Abstract
A low molecular weight β2-globulin (β2-microglobulin), albumin, and total protein were measured in concentrated 24-hr urine specimens from 20 healthy subjects and 30 patients with clinical proteinuria of glomerular or tubular type. Classification of proteinuria was made on the basis of clinical diagnosis and size distribution of urinary proteins after gel chromatography. The molecular radii (Stokes' radii) of β2-microglobulin and albumin, estimated by gel chromatography, were 15 A and 35 A.
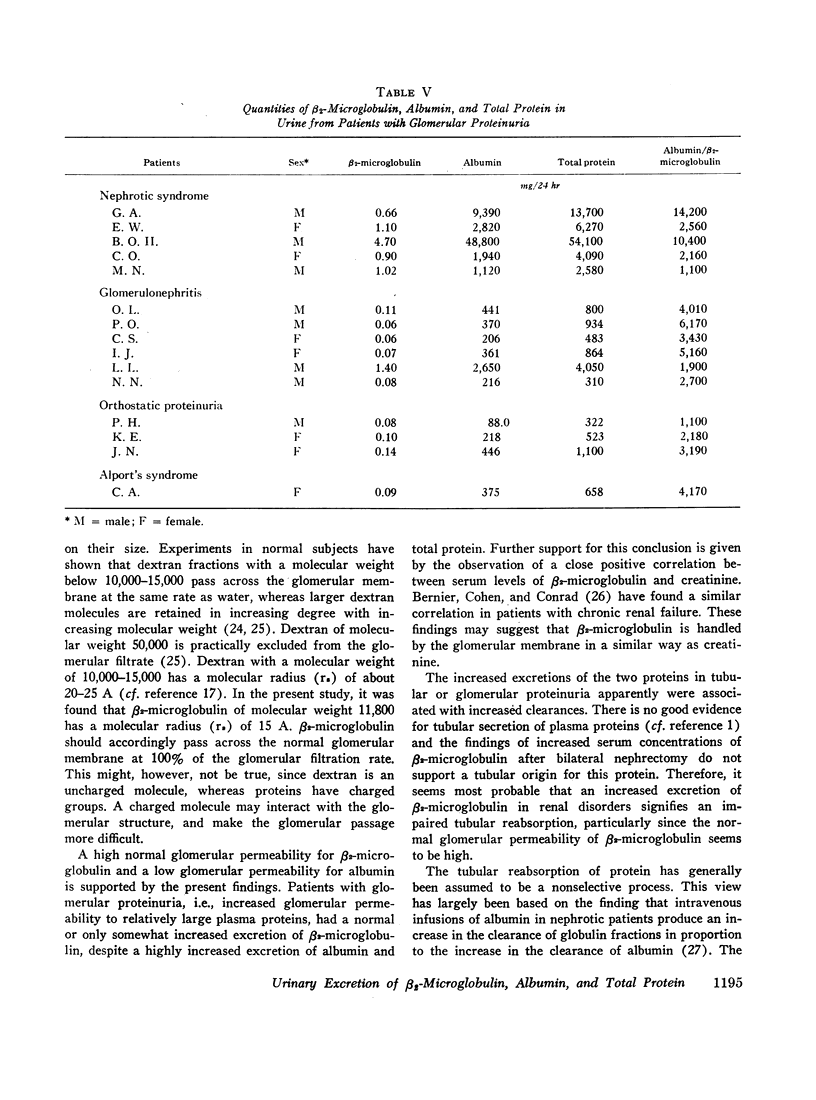
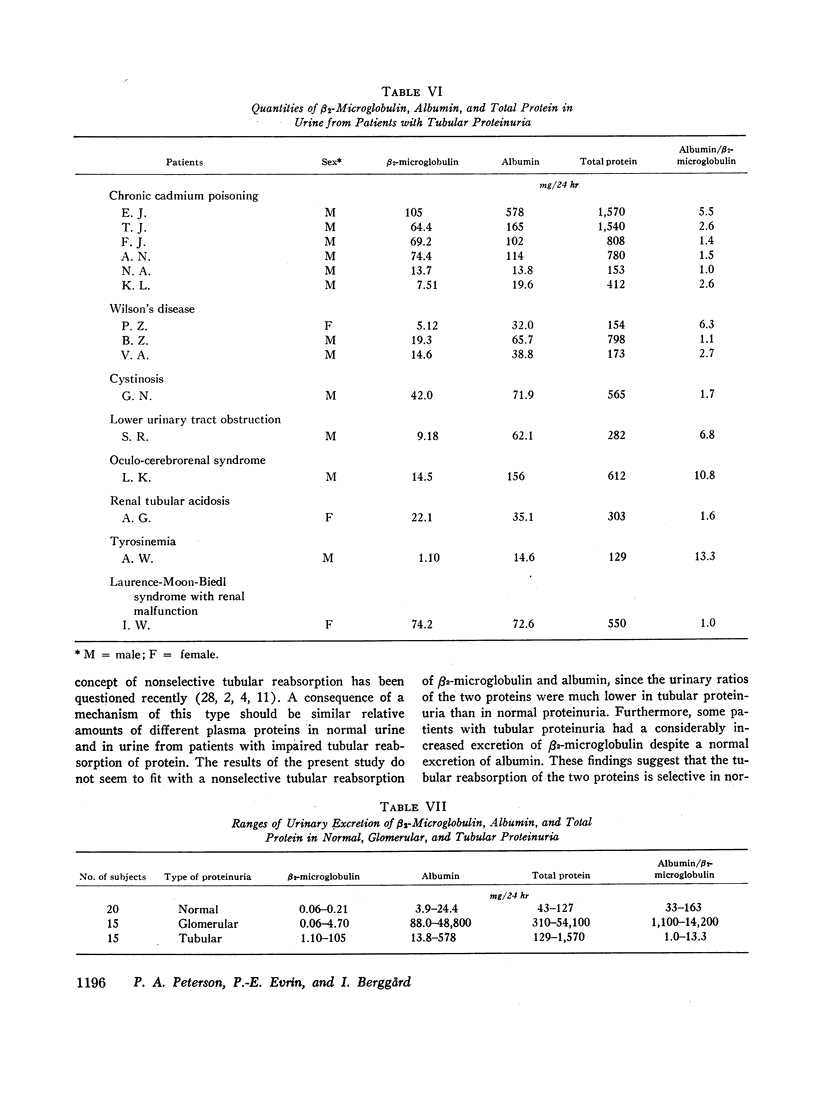
The average 24-hr urinary excretion in healthy subjects was 0.12 mg for β2-microglobulin, 10 mg for albumin, and 80 mg for total protein. The patients with renal glomerular disorders had normal or only somewhat increased excretion of β2-microglobulin, despite considerably increased excretion of albumin and total protein. Most of the patients with tubular dysfunction excreted large amounts of β2-microglobulin, although they excreted normal or only slightly increased amounts of albumin and only moderately increased quantities of total protein. Consequently, the ratio or urinary albumin/urinary β2-microglobulin was high in glomerular proteinuria (1100: 14,200), intermediate in normal proteinuria (33: 163), and low in tubular proteinuria (1.0: 13.3). Determinations of urinary clearances of β2-microglobulin and albumin in four healthy subjects and 11 patients indicated that increased excretions of the two proteins were associated with increased clearances. The results suggest that quantitative determinations of urinary β2-microglobulin and urinary albumin may be useful for detecting disorders of the renal handling of plasma proteins. The findings also seem to suggest a selective tubular reabsorption of the two proteins.
Estimates on sera revealed a close correlation between serum levels of β2-microglobulin and creatinine and also a greatly raised serum concentration of β2-microglobulin after bilateral nephrectomy.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARTURSON G., WALLENIUS G. THE RENAL CLEARANCE OF DEXTRAN OF DIFFERENT MOLECULAR SIZES IN NORMAL HUMANS. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1964;16:81–86. doi: 10.3109/00365516409060486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGGARD I., EDELMAN G. M. Normal counterparts to Bence-Jones proteins: free L polypeptide chains of human gamma-globulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Mar 15;49:330–337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.3.330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGGARD I., RISINGER C. Quantitative immunochemical determination of albumin in normal human urine. Acta Soc Med Ups. 1961;66:217–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTLER E. A., FLYNN F. V. The proteinuria of renal tubular disorders. Lancet. 1958 Nov 8;2(7054):978–980. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(58)90473-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berggård I., Bearn A. G. Isolation and properties of a low molecular weight beta-2-globulin occurring in human biological fluids. J Biol Chem. 1968 Aug 10;243(15):4095–4103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernier G. M., Cohen R. J., Conrad M. E. Microglobulinaemia in renal failure. Nature. 