Abstract
Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor (PPAR) γ coactivator-1α (PGC-1α) is a potent transcriptional coactivator of oxidative metabolism and is induced in response to a variety of environmental cues. It regulates a broad array of target genes by coactivating a whole host of transcription factors. The estrogen-related receptor (ERR) family of nuclear receptors are key PGC-1α partners in the regulation of mitochondrial and tissue-specific oxidative metabolic pathways; these receptors also demonstrate strong physical and functional interactions with this coactivator. Here we perform comprehensive biochemical, biophysical, and structural analyses of the complex formed between PGC-1α and ERRγ. PGC-1α activation domain (PGC-1α2–220) is intrinsically disordered with limited secondary and no defined tertiary structure. Complex formation with ERRγ induces significant changes in the conformational mobility of both partners, highlighted by significant stabilization of the ligand binding domain (ERRγLBD) as determined by HDX (hydrogen/deuterium exchange) and an observed disorder-to-order transition in PGC-1α2–220. Small-angle X-ray scattering studies allow for modeling of the solution structure of the activation domain in the absence and presence of ERRγLBD, revealing a stable and compact binary complex. These data show that PGC-1α2–220 undergoes a large-scale conformational change when binding to the ERRγLBD, leading to substantial compaction of the activation domain. This change results in stable positioning of the N-terminal part of the activation domain of PGC-1α, favorable for assembly of an active transcriptional complex. These data also provide structural insight into the versatile coactivation profile of PGC-1α and can readily be extended to understand other transcriptional coregulators.
Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor (PPAR) γ coactivator-1α (PGC-1α) is a powerful transcriptional coactivator with an established role in key metabolic functions, and has been implicated in the pathogenesis of obesity, type 2 diabetes, neurodegeneration, and cardiomyopathy (1, 2). PGC-1α is unusual or even unique in its ability to respond to a wide variety of physiological signals, coactivate a broad range of transcription factors, and coordinate the regulation of oxidative metabolic gene programs in a tissue-specific manner (1–3). For example, PGC-1α is induced by exercise in skeletal muscle. In this tissue PGC-1α coactivates transcription factors such as nuclear receptors, nuclear respiratory factors, and myocyte-specific enhancer factors, and induces mitochondrial biogenesis, fatty acid oxidation, glucose and lipid uptake, angiogenesis, and resistance to atrophy (1, 4). A substantial portion of PGC-1α function in oxidative metabolism is mediated through the estrogen-related receptor (ERR) subfamily of nuclear receptors (3, 5). ERRγ is a member of the subfamily and plays a significant role in the regulation of energy homeostasis as well as in mitochondrial function (5, 6). PGC-1α and ERRγ share tissue specificity, have overlapping functions, and demonstrate a robust physical and functional interaction (7, 8). Following a coactivator-receptor interaction model (9), the interaction between PGC-1α and ERRγ is mediated at least in part by characteristic nuclear receptor (NR) boxes or LXXLL motifs (denoted as L1, L2, and L3 in Fig. 1 A and B) located within the activation domain of PGC-1α and the nuclear receptor ligand binding domain (LBD). The broad range of physiologic processes mediated by PGC-1α and the large repertoire of nuclear receptors with which it partners necessitate a deeper understanding of how the coactivator achieves specificity despite the similarity in its interactions with members of the superfamily (10–16). Structural analyses of these interactions have been restricted to the use of small peptides representative of single LXXLL motifs. Unfortunately, these studies have not yielded sufficient insights into the overall structure of PGC-1α and its correlation to function. An in-depth investigation of the PGC-1α activation domain (the primary mediator of these interactions) in the context of its interaction with ERRγLBD could help unravel the molecular basis for PGC-1α binding and specificity.
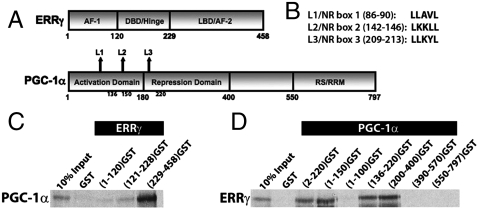
Fig. 1.
Molecular determinants of specificity and affinity for the binary complex. A schematic representation of (A) ERRγ and PGC-1α domains and (B) three NR boxes/LXXLL motifs (L1, L2, and L3). Interaction studies using GST-fusion fragments of (C) ERRγ and 35S-labeled PGC-1α or (D) PGC-1α and 35S-labeled ERRγ.
To address these questions, we performed a comprehensive biochemical and biophysical analysis of a binary complex formed between the activation domain of PGC-1α [PGC-1α2–220/PGC1α220] and the ERRγ ligand binding domain [ERRγLBD]. Combinations of several biophysical approaches (refer to SI Text, Glossary of Terms, for a summary of the terms and techniques used in the study) delineate properties of PGC1α220 that are responsible for its specificity and affinity for ERRγ. Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) studies provide unique solution models of the binary complex. Our results in combination with existing data allow us to propose a structural model of association involving the activation domain and also develop a generalized theory explaining the functional adaptability of PGC-1α.
Results
Biochemical Analysis of Specificity, Affinity, and Stoichiometry for PGC1α/ERRγ.
