Abstract
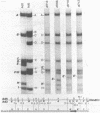
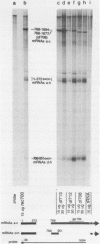
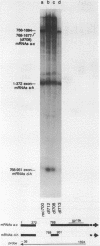
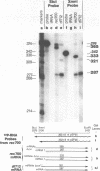
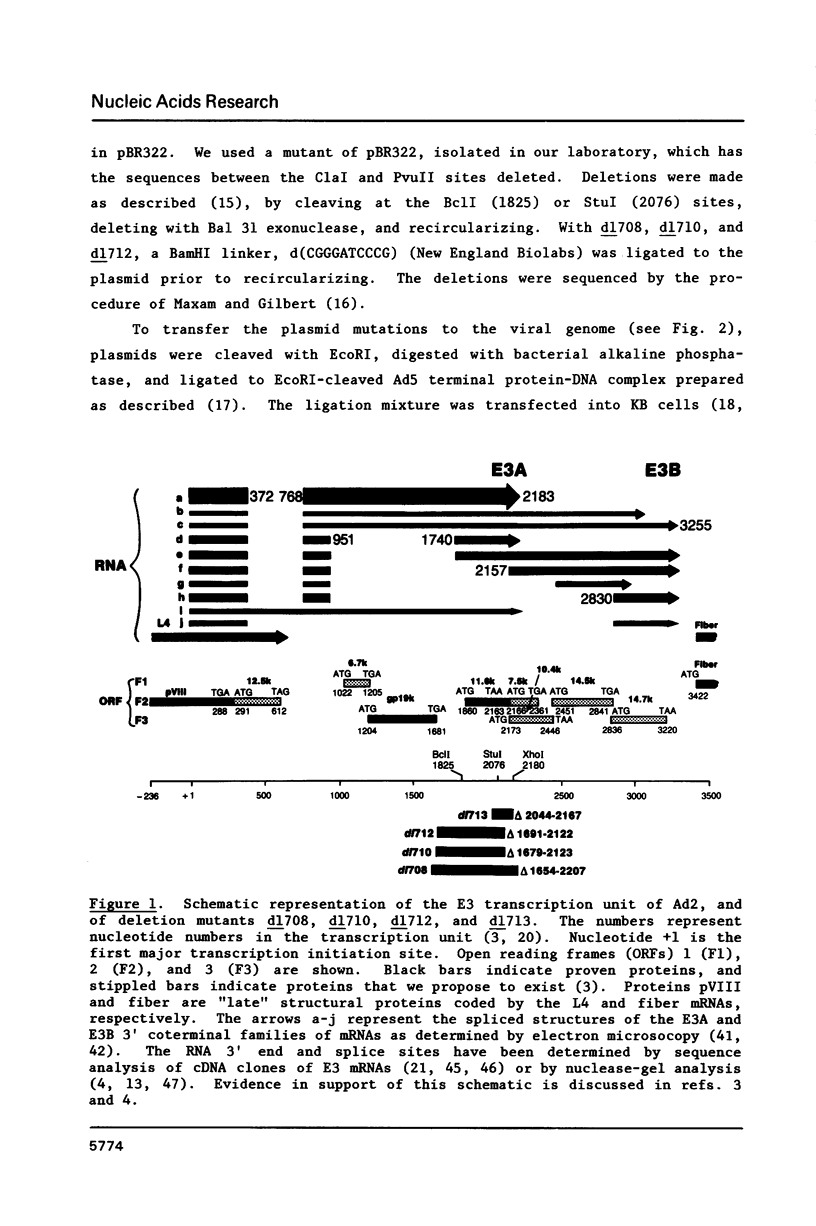
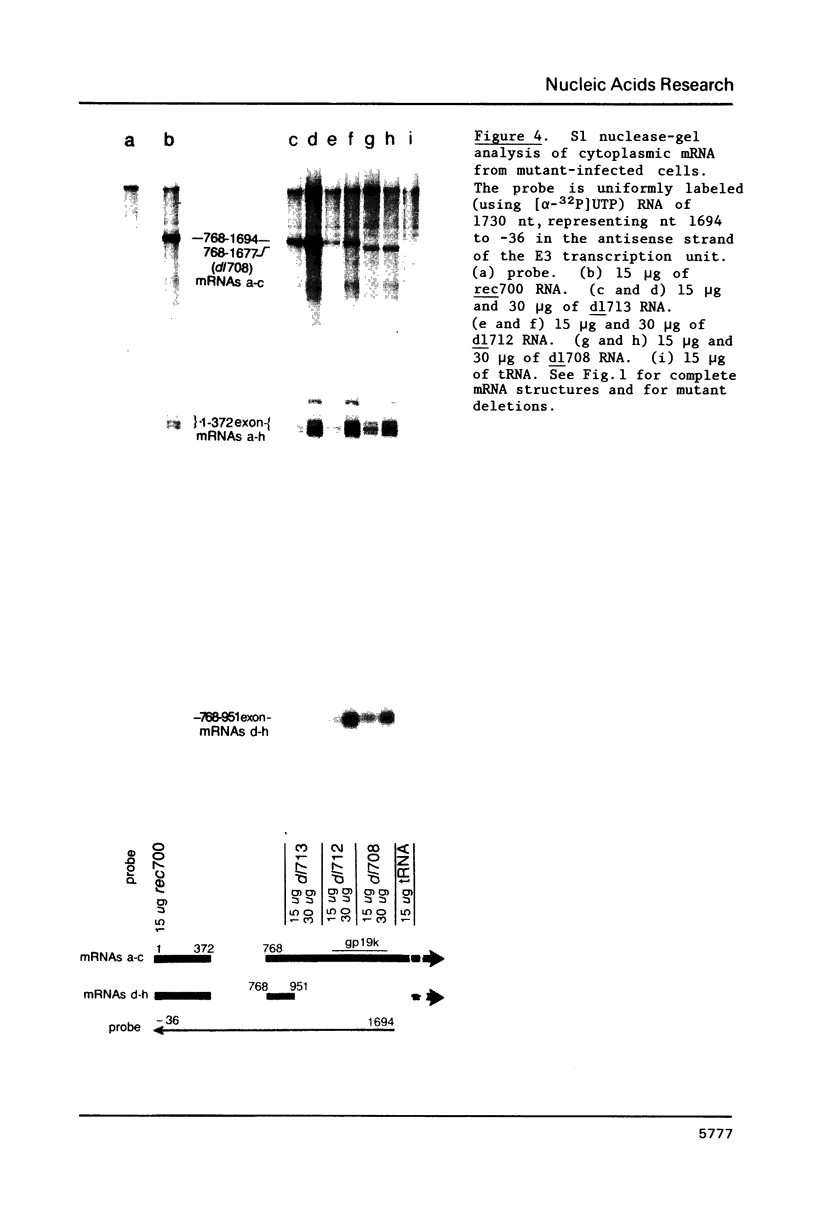
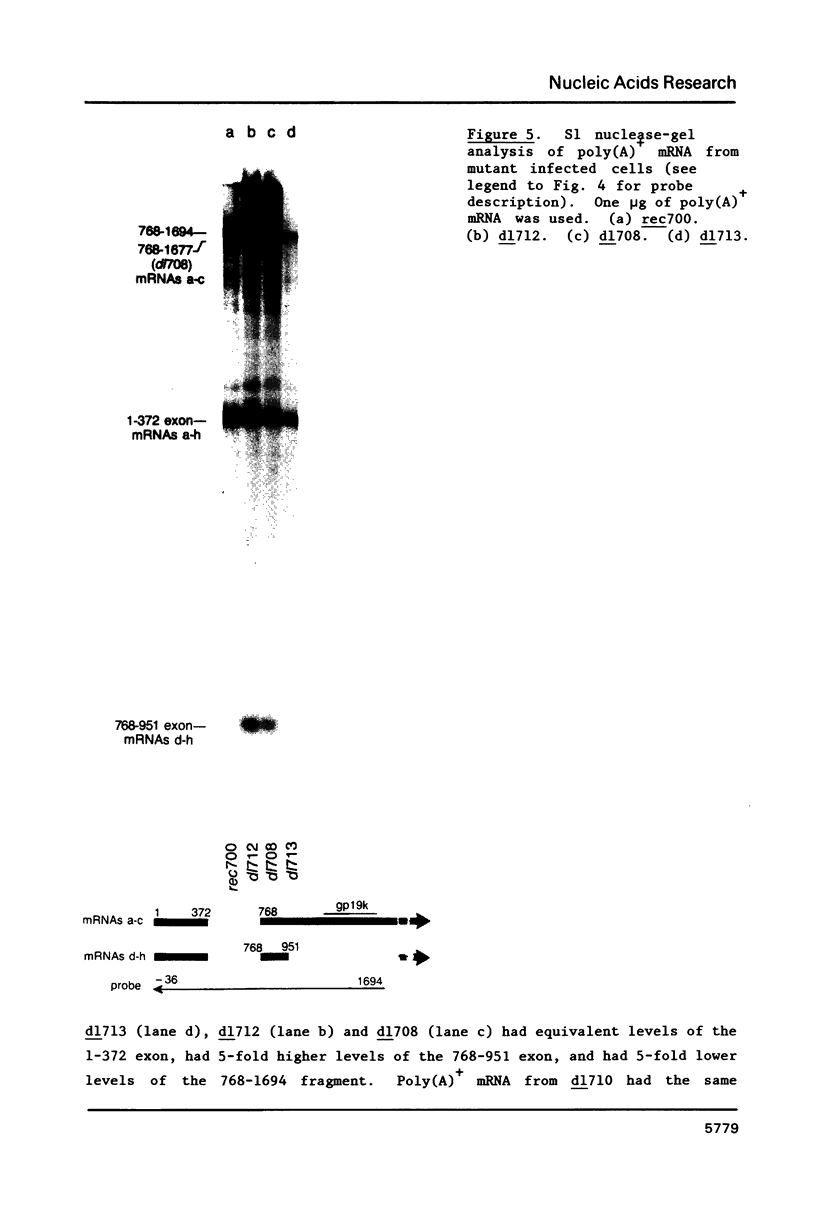
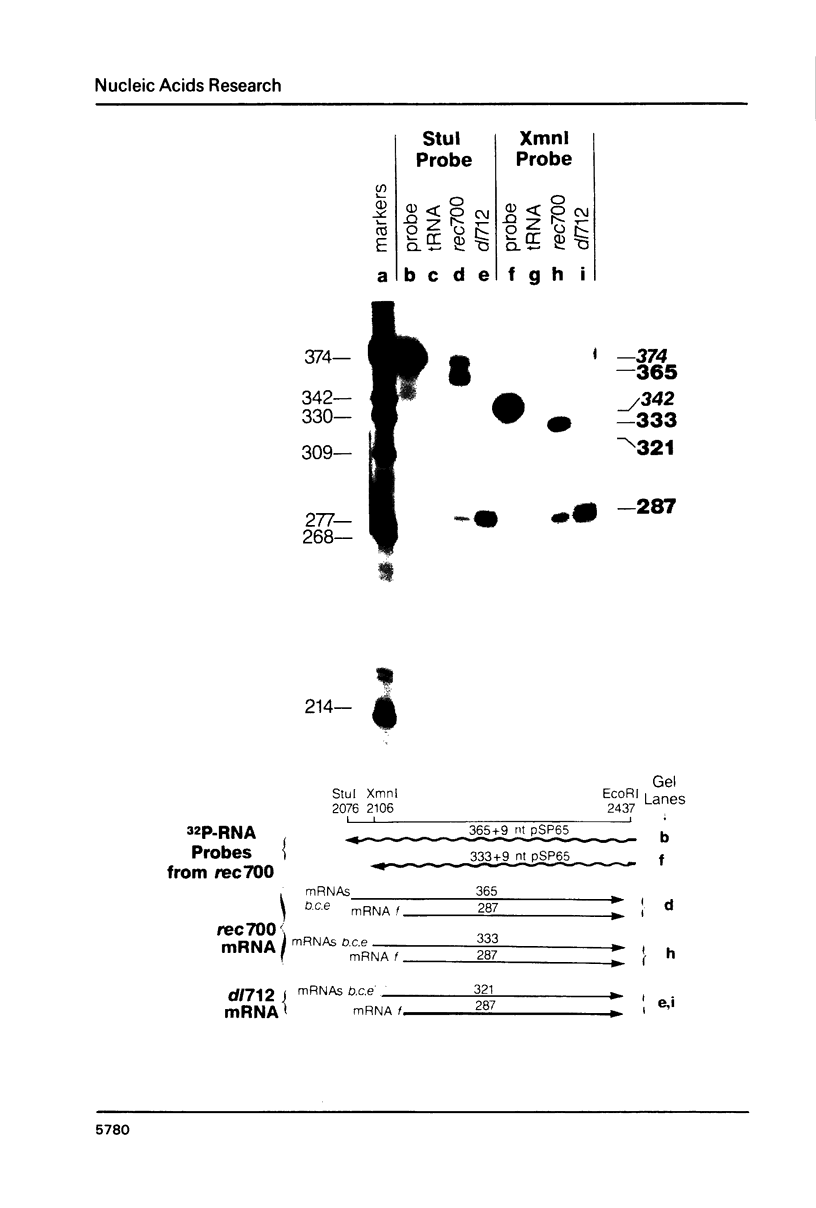
Region E3 of adenovirus is a "complex" transcription unit: i.e. different mRNAs and proteins arise by differential RNA 3' end selection and differential splicing of the primary transcript. We are using viable virus mutants to understand the controls that dictate the specificity and efficiency of the RNA processing signals. We describe a novel class of deletion mutations that enhance a natural 5' splice site located approximately 740 nucleotides (nt) upstream. In particular, deletions within nt 1691-2044 in the E3 transcription unit result in a 5-fold enhancement of the 5' splice site at nt 951 (as reflected in steady-state mRNA). The effect is specific, because the deletions do not affect the 5' splice site at nt 372, and because deletions within nt 2044-2214 do not affect either the 951 or the 372 5' splice sites. As a consequence of the enhanced splicing at the 951 5' site, synthesis of the major E3 mRNA and the major E3 protein (gp19K) are dramatically reduced. At least one of the natural 3' splice sites, located at nt 2157, is the recipient of the enhanced splicing at the 951 5' splice site. We conclude that sequences located within nt 1691-2044 affect (probably in cis) splicing at the 951 5' splice site. We speculate that nt 1691-2044 includes a splicing control region which functions to suppress splicing at the 951 5' splice site.
Full text
PDF













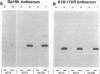
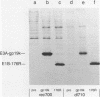
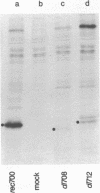
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed C. M., Chanda R., Stow N., Zain B. S. The sequence of 3'-termini of mRNAs from early region III of adenovirus 2. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):297–301. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Structure of the adenovirus 2 early mRNAs. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):695–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90252-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. RNA splicing: three themes with variations. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):713–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90527-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinnadurai G., Chinnadurai S., Brusca J. Physical mapping of a large-plaque mutation of adenovirus type 2. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):623–628. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.623-628.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Broker T. R., Lewis J. B. Complex splicing patterns of RNAs from the early regions of adenovirus-2. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 25;134(2):265–303. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Broker T. R. The spliced structures of adenovirus 2 fiber message and the other late mRNAs. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):497–510. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Sharp P. A. A gene chimaera of SV40 and mouse beta-globin is transcribed and properly spliced. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):378–382. doi: 10.1038/289378a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cladaras C., Bhat B., Wold W. S. Mapping the 5' ends, 3' ends, and splice sites of mRNAs from the early E3 transcription unit of adenovirus 5. Virology. 1985 Jan 15;140(1):44–54. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90444-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cladaras C., Wold W. S. DNA sequence of the early E3 transcription unit of adenovirus 5. Virology. 1985 Jan 15;140(1):28–43. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90443-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr Variety in the level of gene control in eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):365–371. doi: 10.1038/297365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobkin C., Pergolizzi R. G., Bahre P., Bank A. Abnormal splice in a mutant human beta-globin gene not at the site of a mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domdey H., Apostol B., Lin R. J., Newman A., Brody E., Abelson J. Lariat structures are in vivo intermediates in yeast pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):611–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90468-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost E., Williams J. Mapping temperature-sensitive and host-range mutations of adenovirus type 5 by marker rescue. Virology. 1978 Nov;91(1):39–50. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90353-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Piatak M., Mertz J. E., Weissman S. M., Lebowitz P. Altered utilization of splice sites and 5' termini in late RNAs produced by leader region mutants of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):610–624. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.610-624.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M., Wold W. S. Human adenoviruses: growth, purification, and transfection assay. Methods Enzymol. 1979;58:425–435. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)58157-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harter M. L., Shanmugam G., Wold W. S., Green M. Detection of adenovirus type 2-induced early polypeptides using cycloheximide pretreatment to enhance viral protein synthesis. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):232–242. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.232-242.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang L. S., Park J., Gilboa E. Role of intron-contained sequences in formation of moloney murine leukemia virus env mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2289–2297. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hérissé J., Courtois G., Galibert F. Nucleotide sequence of the EcoRI D fragment of adenovirus 2 genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2173–2192. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Alwine J., Goldman N., Gruss P., Jay G. New chimeric splice junction in adenovirus type 2-simian virus 40 hybrid viral mRNA. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):143–151. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.143-151.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Gruss P., Dhar R., Lai C. J. Processing and expression of early SV40 mRNA: a role for RNA conformation in splicing. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):85–92. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90356-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchingman G. R., Westphal H. The structure of adenovirus 2 early nuclear and cytoplasmic RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1980 Feb 15;137(1):23–48. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90155-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühne T., Wieringa B., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Evidence against a scanning model of RNA splicing. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):727–733. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01492.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford C. J., Gallwitz D. Evidence for an intron-contained sequence required for the splicing of yeast RNA polymerase II transcripts. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):519–527. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90433-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford C. J., Klinz F. J., Donath C., Gallwitz D. Point mutations identify the conserved, intron-contained TACTAAC box as an essential splicing signal sequence in yeast. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):645–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90344-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. C., Roeder R. G., Wold W. S. DNA sequences affecting specific initiation of transcription in vitro from the EIII promoter of adenovirus 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):41–45. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. The pathway of eukaryotic mRNA formation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:441–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Konarska M. M., Grabowski P. J., Hardy S. F., Sharp P. A. Lariat RNA's as intermediates and products in the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Science. 1984 Aug 31;225(4665):898–903. doi: 10.1126/science.6206566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Jansson M., Philipson L. Synthesis and genomic site for an adenovirus type 2 early glycoprotein. J Mol Biol. 1980 Feb 5;136(4):375–394. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90396-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Jörnvall H., Zabielski J. Multiple mRNA species for the precursor to an adenovirus-encoded glycoprotein: identification and structure of the signal sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6349–6353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikielny C. W., Teem J. L., Rosbash M. Evidence for the biochemical role of an internal sequence in yeast nuclear mRNA introns: implications for U1 RNA and metazoan mRNA splicing. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):395–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90373-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rautmann G., Matthes H. W., Gait M. J., Breathnach R. Synthetic donor and acceptor splice sites function in an RNA polymerase B (II) transcription unit. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2021–2028. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02085.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. R., Pikielny C. W., Rosbash M. In vivo characterization of yeast mRNA processing intermediates. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90467-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross S. R., Flint S. J., Levine A. J. Identification of the adenovirus early proteins and their genomic map positions. Virology. 