1968 May 11;218(5141):598–599. doi: 10.1038/218598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLEVE H., BEARN A. G. THE EXCRETION OF FIVE PLASMA PROTEINS PREVIOUSLY UNIDENTIFIED IN NORMAL HUMAN URINE. Clin Chim Acta. 1964 Jul;10:1–11. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(64)90208-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREETH J. M., KEKWICK R. A., FLYNN F. V., HARRIS H., ROBSON E. B. An ultracentrifuge study of urine proteins with particular reference to the proteinuria of renal tubular disorders. Clin Chim Acta. 1963 May;8:406–414. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(63)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain M. J., Stimmler L. The renal handling of insulin. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jun;46(6):911–919. doi: 10.1172/JCI105597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. S., Flynn F. V., Platt H. S. The characterisation of urine protein by gel filtration. Clin Chim Acta. 1968 Sep;21(3):357–376. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(68)90066-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVERALL P. H., WRIGHT G. H. Low pressure ultra-filtration of protein-containing fluids. J Med Lab Technol. 1958 Jul;15(3):209–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W. V., Fong S. W., Tan M. Naturally-occurring macroglobulin antibody of foetal origin in the normal human newborn. Immunology. 1966 Mar;10(3):259–270. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn F. V., Platt H. S. The origin of the proteins excreted in tubular proteinuria. Clin Chim Acta. 1968 Sep;21(3):377–399. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(68)90067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDWICKE J., SQUIRE J. R. The relationship between plasma albumin concentration and protein excretion in patients with proteinuria. Clin Sci. 1955 Aug;14(3):509–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. F., Blainey J. D. Low molecular weight proteinuria in chronic renal disease. Clin Sci. 1967 Oct;33(2):381–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. F., Lunt G. S., Scott P., Blainey J. D. Urinary lysozyme, ribonuclease, and low-molecular-weight protein in renal disease. Lancet. 1968 Feb 24;1(7539):371–375. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91350-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. F., Northam B. E. Low molecular weight urine protein investigated by gel filtration. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Nov;14(5):679–688. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90195-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piscator M. Proteinuria in chronic cadmium poisoning. IV. Gel filtration and ion exchange chromatography of urinary proteins from cadmium workers. Arch Environ Health. 1966 Mar;12(3):345–359. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1966.10664381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poortmans J., Jeanloz R. W. Quantitative immunological determination of 12 plasma proteins excreted in human urine collected before and after exercise. J Clin Invest. 1968 Feb;47(2):386–393. doi: 10.1172/JCI105735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wochner R. D., Strober W., Waldmann T. A. The role of the kidney in the catabolism of Bence Jones proteins and immunoglobulin fragments. J Exp Med. 1967 Aug 1;126(2):207–221. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


