Abstract
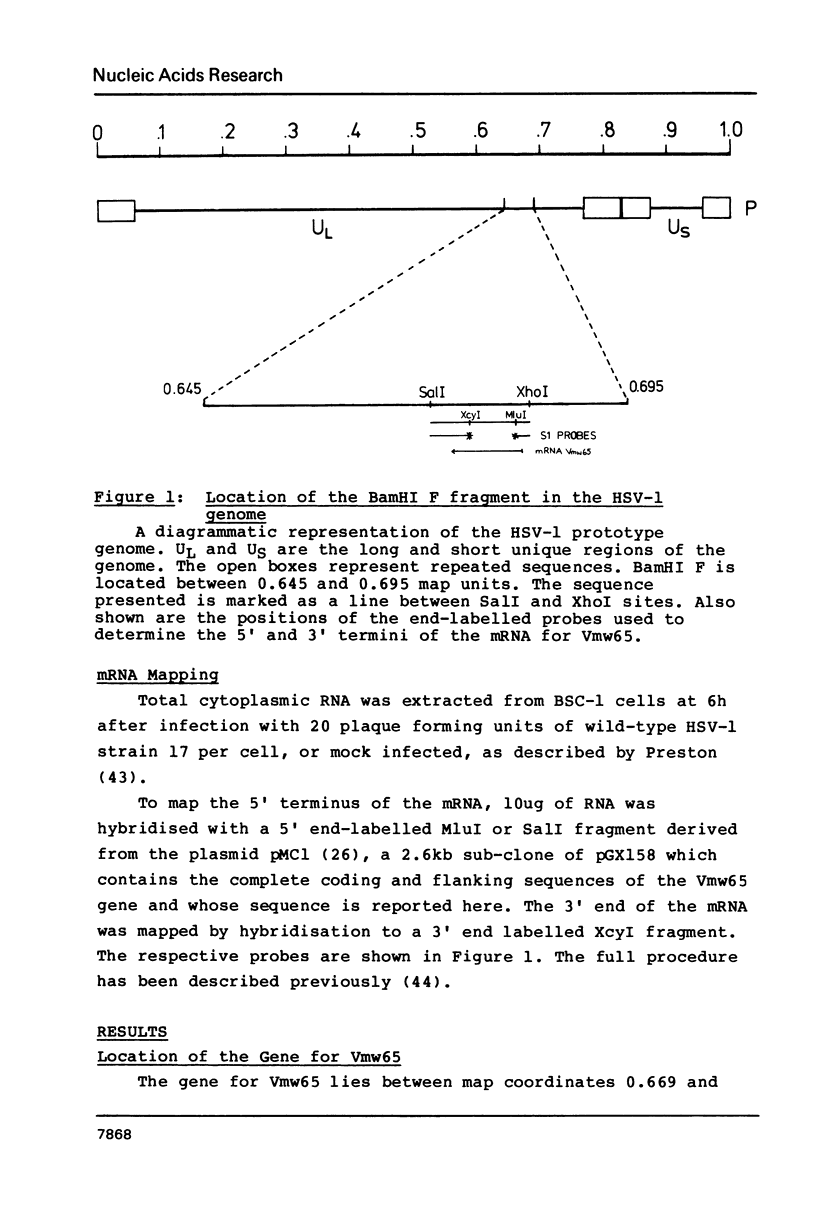
Previous work has shown that transcriptional activation of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) immediate early genes is mediated by a protein species (Vmw65) present in the tegument of infecting virions. This paper describes DNA sequence analysis and mRNA mapping of the Vmw65 gene in HSV-1 strain 17. The Vmw65 coding region was identified as a 490 codon sequence encoding a polypeptide of molecular weight 54,342 and characterised by a high proportion of charged amino acid residues. A homologue to Vmw65 was detected in the genome of varicella-zoster virus, another human herpesvirus. Apart from its role in trans-activation, Vmw65 is a major constituent of the virion. Its possible significance in virus structure is discussed.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batterson W., Roizman B. Characterization of the herpes simplex virion-associated factor responsible for the induction of alpha genes. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):371–377. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.371-377.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker Y., Dym H., Sarov I. Herpes simplex virus DNA. Virology. 1968 Oct;36(2):184–192. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., O'Hare K., Breathnach R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene-sequence of putative control regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):127–142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal R. M., Rice P. J., Roberts R. J. Computer programs for nucleic acid sequence manipulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):91–101. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. E., Palfreyman J. W., Preston C. M. Identification of herpes simplex virus DNA sequences which encode a trans-acting polypeptide responsible for stimulation of immediate early transcription. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90427-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. B., Watson R. J., Wilkie N. M. Temporal regulation of herpes simplex virus type 1 transcription: location of transcripts on the viral genome. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90205-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J., Wasylyk B., Buchwalder A., Sassone-Corsi P., Kedinger C., Chambon P. Promoter sequences of eukaryotic protein-coding genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1406–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6251548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordingley M. G., Campbell M. E., Preston C. M. Functional analysis of a herpes simplex virus type 1 promoter: identification of far-upstream regulatory sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2347–2365. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Scott J. E. DNA sequence of the major inverted repeat in the varicella-zoster virus genome. J Gen Virol. 1985 Feb;66(Pt 2):207–220. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-2-207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L. Random subcloning of sonicated DNA: application to shotgun DNA sequence analysis. Anal Biochem. 1983 Feb 15;129(1):216–223. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierks P., van Ooyen A., Mantei N., Weissmann C. DNA sequences preceding the rabbit beta-globin gene are required for formation in mouse L cells of beta-globin RNA with the correct 5' terminus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1411–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D., Baty D., Chambon P. The repeated GC-rich motifs upstream from the TATA box are important elements of the SV40 early promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2447–2464. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. Trans activation of transcription by herpes virus products: requirement for two HSV-1 immediate-early polypeptides for maximum activity. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3135–3141. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The sequence 5'-AAUAAA-3'forms parts of the recognition site for polyadenylation of late SV40 mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham B. J., Ludwig H., Bronson D. L., Benyesh-Melnick M., Biswal N. Physicochemical properties of the DNA of herpes viruses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 18;259(1):13–23. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90469-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld G. C., de Boer E., Shewmaker C. K., Flavell R. A. DNA sequences necessary for transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in vivo. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):120–126. doi: 10.1038/295120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haarr L., Marsden H. S. Two-dimensional gel analysis of HSV type 1-induced polypeptides and glycoprotein processing. J Gen Virol. 1981 Jan;52(Pt 1):77–92. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-52-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L. M., Draper K. G., Frink R. J., Costa R. H., Wagner E. K. Herpes simplex virus mRNA species mapping in EcoRI fragment I. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):594–607. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.594-607.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. C., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. VIII. The transcription program consists of three phases during which both extent of transcription and accumulation of RNA in the cytoplasm are regulated. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):299–314. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.299-314.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Possible role of flanking nucleotides in recognition of the AUG initiator codon by eukaryotic ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5233–5252. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Separation of sequences defining basal expression from those conferring alpha gene recognition within the regulatory domains of herpes simplex virus 1 alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4065–4069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang J. C., Spandidos D. A., Wilkie N. M. Transcriptional regulation of a herpes simplex virus immediate early gene is mediated through an enhancer-type sequence. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):389–395. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01817.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaster S., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus phosphoproteins. II. Characterization of the virion protein kinase and of the polypeptides phosphorylated in the virion. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):798–811. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.798-811.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Differentiation between alpha promoter and regulator regions of herpes simplex virus 1: the functional domains and sequence of a movable alpha regulator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4917–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Structural features of the herpes simplex virus alpha gene 4, 0, and 27 promoter-regulatory sequences which confer alpha regulation on chimeric thymidine kinase genes. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):939–949. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.939-949.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Haarr L., Preston C. M. Processing of herpes simplex virus proteins and evidence that translation of thymidine kinase mRNA is initiated at three separate AUG codons. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):434–445. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.434-445.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Stow N. D., Preston V. G., Timbury M. C., Wilkie N. M. Physical mapping of herpes simplex virus-induced polypeptides. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):624–642. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.624-642.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Gavis E. R., Kingsbury R., Axel R. Analysis of transcriptional regulatory signals of the HSV thymidine kinase gene: identification of an upstream control region. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):385–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. C., Spence A., Smith M. The distal transcription signals of the herpesvirus tk gene share a common hexanucleotide control sequence. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Gaffney D., Whitton J. L., Clements J. B. The consensus sequence YGTGTTYY located downstream from the AATAAA signal is required for efficient formation of mRNA 3' termini. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1347–1368. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murchie M. J., McGeoch D. J. DNA sequence analysis of an immediate-early gene region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome (map coordinates 0.950 to 0.978). J Gen Virol. 1982 Sep;62(Pt 1):1–15. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-62-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Evidence for a direct role for both the 175,000- and 110,000-molecular-weight immediate-early proteins of herpes simplex virus in the transactivation of delayed-early promoters. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):751–760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.751-760.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus: expression of chimeric genes produced by fusion of thymidine kinase with alpha gene promoters. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M. Control of herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA synthesis in cells infected with wild-type virus or the temperature-sensitive mutant tsK. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):275–284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.275-284.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Cordingley M. G., Stow N. D. Analysis of DNA sequences which regulate the transcription of a herpes simplex virus immediate early gene. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):708–716. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.708-716.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., McGeoch D. J. Identification and mapping of two polypeptides encoded within the herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase gene sequences. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):593–605. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.593-605.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Tannahill D. Effects of orientation and position on the activity of a herpes simplex virus immediate early gene far-upstream region. Virology. 1984 Sep;137(2):439–444. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90238-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M. The cell-free synthesis of herpesvirus-induced polypeptides. Virology. 1977 May 1;78(1):349–353. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90109-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puga A., Gomez-Marquez J., Brayton P. R., Cantin E. M., Long L. K., Barbacid M., Notkins A. L. The immediate-early enhancer element of herpes simplex virus type 1 can replace a regulatory region of the c-Ha-ras1 oncogene required for transformation. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):879–881. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.879-881.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
