Abstract
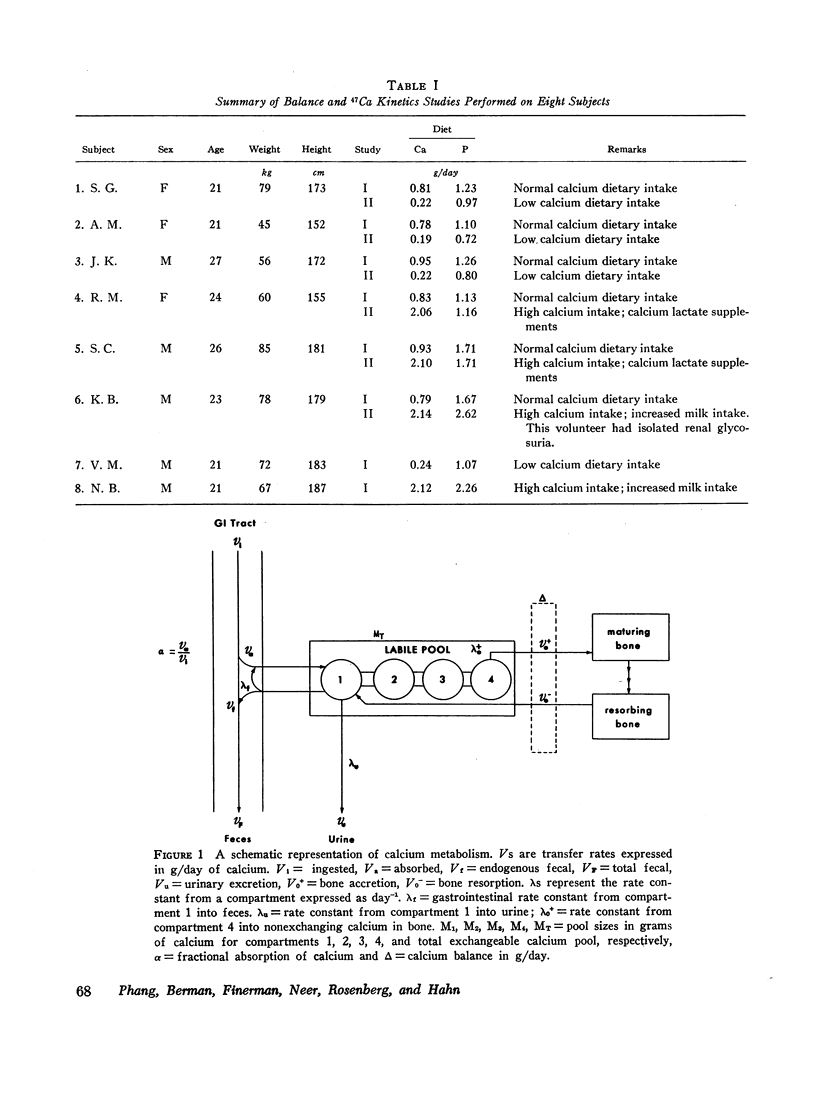
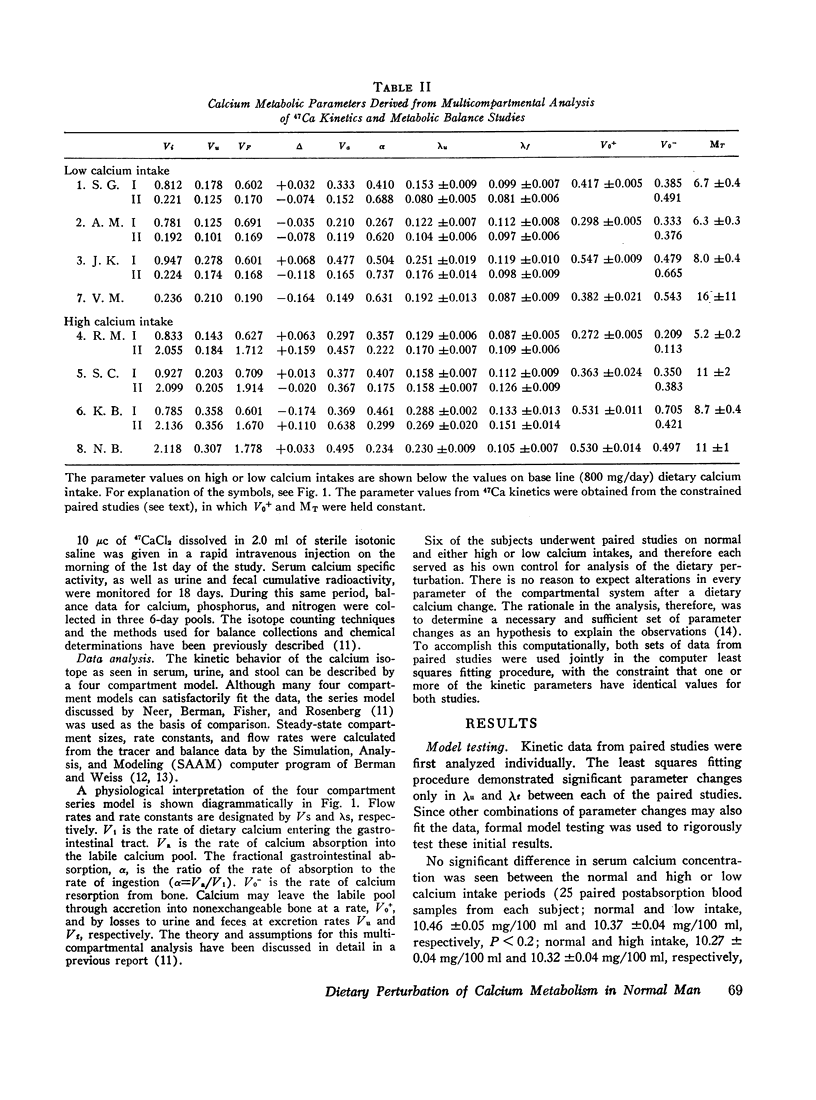
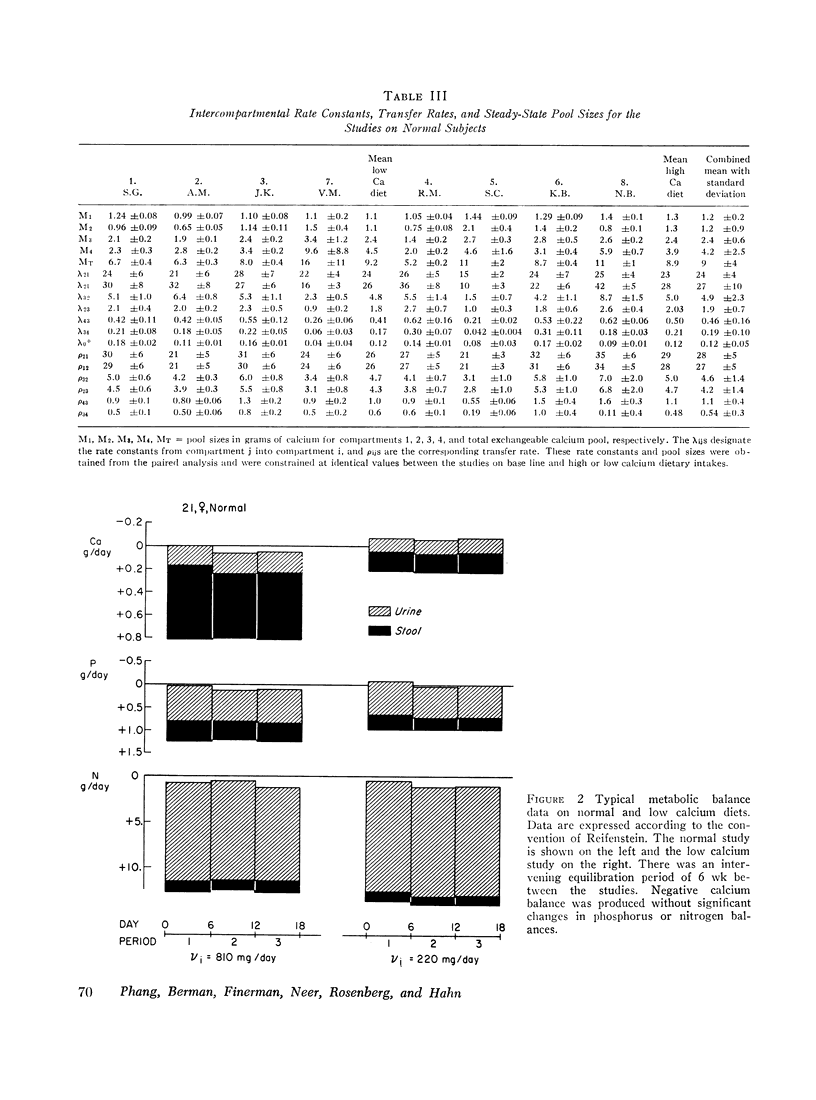
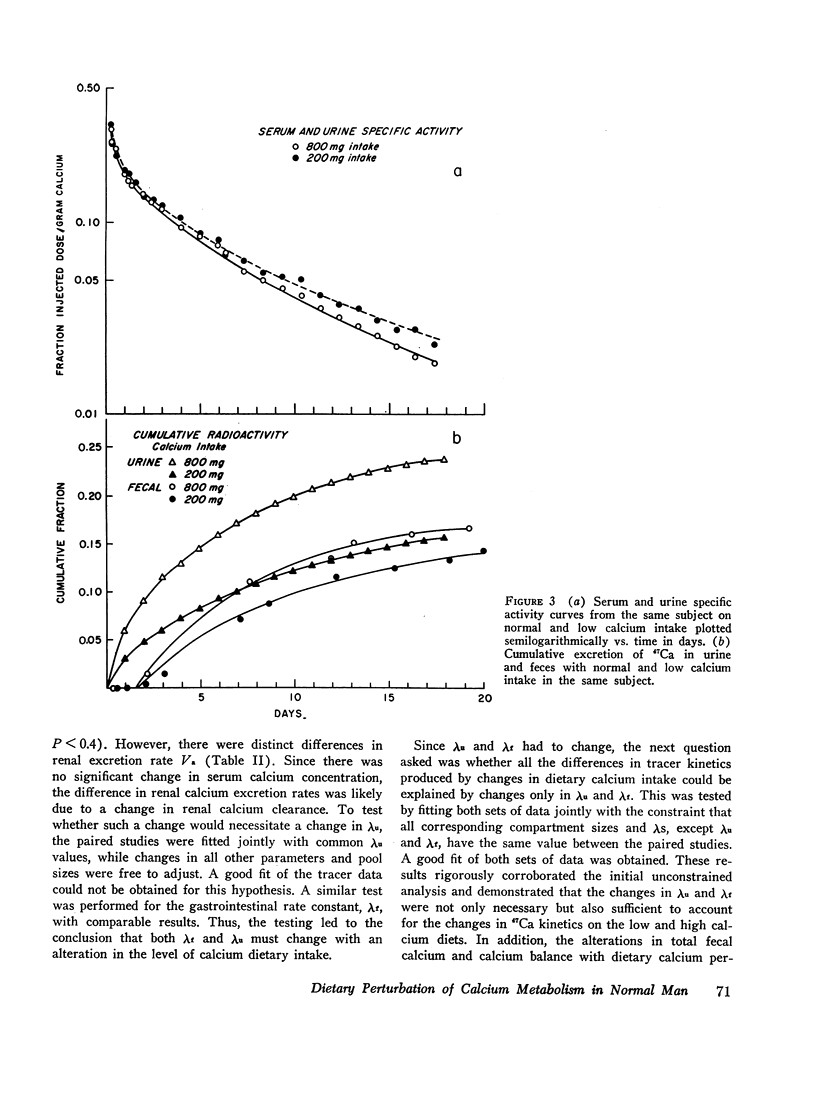
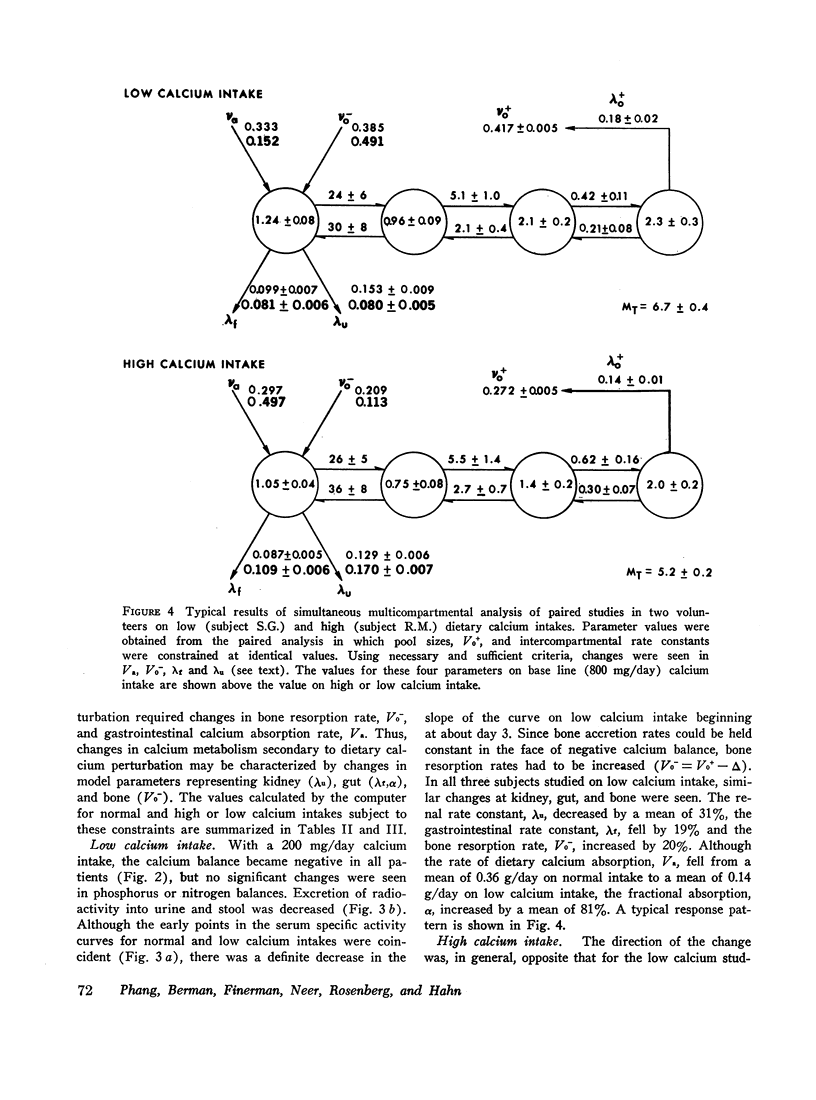
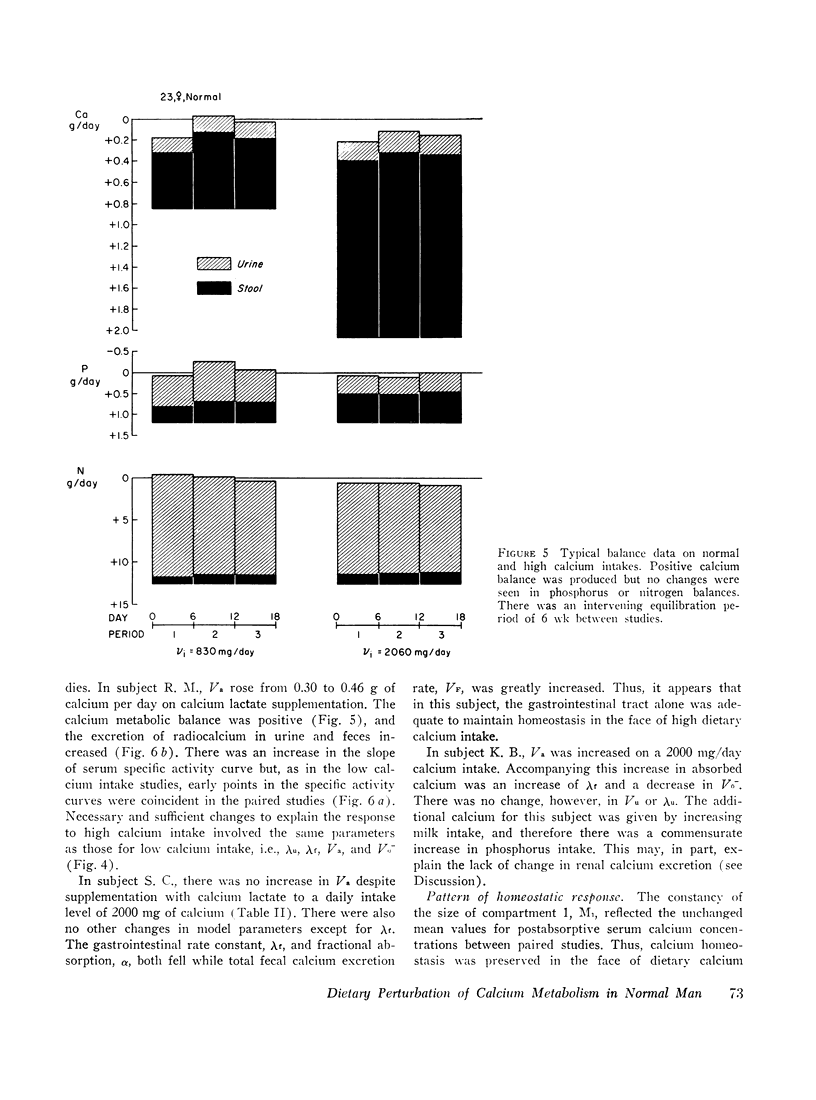
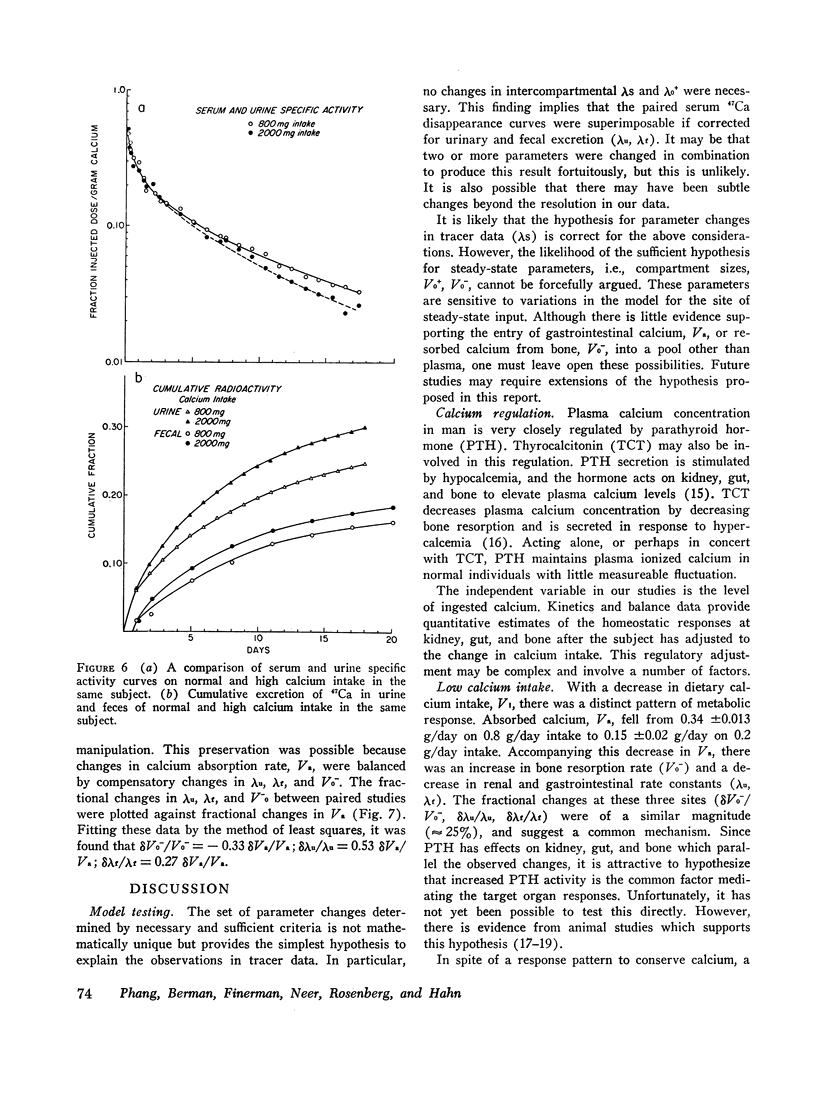
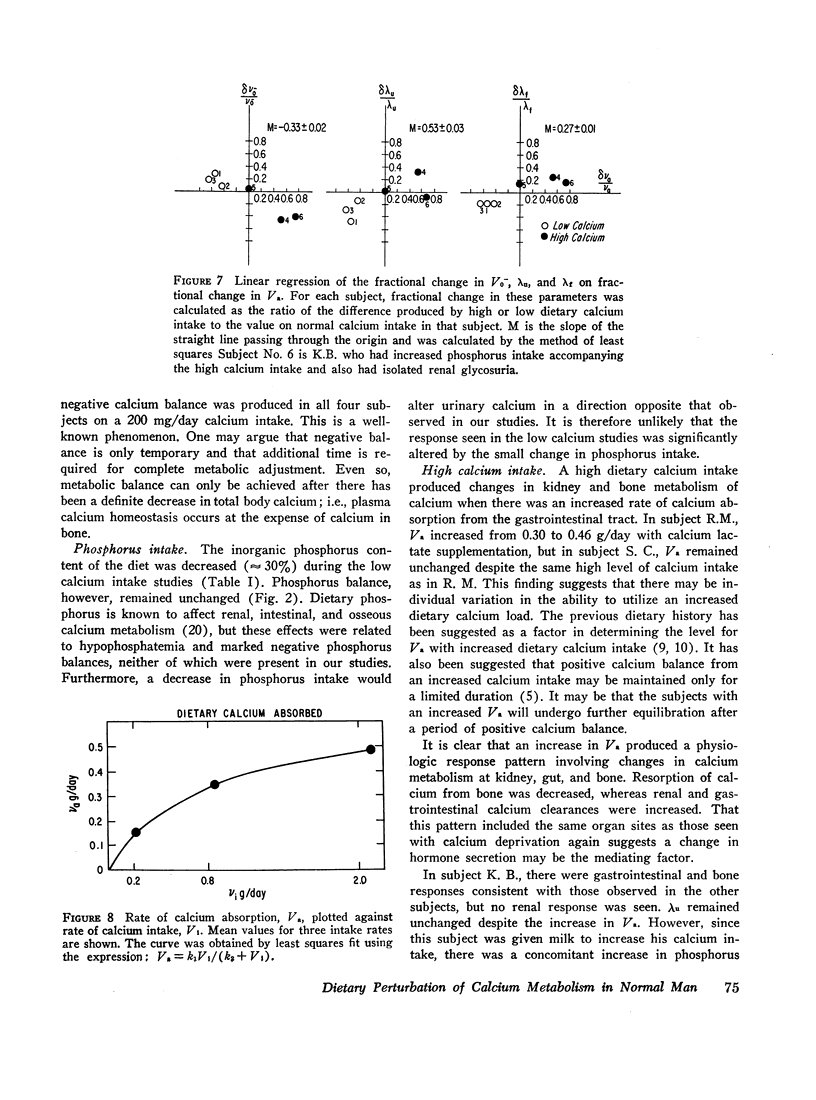
The effect of dietary calcium intake on calcium metabolism was studied in eight normal volunteers by multicompartmental analysis of radiocalcium and balance data. In paired studies of six normal subjects on normal and high or low calcium intakes, necessary and sufficient criteria were used to determine changes in calcium metabolic parameters produced by alterations in dietary calcium. These changes involved gastrointestinal calcium absorption rate, renal and endogenous fecal rate constants, and bone resorption rate. Bone accretion rate and compartment sizes need not change between the paired studies. The changes of parameters involving kidney, gut, and bone were in a direction to