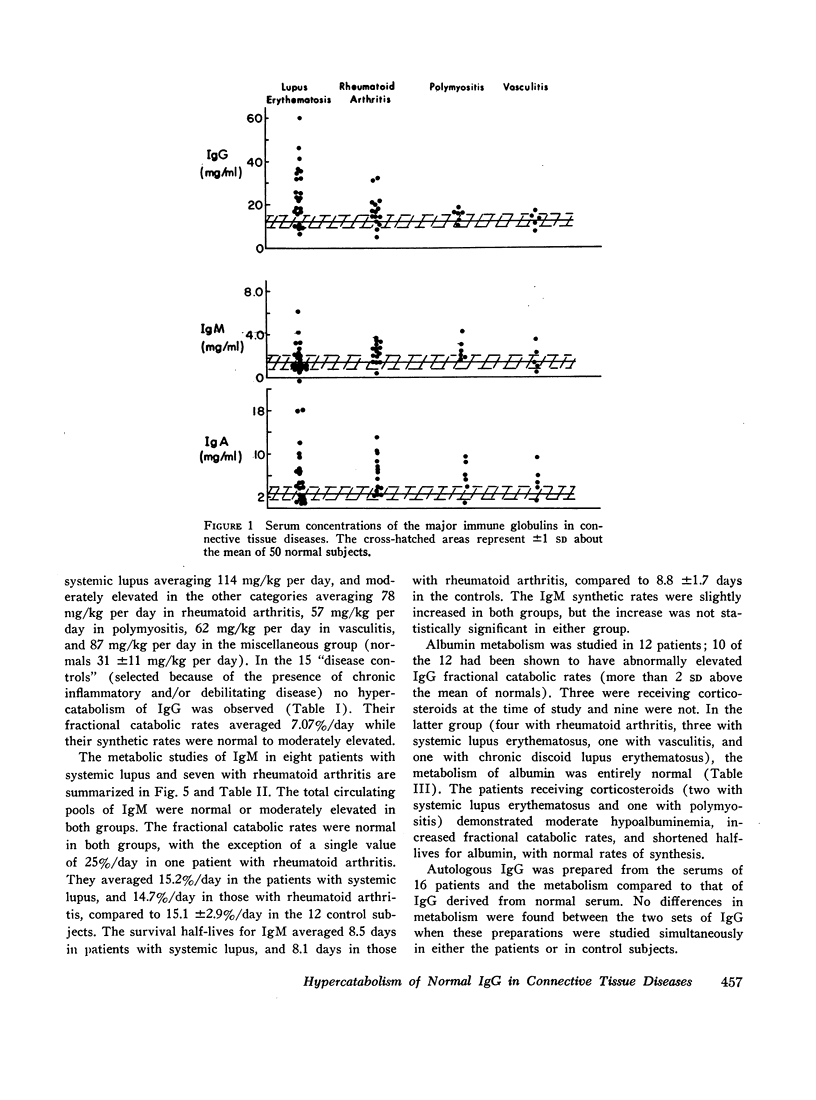
Abstract
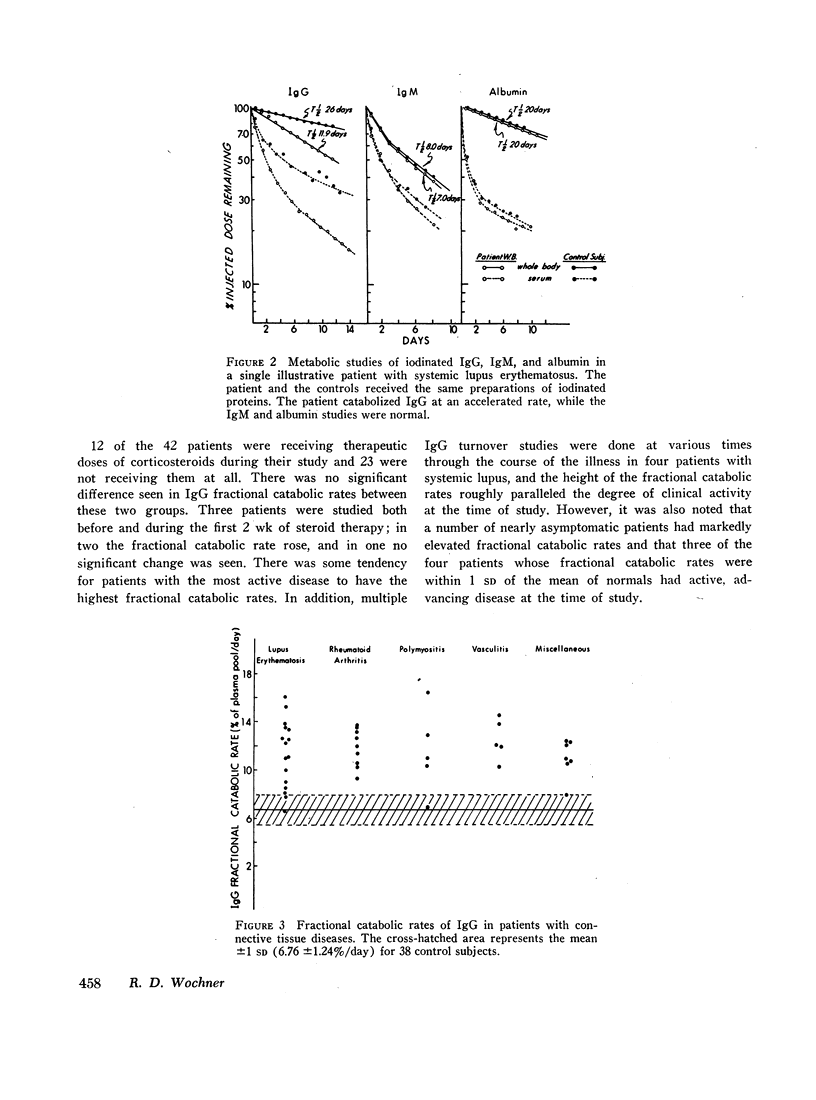
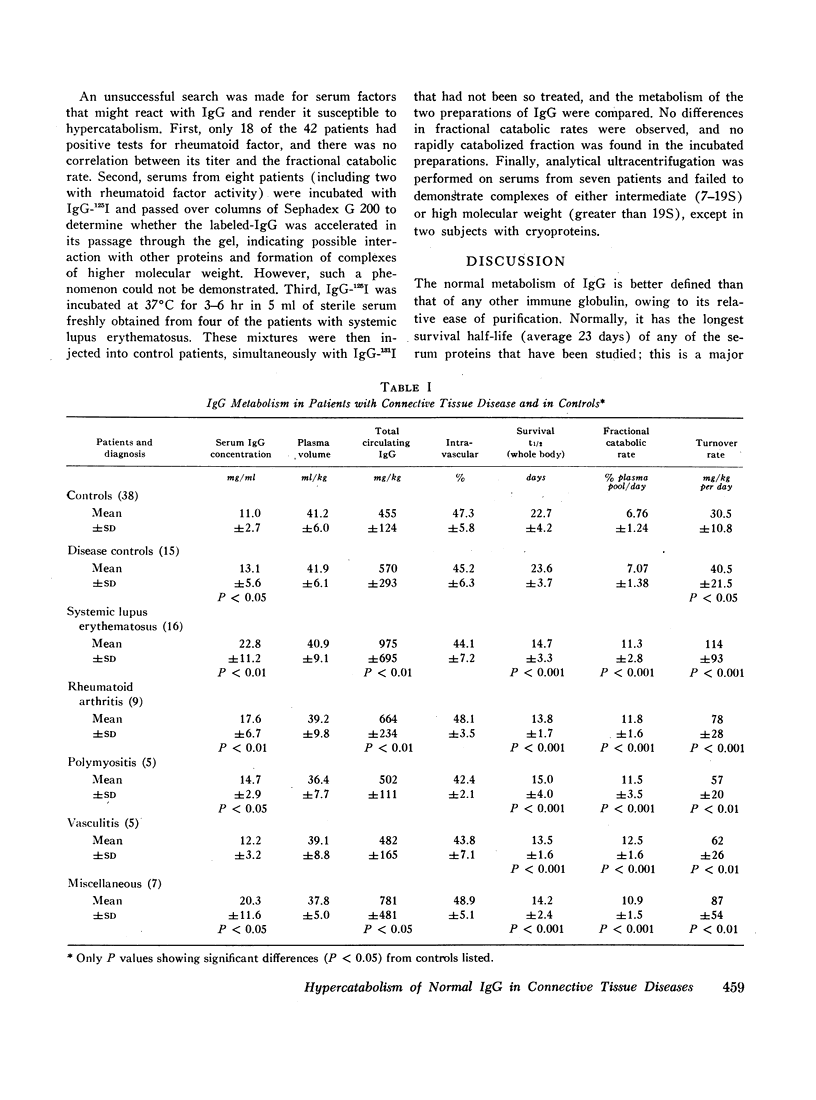
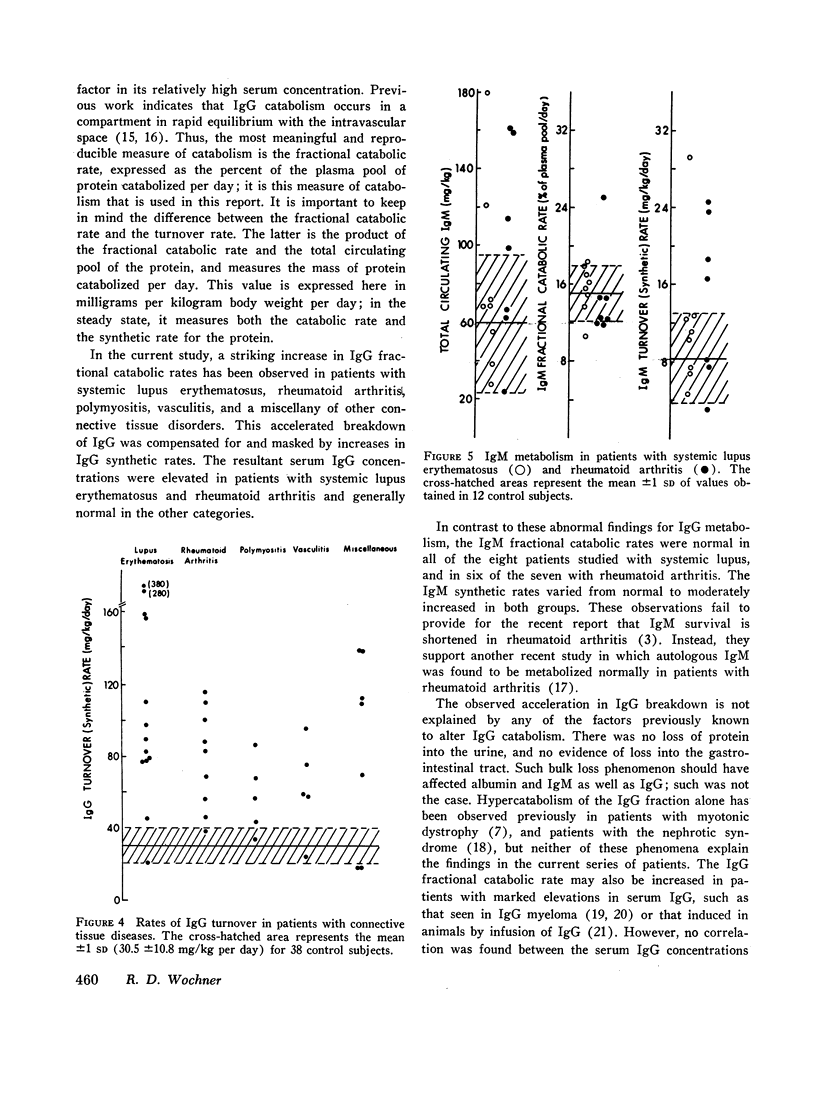
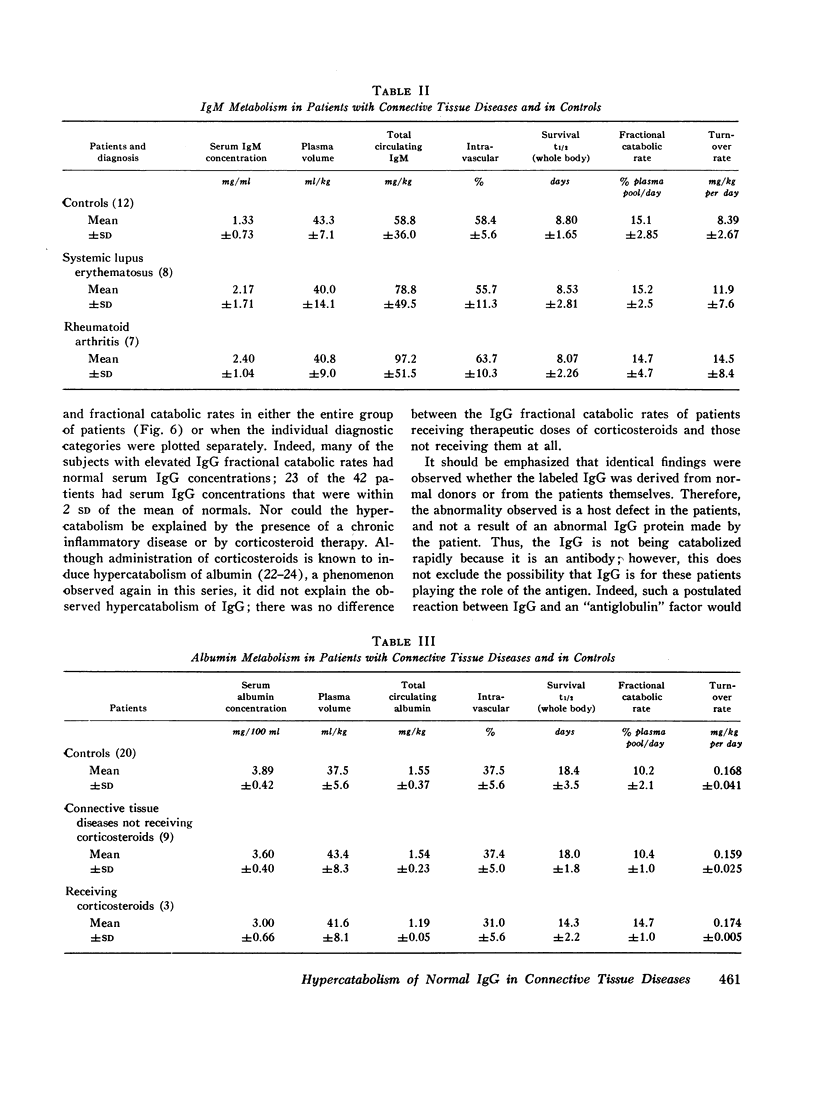
The metabolism of radioiodinated IgG was studied in a series of 42 patients with connective tissue diseases (16 systemic lupus erythematosus, nine rheumatoid arthritis, five polymyositis, five vasculitis, and seven miscellaneous diagnoses). Fractional catabolic rates were increased and survival half-lives were shortened in all diagnostic categories indicating hypercatabolism of IgG. This hypercatabolism was masked by increased IgG synthesis, resulting in elevated serum concentrations of IgG in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis and in generally normal concentrations in the others.
The metabolism of iodinated IgM was also studied in eight patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, in seven with rheumatoid arthritis, and in 12 controls. The fractional catabolic rates were normal in both groups of patients. Serum concentrations of both IgM and IgA were moderately elevated in all diagnostic categories. Serum albumin metabolism was entirely normal in the nine subjects studied who were not receiving corticosteroids; in three who were receiving them, moderate hypercatabolism was observed.
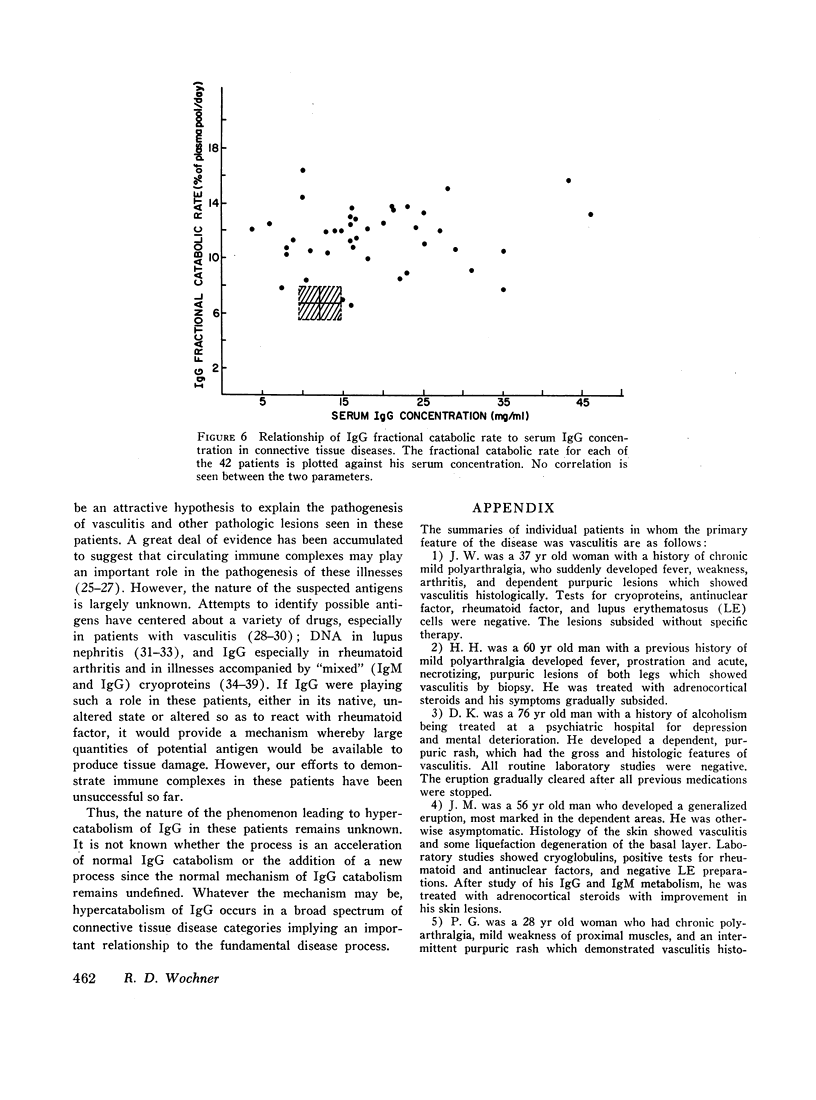