We first investigated the interaction between PGC-1α and ERRγ to establish requirements for binding in vitro. GST pull-down studies demonstrated binding between ERRγLBD and PGC1α220, and fragments nested within PGC1α220 (Fig. 1 A–D). These results in conjunction with coactivation studies (Fig. S1) were in agreement with previous data (7, 8). Our results showed that although L1 is dispensable to the interaction, L2 and L3 are both capable of mediating this interaction independent of each other. Isothermal calorimetry (ITC) is a thermodynamic technique that directly measures the heat released or absorbed when two biomolecules interact and provides thermodynamic parameters including binding constants; hydrogen/deuterium exchange (HDX) mass spectrometry is a study of the rate and percentage of the mass increase of a protein when the amide hydrogens are exchanged with solvent deuterium. These changes are indicative of conformational mobility/stability in the regions studied and can provide insight into the local changes in structure upon complex formation. Analysis of ERRγLBD interactions with PGC-1α136–220 (a fragment containing L2 and L3) by ITC showed that wild type had the highest binding affinity (Kd = 0.95 μM) for the LBD (Fig. S1, Table S1), consistent with data from HDX analysis (Fig. 2). HDX suggests the functional equivalence of PGC-1α136–220 and PGC1α220 in stabilizing the conformational mobility of ERRγLBD, as indicated by the reduction in deuterium exchange kinetics in helices 6, 7, 10/11, and 12 and the beta sheet region (Fig. 2). The noticeable decrease in both affinity and HDX kinetics of the LBD upon mutating L2 suggests that it is the major contributor to the interaction (Fig. 2, Table S1). The modest, yet important, contribution by L3 is evident in data from the L2 mutant; L3 shows micromolar affinity for the LBD in addition to muted stabilization of equivalent regions of the LBD as determined by HDX. The role of both L2 and L3 is underscored by the observation that only a combinatorial mutation involving both L2 and L3 has a dramatic effect.
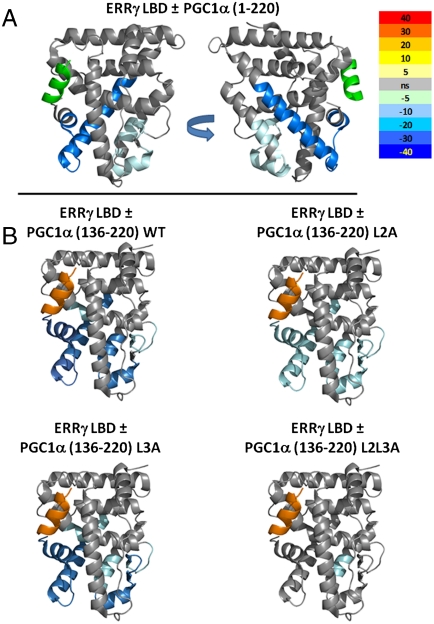
Fig. 2.
HDX analysis of the ERRγLBD/PGC-1α activation domain interaction. HDX analysis of ERRγLBD interaction was performed with five distinct constructs of PGC-1α activation domain. (A) ERRγLBD ± PGC1α220. (B) ERRγLBD ± PGC1α (136–220) WT, L2A, L3A, and L2L3A. The differential HDX between apo ERRγLBD and PGC-1α bound LBD is mapped onto PDB ID code 1KV6. The difference in the mean HDX across six time points for coactivator bound and unbound LBD is represented as percent change and colored according to the key. Gray, no change in HDX between bound and unbound LBD; light to dark blue, slower rates of HDX between compared conditions; yellow to red, faster rates of HDX between compared conditions.
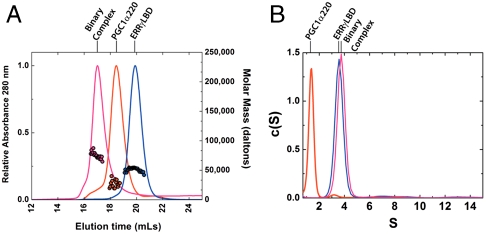
The binary complex between ERRγLBD and PGC1α220 was then further characterized by size-exclusion chromatography in-line with multiangle light scattering (SEC-MALS) and sedimentation velocity (SV) analysis by analytical ultracentrifugation. Parameters determined from SEC-MALS as well as SV analysis provide solution properties of the molecules such as molecular mass, shape, and size. SEC-MALS analysis demonstrates that PGC1α220 exists as a monomer in solution, with a retention time consistent with an extended shape. In contrast, ERRγLBD exists exclusively as a compact dimer (Fig. 3A, Table 1). In agreement with ITC analysis (Table S1), SEC-MALS analysis of the binary complex suggests a molar ratio of 1∶2 (PGC1α220∶ERRγLBD) (Table 1). A molecular mass of 82,747 Da also consistent with a 1∶2 complex, was derived by combining parameters determined from SEC and SV analysis (Fig. S2) (17). Taken together, the 1∶2 stoichiometry thus established for the interaction shows that a single coactivator molecule engages the ERRγLBD homodimer. Helix 12 stabilization seen from HDX data indicates that both L2 and L3 engage helix 12 of the LBD dimer, whereas the variation in binding constants for L2 and L3 (1.61 μM versus 8.69 μM), suggests an asymmetric interaction.
Fig. 3.
