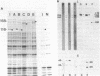
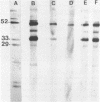
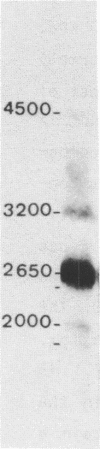
Abstract
Nucleoline (100 kDa) is the major nucleolar protein in exponentially growing cells that behaves like a nucleolar organizer protein and plays a key role in rDNA transcription and prerRNA processing. We reported the isolation of 5 cDNA clones by probing a cDNA library, constructed in the expression vector lambda gt11, with a polyclonal serum raised against nucleoline. A new immunoassay, using hybrid proteins (beta gal-cDNA encoded protein) was developed to establish that the isolated cDNAs encoded parts of nucleoline. A further confirmation resulted from the sequence comparison between the cDNA encoded peptide and a 42 aa peptide isolated from rat nucleoline (1). The 5 cDNAs overlapped extensively and covered more than 90% of a full length cDNA. By probing a Northern blot with the 100 kDa cDNA, a 2650 nucleotide polyA+ RNA was detected that contained just enough information to code for nucleoline.
Full text
PDF


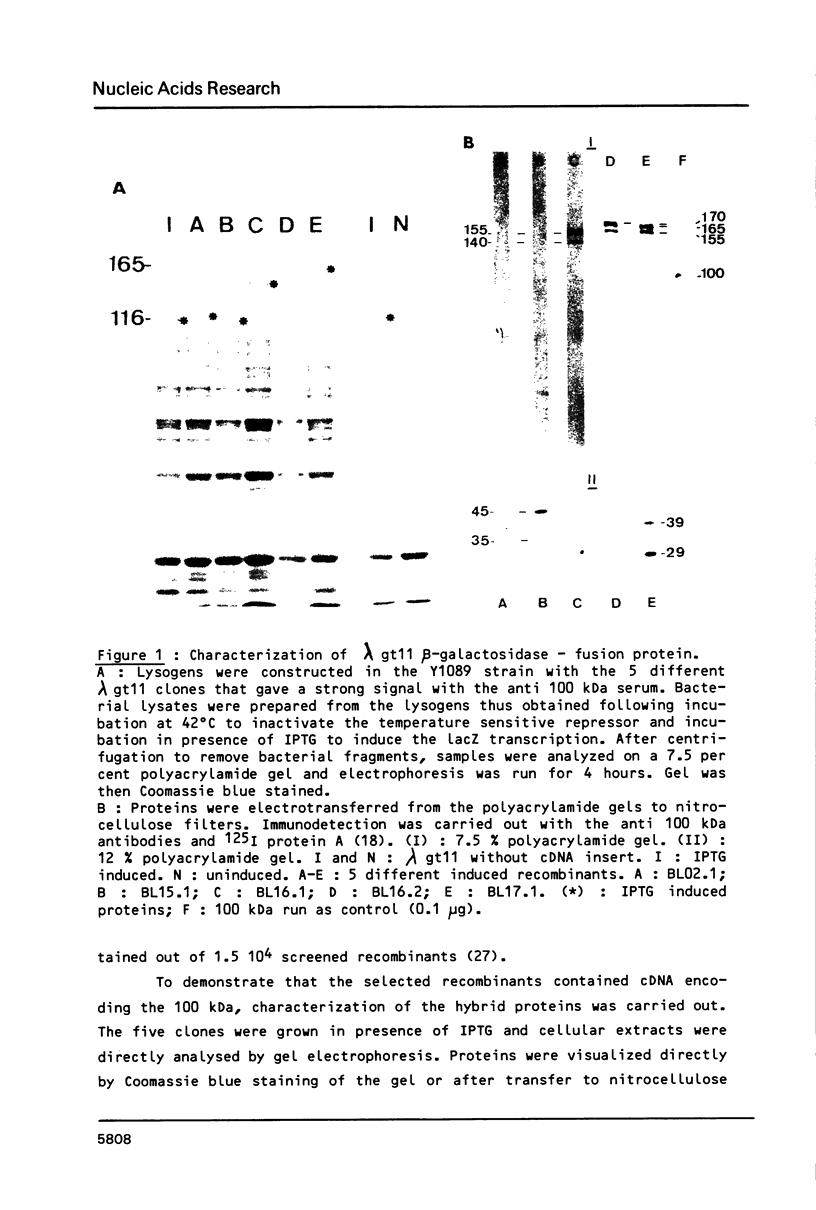







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bouche G., Caizergues-Ferrer M., Bugler B., Amalric F. Interrelations between the maturation of a 100 kDa nucleolar protein and pre rRNA synthesis in CHO cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3025–3035. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourbon H. M., Bugler B., Caizergues-Ferrer M., Amalric F., Zalta J. P. Maturation of a 100 kDa protein associated with preribosomes in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Biol Rep. 1983 May;9(1-2):39–47. doi: 10.1007/BF00777472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozzoni I., Beccari E., Luo Z. X., Amaldi F. Xenopus laevis ribosomal protein genes: isolation of recombinant cDNA clones and study of the genomic organization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 11;9(5):1069–1086. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.5.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugler B., Caizergues-Ferrer M., Bouche G., Bourbon H., Amalric F. Detection and localization of a class of proteins immunologically related to a 100-kDa nucleolar protein. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Nov 15;128(2-3):475–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06989.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caboche M., Bachellerie J. P. RNA methylation and control of eukaryotic RNA biosynthesis. Effects of cycloleucine, a specific inhibitor of methylation, on ribosomal RNA maturation. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Mar 15;74(1):19–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11362.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chooi W. Y., Leiby K. R. An electron microscopic method for localization of ribosomal proteins during transcription of ribosomal DNA: a method for studying protein assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4823–4827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Eustachio P., Meyuhas O., Ruddle F., Perry R. P. Chromosomal distribution of ribosomal protein genes in the mouse. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):307–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90320-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I. Nucleotide sequence requirements for specific initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6908–6911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassouna N., Michot B., Bachellerie J. P. The complete nucleotide sequence of mouse 28S rRNA gene. Implications for the process of size increase of the large subunit rRNA in higher eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 25;12(8):3563–3583. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.8.3563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacq B., Jourdan R., Jordan B. R. Structure and processing of precursor 5 S RNA in Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1977 Dec 15;117(3):785–795. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Warner J. R. Characterization of ribosomal precursor particles from HeLa cell nucleoli. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jan 28;63(2):233–246. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90372-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. O., Dawid I. B. Repeated genes in eukaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:727–764. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamrack M. D., Olson M. O., Busch H. Amino acid sequence and sites of phosphorylation in a highly acidic region of nucleolar nonhistone protein C23. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 24;18(15):3381–3386. doi: 10.1021/bi00582a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss T. Transcription of cloned Xenopus laevis ribosomal DNA microinjected into Xenopus oocytes, and the identification of an RNA polymerase I promoter. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):835–842. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90288-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson M. O., Rivers Z. M., Thompson B. A., Kao W. Y., Case S. T. Interaction of nucleolar phosphoprotein C23 with cloned segments of rat ribosomal deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1983 Jul 5;22(14):3345–3351. doi: 10.1021/bi00283a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepinsky R. B. Localization of lipid-protein and protein-protein interactions within the murine retrovirus gag precursor by a novel peptide-mapping technique. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11229–11235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao S. V., Mamrack M. D., Olson M. O. Localization of phosphorylated highly acidic regions in the NH2-terminal half of nucleolar protein C23. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):15035–15041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raynal F., Michot B., Bachellerie J. P. Complete nucleotide sequence of mouse 18 S rRNA gene: comparison with other available homologs. FEBS Lett. 1984 Feb 27;167(2):263–268. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Brown D. D. Contact points between a positive transcription factor and the Xenopus 5S RNA gene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):395–405. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teem J. L., Abovich N., Kaufer N. F., Schwindinger W. F., Warner J. R., Levy A., Woolford J., Leer R. J., van Raamsdonk-Duin M. M., Mager W. H. A comparison of yeast ribosomal protein gene DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8295–8312. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsutsui K., Tsutsui K., Oda T. Isolation and characterization of a high-molecular-weight acid-soluble nuclear protein from mouse ascites-sarcoma cells. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jul;108(2):497–505. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04747.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolford J. L., Jr, Rosbash M. Ribosomal protein genes rp 39(10 - 78), rp 39(11 - 40), rp 51, and rp 52 are not contiguous to other ribosomal protein genes in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 10;9(19):5021–5036. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.19.5021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]