The hypercatabolism of IgG could not be accounted for by factors previously known to alter IgG metabolism. It was not observed in 15 patients with other chronic, inflammatory diseases and was not explained by concomitant administration of adrenal corticosteroids to some patients. Identical results were obtained whether the IgG was obtained from a patient himself or from a normal donor, demonstrating that the hypercatabolism is a host defect and not an abnormality of the protein. Thus, patients with connective tissue disease of several different diagnostic categories have been shown to have an unexplained immunoglobulin abnormality: they catabolize normal IgG at an accelerated rate.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. C., Kunkel H. G. Hidden rheumatoid factors with specificity for native gamma globulins. Arthritis Rheum. 1966 Dec;9(6):758–768. doi: 10.1002/art.1780090603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen S. B., Jarnum S., Jensen H., Rossing N. Metabolism of gamma-G-globulin in the nephrotic syndrome in adults. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1968;21(1):42–48. doi: 10.3109/00365516809076975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTH W. F., WOCHNER R. D., WALDMANN T. A., FAHEY J. L. METABOLISM OF HUMAN GAMMA MACROGLOBULINS. J Clin Invest. 1964 Jun;43:1036–1048. doi: 10.1172/JCI104987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERSON S. A., YALOW R. S., SCHREIBER S. S., POST J. Tracer experiments with I131 labeled human serum albumin: distribution and degradation studies. J Clin Invest. 1953 Aug;32(8):746–768. doi: 10.1172/JCI102789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERSON S. A., YALOW R. S. The distribution of I131 labeled human serum albumin introduced into ascitic fluid: analysis of the kinetics of a three compartment catenary transfer system in man and speculations on possible sites of degradation. J Clin Invest. 