Biophysical properties of the binary complex. (A) Representative SEC-MALS analyses showing elution profiles for PGC1α220 (red), ERRγLBD (blue), and the binary complex (pink) on a Superdex 200 10/300 column at room temperature. Absorbance profiles are shown in relative units at 280 nm (left y axis). Shown as colored circles on each elution profile are the masses determined from MALS analysis; the right y axis denotes mass in daltons. (B) Sedimentation coefficient distribution [c(S)] analysis of sedimentation velocity data for PGC1α220 (red line, 38 μM at 4 °C), ERRγLBD (blue line, 61 μM at 20 °C), and the binary complex (pink line, 28 μM at 20 °C).
Table 1.
Biophysical properties of PGC1α220/ERRγLBD binary complex and its components
| SEC* |
MALS† |
SV |
Siegel and Monty |
QELS† |
|||
| Protein |
Rs (Å) |
Molar Mass‡ |
Stochiometry§ |
S20,w |
f/fo |
Molar Mass‡ |
Rh (Å) |
| PGC1α220 | 42.9 ± 0.5 | 23,945 ± 3,434 | Monomer (24,456) | 1.3 | 2.0 | 22,598 | ND¶ |
| ERRγLBD | 33.2 ± 0.13 | 53,673 ± 3,094 | Dimer (52,928) | 3.8 | 1.2 | 51,119 | 25.7 ± 1.2 |
| Complex | 51.7 ± 1.8 | 74,175 ± 473 | 1∶2 (77,386) | 4.0 | 1.5 | 82,747 | ND |
*The results presented are the average of 2–4 replicates.
†SEC-MALS-quasi-elastic light scattering (QELS) measurements were made at room temperature.
‡Molar masses are presented in units of daltons.
§Stoichiometry as inferred from experimentally determined molecular mass. In parentheses, theoretical values as computed from primary sequence using SEDNTERP are presented.
¶ND, not determined
PGC1α220 is Intrinsically Disordered.
Given the importance of the PGC1α220 domain for nuclear receptor coactivation, we examined the solution properties of this domain alone. Bioinformatic analysis of the PGC1α220 sequence indicates the presence of ordered regions in the N-terminal half of the protein, but clearly predicts significant disorder in the regions following L1 (Fig. S3). A protein of this mass is predicted to have Stokes radii (Rs) of 39.1, 41.1, and 52.6 Å, in the native, molten globule, and unfolded states, respectively (18). Despite being monomeric by mass as indicated by SEC-MALS, a Stokes radius of Rs of 42.9 Å ± 0.46 was determined, indicative of a molten-globular, extended conformation in solution (Fig. 3A, Table 1). This extended conformation is recapitulated in SV analysis, which at 4 °C yields a frictional coefficient ratio (f/fo) of 2.7 (a globular particle has an f/fo of approximately 1.2, whereas a value greater than 1.8 indicates asymmetry in shape), indicating an extremely elongated shape (Fig. 3B, Table 1). HDX analysis of PGC1α220 revealed that most of the backbone amides were fully exchanged after 10 s incubation with deuterium, consistent with the predicted disorder (Table S2). CD spectroscopy provides a qualitative and quantitative estimation of secondary structure in a macromolecular species. CD analysis of PGC1α220 estimated only 27% native secondary structure in the activation domain (Fig. 4A, Table 2).
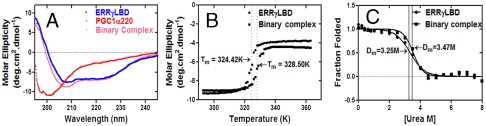
Fig. 4.
Thermodynamic and structural stability of the binary complex. (A) Far-UV CD spectra of PGC1α220 (red), ERRγLBD (blue), and binary complex (pink). Spectra were normalized to molar ellipticity, secondary structure was quantified using CDFIT and summarized in Table 2. (B) Thermal denaturation of ERRγLBD (●) and binary complex (▪). The CD signal at 222 nm was monitored as a function of temperature. (C) Chemical denaturation ERRγLBD (●) and binary complex (▪). Intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence was monitored as a function of increasing urea concentration. Tm and Dm values were calculated as described in Materials and Methods and are summarized in Table 3.
Table 2.
Characterization of secondary structure and thermal and chemical stability of the complex by CD and fluorescence
| PGC1α220 | ERRγLBD | Binary complex | ||
| Secondary structure* | % alpha | 21.69 (47-aa) | 68.06 (157-aa) | 52.38 (236-aa) |
| % beta | 5.39 | 2.35 | 4.76 | |
| % coil | 72.91 | 29.59 | 42.86 | |
| Thermal denaturation | Tm† [K] | Indeterminate | 324.42 ± 0.059750 | 328.51 ± 0.055400 |
| Chemical denaturation | Dm† [M]urea | Indeterminate | 3.25 ± 0.095 | 3.47 ± 0.075 |
*Secondary structure estimation was calculated using CDFIT.
†Tm and Dm values reported for each species are obtained from an average of three different experiments. The error reported is the standard deviation.
SAXS is an established method for the characterization of biological macromolecules in solution and is extremely well-suited to study flexible and extended macromolecules. Structural parameters such as the mean particle size (radius of gyration, Rg) and maximal intramolecular distance (Dmax) can be derived from SAXS analysis. These data can then be used to determine molecular characteristics such as mass, shape, and volume; furthermore, recent innovations allow for the three-dimensional modeling of molecular shape in solution at low resolution.
