Abstract
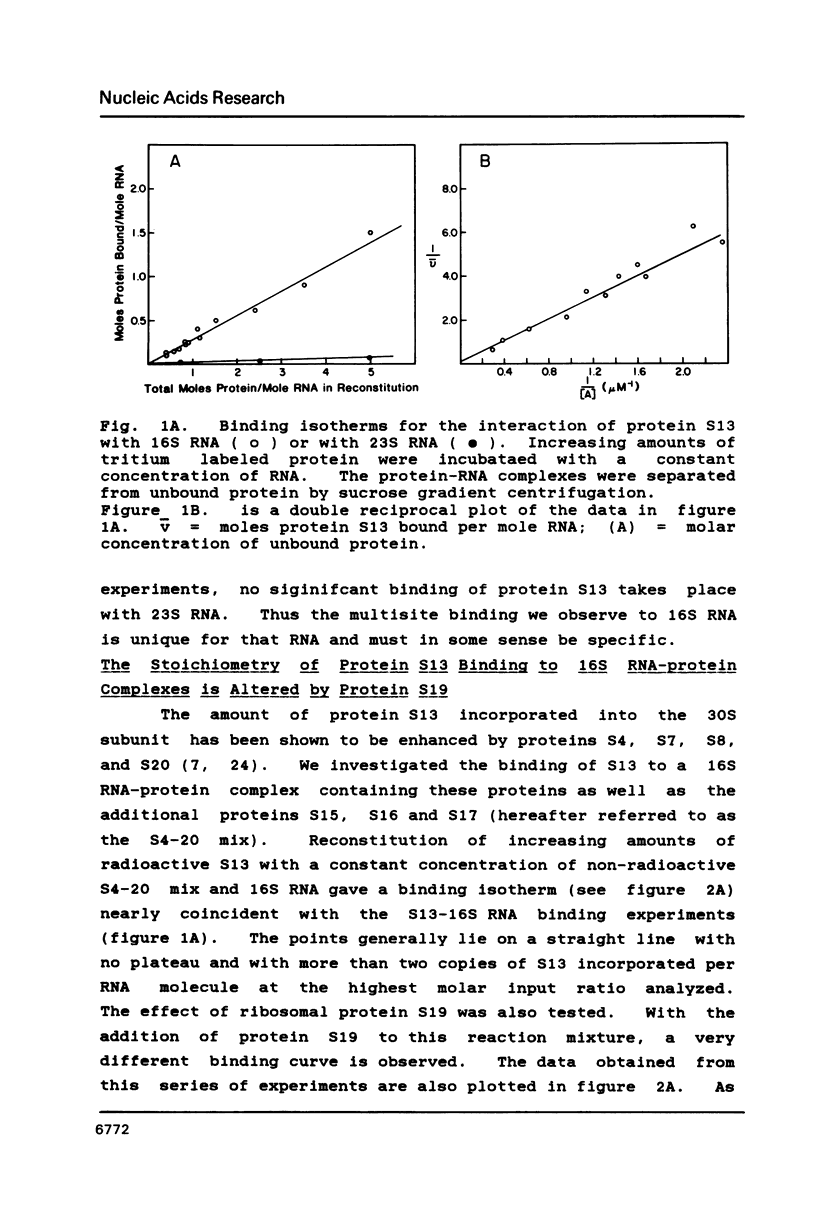
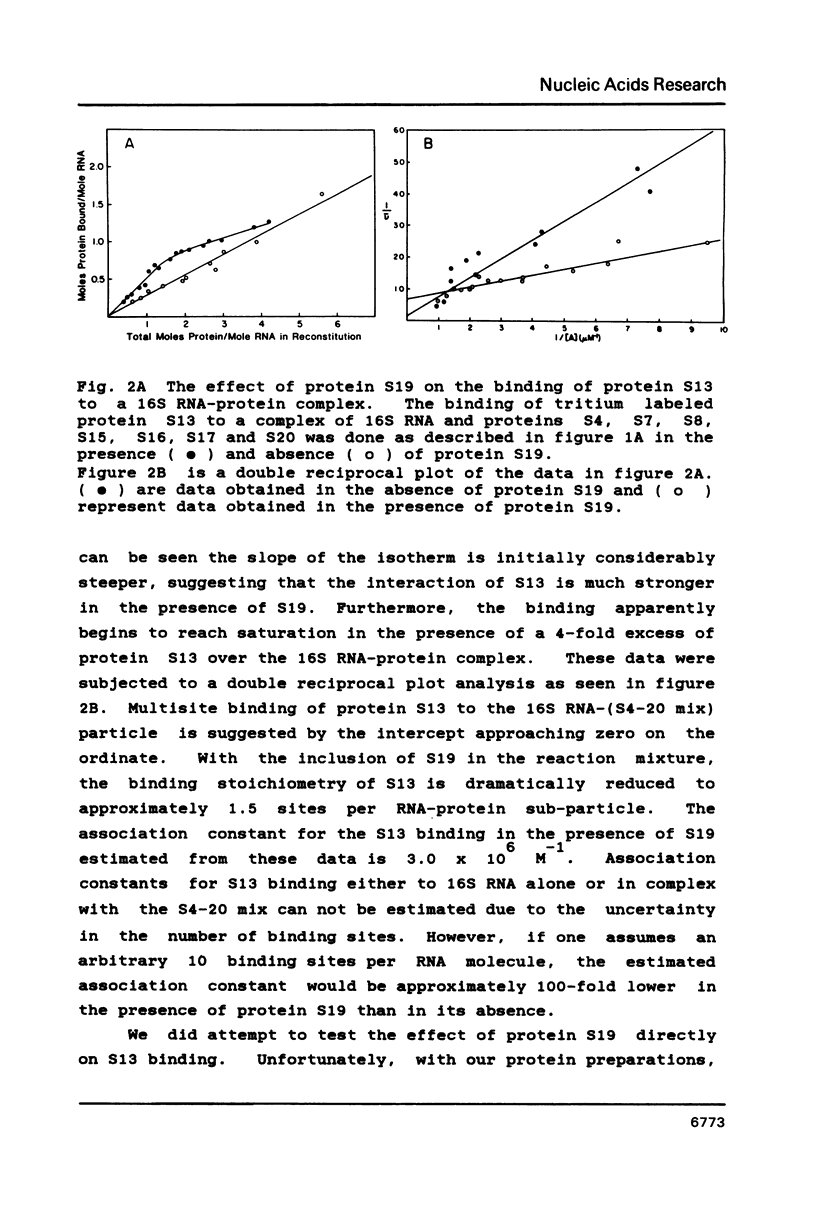
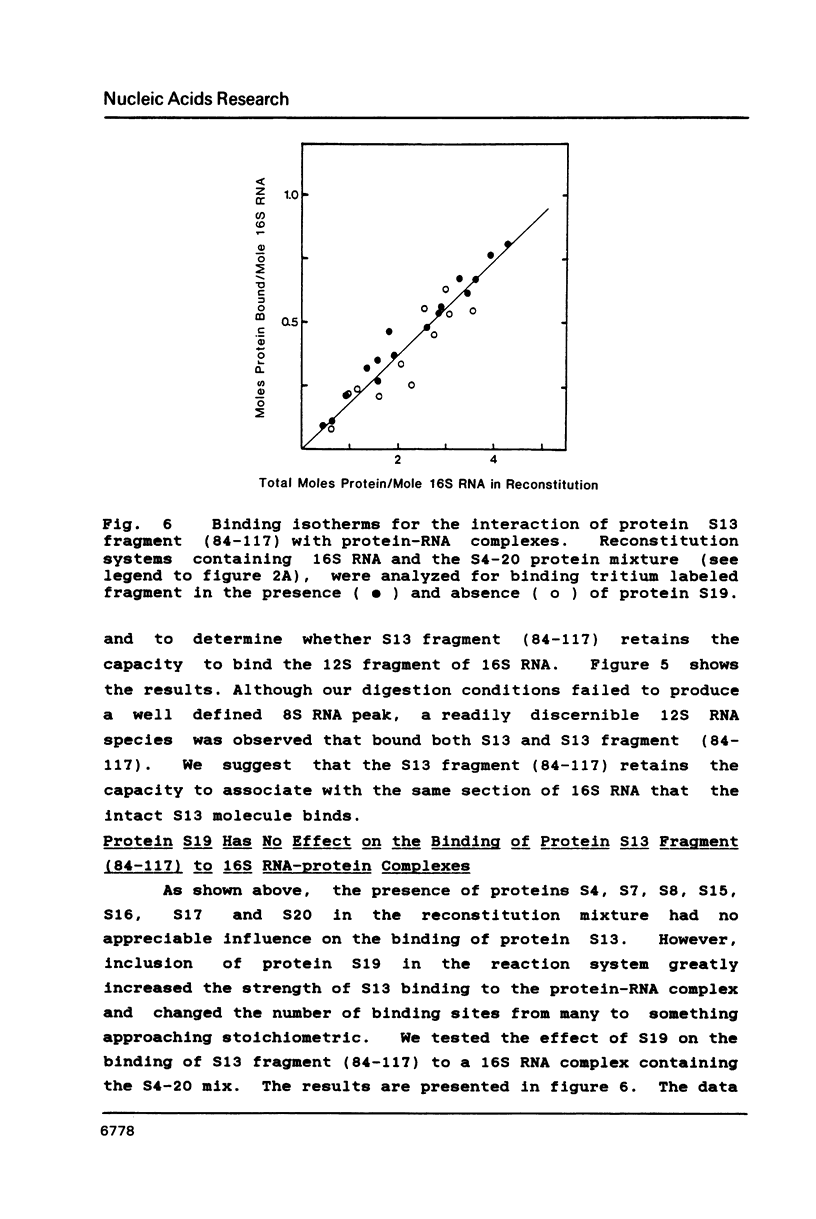
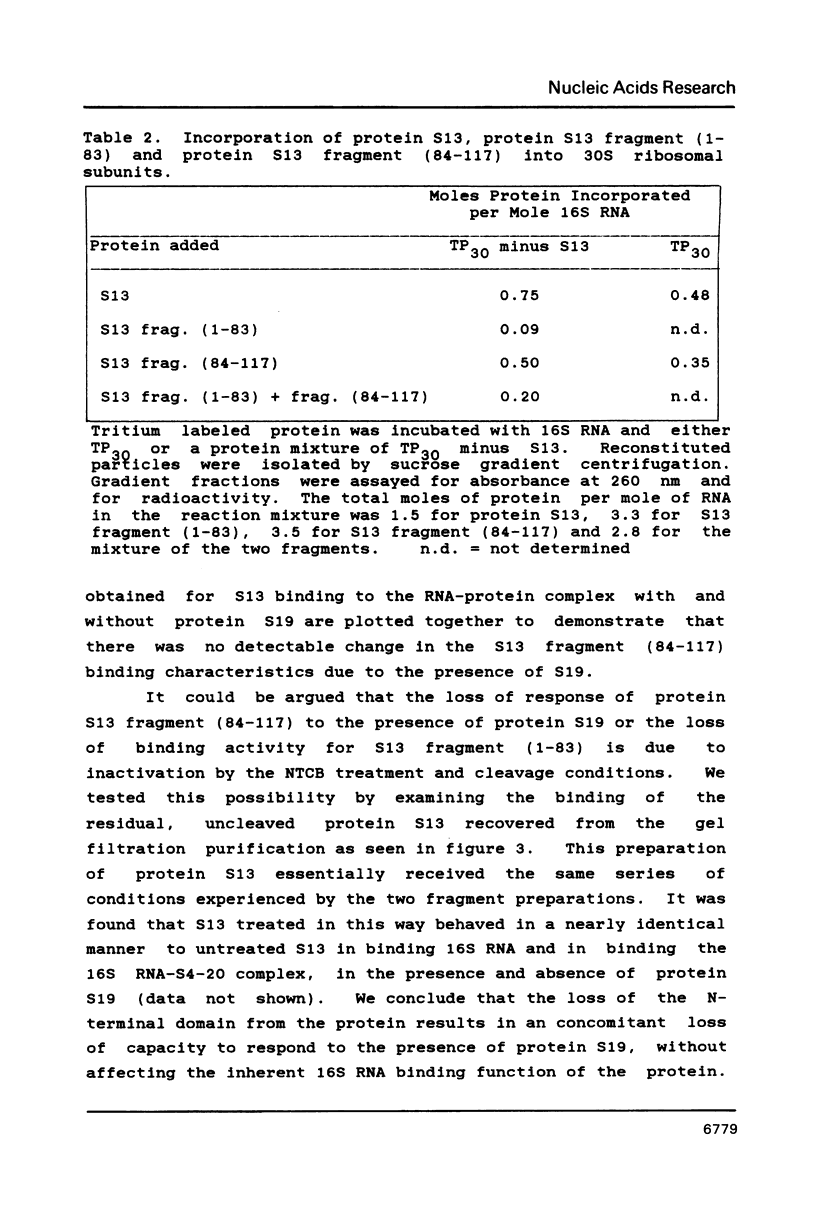
We have found that E. coli ribosomal protein S13 recognizes multiple sites on 16S RNA. However, when protein S19 is included with a mixture of proteins S4, S7, S8, S16/S17 and S20, the S13 binds to the complex with measurably greater strength and with a stoichiometry of 1.5 copies per particle. This suggests that the protein may have two functional domains. We have tested this idea by cleaving the protein into two polypeptides. It was found that one of the fragments, composed of amino acid residues 84-117, retained the capacity to bind 16S RNA at multiple sites. Protein S19 had no affect on the strength or stoichiometry of the binding of this fragment. These data suggest that S13 has a C-terminal domain primarily responsible for RNA recognition and possibly that the N-terminal region is important for association with protein S19.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruce J., Firpo E. J., Schaup H. W. Ribosomal protein-nucleic acid interactions. I. Isolation of a polypeptide fragment from 30S protein S8 which binds to 16S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Oct;4(10):3327–3340. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.10.3327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C., Craven G. R. Identification of several proteins involved in the messenger RNA binding site of the 30 S ribosome by inactivation with 2-methoxy-5-nitrotropone. J Mol Biol. 1977 Dec 5;117(2):401–418. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90135-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changchien L. M., Craven G. R. Studies on the role of amino acid residues 31 through 46 of ribosomal protein S4 in the mechanism of 30 S ribosome assembly. J Mol Biol. 1978 Oct 15;125(1):43–56. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90253-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changchien L. M., Craven G. R. The function of the N-terminal region of ribosomal protein S4. J Mol Biol. 1976 Dec;108(2):381–401. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80126-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changchien L. M., Schwarzbauer J., Cantrell M., Craven G. R. On the role of protein S4 N-terminal residues 1 through 30 in 30S ribosome function. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Aug;5(8):2789–2799. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.8.2789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cover J. A., Lambert J. M., Norman C. M., Traut R. R. Identification of proteins at the subunit interface of the Escherichia coli ribosome by cross-linking with dimethyl 3,3'-dithiobis(propionimidate). Biochemistry. 1981 May 12;20(10):2843–2852. doi: 10.1021/bi00513a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven G. R., Gupta V. Three-dimensional organization of the 30S ribosomal proteins from Escherichia coli. I. Preliminary classification of the proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1329–1336. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijk J., Littlechild J., Garrett R. A. The RNA binding properties of "native" protein-protein complexes isolated from the Escherichia coli ribosome. FEBS Lett. 1977 May 15;77(2):295–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80255-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy S. J., Kurland C. G., Voynow P., Mora G. The ribosomal proteins of Escherichia coli. I. Purification of the 30S ribosomal proteins. Biochemistry. 1969 Jul;8(7):2897–2905. doi: 10.1021/bi00835a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimark R. L., Kahan L., Johnston K., Hershey J. W., Traut R. R. Cross-linking of initiation factor IF3 to proteins of the Escherichia coli 30 S ribosomal subunit. J Mol Biol. 1976 Aug 5;105(2):219–230. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90108-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson G. R., Schaffer M. H., Stark G. R., Vanaman T. C. Specific chemical cleavage in high yield at the amino peptide bonds of cysteine and cystine residues. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6583–6591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindemann H., Wittmann-Liebold B. Primary structure of protein S13 from the small ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1976 Dec 1;71(2):251–255. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80944-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima S., Nomura M. Assembly mapping of 30S ribosomal proteins from E. coli. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1214–1214. doi: 10.1038/2261214a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto A., Ehresmann C., Fellner P., Zimmermann R. A. RNA-protein interactions in the ribosome. I. Characterization and ribonuclease digestion of 16 S RNA-ribosomal protein complexes. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 25;86(2):411–432. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newberry V., Yaguchi M., Garrett R. A. A trypsin-resistant fragment from complexes of ribosomal protein S4 with 16-S RNA of Escherichia coli and from the uncomplexed protein. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jun 1;76(1):51–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11569.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Mizushima S., Ozaki M., Traub P., Lowry C. V. Structure and function of ribosomes and their molecular components. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:49–61. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pongs O., Stöffler G., Lanka E. The codon binding site of the Escherichia coli ribosome as studied with a chemically reactive A-U-G analog. J Mol Biol. 1975 Dec 5;99(2):301–315. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice R. H., Means G. E. Radioactive labeling of proteins in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 10;246(3):831–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suryanarayana T., Subramanian A. R. Functional domains of Escherichia coli Ribosomal Protein S1. Formation and characterization of a fragment with ribosome-binding properties. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jan 5;127(1):41–54. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90458-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]