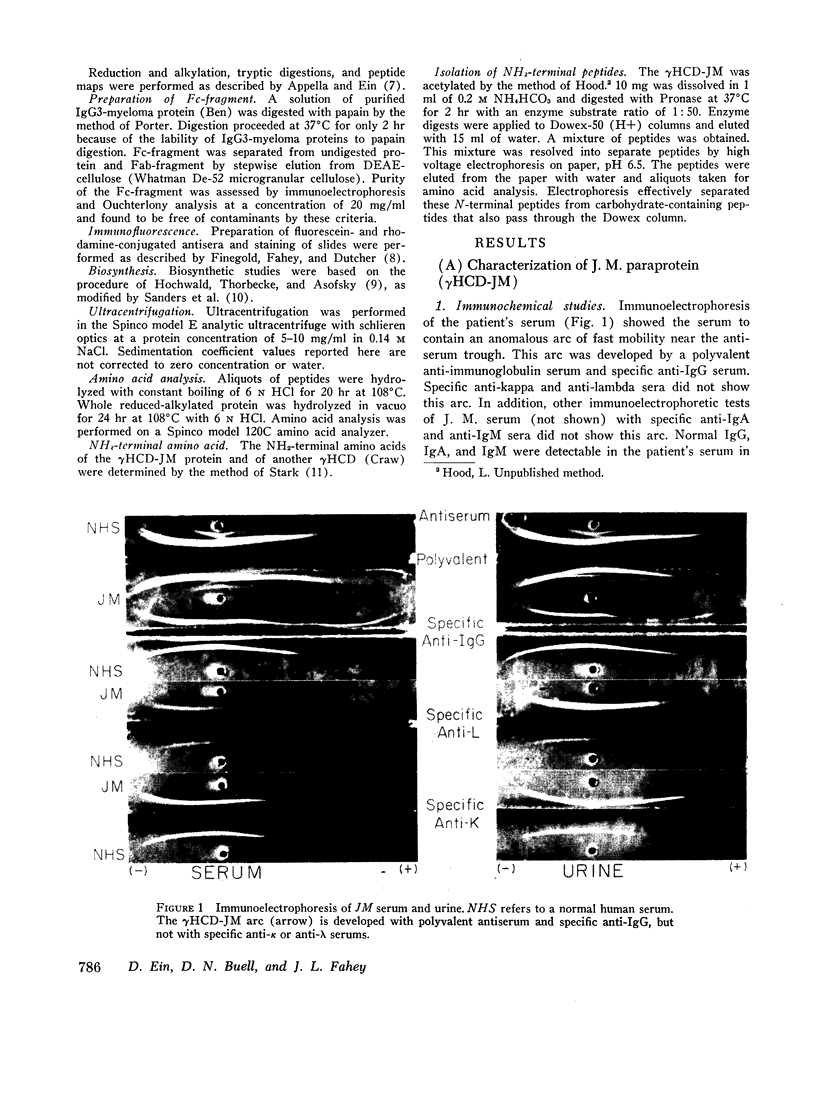
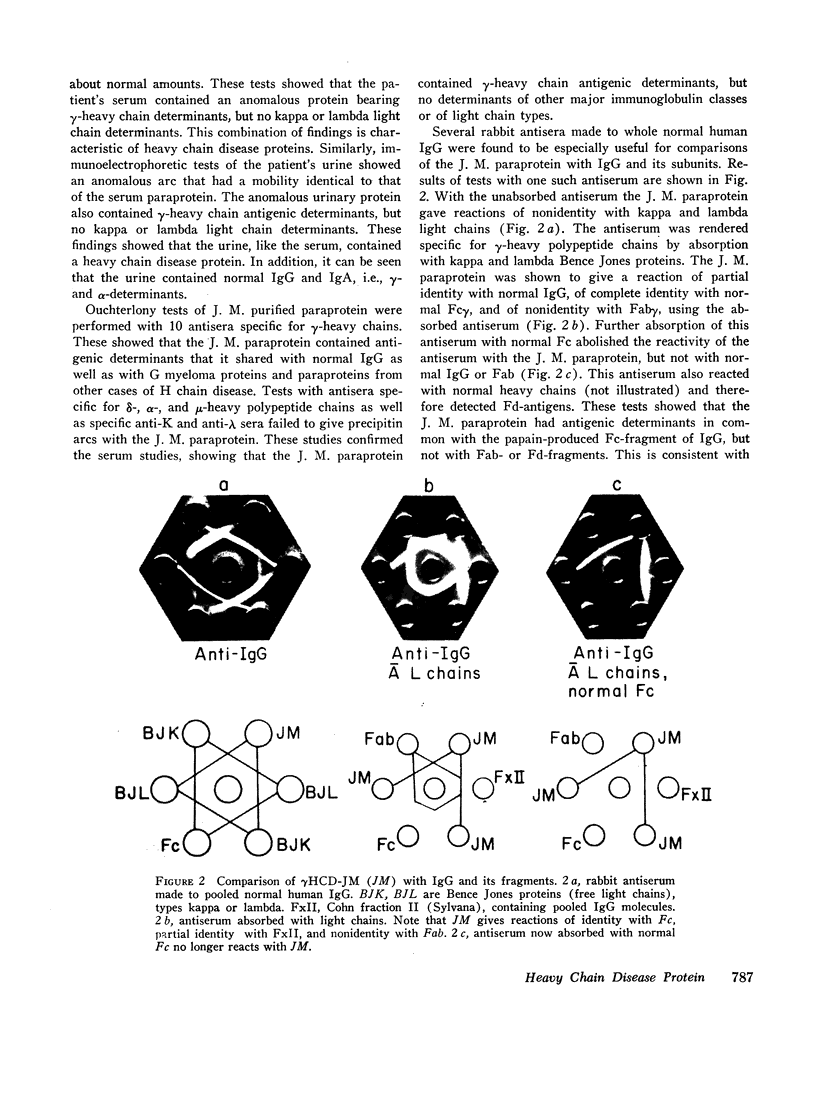
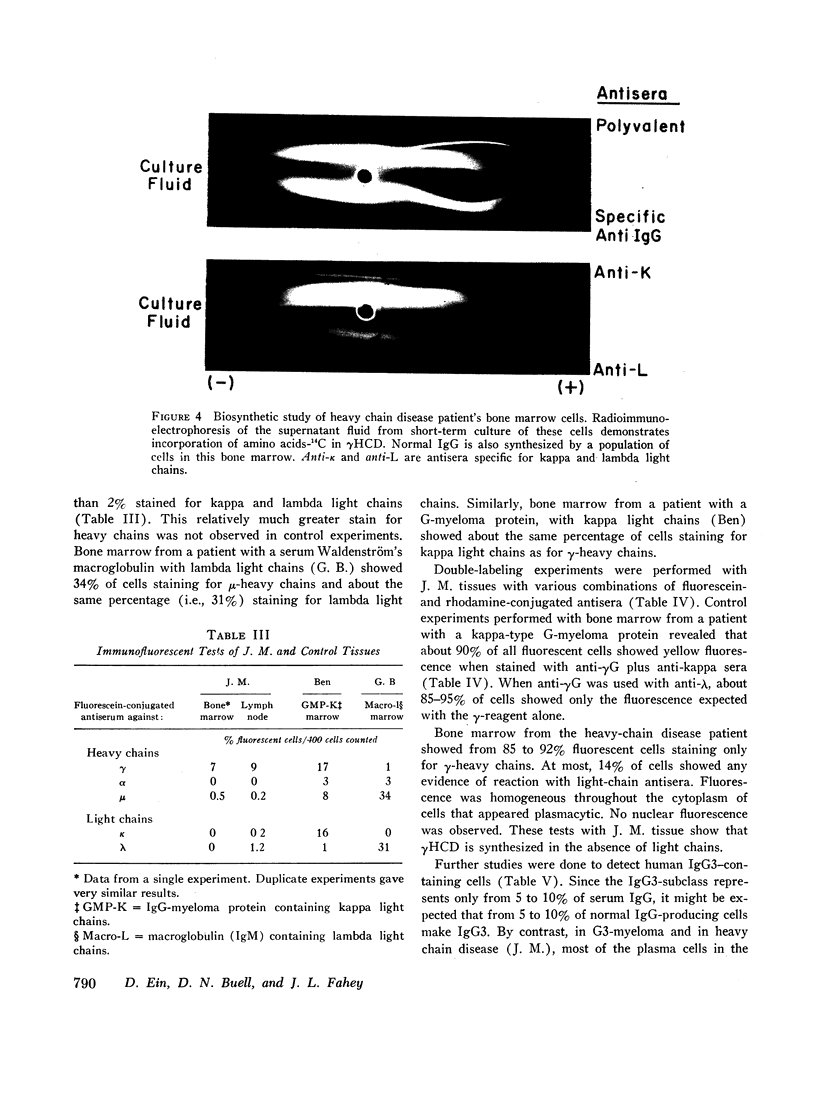
Abstract
A new heavy chain disease protein (γHCD-JM) has been characterized by antigenic and structural criteria. The protein belongs to the IgG3-subclass and is closely related to Fc-fragment of G3-immunoglobulins. The predominant N-terminal amino acid of this protein is glutamic acid in the uncyclized form, and that of another γHCD is glycine.