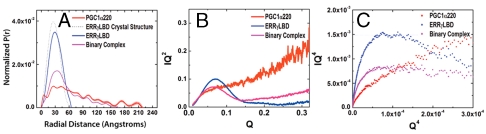
SAXS analysis of PGC1α220 yielded consistent data and indicated a monodisperse particle (Table 3, Table S3). By Flory’s law (19) a protein of this size is expected to have an Rg of 18.6 Å when natively folded and an Rg of 78.2 Å as an extended polymer. SAXS analysis of PGC1α220 determined an Rg of 60 Å and is consistent with other data that indicate a protein with high flexibility and low residual structure. This low level of compactness is further underscored by an Rs/Rg value of approximately 1.45 for PGC1α220, similar to that expected for a random coil (∼1.5), rather than that for a globular protein (∼0.8) or a premolten globule (∼0.9) (20, 21). The asymmetry in the P(r) profile derived from SAXS data for PGC1α220 with a Dmax of approximately 240 Å correlates to anisotropy in molecular shape (Fig. 5A). The Kratky and Porod–Debye plots (22–26) for PGC1α220 are clearly indicative of a largely disordered species lacking a well-packed core (Fig. 5 B and C). In summary, these orthogonal measurements clearly establish PGC1α220 as a predominantly disordered species with limited secondary structure.
Table 3.
Table of structural parameters derived from SAXS analysis
| Sample | Range of concentrations examined | Rg (Å) | Dmax (Å)* |
| mg/mL | |||
| PGC1α220 | 2.5–4.5 | 61.3† | 240 |
| ERRγLBD | 1.6–11.5 | 25.3 †,‡ | 90 |
| PGC1α220—ERRγLBD | 1.2–5.6 | 42.3†,‡ | 175 |
A complete listing of structural parameters derived from SAXS measurements is available in Table S3.
*As determined by GNOM analysis.
†By Guinier analysis.
‡Extrapolated to infinite dilution.
Fig. 5.
Solution properties of the binary complex and its individual components determined using SAXS. (A) Shape distribution [P(r)] functions derived from SAXS analysis for PGC1α220 (red), ERRγLBD (blue), and the binary complex (pink). (B) Kratky plot analysis for the proteins examined, where the intensity of scattering is plotted as IQ2 versus Q. I is the scattering intensity and Q is scattering angle (Q = 4π sin θ/λ). (C) Porod–Debye plot of the SAXS data for the samples examined in the study, shown as IQ4 versus Q4.
PGC1α220 Undergoes a Disorder-to-Order Transition upon Complex Formation with ERRγLBD.
Next we investigated the nature of complex assembly. HDX studies showed that despite the absence of HDX perturbations in PGC1α220 upon complex formation (Table S4), docking of the coactivator results in significant stabilization of the conformational mobility of ERRγLBD (Fig. 2). This result is in agreement with secondary structure analysis, which estimated 52% alpha-helical content in the binary complex (Table 2), illustrating an increase in total secondary structure induced by protein interaction. This phenomenon translates into increased stability of the binary complex, as seen in thermal and chemical denaturation studies (Fig. 4 B and C, Table 2). Despite the disordered nature of PGC1α220 alone, the increase in stability indicates that the interaction confers conformational stability to the complex.
The properties of this complex were further investigated using SV analysis (Table 1). The differences in f/f0 between ERRγLBD alone and the binary complex (1.2 versus 1.5) indicate a change from a compact to a more elongated state upon complex formation. The reduction in f/f0 between PGC1α220 and the binary complex (2.0 versus 1.5) is suggestive of coactivator compaction upon complex formation.
SAXS analysis provides structural insight into the nature of these differences in shape. Structural parameters derived from SAXS measurements on the binary complex were constant across the range of concentrations examined (Fig. 5A, Table S3). A comparison of the Rg and Dmax values for the binary complex upon extrapolation to infinite dilution (45 Å and 175 Å) and PGC1α220 (60 Å and 240 Å) shows a contraction of the maximum dimension upon complex formation, whereas the Kratky and Porod–Debye plots for the complex are indicative of a well-folded globular particle (Fig. 5 B and C). If the PGC1α220 component remained intrinsically disordered upon complex formation, we would have expected to observe an even larger spatial extent for the complex than seen with either component alone. Combined, these experiments indicate that PGC1α220 undergoes a disorder-to-order transition (27, 28) upon docking onto the LBD, resulting in a binary complex, which is significantly more compact and structured.
Shape Reconstruction of PGC1α220/ERRγLBD Binary Complex from SAXS Data.
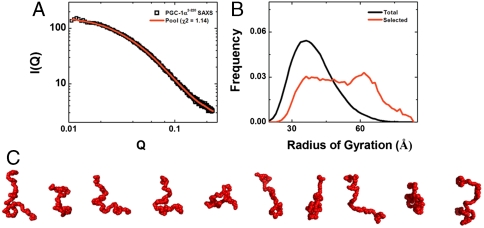
For well-folded globular species, SAXS data can be used to reconstruct solution shape at low resolution (29, 30). However, these methods are not suitable for modeling intrinsically disordered proteins such as PGC1α220. Instead, these species are better described as ensembles in solution. Using the ensemble optimization method (EOM) (31, 32) (see Materials and Methods) we identified a pool of conformers that collectively reproduce the experimental solution data (Fig. 6 A and B). A gallery of EOM-generated models for PGC1α220 clearly illustrates the lack of globularity and the conformational diversity that is compatible with the intrinsic properties of the protein (Fig. 6C).