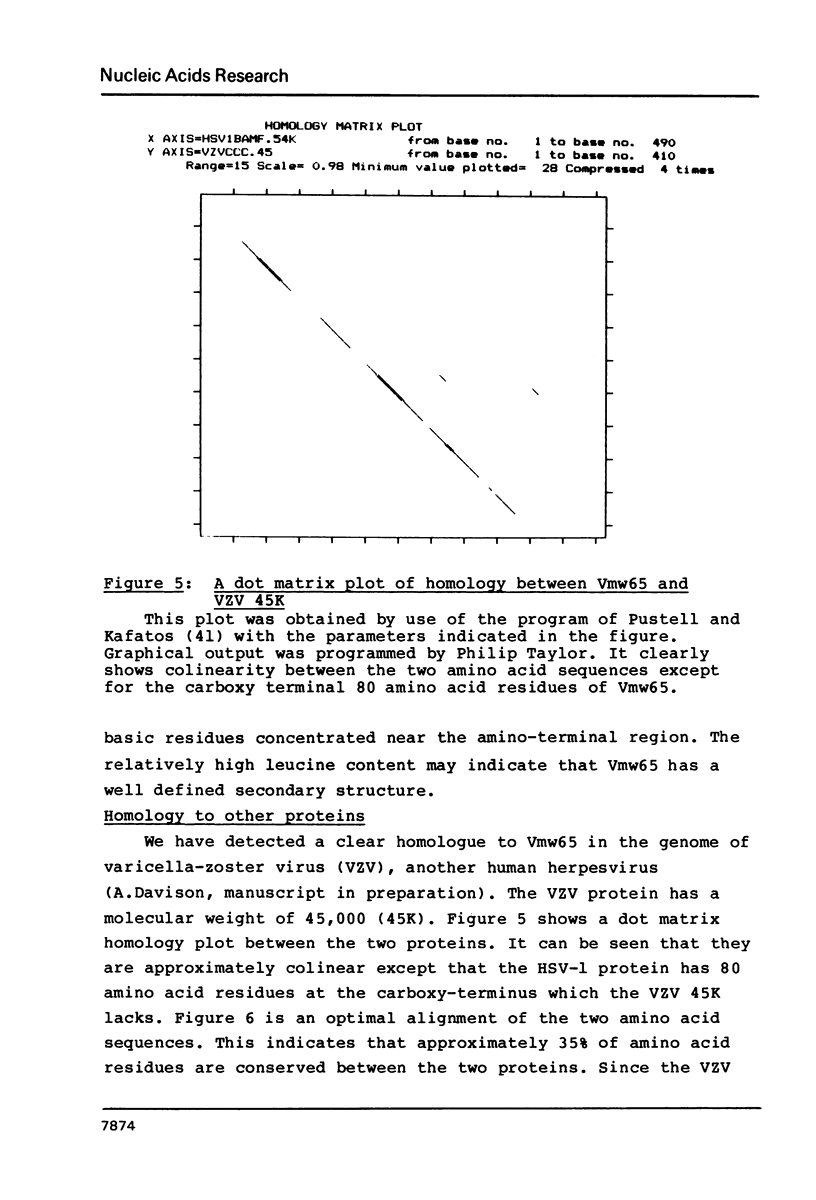
- Pustell J., Kafatos F. C. A high speed, high capacity homology matrix: zooming through SV40 and polyoma. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 11;10(15):4765–4782. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.15.4765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan M. P., Knipe D. M. Stimulation of expression of a herpes simplex virus DNA-binding protein by two viral functions. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):957–963. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rixon F. J., Clements J. B. Detailed structural analysis of two spliced HSV-1 immediate-early mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 10;10(7):2241–2256. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.7.2241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Automation of the computer handling of gel reading data produced by the shotgun method of DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 11;10(15):4731–4751. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.15.4731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R., McLachlan A. D. Codon preference and its use in identifying protein coding regions in long DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):141–156. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanstrom R. I., Pivo K., Wagner E. K. Restricted transcription of the herpes simplex virus genome occurring early after infection and in the presence of metabolic inhibitors. Virology. 1975 Jul;66(1):140–150. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90185-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taya Y., Devos R., Tavernier J., Cheroutre H., Engler G., Fiers W. Cloning and structure of the human immune interferon-gamma chromosomal gene. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):953–958. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01277.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. A fast homology program for aligning biological sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):447–455. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twigg A. J., Sherratt D. Trans-complementable copy-number mutants of plasmid ColE1. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):216–218. doi: 10.1038/283216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernon S. K., Lawrence W. C., Long C. A., Rubin B. A., Sheffield J. B. Morphological components of herpesvirus. IV. Ultrastructural features of the envelope and tegument. J Ultrastruct Res. 1982 Nov;81(2):163–171. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(82)90072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILDY P., RUSSELL W. C., HORNE R. W. The morphology of herpes virus. Virology. 1960 Oct;12:204–222. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90195-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Clements J. B. A herpes simplex virus type 1 function continuously required for early and late virus RNA synthesis. Nature. 1980 May 29;285(5763):329–330. doi: 10.1038/285329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitton J. L., Clements J. B. Replication origins and a sequence involved in coordinate induction of the immediate-early gene family are conserved in an intergenic region of herpes simplex virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 24;12(4):2061–2079. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.4.2061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitton J. L., Rixon F. J., Easton A. J., Clements J. B. Immediate-early mRNA-2 of herpes simplex viruses types 1 and 2 is unspliced: conserved sequences around the 5' and 3' termini correspond to transcription regulatory signals. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6271–6287. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]