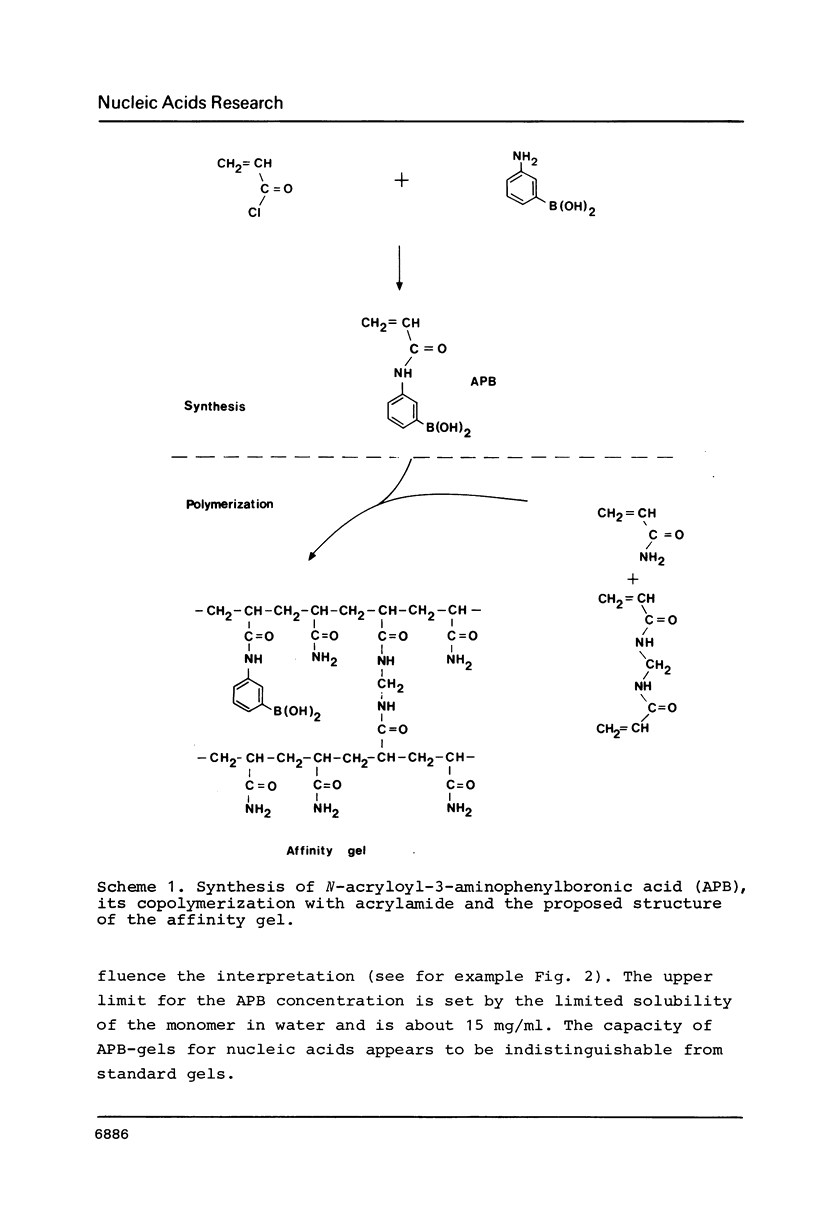
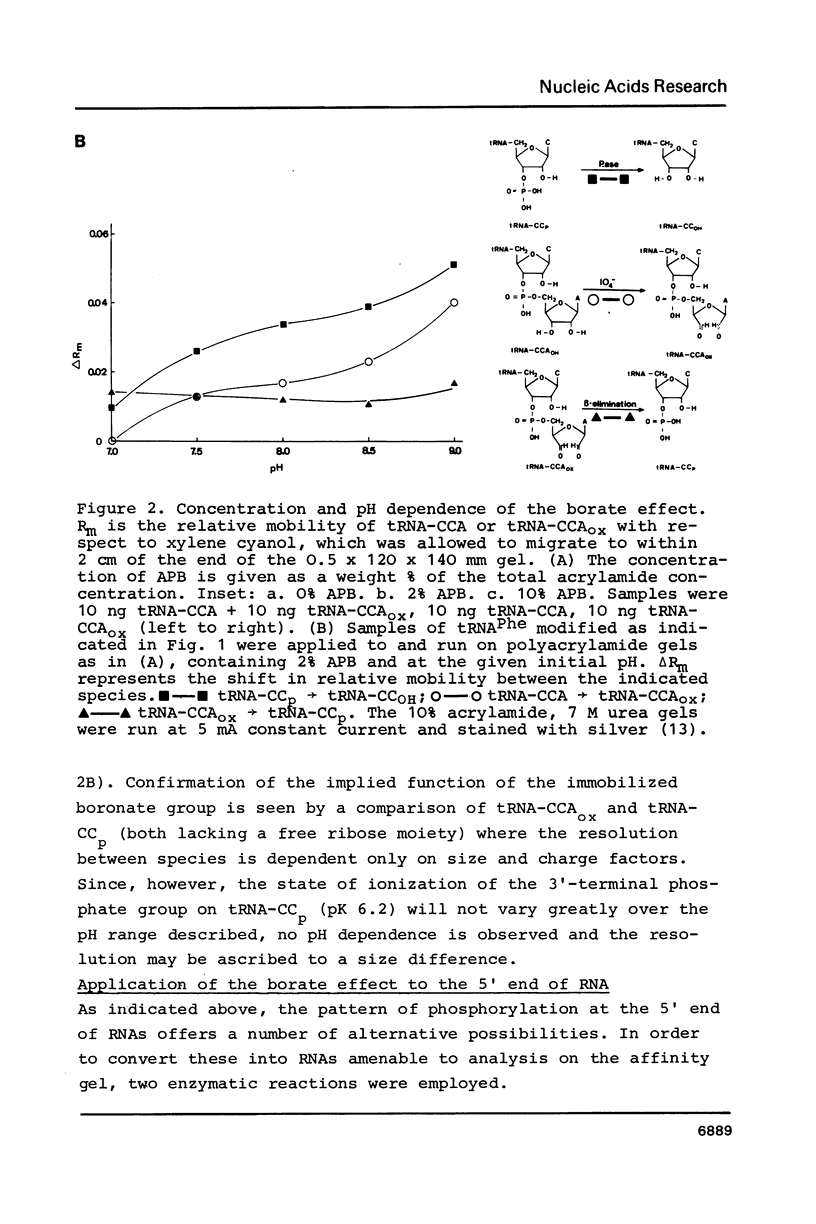
Abstract
An affinity electrophoretic method has been developed to study the state of terminal phosphorylation of RNAs and the presence of the hypermodified base Q in tRNA. It is based on the copolymerization of acryloylaminophenylboronic acid into standard polyacrylamide gels and the interaction of this derivative with free cis-diol groups present in the RNA. In the case of terminal phosphorylation, free ribose groups are present either as such, or may be introduced by enzymatic reactions specific for a particular phosphorylation pattern (e.g. using T4 RNA ligase or guanylyltransferase). Additionally, tRNA species containing the Q base may be resolved from Q-lacking tRNAs by boronate affinity electrophoresis. The introduction of a non-destructive, one-step electrophoretic procedure not only offers an alternative to classical analytical methods, but also provides a means of isolating such populations of RNAs for which other methods are unavailable or are less convenient.