1954 Mar;33(3):377–387. doi: 10.1172/JCI102910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley J., Normansell D., Rowe D. S. The metabolism of autologous IgM and 19S rheumatoid factor in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 May;4(5):537–553. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christian C. L. Immune-complex disease. N Engl J Med. 1969 Apr 17;280(16):878–884. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196904172801610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON F. J., VAZQUEZ J. J., WEIGLE W. O., COCHRANE C. G. Pathogenesis of serum sickness. AMA Arch Pathol. 1958 Jan;65(1):18–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHEY J. L., MCKELVEY E. M. QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF SERUM IMMUNOGLOBULINS IN ANTIBODY-AGAR PLATES. J Immunol. 1965 Jan;94:84–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHEY J. L., MCLAUGHLIN C. PREPARATION OF ANTISERA SPECIFIC FOR 6.6 S GAMMA-GLOBULINS, BETA 2A-GLOBULINS, GAMMA-1.-MACROGLOBULINS, AND FOR TYPE I AND II COMMON GAMMA-GLOBULIN DETERMINANTS. J Immunol. 1963 Oct;91:484–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHEY J. L., ROBINSON A. G. FACTORS CONTROLLING SERUM GAMMA-GLOBULIN CONCENTRATION. J Exp Med. 1963 Nov 1;118:845–868. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.5.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERMUTH F. G., Jr, MCKINNON G. E. Studies on the biological properties of antigen-antibody complexes. I. Anaphylatic shock induced by soluble antigen-antibody complexes in unsensitized normal guinea pigs. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1957 Jul;101(1):13–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLANDER J. L., MCCARTY D. J., Jr, ASTORGA G., CASTRO-MURILLO E. STUDIES ON THE PATHOGENESIS OF RHEUMATOID JOINT INFLAMMATION. I. THE "R.A. CELL" AND A WORKING HYPOTHESIS. Ann Intern Med. 1965 Feb;62:271–280. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-62-2-271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanauer L. B., Christian C. L. Studies of cryoproteins in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1967 Mar;46(3):400–408. doi: 10.1172/JCI105541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNKEL H. G., MULLER-EBERHARD H. J., FUDENBERG H. H., TOMASI T. B. Gamma globulin complexes in rheumatoid arthritis and certain other conditions. J Clin Invest. 1961 Jan;40:117–129. doi: 10.1172/JCI104224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffler D., Schur P. H., Kunkel H. G. Immunological studies concerning the nephritis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1967 Oct 1;126(4):607–624. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.4.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan C., Kaplan M. H. Immunopathologic studies of systemic lupus erythematosus. II. Antinuclear reaction of gamma-globulin eluted from homogenates and isolated glomeruli of kidneys from patients with lupus nephritis. J Clin Invest. 1967 Apr;46(4):569–579. doi: 10.1172/JCI105558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIPPINCOTT S. W., KORMAN S., FONG C., STICKLEY E., WOLINS W., HUGHES W. L. Turnover of labeled normal gamma globulin in multiple myeloma. J Clin Invest. 