support calcium homeostasis and were compatible with the pattern of changes produced by parathyroid hormone. However, the source of the stimulus for hormone secretion was not apparent since plasma calcium concentrations showed no significant difference between paired studies. The implications of these findings relative to control of hormone secretion, calcium regulatory mechanisms, and metabolic bone disease are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AVIOLI L. V., MCDONALD J. E., SINGER R. A., HENNEMAN P. H. A NEW ORAL ISOTOPIC TEST OF CALCIUM ABSORPTION. J Clin Invest. 1965 Jan;44:128–139. doi: 10.1172/JCI105119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Au W. Y., Raisz L. G. Effect of vitamin D and dietary calcium on parathyroid activity. Am J Physiol. 1965 Sep;209(3):637–642. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.3.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman M. A postulate to aid in model building. J Theor Biol. 1963 May;4(3):229–236. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(63)90001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUPRE J. AN INTESTINAL HORMONE AFFECTING GLUCOSE DISPOSAL IN MAN. Lancet. 1964 Sep 26;2(7361):672–673. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)92481-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRISON M., FRASER R., MULLAN B. Calcium metabolism in osteoporosis. Acute and long-term responses to increased calcium intake. Lancet. 1961 May 13;1(7185):1015–1019. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)91828-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEANEY R. P., SKILLMAN T. G. SECRETION AND EXCRETION OF CALCIUM BY THE HUMAN GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Jul;64:29–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOWSEY J., GERSHON-COHEN J. EFFECT OF DIETARY CALCIUM LEVELS ON PRODUCTION AND REVERSAL OF EXPERIMENTAL OSTEOPOROSIS IN CATS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Jun;116:437–441. doi: 10.3181/00379727-116-29272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIMBERG D. V., SCHACHTER D., SCHENKER H. Active transport of calcium by intestine: effects of dietary calcium. Am J Physiol. 