Full text
PDF















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beier H., Barciszewska M., Sickinger H. D. The molecular basis for the differential translation of TMV RNA in tobacco protoplasts and wheat germ extracts. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1091–1096. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01934.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce A. G., Uhlenbeck O. C. Reactions at the termini of tRNA with T4 RNA ligase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Oct;5(10):3665–3677. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.10.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooley L., Appel B., Söll D. Post-transcriptional nucleotide addition is responsible for the formation of the 5' terminus of histidine tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6475–6479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Kafatos F. C., Maxam A. M., Maniatis T. Enzymatic in vitro synthesis of globin genes. Cell. 1976 Feb;7(2):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90027-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horejsí V. Affinity electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1984;104:275–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horejsí V. Review: Affinity electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1981 Mar 15;112(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90252-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igloi G. L. A silver stain for the detection of nanogram amounts of tRNA following two-dimensional electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1983 Oct 1;134(1):184–188. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90281-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igloi G. L., von der Haar F., Cramer F. Experimental proof for the misactivation of amino acids by aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Methods Enzymol. 1979;59:282–291. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)59091-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson B. J. Synthesis of a nitrobenzeneboronic acid substituted polyacrylamide and its use in purifying isoaccepting transfer ribonucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1981 Oct 13;20(21):6103–6108. doi: 10.1021/bi00524a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai H., Oashi Z., Harada F., Nishimura S., Oppenheimer N. J., Crain P. F., Liehr J. G., von Minden D. L., McCloskey J. A. Structure of the modified nucleoside Q isolated from Escherichia coli transfer ribonucleic acid. 7-(4,5-cis-Dihydroxy-1-cyclopenten-3-ylaminomethyl)-7-deazaguanosine. Biochemistry. 1975 Sep 23;14(19):4198–4208. doi: 10.1021/bi00690a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau C. K., Fujitaki J. M. An improved method of microdialysis. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jan 1;110(1):144–145. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90125-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levens D., Ticho B., Ackerman E., Rabinowitz M. Transcriptional initiation and 5' termini of yeast mitochondrial RNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5226–5232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan T. F., Gilham P. T., Söll D. An improved method for the purification of tRNA by chromatography on dihydroxyboryl substituted cellulose. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Jun;2(6):853–864. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.6.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroy G., Spencer E., Hurwitz J. Characteristics of reactions catalyzed by purified guanylyltransferase from vaccinia virus. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4490–4498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura S. Structure, biosynthesis, and function of queuosine in transfer RNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1983;28:49–73. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60082-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schott H., Rudloff E., Schmidt P., Roychoudhury R., Kössel H. A dihydroxyboryl-substituted methacrylic polymer for the column chromatographic separation of mononucleotides, oligonucleotides, and transfer ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb 27;12(5):932–938. doi: 10.1021/bi00729a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singhal R. P., Bajaj R. K., Buess C. M., Smoll D. B., Vakharia V. N. Reversed-phase boronate chromatography for the separation of O-methylribose nucleosides and aminoacyl-tRNAs. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. M., Reeve A. E., Huang R. C. Transcription of bacteriophage lambda DNA in vitro using purine nucleoside 5'-[gamma-S]triphosphates as affinity probes for RNA chain initiation. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 7;17(3):493–500. doi: 10.1021/bi00596a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprinzl M., Cramer F. The -C-C-A end of tRNA and its role in protein biosynthesis. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1979;22:1–69. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60798-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter G., Gozdzicka-Jozefiak A., Kössel H. Identification of an rRNA operon promoter from Zea mays chloroplasts which excludes the proximal tRNAValGAC from the primary transcript. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):599–604. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03672.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Snoper T. J., Cozzarelli N. R. Bacteriophage T4 RNA ligase. Reaction intermediates and interaction of substrates. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 10;252(5):1732–1738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeo K., Nakamura S. Dissociation constants of glucan phosphorylases of rabbit tissues studied by polyacrylamide gel disc electrophoresis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Nov;153(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90413-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tal J., Deutscher M. P., Littauer U. Z. Biological activity of Escherichia coli tRNA Phe modified in its C-C-A terminus. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Aug 4;28(4):478–491. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01935.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weith H. L., Wiebers J. L., Gilham P. T. Synthesis of cellulose derivatives containing the dihydroxyboryl group and a study of their capacity to form specific complexes with sugars and nucleic acid components. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 27;9(22):4396–4401. doi: 10.1021/bi00824a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitesides G. M., Lamotte A., Adalsteinsson O., Colton C. K. Covalent immobilization of adenylate kinase and acetate kinase in a polyacrylamide gel: enzymes for ATP regeneration. Methods Enzymol. 1976;44:887–897. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)44064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittenberg W. L., Uhlenbeck O. C. Specific replacement of functional groups of uridine-33 in yeast phenylalanine transfer ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1985 May 21;24(11):2705–2712. doi: 10.1021/bi00332a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]