1980 Jan 30;100(2):419–432. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90533-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Green M. R. Excision of an intact intron as a novel lariat structure during pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):317–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90553-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindler K. R., Rosser D. S., Berk A. J. Analysis of adenovirus transforming proteins from early regions 1A and 1B with antisera to inducible fusion antigens produced in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):132–141. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.132-141.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stålhandske P., Persson H., Perricaudet M., Philipson L., Pettersson U. Structure of three spliced mRNAs from region E3 of adenovirus type 2. Gene. 1983 May-Jun;22(2-3):157–165. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90099-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieringa B., Hofer E., Weissmann C. A minimal intron length but no specific internal sequence is required for splicing the large rabbit beta-globin intron. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):915–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90426-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold W. S., Cladaras C., Deutscher S. L., Kapoor Q. S. The 19-kDa glycoprotein coded by region E3 of adenovirus. Purification, characterization, and structural analysis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2424–2431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold W. S., Cladaras C., Magie S. C., Yacoub N. Mapping a new gene that encodes an 11,600-molecular-weight protein in the E3 transcription unit of adenovirus 2. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):307–313. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.307-313.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold W. S., Green M. Adenovirus type 2 early polypeptides immunoprecipitated by antisera to five lines of adenovirus-transformed rat cells. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):297–310. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.297-310.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeitlin S., Efstratiadis A. In vivo splicing products of the rabbit beta-globin pre-mRNA. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):589–602. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90466-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]