Studies of the N-terminal peptides indicate that the N-terminal portion of the γ3-heavy polypeptide chain is absent from the γHCD-JM. These findings rule out a process of normal heavy chain initiation and a large deletion of the Fd region as being responsible for these two heavy chain disease proteins.
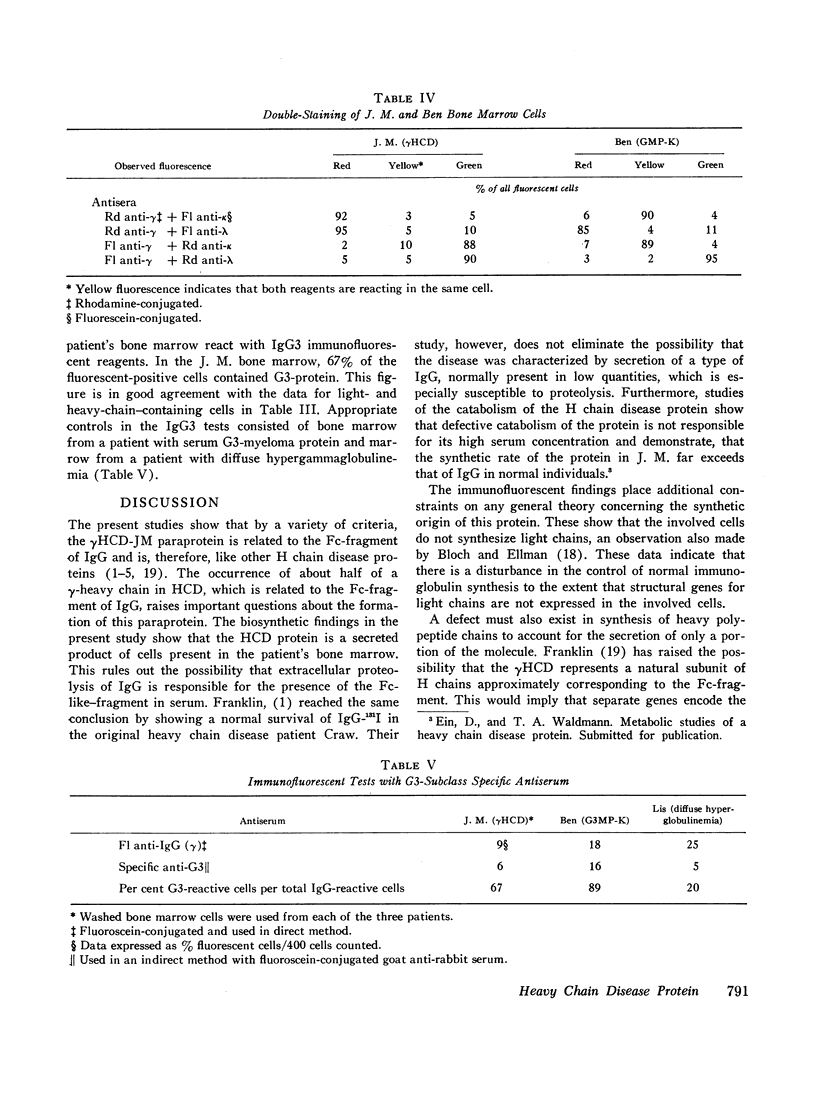
The γHCD-JM is a secretory product of cells from bone marrow as shown by studies of in vitro incorporation of amino acids-14C. Bone marrow and lymph node have a population of lymphoplasmacytic cells which by immunofluorescence contain γ-heavy chain antigens in the absence of light chain antigens.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appella E., Ein D. Two types of lambda polypeptide chains in human immunoglobulins based on an amino acid substitution at position 190. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1449–1454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askonas B. A., Williamson A. R. Biosynthesis of immunoglobulins on polyribosomes and assembly of the IgG molecule. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1966 Nov 22;166(1003):232–243. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1966.0096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ein D. Nonallelic behavior of the Oz groups in human lambda immunoglobulin chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):982–985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellman L. L., Bloch K. J. Heavy-chain disease. Report of a seventh case. N Engl J Med. 1968 May 30;278(22):1195–1201. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196805302782203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHEY J. L., MCLAUGHLIN C. PREPARATION OF ANTISERA SPECIFIC FOR 6.6 S GAMMA-GLOBULINS, BETA 2A-GLOBULINS, GAMMA-1.-MACROGLOBULINS, AND FOR TYPE I AND II COMMON GAMMA-GLOBULIN DETERMINANTS. J Immunol. 1963 Oct;91:484–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKLIN E. C., LOWENSTEIN J., BIGELOW B., MELTZER M. HEAVY CHAIN DISEASE- A NEW DISORDER OF SERUM GAMMA-GLOBULINS : REPORT OF THE FIRST CASE. Am J Med. 1964 Sep;37:332–350. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90191-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKLIN E. C. STRUCTURAL STUDIES OF HUMAN 7S GAMMA-GLOBULIN (G IMMUNOGLOBULIN). FURTHER OBSERVATIONS OF A NATURALLY OCCURRING PROTEIN RELATED TO THE CRYSTALLIZABLE (FAST) FRAGMENT. J Exp Med. 1964 Nov 1;120:691–709. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.5.