Fig. 6.
Shape reconstruction for PGC1α220 from SAXS data using EOM analysis. (A) EOM fit (red line) to the SAXS data for PGC1α220 (open squares), with χ2 of 1.14 for the best selected pool solution. (B) Rg distributions for the pool (black) and optimized (red) ensembles generated by EOM analysis. (C) Representative gallery of bead models for PGC1α220 derived from EOM analysis. The bead radius used in these models is 3.4 Å, and this figure was generated using PyMOL.
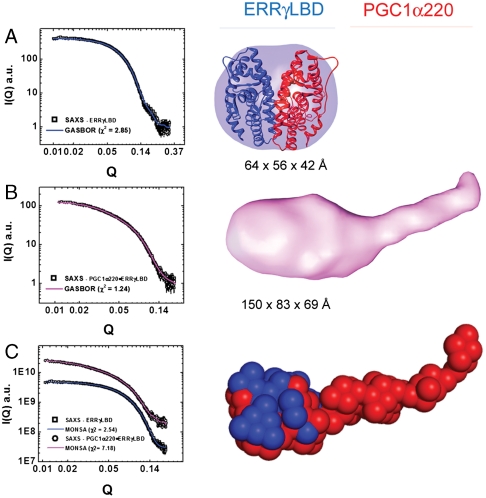
Shape reconstructions for ERRγLBD were generated using the programs DAMMIN and GASBOR (29, 30). Both approaches reproducibly yielded envelopes with good correlations between experimental and calculated scattering data [sqrt(χ) ∼1.5; normalized spatial discrepancies (NSDs) ranging from 1.0 to 1.3] (Fig. 7A). The averaged envelope is a globular particle with a dimension of 76 × 52 × 48 Å (Fig. S4). Shape reconstructions of the binary complex were also performed in the same manner and the GASBOR results are discussed here. Reproducible envelopes with good correlations between experimental and calculated scattering data were obtained [sqrt(χ) ∼1.2, NSDs ranging from 1.4 to 1.5]; because of the inherent asymmetry suggested by its 1∶2 stochiometry, no symmetry restraints were applied (Fig. 7B). The final averaged envelope is an asymmetric and elongated prolate ellipsoid with a dimension of 83 × 150 × 69 Å (Fig. S4). The hydrodynamic properties calculated for these shapes also closely resemble those determined experimentally (Table S5).
Fig. 7.
Shape reconstruction of ERRγLBD and its binary complex with PGC1α220. (A, Left) GASBOR fit (blue line) to primary scattering data (black squares) for ERRγLBD. (Right) SAXS envelope calculated using GASBOR and rigid body docking of structural model of ERRγLBD into the envelope (B, Left) GASBOR fit (red line) to primary scattering data (black squares) for binary complex. (Right) SAXS envelope of the binary complex calculated using GASBOR. (C, Left) MONSA fit to primary data (ERRγLBD, blue line and black squares; binary complex, red line and black squares), (Right) SAXS envelope of the binary complex calculated using MONSA.
Solution Data-Based Structural Model for the Binary Complex.
Finally, we combined our results from SAXS analysis with the existing structural data on ERRγLBD [Protein Data Bank (PDB) ID code 1KV6] to model the binary complex. We first evaluated the scattering data and solution parameters for the LBD against the available crystal structure using CRYSOL and HYDROPRO (see Materials and Methods), respectively, demonstrating general concordance, with some variations observed between the crystallographic model and its solution state (Table 3, Fig. S4). Superposition of the crystal structure into the molecular envelopes reveals good spatial agreement with the solution data (Fig. 7A) and allows inference of the position of PGC1α220 relative to the ERRγLBD domain (Fig. 7B). We then implemented the program MONSA, which derives the relative positions of the different components of a composite particle by simultaneously fitting multiple scattering profiles from both the overall particle and its component parts (29, 33). By this approach, the shape determined recapitulates the shapes observed by the DAMMIN and GASBOR approaches, and corroborates our assignment of locating ERRγLBD (Fig. 7C).
This analysis provides important insights into the solution structure and mechanism of interaction between PGC1α220 and ERRγLBD. SAXS analysis shows how the highly disordered region engages the well-structured LBD to form an elongated and asymmetric, but overall more compact and globular structure (Fig. 7 B and C). Although SAXS data alone cannot provide high-resolution structural details of the binding interface, a comprehensive experimental approach allows us to propose an interaction model for the binary complex (Fig. 8). Our studies reveal that PGC1α220 is involved in a bipartite interaction with the LBD dimer through high affinity L2 and low affinity L3 interactions. The binding of a single PGC1α220 molecule to the LBD dimer is facilitated by the intrinsic disorder in the coactivator. PGC1α220 simultaneously occupies coactivator grooves on both LBD units and stabilizes the dimerization interface by navigating the region via the flexible spacer. Such an asymmetric interaction clearly distinguishes PGC-1α/ERRγ complex from those with other receptors such as PPARγ, hepatocyte nuclear factor-4α (HNF4α), and ERRα (Fig. S5) (13, 15, 16) and has important functional consequences.