1961 Jun;200:1256–1262. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.6.1256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIBERT O. Contribution a l'etude des hormones steroides derivees du pregnane chez la lapine. I. Metabolisme de la progesterone et de la desoxycorticosterone d'origine endogene. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1950;5(1):1–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotz M., Zisman E., Bartter F. C. Evidence for a phosphorus-depletion syndrome in man. N Engl J Med. 1968 Feb 22;278(8):409–415. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196802222780802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACFADYEN I. J., NORDIN B. E., SMITH D. A., WAYNE D. J., RAE S. L. EFFECT OF VARIATION IN DIETARY CALCIUM ON PLASMA CONCENTRATION AND URINARY EXCRETION OF CALCIUM. Br Med J. 1965 Jan 16;1(5428):161–164. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5428.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALM O. J. On phosphates and phosphoric acid as dietary factors in the calcium balance of man. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1953;5(1):75–84. doi: 10.3109/00365515309093516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MENCZEL J., SCHRAER R., PAKIS G., POSNER A. S., LIKINS R. C. Effect of a low calcium diet on bone crystallinity and skeletal uptake of Ca45 in rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Jan;112:128–132. doi: 10.3181/00379727-112-27970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre N., Holdsworth C. D., Turner D. S. Intestinal factors in the control of insulin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1317–1324. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. L. Thyrocalcitonin. Ann Intern Med. 1966 Jun;64(6):1353–1357. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-64-6-1353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORDIN B. E. The pathogenesis of osteoporosis. Lancet. 