Abstract
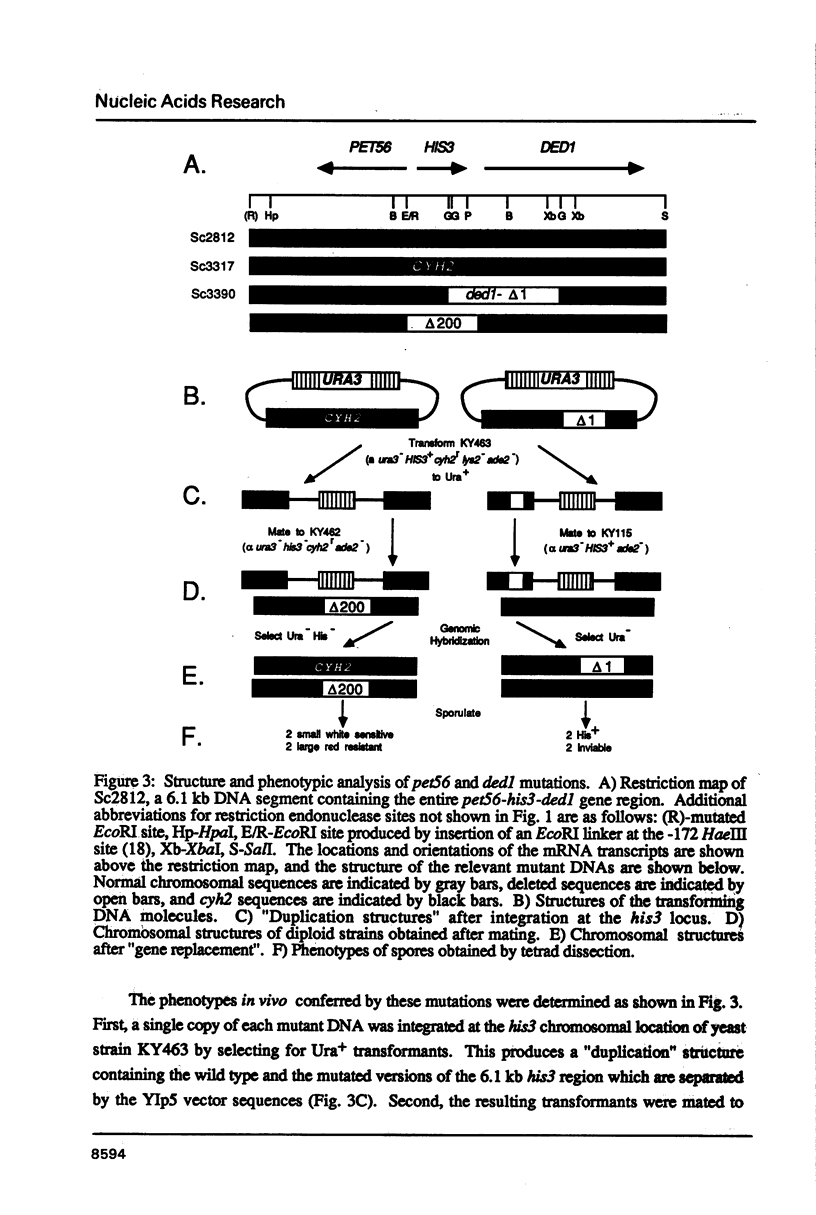
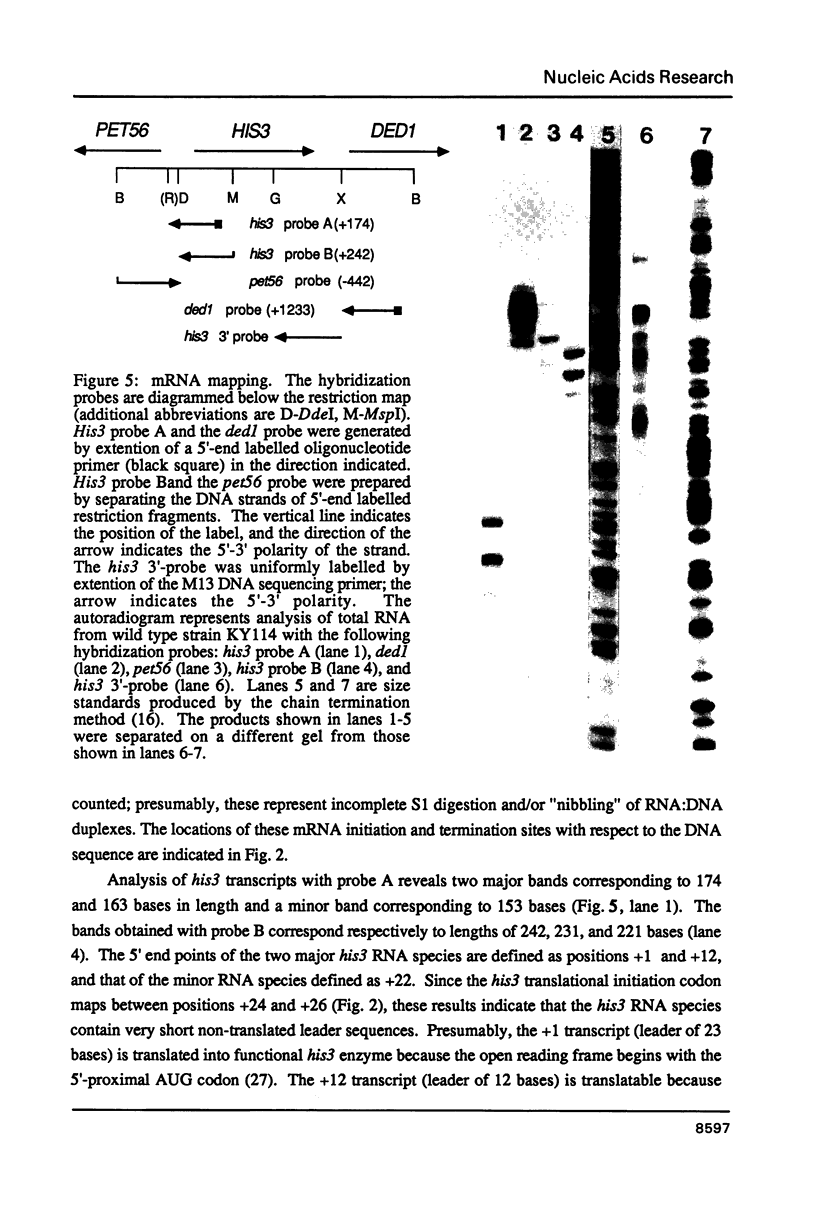
Genes of the baker's yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae are densely clustered on 16 linear chromosomes. Here, I characterize a 1.8 kb region of chromosome XV containing the entire structural gene for the histidine biosynthetic enzyme imidazoleglycerolphosphate (IGP) dehydratase (his3) as well as the promoter sequences and 5'-proximal mRNA coding regions for the adjacent genes. The his3 gene encodes several mRNA species averaging 820 bases in length, all of which contain an open reading frame of 219 codons. The location of this open reading frame coincides with the his3 gene as defined by functional criteria, suggesting that the primary translation product of yeast IGP dehydratase has a molecular weight of 23,850. Phenotypic analysis of mutations constructed in vitro indicate that one of the adjacent genes (pet56) is required for mitochondrial function, whereas the other gene (ded1) is essential for cell viability. The pet56 and his3 genes are transcribed divergently from initiation sites that are separated by only 192 bp. Transcription of the ded1 gene is initiated only 130 bp beyond the 3'-end of the his3 mRNA coding region. These results suggest that these unrelated genes are located extremely close together and that the spacer regions between them consist largely of promoter and terminator sequences.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. Codon selection in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3026–3031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue T. F., Daves R. S., Lucchini G., Fink G. R. A short nucleotide sequence required for regulation of HIS4 by the general control system of yeast. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):89–98. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90499-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINK G. R. GENE-ENZYME RELATIONS IN HISTIDINE BIOSYNTHESIS IN YEAST. Science. 1964 Oct 23;146(3643):525–527. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3643.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried H. M., Warner J. R. Molecular cloning and analysis of yeast gene for cycloheximide resistance and ribosomal protein L29. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 25;10(10):3133–3148. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.10.3133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrick-Silversmith L., Hartman P. E. Histidine-requiring mutants of Escherichia coli K12. Genetics. 1970 Oct;66(2):231–244. doi: 10.1093/genetics/66.2.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward G. S. Gel electrophoretic separation of the complementary strands of bacteriophage DNA. Virology. 1972 Jul;49(1):342–344. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(72)80042-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L. M., Rosbash M. Number and distribution of polyadenylated RNA sequences in yeast. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):453–462. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90032-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G., Fink G. R. Repeated DNA sequences upstream from HIS1 also occur at several other co-regulated genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5238–5247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwich A. L., Kalousek F., Rosenberg L. E. Arginine in the leader peptide is required for both import and proteolytic cleavage of a mitochondrial precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4930–4933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback D. B., Angerer L. M., Davidson N. Improved methods for the formation and stabilization of R-loops. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jun 11;6(7):2499–2317. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.7.2499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer R. K., Schild D. Genetic map of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Dec;44(4):519–571. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.4.519-571.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oettinger M. A., Struhl K. Suppressors of Saccharomyces cerevisiae his3 promoter mutations lacking the upstream element. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1901–1909. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W., Rothstein R. J. Yeast transformation: a model system for the study of recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6354–6358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROMAN H. Studies of gene mutation in Saccharomyces. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1956;21:175–185. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1956.021.01.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHERMAN F., SLONIMSKI P. P. RESPIRATION-DEFICIENT MUTANTS OF YEAST. II. BIOCHEMISTRY. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jul 15;90:1–15. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman F., Stewart J. W., Schweingruber A. M. Mutants of yeast initiating translation of iso-1-cytochrome c within a region spanning 37 nucleotides. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):215–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90249-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K., Cameron J. R., Davis R. W. Functional genetic expression of eukaryotic DNA in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1471–1475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K., Davis R. W. A physical, genetic and transcriptional map of the cloned his3 gene region of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jan 25;136(3):309–332. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90376-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K., Davis R. W. Promotor mutants of the yeast his3 gene. J Mol Biol. 1981 Nov 5;152(3):553–568. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90268-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K., Davis R. W. Transcription of the his3 gene region in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol. 1981 Nov 5;152(3):535–552. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90267-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Deletion mapping a eukaryotic promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4461–4465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Direct selection for gene replacement events in yeast. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):231–241. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90193-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Genetic properties and chromatin structure of the yeast gal regulatory element: an enhancer-like sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7865–7869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K., Stinchcomb D. T., Scherer S., Davis R. W. High-frequency transformation of yeast: autonomous replication of hybrid DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1035–1039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. The yeast his3 promoter contains at least two distinct elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7385–7389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalkin H., Yanofsky C. Yeast gene TRP5: structure, function, regulation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1491–1500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Sherman F. DNA sequence required for efficient transcription termination in yeast. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]