1960 Apr;39:565–572. doi: 10.1172/JCI104069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHEWS C. M. The theory of tracer experiments with 131I-labelled plasma proteins. Phys Med Biol. 1957 Jul;2(1):36–53. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/2/1/305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLS J. A., CALKINS E., COHEN A. S. The plasma disappearance time and catabolic half-life of I-131-labeled normal human gamma globulin in amyloidosis and inrheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1961 Oct;40:1926–1934. doi: 10.1172/JCI104418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCORMICK R. V. Periarteritis occurring during propylthiouracil therapy. J Am Med Assoc. 1950 Dec 23;144(17):1453–1454. doi: 10.1001/jama.1950.62920170007008a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer M., Franklin E. C., Elias K., McCluskey R. T., Cooper N. Cryoglobulinemia--a clinical and laboratory study. II. Cryoglobulins with rheumatoid factor activity. Am J Med. 1966 Jun;40(6):837–856. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(66)90200-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normansell D. E., Stanworth D. R. Ultracentrifugal studies of the reactions of rheumatoid factor with native human gamma-G-globulin. Immunology. 1966 Jun;10(6):527–533. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLHAGEN B., BIRKE G., PLANTIN L. O., AHLINDER S. ISOTOPE STUDIES OF GAMMAGLOBULIN CATABOLISM IN COLLAGEN DISORDERS. Acta Rheumatol Scand. 