1961 May 13;1(7185):1011–1015. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)91827-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer R., Berman M., Fisher L., Rosenberg L. E. Multicompartmental analysis of calcium kinetics in normal adult males. J Clin Invest. 1967 Aug;46(8):1364–1379. doi: 10.1172/JCI105629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RASMUSSEN H. Parathyroid hormone. Nature and mechanism of action. Am J Med. 1961 Jan;30:112–128. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(61)90068-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RASMUSSEN H. The influence of parathyroid function upon the transport of calcium in isolated sacs of rat small intestine. Endocrinology. 1959 Sep;65:517–519. doi: 10.1210/endo-65-3-517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramberg C. F., Jr, Mayer G. P., Kronfeld D. S., Aurbach G. D., Sherwood L. M., Potts J. T., Jr Plasma calcium and parathyroid hormone responses to EDTA infusion in the cow. Am J Physiol. 1967 Oct;213(4):878–882. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.4.878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ E., PANARIELLO V. A., SAELI J. RADIOACTIVE CALCIUM KINETICS DURING HIGH CALCIUM INTAKE IN OSTEOPOROSIS. J Clin Invest. 1965 Sep;44:1547–1560. doi: 10.1172/JCI105261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPENCER H., MENCZEL J., LEWIN I., SAMACHSON J. ABSORPTION OF CALCIUM IN OSTEOPOROSIS. Am J Med. 1964 Aug;37:223–234. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPENCER H., MENCZEL J., LEWIN I., SAMACHSON J. EFFECT OF HIGH PHOSPHORUS INTAKE ON CALCIUM AND PHOSPHORUS METABOLISM IN MAN. J Nutr. 1965 Jun;86:125–132. doi: 10.1093/jn/86.2.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHEDON G. D. Effects of high calcium intakes on bones, blood and soft tissue: relationship of calcium intakes to balance in osteoporosis. Fed Proc. 1959 Dec;18:1112–1118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


