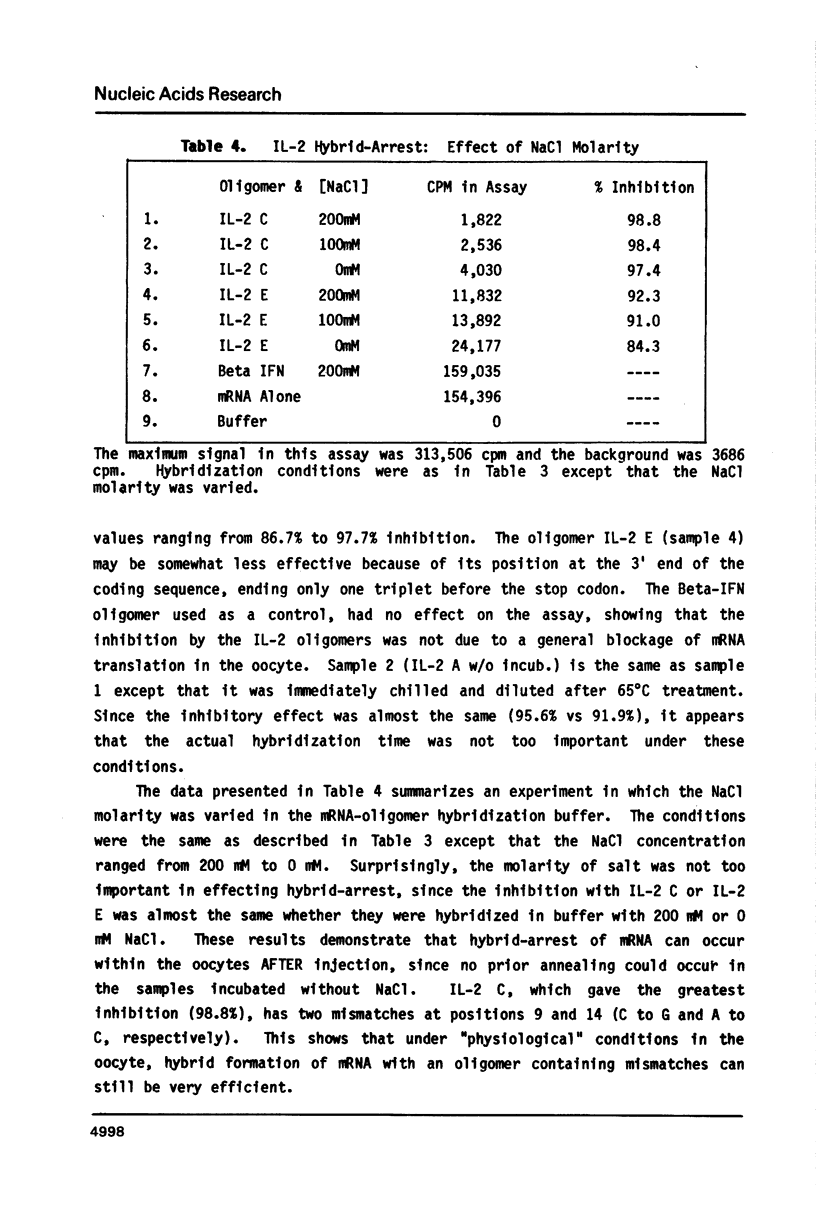




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger S. L., Birkenmeier C. S. Inhibition of intractable nucleases with ribonucleoside--vanadyl complexes: isolation of messenger ribonucleic acid from resting lymphocytes. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 13;18(23):5143–5149. doi: 10.1021/bi00590a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. O., Morton J. G., Rosbash M., Richardson M. Three abundance classes in HeLa cell messenger RNA. Nature. 1974 Jul 19;250(463):199–204. doi: 10.1038/250199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler P. M. The use of single-stranded phage DNAs in hybrid arrest and release translation. Anal Biochem. 1982 Nov 15;127(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90137-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J., Green P. J., Inouye M. The use of RNAs complementary to specific mRNAs to regulate the expression of individual bacterial genes. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90373-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devos R., Plaetinck G., Cheroutre H., Simons G., Degrave W., Tavernier J., Remaut E., Fiers W. Molecular cloning of human interleukin 2 cDNA and its expression in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 11;11(13):4307–4323. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.13.4307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt H., Lührmann R. Blocking of the initiation of protein biosynthesis by a pentanucleotide complementary to the 3' end of Escherichia coli 16 S rRNA. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11185–11188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R., Yanofsky C. Use of complementary DNA oligomers to probe trp leader transcript secondary structures involved in transcription pausing and termination. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3295–3302. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung M. C., Hapel A. J., Ymer S., Cohen D. R., Johnson R. M., Campbell H. D., Young I. G. Molecular cloning of cDNA for murine interleukin-3. Nature. 1984 Jan 19;307(5948):233–237. doi: 10.1038/307233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Lane C. D., Woodland H. R., Marbaix G. Use of frog eggs and oocytes for the study of messenger RNA and its translation in living cells. Nature. 1971 Sep 17;233(5316):177–182. doi: 10.1038/233177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpold M. M., Dobner P. R., Evans R. M., Bancroft F. C. Construction and identification by positive hybridization-translation of a bacterial plasmid containing a rat growth hormone structural gene sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jun;5(6):2039–2053. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.6.2039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Keller J., Greenberger J. S., Henderson L., Yetter R. A., Morse H. C., 3rd Phenotypic characteristics of cell lines requiring interleukin 3 for growth. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1377–1383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izant J. G., Weintraub H. Inhibition of thymidine kinase gene expression by anti-sense RNA: a molecular approach to genetic analysis. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1007–1015. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90050-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaraman K., McParland K., Miller P., Ts'o P. O. Selective inhibition of Escherichia coli protein synthesis and growth by nonionic oligonucleotides complementary to the 3' end of 16S rRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1537–1541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Hapel A. J., Ihle J. N. Constitutive production of a unique lymphokine (IL 3) by the WEHI-3 cell line. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2393–2398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Boyle J. A., Mount S. M., Wolin S. L., Steitz J. A. Are snRNPs involved in splicing? Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):220–224. doi: 10.1038/283220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mark D. F., Lu S. D., Creasey A. A., Yamamoto R., Lin L. S. Site-specific mutagenesis of the human fibroblast interferon gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5662–5666. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A. Injected anti-sense RNAs specifically block messenger RNA translation in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):144–148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Chou M. Y., Inouye M. A unique mechanism regulating gene expression: translational inhibition by a complementary RNA transcript (micRNA). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1966–1970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Pettersson I., Hinterberger M., Karmas A., Steitz J. A. The U1 small nuclear RNA-protein complex selectively binds a 5' splice site in vitro. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):509–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90432-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. M., Carrasco A. E., DeRobertis E. M. A homeo-box-containing gene expressed during oogenesis in Xenopus. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):157–162. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90201-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Mount S. M., Steitz J. A., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors is inhibited by antisera to small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):101–107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90212-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson B. M., Roberts B. E., Kuff E. L. Structural gene identification and mapping by DNA-mRNA hybrid-arrested cell-free translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4370–4374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Miller J. S., Roberts B. E. Purification and mapping of specific mRNAs by hybridization-selection and cell-free translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4927–4931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Wall R. A mechanism for RNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1877–1879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Grimm E. A., McGrogan M., Doyle M., Kawasaki E., Koths K., Mark D. F. Biological activity of recombinant human interleukin-2 produced in Escherichia coli. Science. 1984 Mar 30;223(4643):1412–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6367046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg U. B., Preiss A., Seifert E., Jäckle H., Knipple D. C. Production of phenocopies by Krüppel antisense RNA injection into Drosophila embryos. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):703–706. doi: 10.1038/313703a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Kleckner N. Translational control of IS10 transposition. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):683–691. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90401-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson M. L., Zamecnik P. C. Inhibition of Rous sarcoma viral RNA translation by a specific oligodeoxyribonucleotide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):285–288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Matsui H., Fujita T., Takaoka C., Kashima N., Yoshimoto R., Hamuro J. Structure and expression of a cloned cDNA for human interleukin-2. Nature. 1983 Mar 24;302(5906):305–310. doi: 10.1038/302305a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Weissmann C. Inhibition of Qbeta RNA 70S ribosome initiation complex formation by an oligonucleotide complementary to the 3' terminal region of E. coli 16S ribosomal RNA. Nature. 1978 Oct 26;275(5682):770–772. doi: 10.1038/275770a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomizawa J., Itoh T. Plasmid ColE1 incompatibility determined by interaction of RNA I with primer transcript. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6096–6100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A., Lu S. D., Mark D. F. Site-specific mutagenesis of the human interleukin-2 gene: structure-function analysis of the cysteine residues. Science. 1984 Jun 29;224(4656):1431–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.6427925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler M. E., Mullis K., Barnett J., Stroynowski I., Yanofsky C. Transcription termination at the tryptophan operon attenuator is decreased in vitro by an oligomer complementary to a segment of the leader transcript. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2181–2185. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota T., Lee F., Rennick D., Hall C., Arai N., Mosmann T., Nabel G., Cantor H., Arai K. Isolation and characterization of a mouse cDNA clone that expresses mast-cell growth-factor activity in monkey cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1070–1074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamecnik P. C., Stephenson M. L. Inhibition of Rous sarcoma virus replication and cell transformation by a specific oligodeoxynucleotide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):280–284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