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold I., Fahey J. L., Dutcher T. F. Immunofluorescent studies of immunoglobulins in human lymphoid cells in continuous culture. J Immunol. 1968 Aug;101(2):366–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischman J. B. Synthesis of the gamma-G heavy chain in rabbit lymph node cells. Biochemistry. 1967 May;6(5):1311–1320. doi: 10.1021/bi00857a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangione B., Milstein C. Variations in the S-S bridges of immunoglobins G: interchain disulfide bridges of gamma G3 myeloma proteins. J Mol Biol. 1968 May 14;33(3):893–906. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90326-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopf P. M., Parkhouse R. M., Lennox E. S. Biosynthetic units of an immunoglobulin heavy chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Dec;58(6):2288–2295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebreton J. P., Rivat C., Rivat L., Guillemot L., Ropartz C. Une immunoglobulinopathie méconnue: la maladie des chaines lourdes. Presse Med. 1967 Oct 28;75(45):2251–2254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSSERMAN E. F., TAKATSUKI K. CLINICAL AND IMMUNOCHEMICAL STUDIES OF FOUR CASES OF HEAVY (H-GAMMA-2) CHAIN DISEASE. Am J Med. 1964 Sep;37:351–373. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90192-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggot P. J., Press E. M. Cyanogen bromide cleavage and partial sequence of the heavy chain of a pathological immunoglobulin G. Biochem J. 1967 Aug;104(2):616–626. doi: 10.1042/bj1040616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prahl J. W. N- and C-terminal sequences of a heavy chain disease protein and its genetic implications. Nature. 1967 Sep 23;215(5108):1386–1387. doi: 10.1038/2151386a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHARFF M. D., UHR J. W. FUNCTIONAL RIBOSOMAL UNIT OF GAMMA-GLOBULIN SYNTHESIS. Science. 1965 Apr 30;148(3670):646–648. doi: 10.1126/science.148.3670.646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRY W. D., FAHEY J. L. SUBCLASSES OF HUMAN GAMMA-2-GLOBULIN BASED ON DIFFERENCES IN THE HEAVY POLYPEPTIDE CHAINS. Science. 1964 Oct 16;146(3642):400–401. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3642.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry W. D., Fahley J. L., Steinberg A. G. GM and INV factors in subclasses of human IgG. J Exp Med. 1965 Dec 1;122(6):1087–1102. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.6.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]