1963;9:88–93. doi: 10.3109/rhe1.1963.9.issue-1-4.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEARSON J. D., VEALL N., VETTER H. A practical method for plasma albumin turnover studies. Strahlentherapie. 1958;107(SONDERBD):290–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOLOMON A., WALDMANN T. A., FAHEY J. L. Clinical and experimental metabolism of normal 6.6s gamma-globulin in normal subjects and in patients with macroglobulinemia and multiple myeloma. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Jul;62:1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterling K. THE EFFECT OF CUSHING'S SYNDROME UPON SERUM ALBUMIN METABOLISM. J Clin Invest. 1960 Dec;39(12):1900–1908. doi: 10.1172/JCI104214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Schur P. H., Carr R. I., Kunkel H. G. Deoxybonucleic acid (DNA) and antibodies to DNA in the serum of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1966 Nov;45(11):1732–1740. doi: 10.1172/JCI105479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wochner R. D., Drews G., Strober W., Waldmann T. A. Accelerated breakdown of immunoglobulin G (IgG) in myotonic dystrophy: a hereditary error of immunoglobulin catabolism. J Clin Invest. 1966 Mar;45(3):321–329. doi: 10.1172/JCI105346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wochner R. D., Weissman S. M., Waldmann T. A., Houston D., Berlin N. I. Direct measurement of the rates of synthesis of plasma proteins in control subjects and patients with gastrointestinal protein loss. J Clin Invest. 1968 May;47(5):971–982. doi: 10.1172/JCI105812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