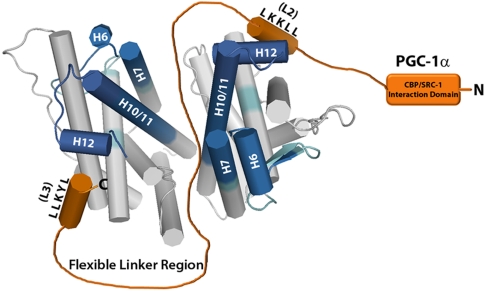
Fig. 8.
Predicted interaction model for the binary complex. A structural model for ERRγLBD and PGC1α220 interaction proposed based on a summary of our data. HDX data is mapped onto the ERRγLBD dimer (PDB ID code 1KV6) to indicate regions of the LBD affected by the interaction and PGC1α220 is shown in orange.
The solution model also illustrates the structure-function relationship of the activation domain with consequences to PGC-1α-mediated transcription complex assembly. Our data show that PGC1α220 is tethered to the LBD via LXXLL-mediated interactions. With the C-terminal portion of PGC1α220 (PGC-1α136–220) wrapped across the LBD, it is evident that the N-terminal half (PGC-1α2–135) contributes to the asymmetry in shape seen in the envelope structure. This region contains the CREB binding protein (CBP)/p300 and steroid receptor coactivator-1 (SRC-1) interaction domain and appears to be locked into a stable position in the binary complex in comparison to the isolated structure. The compaction and securing of the LXXLL motif-containing region stably positions the N-terminal portion unhindered by the C-terminal disorder, in an orientation accessible for CBP/p300 recruitment, a crucial step in the assembly of an active transcriptional complex.
Discussion
PGC-1α is a highly versatile coactivator, featuring an extremely broad repertoire of transcriptional partners. This versatility is presumed to be the biochemical basis for a huge array of physiological processes under control or modulated by PGC-1α. The ERRs are key PGC-1α partners with the PGC-1α/ERR interaction complexes regulating energy homeostasis in metabolically active tissues. These functions make them attractive drug design targets for metabolic disorders, necessitating a thorough understanding of the molecular nature of these interactions. Despite the existing body of work examining PGC-1α interactions with nuclear receptors, the paucity of structural data has left important questions about its function unanswered. The work presented here provides a unique structural model for PGC-1α interaction with ERRγ and establishes a foundation for its functional adaptability.
Our multipronged approach unravels features of the PGC-1α/ERRγ interaction elusive to traditional structural methods and allows us to propose an interaction model for the binary complex. This model is distinguished from those proposed for SRC-1 binding to PPARγLBD (34) and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor (VDR)–retinoid X receptor heterodimer (35), in that it involves the entire activation domain of PGC-1α and is supported by a low resolution solution model.
The results presented here firmly establish that intrinsic disorder in PGC-1α is the principal physical basis for its versatility. For example, despite the high degree of sequence similarity, PGC-1α is able to distinguish between ERRγ and ERRα by engaging distinct interaction interface and receptor∶coactivator stoichiometry; this ability is highly dependent on its structural flexibility. These differences have important consequences vis-à-vis drug design targeting PGC-1α interactions with the ERRs and provide a framework for the design of subtype specific drugs. Furthermore, such structural flexibility presumably allows PGC-1α to simultaneously engage transcription factors as well as chromatin remodeling proteins (CBP/p300). We also provide a biophysical and spatial illustration of transcription factor-induced conformational changes in PGC-1α and can infer the functional correlation between PGC-1α structure and its coactivation. Interaction between the two partners restricts conformational flexibility of the coactivator and provides structural stability to the N-terminal region of the activation domain; this series of events then primes the coactivator for CBP/p300 recruitment, an important step in transcriptional activation.
These results demonstrate the utility of combining different biophysical methods to study PGC-1α interactions and expose the absence of equivalent data from traditional structural analysis; the lack of electron density for these regions in crystal structures is directly attributable to the intrinsic disorder (13, 15). Transcriptional coregulators are typically characterized by large molecular size and small structured domains separated by long stretches of disorder (36, 37). Recent studies including our current work demonstrate that SAXS is well-suited for the study of coregulator structure (16), provide a strong case for the continued application of SAXS as a complementary technique to traditional structural studies of transcriptional coregulators, and could contribute to a comprehensive understanding of these interactions.
Materials and Methods
Detailed methods are available in SI Text.
Cloning, Protein Expression, and Purification.
Protein domains were cloned as GST-fusion or His-tagged proteins and purified by affinity chromatography using the manufacturer’s protocols (GE Healthcare and Qiagen, respectively).
Domain-Mapping Studies.
GST pull-down studies were performed by incubating Sepharose bead-bound GST-fusion protein with in vitro translated labeled protein (using a Promega T7 TNT reticulocyte lysate kit) and bound protein was detected using autoradiography.
Isothermal Titration Calorimetry.
ITC experiments were performed on a VP-ITC Microcal Isothermal Titration Calorimeter (GE Healthcare) following manufacturer’s protocol and the resulting data analyzed using the software Origin 7.0 (MicroCal).
Size-Exclusion Chromatography and Multiangle Light Scattering.
SEC-MALS experiments were performed using a MALS detector coupled in-line with size-exclusion chromatography and an interferometric refractometer. Data analysis was performed using ASTRA software version 5.2 (Wyatt Technology Corp.).
Sedimentation Velocity Analysis.
Sedimentation velocity ultracentrifugation experiments were performed at 25 °C with an XL-A analytical ultracentrifuge (Beckman) and a TiAn60 rotor. Data were fit using SEDFIT (38) to determine S and f/f0 and SEDNTERP was used to determine solvent density and viscosity.
HDX Mass Spectrometry.
HDX experiments were performed as described previously (39). Briefly, protein solutions consisting either of individual proteins or of relevant complexes were exchanged into an equivalent deuterium buffer solution, exchange quenched, and the peptides subjected to mass spectrometry. Data were processed using in-house software.
Bioinformatic Analyses.
For structural variability predictions for PGC1α220, the DISOPRED2 algorithm was used, which predicts intrinsic disorder from primary sequence information.
CD Spectroscopy.
CD spectra were measured on a J-715 Jasco spectropolarimeter and normalized data was processed using CDFIT and JASCO spectral analysis software.
Fluorescence Spectroscopy.
Chemical unfolding of the proteins was characterized using changes in intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence during urea denaturation. Data was collected on a T-format PTI QuantaMaster C-61 spectrofluorimeter following standard protocol and analyzed with Prism 5 (GraphPad).
Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering.
X-ray scattering data were measured using synchrotron radiation; specific details are provided in SI Text. Forward scattering from the samples examined was recorded on a CCD detector and circularly averaged to yield one-dimensional intensity profiles as a function of Q. Scattering data was analyzed using Guinier, Kratky, and Porod–Debye plots, as well as the inverse Fourier transform using the program GNOM (40). Shape analyses using the programs EOM (32), DAMMIN (29), GASBOR (30), and MONSA (29) were performed as described in SI Text.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments.
We thank Drs. Jorge L. Ruas, Sandra Kleiner, and Chi Wang for helpful discussions, Prof. Scott Banta (Columbia University) for use of laboratory equipment, Bruce Pascal and Scott Novick for help with hydrogen/deuterium exchange data acquisition and tools for data analysis and Gregory Hura, Jane Tanamachi, Kevin Dyer, and Michael Hammel [Advanced Light Source (ALS)], and Richard Gillilan [Cornell High Energy Synchrotron Source (CHESS)] for assistance with data collection. CHESS is supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF) and National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Institute of General Medical Sciences via NSF award DMR-0936384, and the MacCHESS resource is supported by NIH/National Center for Research Resources award RR-01646. X-ray scattering and diffraction technologies and their applications to the determination of macromolecular shapes and conformations at the SIBYLS beamline at the ALS, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, are supported in part by the Department of Energy (DOE) program Integrated Diffraction Analysis Technologies and the DOE program Molecular Assemblies Genes and Genomics Integrated Efficiently under contract DE-AC02-05CH11231 with the US Department of Energy. This work was supported by NIH Grants R01 DK54477 and R01 DK061562 (to B.M.S), R01 GM084041 (to P.R.G), U54GM074958 and U54GM094597 (to Northeast Structural Genomics Consortium), and Susan Komen Breast Cancer Foundation Postdoctoral Fellowship and the Naomi Berrie Fellowship for Diabetes Research (S.D.).
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1113813108/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Lin J, Handschin C, Spiegelman BM. Metabolic control through the PGC-1 family of transcription coactivators. Cell Metab. 2005;1:361–370. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2005.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ventura-Clapier R, Garnier A, Veksler V. Transcriptional control of mitochondrial biogenesis: The central role of PGC-1alpha. Cardiovasc Res. 2008;79:208–217. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvn098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jornayvaz FR, Shulman GI. Regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis. Essays Biochem. 2010;47:69–84. doi: 10.1042/bse0470069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Olesen J, Kiilerich K, Pilegaard H. PGC-1alpha-mediated adaptations in skeletal muscle. Pflugers Arch. 2010;460:153–162. doi: 10.1007/s00424-010-0834-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Giguere V. Transcriptional control of energy homeostasis by the estrogen-related receptors. Endocr Rev. 2008;29:677–696. doi: 10.1210/er.2008-0017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dufour CR, et al. Genome-wide orchestration of cardiac functions by the orphan nuclear receptors ERRalpha and gamma. Cell Metab. 2007;5:345–356. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2007.03.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Huss JM, Kopp RP, Kelly DP. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor coactivator-1alpha (PGC-1alpha) coactivates the cardiac-enriched nuclear receptors estrogen-related receptor-alpha and -gamma. Identification of novel leucine-rich interaction motif within PGC-1alpha. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:40265–40274. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M206324200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Liu D, Zhang Z, Teng CT. Estrogen-related receptor-gamma and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1alpha regulate estrogen-related receptor-alpha gene expression via a conserved multi-hormone response element. J Mol Endocrinol. 2005;34:473–487. doi: 10.1677/jme.1.01586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Xu L, Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG. Coactivator and corepressor complexes in nuclear receptor function. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1999;9:140–147. doi: 10.1016/S0959-437X(99)80021-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bourdoncle A, et al. The nuclear receptor coactivator PGC-1alpha exhibits modes of interaction with the estrogen receptor distinct from those of SRC-1. J Mol Biol. 2005;347:921–934. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.01.048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Greschik H, et al. Communication between the ERRalpha homodimer interface and the PGC-1alpha binding surface via the helix 8–9 loop. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:20220–20230. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M801920200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kallen J, et al. Evidence for ligand-independent transcriptional activation of the human estrogen-related receptor alpha (ERRalpha): Crystal structure of ERRalpha ligand binding domain in complex with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor coactivator-1alpha. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:49330–49337. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M407999200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Li Y, Kovach A, Suino-Powell K, Martynowski D, Xu HE. Structural and biochemical basis for the binding selectivity of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma to PGC-1alpha. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:19132–19139. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M802040200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Puigserver P, et al. Activation of PPARgamma coactivator-1 through transcription factor docking. Science. 1999;286:1368–1371. doi: 10.1126/science.286.5443.1368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Rha GB, Wu G, Shoelson SE, Chi YI. Multiple binding modes between HNF4alpha and the LXXLL motifs of PGC-1alpha lead to full activation. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:35165–35176. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.052506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jin KS, et al. Small-angle X-ray scattering studies on structures of an estrogen-related receptor alpha ligand binding domain and its complexes with ligands and coactivators. J Phys Chem B . 2008;112:9603–9612. doi: 10.1021/jp800120r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Siegel LM, Monty KJ. Determination of molecular weights and frictional ratios of proteins in impure systems by use of gel filtration and density gradient centrifugation. Application to crude preparations of sulfite and hydroxylamine reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966;112:346–362. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Uversky VN. Use of fast protein size-exclusion liquid chromatography to study the unfolding of proteins which denature through the molten globule. Biochemistry. 1993;32:13288–13298. doi: 10.1021/bi00211a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hyeon C, Dima RI, Thirumalai D. Size, shape, and flexibility of RNA structures. J Chem Phys. 2006;125:194905. doi: 10.1063/1.2364190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Damaschun G, et al. Streptokinase is a flexible multi-domain protein. Eur Biophys J. 1992;20:355–361. doi: 10.1007/BF00196594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gast K, et al. Compactness of protein molten globules: Temperature-induced structural changes of the apomyoglobin folding intermediate. Eur Biophys J. 1994;23:297–305. doi: 10.1007/BF00213579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Feigin L, Svergun DI. Structural Analysis by Small-Angle X-ray and Neutron Scattering. New York: Plenum; 1987. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Glatter O, Kratky O. Small Angle X-ray Scattering. London: Academic; 1982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Semisotnov GV, et al. Protein globularization during folding. A study by synchrotron small-angle X-ray scattering. J Mol Biol. 1996;262:559–574. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Uversky VN, et al. Anion-induced folding of Staphylococcal nuclease: Characterization of multiple equilibrium partially folded intermediates. J Mol Biol. 1998;278:879–894. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1998.1741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Rambo RP, Tainer JA. Characterizing flexible and intrinsically unstructured biological macromolecules by SAS using the Porod–Debye law. Biopolymers. 2011;95:559–571. doi: 10.1002/bip.21638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Dyson HJ, Wright PE. Intrinsically unstructured proteins and their functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:197–208. doi: 10.1038/nrm1589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Fong JH, et al. Intrinsic disorder in protein interactions: Insights from a comprehensive structural analysis. PLoS Comput Biol. 2009;5:e1000316. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Svergun DI. Restoring low resolution structure of biological macromolecules from solution scattering using simulated annealing. Biophys J. 1999;76:2879–2886. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(99)77443-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Svergun DI, Petoukhov MV, Koch MH. Determination of domain structure of proteins from X-ray solution scattering. Biophys J. 2001;80:2946–2953. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(01)76260-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bernado P. Effect of interdomain dynamics on the structure determination of modular proteins by small-angle scattering. Eur Biophys J. 2010;39:769–780. doi: 10.1007/s00249-009-0549-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bernado P, Mylonas E, Petoukhov MV, Blackledge M, Svergun DI. Structural characterization of flexible proteins using small-angle X-ray scattering. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:5656–5664. doi: 10.1021/ja069124n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Svergun DI, Nierhaus KH. A map of protein-rRNA distribution in the 70 S Escherichia coli ribosome. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:14432–14439. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.19.14432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Nolte RT, et al. Ligand binding and co-activator assembly of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. Nature. 1998;395:137–143. doi: 10.1038/25931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Zhang J, et al. DNA binding alters coactivator interaction surfaces of the intact VDR–RXR complex. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011;18:556–564. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Huang P, Chandra V, Rastinejad F. Structural overview of the nuclear receptor superfamily: Insights into physiology and therapeutics. Annu Rev Physiol. 2010;72:247–272. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021909-135917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Bulynko YA, O’Malley BW. Nuclear receptor coactivators: Structural and functional biochemistry. Biochemistry. 2011;50:313–328. doi: 10.1021/bi101762x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Schuck P. A model for sedimentation in inhomogeneous media. I. Dynamic density gradients from sedimenting co-solutes. Biophys Chem. 2004;108:187–200. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2003.10.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Chalmers MJ, et al. Probing protein ligand interactions by automated hydrogen/deuterium exchange mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2006;78:1005–1014. doi: 10.1021/ac051294f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Semenyuk AV, Svergun DI. Gnom—a program package for small-angle scattering data-processing. J Appl Crystallogr. 1991;24:537–540. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.